IB Biology: Evolution and Speciation Key Concepts and Evidence
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Evolution
Change in the heritable characteristics of a population over generations
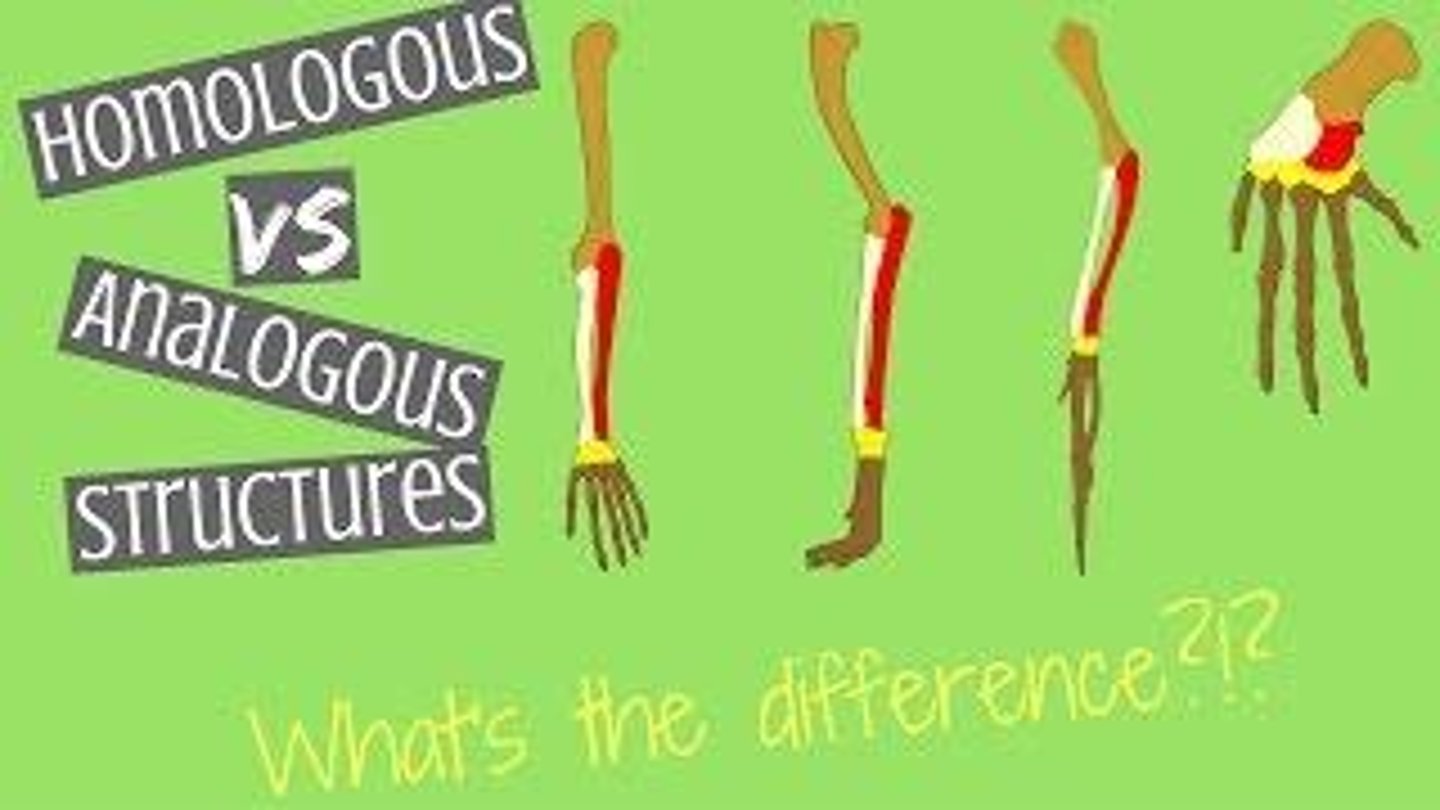
Homologous Structures
Structures that are similar in different species due to common ancestry.
Selective Breeding
The process by which humans breed plants and animals for particular genetic traits.

Common Ancestor
An ancestral species from which multiple species have evolved.
Pentadactyl Limb
A limb structure with five digits found in many vertebrates, indicating common ancestry.
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area.
Convergent Evolution
The process by which unrelated organisms develop similar traits due to similar environmental pressures.
Analogous Structures
Structures that serve similar functions in different species but do not share a common ancestry.
Extinction
The end of an organism or a group of organisms, typically due to environmental changes or loss of habitat.
Reproductive Isolation
A mechanism that prevents species from mating and producing viable offspring.
