Bio 120- Energy and Enzymes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is bio energy
The energy required for living cells
Anything that can be transformed into heat
What is chemical energy?
The energy stored in all chemical molecules
What is dependant on the energy stored in chemical?
The potential energy is different according to the arrangement of there atoms
How can potential energy be maximized in a molecule?
BY breaking down energy rich food (sugars and fats) to simpler compounds such as CO2 and H2O
What is cellular metabolism?
the sum of chemical activities within a cell
What are the two metabolic pathways? Explain
Anabolism:
Complexe molecules being synthesized from simple compounds
Catabolism (cataclysm):
Large molecules being broken down to smaller ones
What’s a metabolic pathway?
The sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Which way does the energy go in anabolitic Rx?
It is brought into THE rx to create energy rich molecules
Which way does the energy go in catabolitic Rx?
It is produced from the rx- energy output
What needs to be constant for the energy in a system to be able to perform work?
Temperature and Pressure
What is free energy?
It’s delta G
The maximum amount of free energy available to do work
Reactant(A)———- Product (B) + delta G
Describe a spontaneous rx
A reaction that happens on its own without outside energy input
Describe an exergonic Reaction
When energy is released as the result of the reaction. The products have less PE than reactants
Describe an endergonic reaction?
When a reaction requires energy to react. The products have more PE than the reactants
