org chem p8
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
C. Amine
Which of the following functional groups is the most basic?
A. Imide C. Amine
B. Amide D. Aniline
C. Aniline derivative
Paracetamol chemically is a/an
A. Salicylate derivative
B. Azocaine derivative
C. Aniline derivative
D. Pyrazolone derivative
C. Indole
The following structure is the side chain of amino acid tryptophan. What is the name of the following structure?
A. Purine C. Indole
B. Pyrimidine D. Quinoline
D. I, II, III, IV
Aromatic Phenothiazine derivatives
I. Chlorpromazine III. Triflupromazine
II. Promazine IV. Prochlorperazine
A. I only C. I, II, III
B. I, II D. I, II, III, IV
A. Thioridazine
Phenothiazine derivative
A. Thioridazine C. Hydroxyzine
B. Chlorprothixene D. Molindone
A. Chlorpromazine
An aliphatic phenothiazine derivative
A. Chlorpromazine C. Fluphenazine
B. Thiorizadine D. Perphenazine
A. I, II, IV, VIII
Which of the listed phytopharmaceuticals are classified as alkaloids?
I. Atropine V. Gingerol
II. Colchicine VI. Eugenol
III. Curcumin VII. Hesperidin
IV. Digoxin VIII. Quinine
A. I, II, IV, VIII C. III, IV, V, VIII
B. I, IV, VII, VIII D. I, III, V, VII
A. Atropine
Which of the following is identified by the Vitali-Morris (Vitali-Morin) reaction whereby a violet coloration is observed when the residue of the unknown is treated with a drop of freshly prepared potassium hydroxide solution?
A. Atropine C. Hesperidin
B. Quinine D. Digoxin
A. Quinine
Which of the following is identified by the Thalleoquin test?
A. Quinine C. Digoxin
B. Atropine D. Hesperidin
D. Phenyl-ethylamine
Mescaline is a/an _____ derivative.
A. Steroid C. Indole-ethylamine
B. Xanthine D. Phenyl-ethylamine
B. May be dissolved in water by addition of a small amount of sulphuric acid to convert it to more soluble bisulfate
Which is True to the alkaloid quinine sulphate?
A. Has a sweet and pleasant taste.
B. May be dissolved in water by addition of a small amount of sulphuric acid to convert it to more soluble bisulfate
C. This alkaloid is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
D. Is not damaged by exposure to light
Amides
General Formula → RCONH2
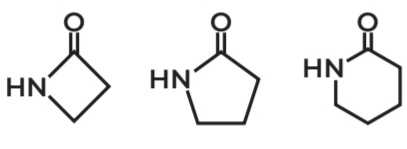
Properties of Amides
Cyclic amides → LACTAM
Based on the pic
1 is Beta Lactam
2 is Gamma lactam
3 is Delta Lactam
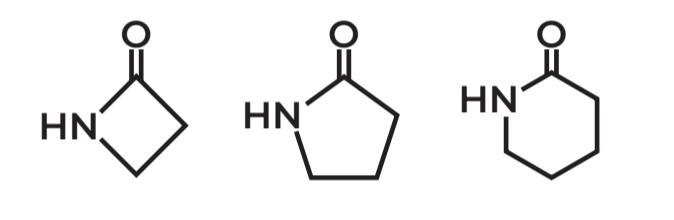
Properties of Amides
Susceptible to hydrolysis
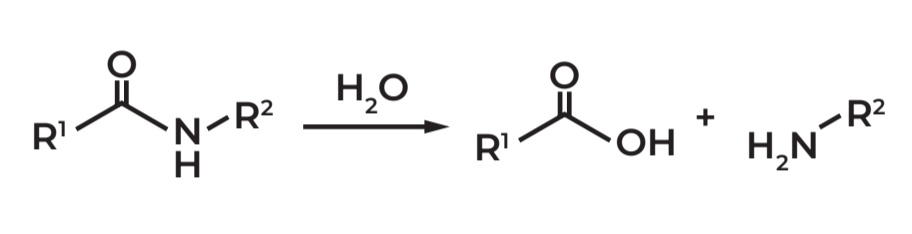
Amides undergo hydrolysis because the carbonyl carbon is reactive and gets attacked by nucleophiles, breaking the bond and forming CARBOXYLIC ACID + AMINE products.