Geographical Isolation
A form of reproductive isolation where species are separated by physical barriers.
Evidence for evolution from base sequences in DNA or RNA and amino acid sequences in proteins
Sequence data gives powerful evidence of common ancestry.
Evidence for evolution from selective breeding of domesticated animals and crop plants
Demonstrates how human intervention can lead to significant changes in species over time.
Evidence for evolution from homologous structures
Indicates common ancestry through structural similarities in different species.
Speciation by splitting of pre-existing species
Occurs when a population diverges into two or more distinct species.
Roles of reproductive isolation and differential selection in speciation
Reproductive isolation prevents interbreeding, while differential selection drives adaptation and divergence.
Evidence for Evolution
The biomolecules DNA, RNA and proteins provide strong evidence for evolution.
Mutations
Differences in the base sequences of DNA (and therefore RNA and proteins) are the result of mutations.
Mutation Rate
Mutations accumulate gradually over long periods of time at a constant rate.
Closely Related Species
Closely related species have very similar gene and protein sequences, as there will be a small number of mutations because they diverged from a common ancestor.
Selective Breeding of Dogs
Dogs (Canis lupus familiaris) were domesticated from wolves (Canis lupus) 15000 years ago.

Pentadactyl Limbs
Pentadactyl limbs are an example of homologous structures.
Function of Pentadactyl Limbs
The structure of the limb is similar in all species, but has evolved modifications for a variety of purposes such as carrying tools in humans, running in dogs, flying in birds and swimming in whales.
Example of Analogous Structures
Wings of birds, bats and insects are analogous structures, as they have the same function (flight) but do not share a common ancestor.
Geographical Isolation of Apes
The population of the ancestor became geographically isolated into two distinct populations which were separated as the Congo river became wider.
Reproductive Isolation of Apes
The ape populations were reproductively isolated, as members of each population were unable to reproduce with each other.
Differential Selection
The selection pressures were different on the two sides of the Congo river, leading to different traits being selected in the apes.
Sympatric Speciation
The evolution of new species from a single ancestral species while inhabiting the same geographic region.
Allopatric Speciation
The evolution of new species due to geographical isolation.
Behavioural Isolation
Reproductive isolation due to differences in mating behaviors.
Temporal Isolation
Reproductive isolation due to organisms reproducing at different times.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Niche
The role or function of an organism or species within an ecosystem.
Adaptive Radiation
The diversification of a group of organisms into forms filling different ecological niches.
Hybridization
The process of combining different varieties of organisms to create hybrids.
Prezygotic Barriers
Factors that prevent mating or fertilization between species.
Postzygotic Barriers
Factors that prevent hybrid offspring from developing into viable adults.
Sterile
Incapable of producing offspring.
Hybrid Inviability
A condition where hybrid offspring do not survive to maturity.
Hybrid Infertility
A condition where hybrid offspring are unable to reproduce.
Hybrid Breakdown
A condition where the second generation of hybrids is inviable or sterile.
Polyploidy
The condition of having more than two complete sets of chromosomes.
Triploid
An organism with three sets of chromosomes.
Tetraploid
An organism with four sets of chromosomes.
Cicadas
Different species of cicada have different life cycle lengths: either 13 or 17 years.
Cicada Life Cycle
Cicadas remain as larvae underground during most of their life cycle. At the end of the life cycle the adults emerge, live for a short time above ground and reproduce, then die.
Temporal Isolation in Cicadas
The adult cicadas with a 13 year life cycle will rarely be present at the same time as the cicadas with a 17 year life cycle.
Adaptive Radiation of Darwin's Finches
Darwin's finches evolved by adaptive radiation from a single mainland species which moved into the different niches available on the Galapagos Islands.
Adaptive Radiation Increases Biodiversity
Adaptive radiation and divergent evolution increase the biodiversity of an ecosystem with vacant niches.
Mule
A mule is an example of a sterile hybrid, being the offspring of a male donkey and a female horse.
Barriers to Hybridization
Hybrids are rarely formed between different species due to prezygotic or postzygotic barriers.
Mechanical Isolation
Mechanical isolation occurs when physical differences between organisms prevent sexual intercourse.
Polyploidy Results
Results from non-disjunction, an error during meiosis (while producing gametes).
Immediate Speciation
Polyploidy can produce immediate speciation, as an organism is produced with a different number of chromosomes.
Persicaria maculosa
A tetraploid (4n) plant known for producing bigger fruits.
Uneven Number of Chromosomes
Polyploid plants with an uneven number of sets of chromosomes (3n, 5n, 7n ...) are sterile.
Adaptive radiation
occurs when many similar but distinct species evolve rapidly from a single species →Darwin’s finches