Ex: glucose synthesis (photosynthesis)
Energy coupling reaction?
Using energy produced from an exergonic reaction to do an endergonic reaction
What do reactions need to regulate their Reactions?
Enzymes
What is the energy of activation?
An amount of energy needed before a reaction can occur. Also thought as an energy barrier
What is the main role of (protein) enzymes?
To lower the energy of activation of specific rxs
What is an enzyme?
A protein complex/ single polypeptide that serves as a catalyst. It is not a part of the reaction
What are some secondary roles of enzymes?
Allows equilibrium to be attained faster
What is the difference between an enzyme and a substrate?
How can enzyme activity be regulated?
inhibitors, pH, temperature
What are some different non-protein complexe enzymes require?
Cofactor
Coenzymes
Prosthetic group
What’s a cofactor?
Inorganic ions:
copper
iron
zinc
all binds to certain enzymes
What’s a coenzyme?
Organic carbon molecules.
Energy carriers
Not permanently attached
CoA,
NAD
FADATP
What’s a Prosthetic group?
Distinct molecules that are permanently bound to enzyme
EX: hemoglobin to blood that carries the O2 in blood
What’s the main bioenergy carrier in living cells ?
ATP or adenosine 5’-triphosphate
Describe the ATP dynamic within a cell
For immediate use, the energy is stored in ATP
Very active
The energy is stored in form of chemical bonds
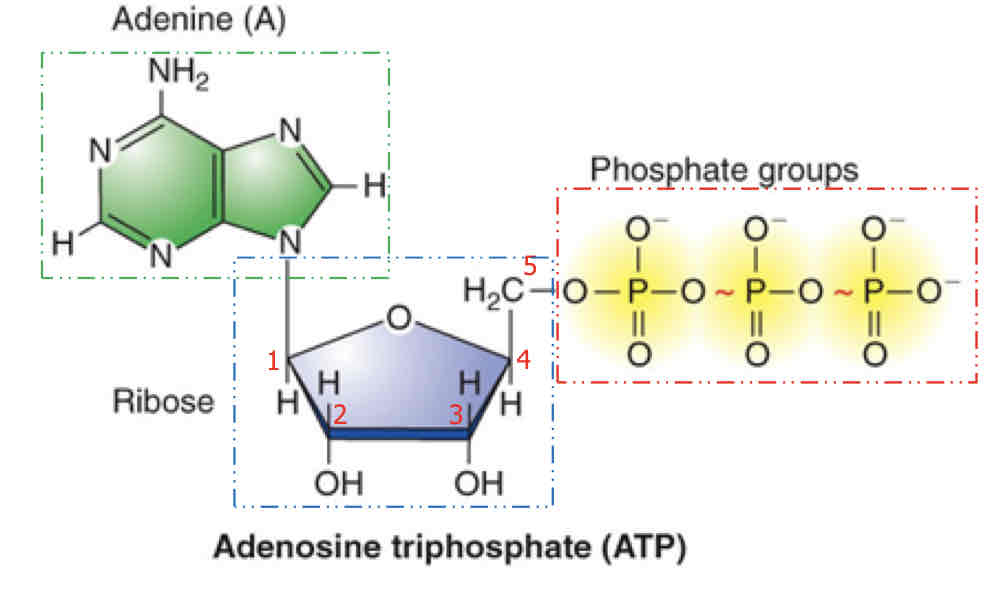
What’s the structure of ATP
Adenine-nitrogen organic base
Ribose- 5 carbon sugar
Three phosphate groups (oxygen around phosphorus
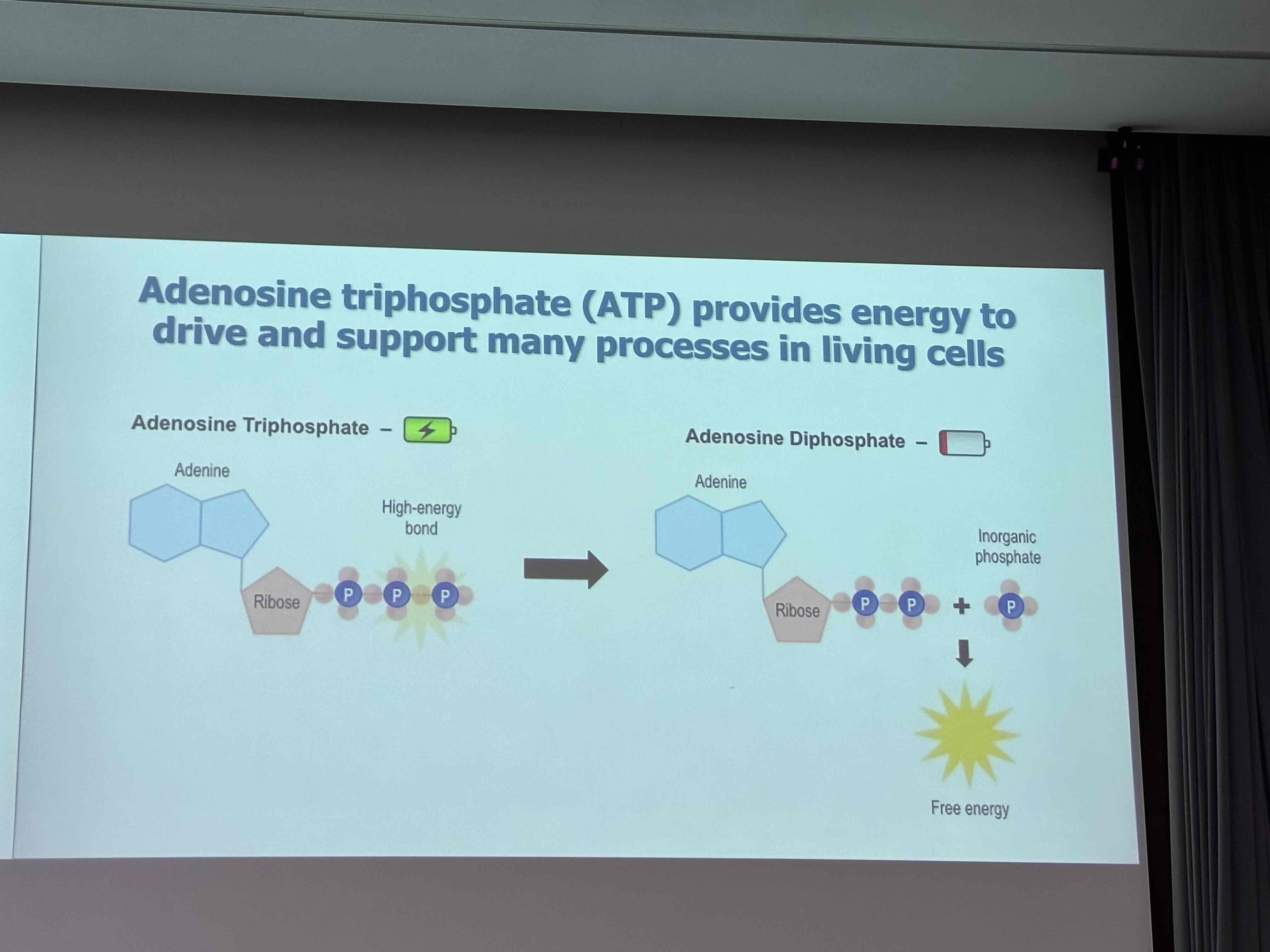
How does ATP release energy? What type of reaction is it?