Nomenclature of Amides
Common name: Common prefix + amine
IUPAC name: Alkan + amide
Cyclic ring: USE GREEK PREFIX + LACTAM
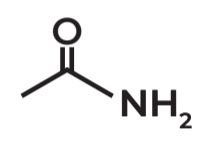
Acetamide
IUPAC Name → Ethanamide
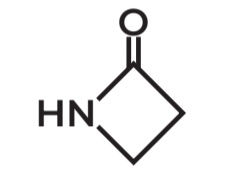
Beta Lactam
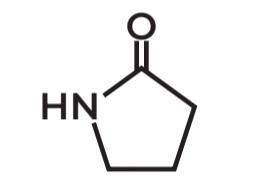
Gamma Lactam
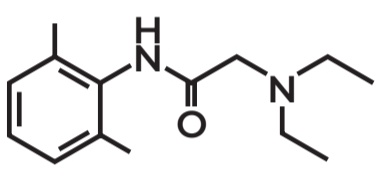
Lidocaine
Amide Local Anesthetics
Remember that that if there are two i in its name it is amide local anesthetics
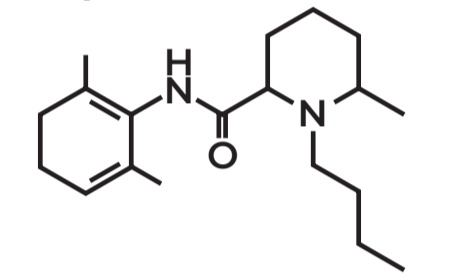
Bupivacaine
Amide Local Anesthetics
Dibucaine
Amide Local Anesthetics
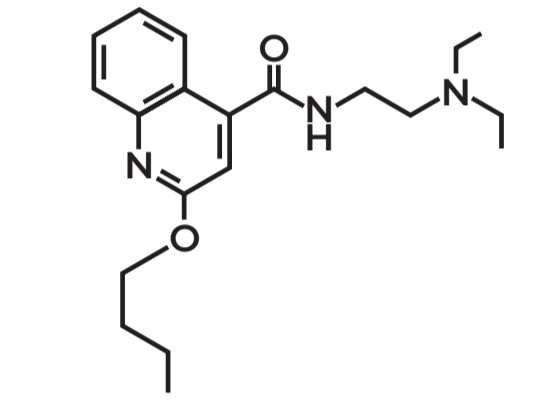
C. Amide
Functional group of the beta-lactam ring
A. Ether C. Amide
B. Ketone D. Carbonyl
SULFUR-CONTAINING COMPOUNDS
Thiols - RSH
Thioethers - RSR
Thioesters - RCOSR/RCSOR
Thiols
General Formula → R—SH
Nomenclature of Thiols
Common name: Alkyl + Mercaptan
IUPAC name: Alkane + thiol
Methylmercaptan
IUPAC Name → Methanethiol
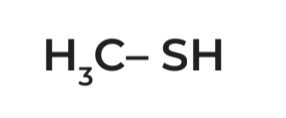
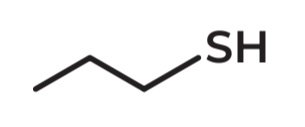
Propylmercaptan
IUPAC Name →Propane-1-thiol
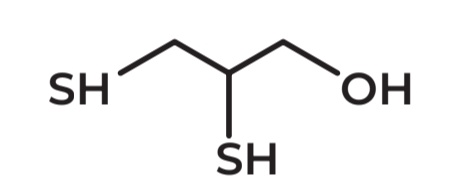
BAL - British Anti Lewisite
AKA: Dimercaprol
IUPAC Name → 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol
Thioethers
