Bio160 Practice Questions
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
When did mammals first appear?
Arose about 220 mya
• Coexisted with dinosaurs for millions of years
• After extinction of non-avian dinosaurs, mammals diversified and grew larger
• Primitively, laid eggs • Two species still do! • Platypus, echidna
What are the Mammalian Traits?
Derived Similarities:
Hair
Lactation
Sweat Glands
Do all mammals give live birth?
No, there are two species that lay eggs and are considered mammals
ex. platypus, echidna (spiny anteaters)

What is the process of mammalian development?
Eggs are fertilized with the female’s body
Embryos start development in the uterus
The embryo is contained in an amniotic sac and connected to the uterine wall by the placenta
The placenta allows for nutrient gas exchange and waste elimination
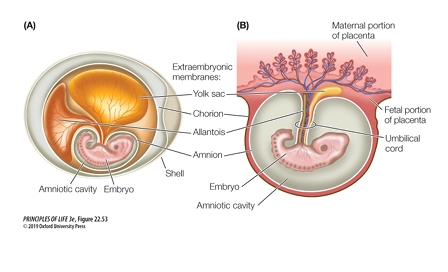
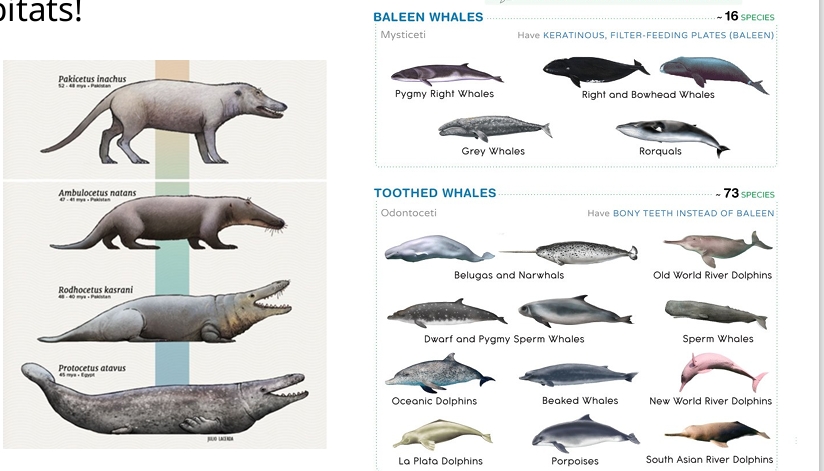
What is one example of mammals that went back into aquatic habitats?
Cetaceans - ex. baleen & toothed whales
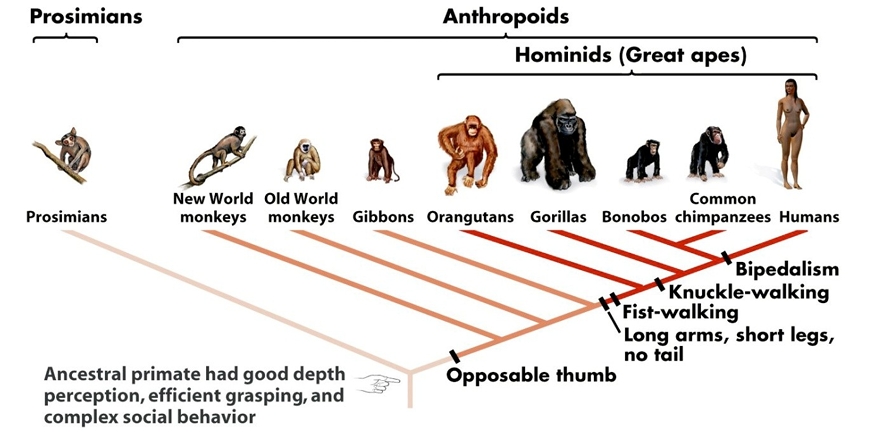
What did primates evolve from? When did they evolve? When was the split between humans chimps
Primates evolved from a lineage of small, arboreal (living in trees), insectivorous eutherians (mammals that give birth that primarily eat insects)
• 35 mya: The ape lineage separated from Old World monkeys
• 6 mya in Africa: Ancestral split that would eventually lead to the chimpanzees and the humans
How did humans evolve? What are some types of evidence proving this?