Hydrolysis- exergonic Rx (addition of water to separate a phosphate group)
Releases -7.6Cal/ mol
When the phosphate group does not bind to another molecule
ATP + H20————-ADP + Pi + delta G(-7.4kcal/ mol)
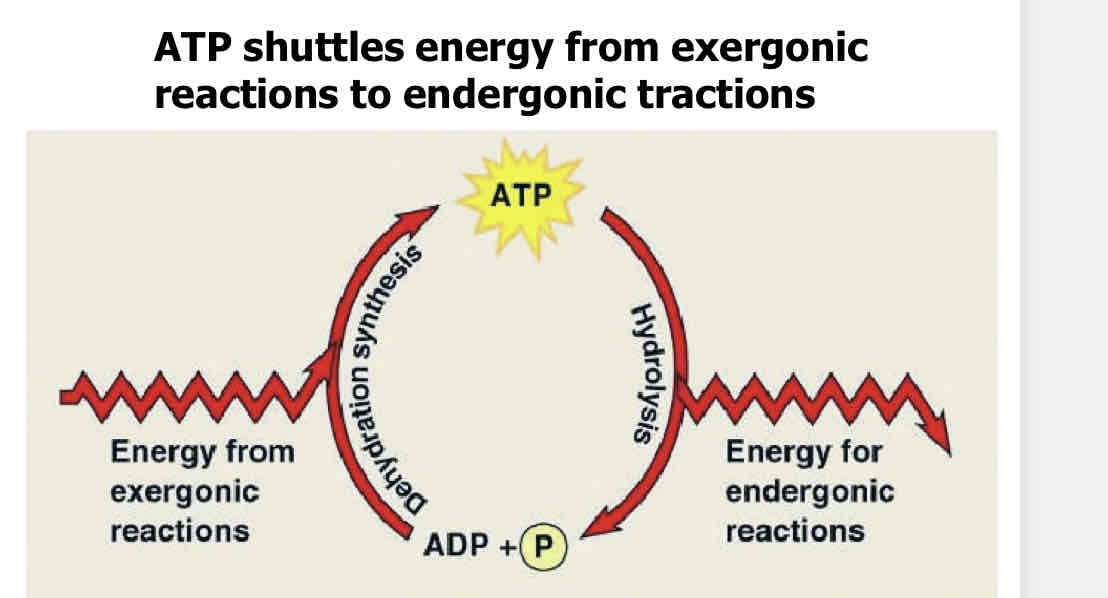
Most cellular works depend on which reaction reaction?
Phosphorylation: when ATP energizes other molecules by transferring a phosphate group
Describe the formation of sucrose?
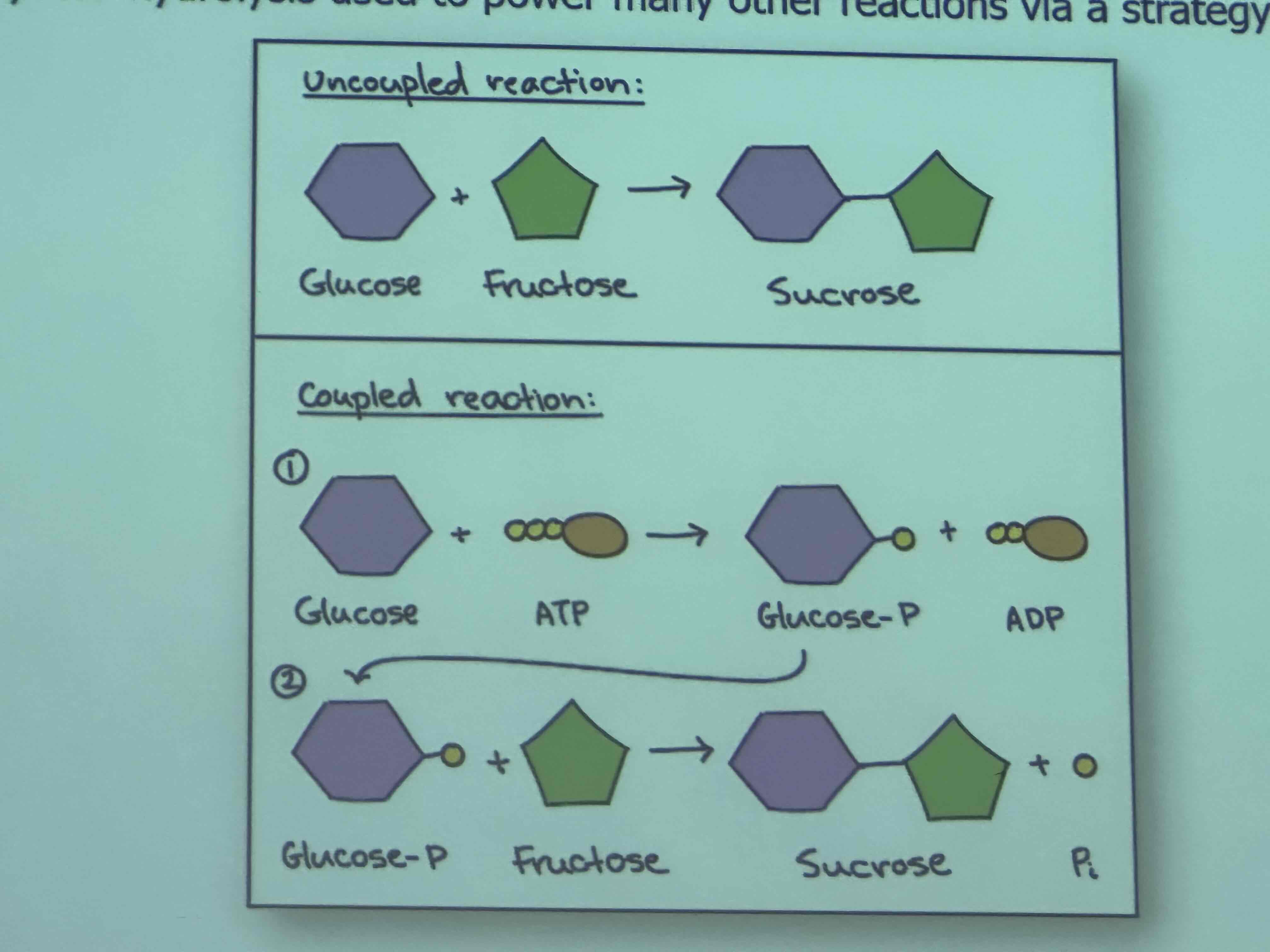
Through what type of reaction does the formation of glucose occur?
A coupling reaction (redox rx)
Describe how ATP drives cellular work
Moto proteins move via cytoskeletal actin filaments to do mechanisms activated by the hydrolysis of ATP
What are examples of coupling reaction that ATP hydrolysis powers?
sucrose formation
protein phosphorylation (change structures that aids in signaling transduction)
yin-yang
Explain a coupling reaction
ATP works through a phosphorylation (addition of a phosphate group to a molecule)
What is the most ancient passing of cells in the making of ATP?
The formation of glucose as a substrate-level phosphorylation
What are the two ways to generate ATP?
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
Describe how substrate-level phosphorylation works
When a phosphate group is transferred to ADP from an intermediate compound called substrate
Describe how chemiosmosis works
When the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP is linked to the transfer of an electron through and electron transport chain.
What are the two types of chemiosmosis?
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Photophosphorylation
Describe how oxidative phosphorylation works
When ATP synthesis comes from the transfer of electron to oxygen (last part of cell respiration)
Describe how photophosphorylation works
ATP synthesis driven by light (sunlight such as photosynthesis)
How do cells transfer energy?
Through REDOX reactions
Substance oxidized looses energy (electrons)
Substrate reduced gains energy (gains said electron)
Which are the most common acceptor molecules in a living cell?
NAD+ to NADH :
NADP+ to NADPH
FAD+ to FADH2
Cytochromes (Feiii) to Cytochromes (Feii)
Quinone (Q) to Quinone (QH2)
What are the bioenergy carrier important for (process)?
Photosynthesis and cellula