General Formula → R—S—R'
Nomenclature of thioethers
Common name: Alkyl + sulfide
IUPAC nane: Alkylthio + Alkane
Methyl propyl sulfide
IUPAC Name → Methylthiopropane
Propane - 3-carbon straight chain (CH3CH2CH2–)
Methylthio - (–SCH₃) A methyl group connected through sulfur
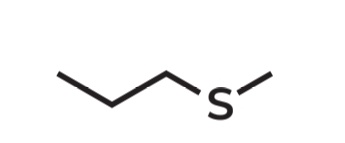
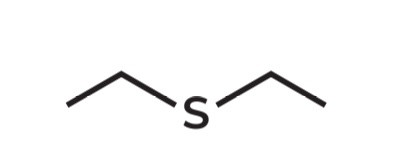
Diethyl sulfide
IUPAC Name → Ethylthioethane
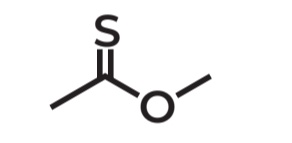
Thioesters
General Formula → RCOSR' or RCSOR
Nomenclature of thioesters
Common name: Alkyl + thio prefix -ate
IUPAC name: Alkyl + Alkane -thioate
Methylthioacetate
IUPAC Name → methylethanethioate
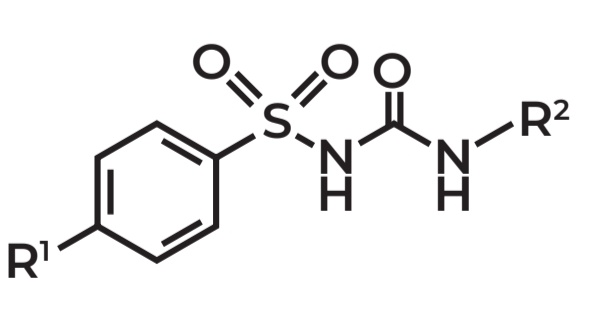
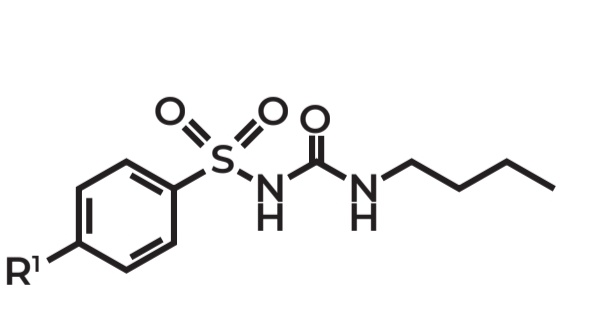
Benzylsulfanylurea
Example: Tolbutamide
Use: Oral hypoglycemic agent
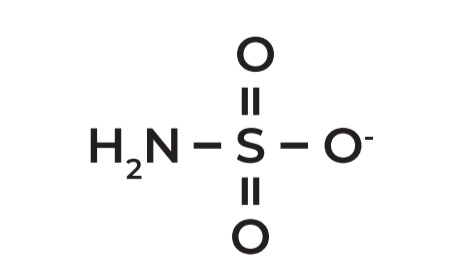
Sulfamate
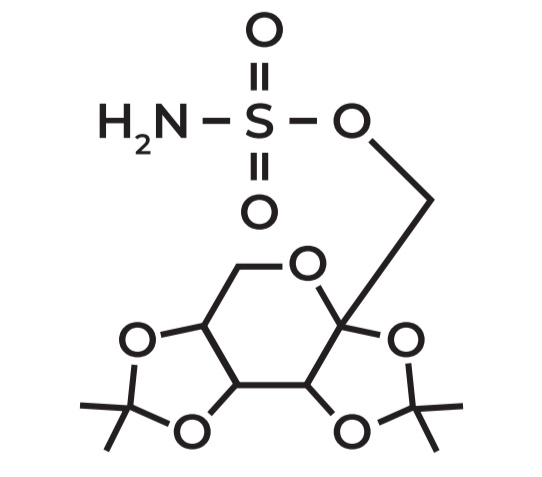
Example: Topiramate
Sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide
Derived from D-fructose
Use: ANTI EPILEPTIC agent
D. A and B
BAL is
A. British Anti-Lewisite
B. 2,3–dimercaptopropanol
C. 3,2–dimercaptopropanol
D. A and B
C. Oral hypoglycemics
Derivatives of benzylsulfonyl urea are useful as
A. Spasmolytics
B. Anti-inflammatory