Humans did not evolve from modern apes BUT from the common ancestor of chimpanzees & humans
Evidence from: Shared morphological traits with modern chimpanzees & humans, Fossil evidence, DNA evidence
What are some uniquely human traits?
Bipedal locomotion, Brain size expansion, shorter gut (diet change to more meat), Hair changes (less body hair, longer head hair), Bigger newborns (fun fact: human babies have the highest fat content of all mammalian species at ~15%) and long development ~ More complicated labor and birth, No penis bone! (present in all other great apes), Handedness (other primates do not show preference!), Emotional weeping, new behaviors: symbolic thinking, personal ornaments, art, trade
What are the benefits of Bipedalism?
Frees forelimbs to manipulate objects/ carry items
• Walking on two legs is energetically economical (less energy to go farther)
What are the benefits and drawbacks of brain size expansion of humans?
Benefits
greater cognitive ability which helped in unpredictable environment
Drawbacks
Challenging birth (if head is too big won’t come out pelvic cavity)
Brains are energetically expensive (more nutrients need for neuron cells)
Longer juvenile period requiring parental care (26 years old when brain is fully developed)
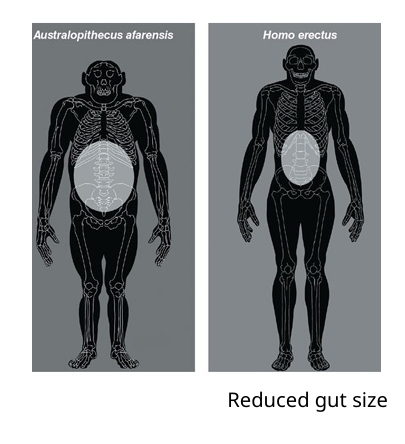
What are the benefits and drawbacks of having a shorter gut and different diet
Benefits
Meat is easier to digest
Drawbacks
Digestion and gut tissue are energetically expensive
How long ago did modern humans move to North America?
Between 20,000 and 12,000 years ago
What do trait and DNA evidence suggest about human ancestry among the great apes?
Humans and Apes have many similar morphological traits for ex.
opposable thumbs, no tail,
Genetic differences are often smaller than benchmarks for Genetic Cluster Species Concept Example: sequence Xq13.3 on X chromosome Differences:
• 0.9% between humans and chimps
• 1.4% between humans and gorillas
• 2.9% between humans and orangutang
What traits changed over hominin evolution towards the Homo sapiens (human) species?
3.9-3.0 mya
fully bipedal
femur to humerus ratio (Long arms, short legs)
Lucy
2.5 mya
Homo genus evolves
Larger brain
tools
150,000 ya
Homo neanderthalensis
Art, jewelry
Burial ritual
100,000 ya
Africa first then elsewhere
Did more than of hominin exist at the same time? What were the consequences of this?
Multiple species of bipedal hominins lived together at the same time
Competition for resources – different hominin species may have competed for food, water, and shelter.
Interbreeding – some species, like Neanderthals and modern humans, interbred, leaving genetic traces in modern populations.
Diverse adaptations – multiple species allowed hominins to occupy different ecological niches and survive in varied environments.
How many surviving members of the genus Homo exist today? Were there more in the past?
Only one species of homo left (us)
there were more in the past they are extinct
What are some examples of traits that differ among humans due to natural selection?
Skin color (darker with stronger UV radiation)
• Vitamin D deficiency (common farther from the equator)
• Eye color (lighter with limited light)
• Cranial capacity (slightly larger in colder regions)
• Lactose intolerance (mutation most common in Europe)
• Malaria resistance (sickle cell)
What are some examples of human evolution in more recent times? How is the human society reducing selective forces?
Glasses emerged in Northern Italy during the 13th century, around the 1200s
• Reductions in jaw size over evolution meant crowding of teeth
• Third molars are now removed (wisdom tooth removal) in many
• Childbirth previously was a selective force on child and head size
• C-sections which reduce mortality may relax selection
• Heavy smoking leads to Alzheimer's and cardiovascular issues despite interventions
• Sexual selection is at play
What is “Lucy”
Skeleton discovered in 1974
• Provided evidence that bipedalism preceded large brain