3.1.2 - AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Mole definition
Unit of measurement of amount of substance
Avogadro’s constant
Number of particles in a mole
Formula for number of particles
Num of particles = Moles * Avogadro’s constant
Formula for moles
Moles = mass (g) / Mᵣ
Formula for concentration of solution
Moles = conc. (mol dm⁻³) * volume (dm³)
Ideal gas equation
pV = nRT
What does each symbol in ideal gas equation stand for?
p = pressure (Pa)
V = volume (m³)
n = num of moles
R = gas constant
T = temp. (K)
Empirical formula definition
Smallest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
Example empirical formula calculation
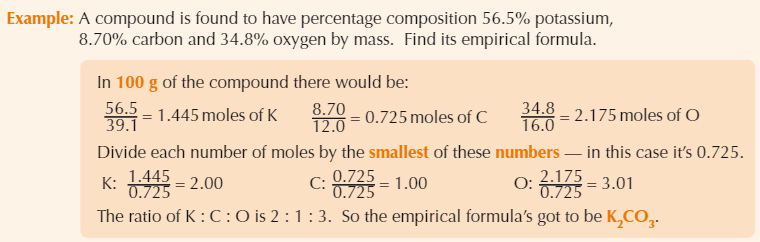
Molecular formula
Gives the actual numbers of atoms of each element in a compound
Relationship between molecular and empirical formula
Molecular formula is made up of a whole number of empirical units

Ionic equations
Can be written for any reaction involving ions that happens in solution
Only includes reacting particles (and the products they form)
Charges must be balanced on either side
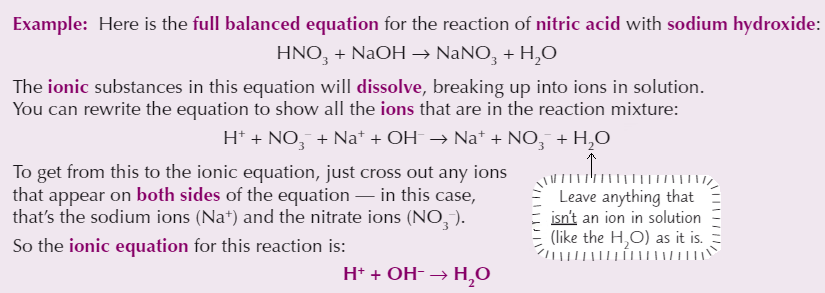
What is a spectator ion?
Ion that’s present in reaction mixture, but not involved in reaction
What is theoretical yield?
Mass of product that should be formed in reaction - assuming no chemicals are lost in process
Calculated using masses of reactants and balanced equation
Actual yield is always ____ than theoretical yield
less
Reasons why actual yield may be less than theoretical
Not all reactants react fully
Some reactants lost, e.g. lost during transfer between containers
Formula for percentage yield
Percentage yield = Actual yield / Theoretical yield * 100
Atom economy definition
A measure of the proportion of reactant atoms that become part of desired product (rather than by-products)
Formula for atom economy
% atom economy = Mᵣ of desired product / sum of Mᵣ of all reactants * 100
Example atom economy calculation
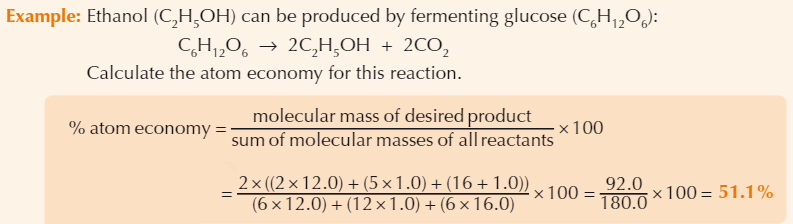
Advantages of processes with high atom economies
Better for environment - less waste
More sustainable - make more efficient use of raw materials
Less expensive - less money spent on separating waste from desired product