C. Oral hypoglycemics
D. Diuretics
A. Topiramate
Sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide (related to fructose)
A. Topiramate
B. Valproic acid
C. Lamotrigine
D. Carbamazepine
HALOGEN-CONTAINING COMPOUNDS
Alkyl halides - R-X
Aryl halides - Ar-X
Acyl halides - RCOX
Alkyl Halides
General Formula → R—X (X = F, Cl, Br, I)
Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
IUPAC name: Halogen prefix + alkane
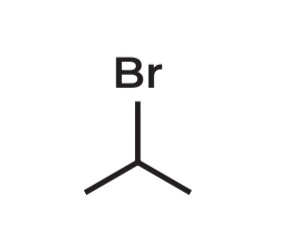
2-bromopropane
IUPAC Name →
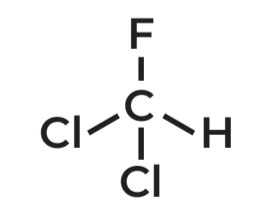
Dichlorofluoromethane
IUPAC Name →
AKA FREON R-21
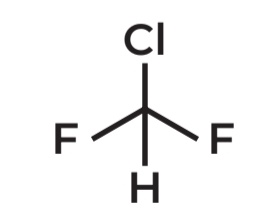
Chlorodifluoromethane
IUPAC Name →
AKA FREON R-22
Aryl Halides
→ General Formula: Ar-X
Nomenclature of Aryl Halides
IUPAC name: Halogen prefix + Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Acyl Halides
→ General Formula: RCOX
Nomenclature of Acyl Halides
IUPAC name: IUPAC prefix + oyl + halogen (-ide)
Easier way: Alkan + oyl halide
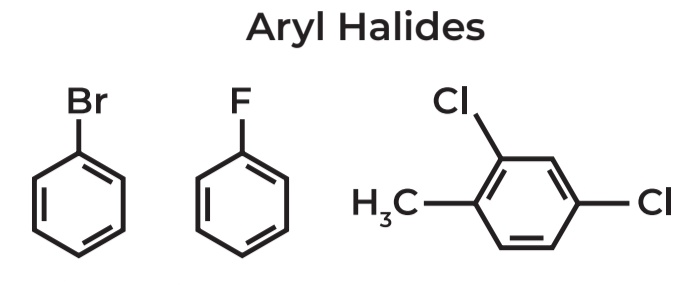
Aryl Halides
→ IUPAC Name: BROMOBENZENE
→ IUPAC Name: FLUOROBENZENE
→ IUPAC Name: 2,4-DICHLOROMETHYLBENZENE
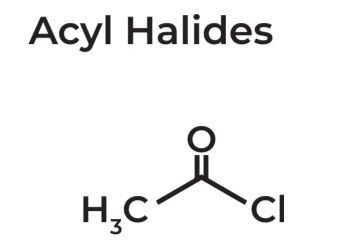
Acyl Halides
→ IUPAC Name: Ethanoylchloride
D. Dichlorofluoromethane
Freon
A. Dichloromethane
B. Difluoroethane
C. Dibromomethane
D. Dichlorofluoromethane
C. Acid Halide
Functional group present in CH₃COCl
A. Alcohol
B. Aldehyde
C. Acid Halide
D. Ketone
ISOMERISM
→ Same MOLECULAR FORMULA, different STRUCTURE
true
ISOMER has two types:
CONSTITUTIONAL
STEREOISOMER
CONSTITUTIONAL:
Chain
Positional
Functional
STEREOISOMER: divided into TWO
CONFORMATIONAL
Ring conformers
Rotamers
CONFIGURATIONAL
Geometric
Optical
CONSTITUTIONAL / STRUCTURAL ISOMERS
→ Compounds with:
• SAME molecular formula
• DIFFERENT structure
• DIFFERENT connectivity
Chain/Skeletal
Same:
Molecular Formula
Different:
Structure
Parent name
Branching
Positional
Same:
Molecular Formula
Parent name
Different:
Structure
Position
Functional
Same:
Molecular Formula
Different:
Structure
Functional group
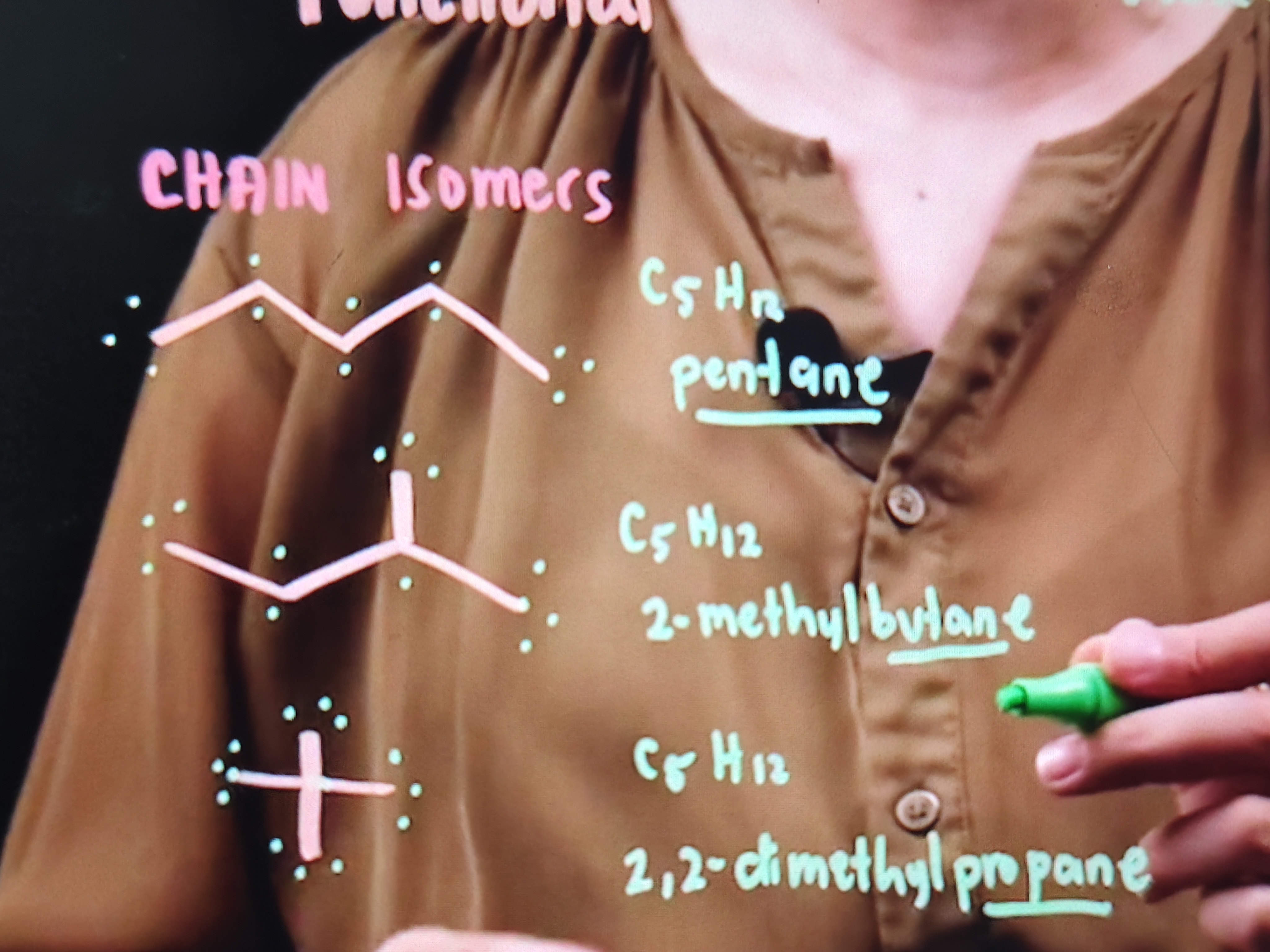
Pentane
CHAIN / SKELETAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C5H12
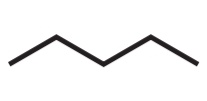
2-methylbutane
CHAIN / SKELETAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C5H12
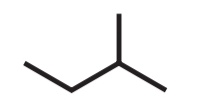
2,2-dimethylpropane
CHAIN / SKELETAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C5H12
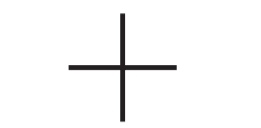
true
these are chain isomers
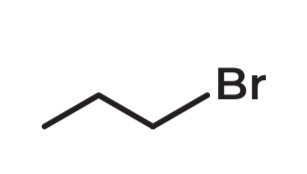
1-bromopropane
POSITIONAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C3H7Br
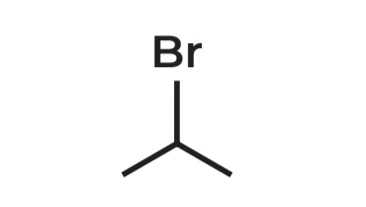
2-bromopropane
POSITIONAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C3H7Br
true
these are positional isomers
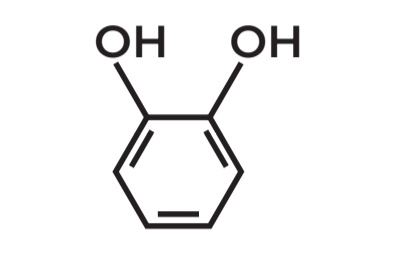
Benzene-1,2-diol
POSITIONAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C6H6O2
Benzene-1,3-diol
POSITIONAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C6H6O2
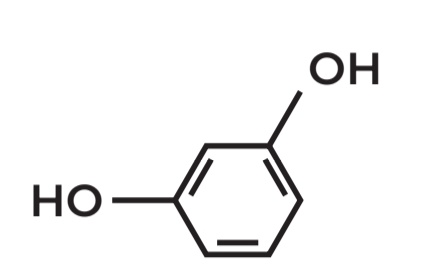
Benzene-1,4-diol
POSITIONAL ISOMERS
• Molecular Formula: C6H6O2
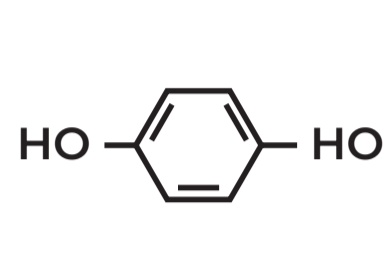
true
these are all positional isomers

Functional Isomers Example
✓ Same Molecular Formula: C2H6O
✓ Different structure and functional group: Ethanol and Dimethyl ether
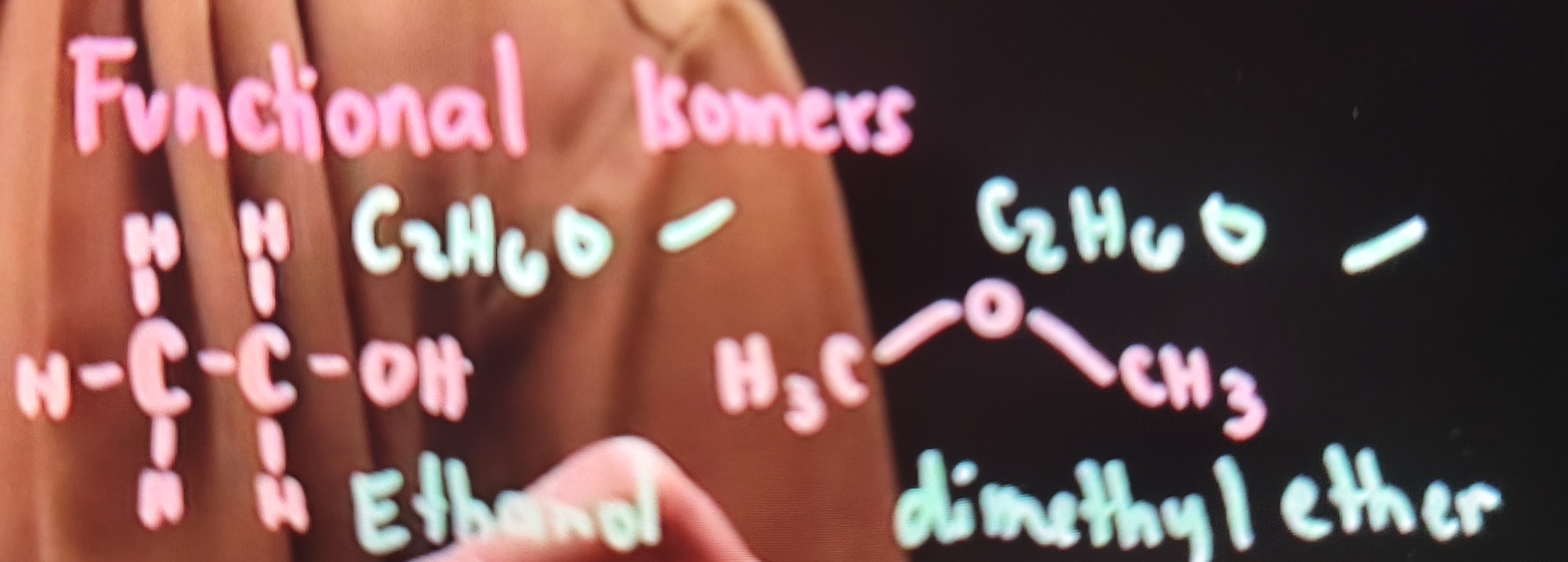
FUNCTIONAL ISOMERS (Tautomers)
“facile interconversion” - effortless interconversion
Tautomerism - Rapid shifting between 2 isomeric forms
Facile interconversion - The switch happens easily and quickly
Propanone (acetone) - ketone form
1-propen-1-ol - enol form
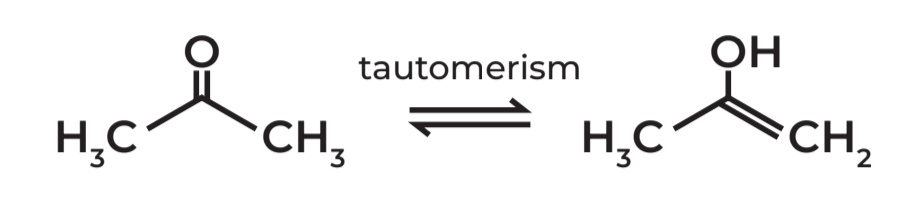
C. 2-propanol
Which of the following can be considered as an isomer of n-propanol?
A. Acetone
B. Methoxymethane
C. 2-propanol
D. B and C
B. Positional isomers
2-pentanol and 3-pentanol are:
A. Functional isomers
B. Positional isomers
C. Chain isomers
D. Optical isomers
D. Tautomers
Propanone and 1-propen-1-ol are considered as:
A. Positional isomers
B. Configurational isomers
C. Chain isomers
D. Tautomers
D. Both A and B
A compound with a molecular formula of C₂H₆O is most likely to be a/an ______.
A. Alcohol
B. Ether
C. Ketone
D. Both A and B
STEREOISOMERS
→ Compounds with:
• SAME molecular formula
• DIFFERENT structure
• SAME order of atoms and connectivity
• DIFFRENT arrangement of atoms in space (configuration)
Conformational
Can be interconverted just by rotations ("TEMPORARY DIFFERENCE")
Ex.
Ring conformers
Rotamers
Configurational
Can be interconverted only by breaking bonds ("PERMANENT DIFFERENCE")
Ex.
Geometric
Optical
A. I, III
Which statements best characterize stereoisomers?
I. They do not differ in the order of their atoms.
II. They differ in the order and kind of atoms.
III. They differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
IV. They do not differ in their configuration.
A. I, III
B. III,IV
C. II,III
D. I,IV