communication and collaboration in professional nursing - lecture 3 pt 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what happens when we fail to communicate

miscommunication
Up to 80 percent of serious medical errors can be attributed to __________________ (the joint commission, 2016)
interpersonal skills
-WHAT PROMOTES COMMUNICATION?
-WHAT IMPEDES COMMUNICATION?
joseph priestley
the more elaborate our means of communication, the less we communicate
george bernard shaw
The single biggest problem with communication is the illusion that it has taken place
peplau
(1952) Interpersonal Relations
nurse pioneer
1952- book- Interpersonal Relations (Nurse/Patient/Relationship)
"therapeutic use of self"
-Orientation phase: trust
-Working phase: tasks
-Termination phase
-SELF AWARENESS
-PROFESSIONAL BOUNDARIES
-Social vs. professional relationships (compare box 12-1 p 269) ***
-REFLECTIVE PRACTICE
-AVOID STEREOTYPES
-NON - JUDGMENTAL
-acceptance
-PATIENT CENTERED CARE
--Caring is key
what are key elements impacting communication and collaboration
-verbal
-congruence
-nonverbal
communication theory
five elements of the communication process
-The sender is the person sending the message
-the message is what is actually said plus accompanying nonverbal communication
-the receiver is the person acquiring the message. A response to a message is termed feedback. The setting in which an interaction occurs, including the mood, relationship between sender and receiver, and other factors, is known as the context.
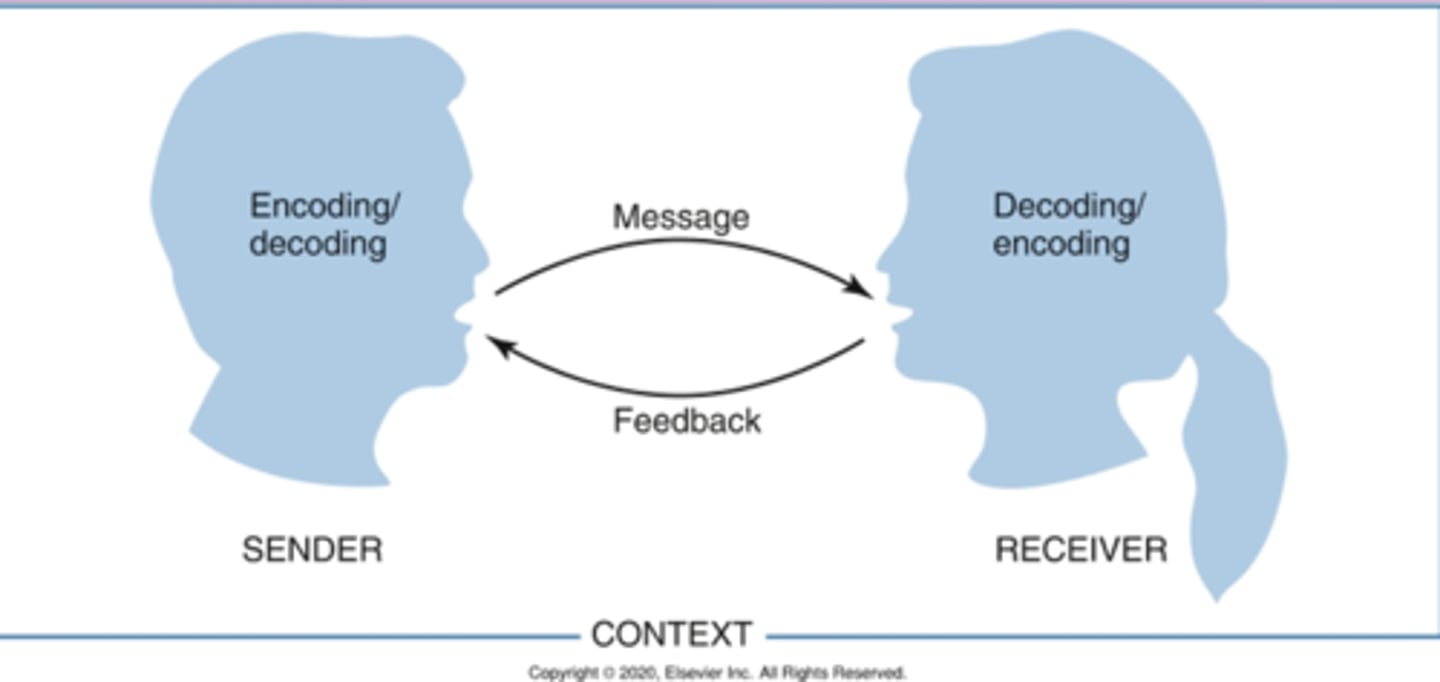
perception
-"selection, organization, and interpretation of incoming signals into meaningful messages."
-"individual's perceptual screen, through which all incoming messages are filtered."
evaluation
"analysis of received information"
Individualized
_______________ and impacted by gender, age, culture, interest, mood, value, clarity, length of message, feedback, intellect, sociocultural conditioning….very complex
Electronic health records, telemedicine
What about some topics for todays nursing practice?
somatic language
consists of crying; changing skin color; fast, shallow breathing; facial expressions; and flexing of their arms and legs. These are all things you see an infant doing that does not talk
action language
Consists of reaching out, pointing, crawling toward a desired object, or closing the lips and turning the head when an undesired food is offered.
verbal language
develops last, beginning with repetitive noises and sounds and progressing to words, phrases, and complete sentences.
feedback
Receiver relays to a sender the effect of the sender's message, feedback has occurred.
appropriateness
correct "fit" of a reply, that is, when it matches the message, EG. Usual greetings
efficiency
Using simple, clear words that are timed well
flexibility
Bases messages on the immediate situation
active listening
involves focusing solely on a person and acknowledging feelings in a nonjudgmental manner.
open posture
(sitting up straight, relaxed, arms uncrossed) also communicate interest.
empathy
consists of awareness of, sensitivity to, and identification with the feelings of another person
open-ended questions
not Yes n No answers
giving information
includes sharing knowledge that the recipients are not expected to know.
reflection
mirror, demonstrates understanding and acceptance
silence
means allowing periods of quiet thought during an interaction without feeling pressure to fill the silence with conversation or activity.
language barriers
Spanish is the 2nd most common language in US. Need to use translators
-Fail to see uniqueness of individual
-Fail to recognize level of meaning
-Use value statements and clichés
-False reassurance
-Failure to clarify
-Ineffective use of electronic communication devices
-Failure to value culture or generation differences
why does communication fail?
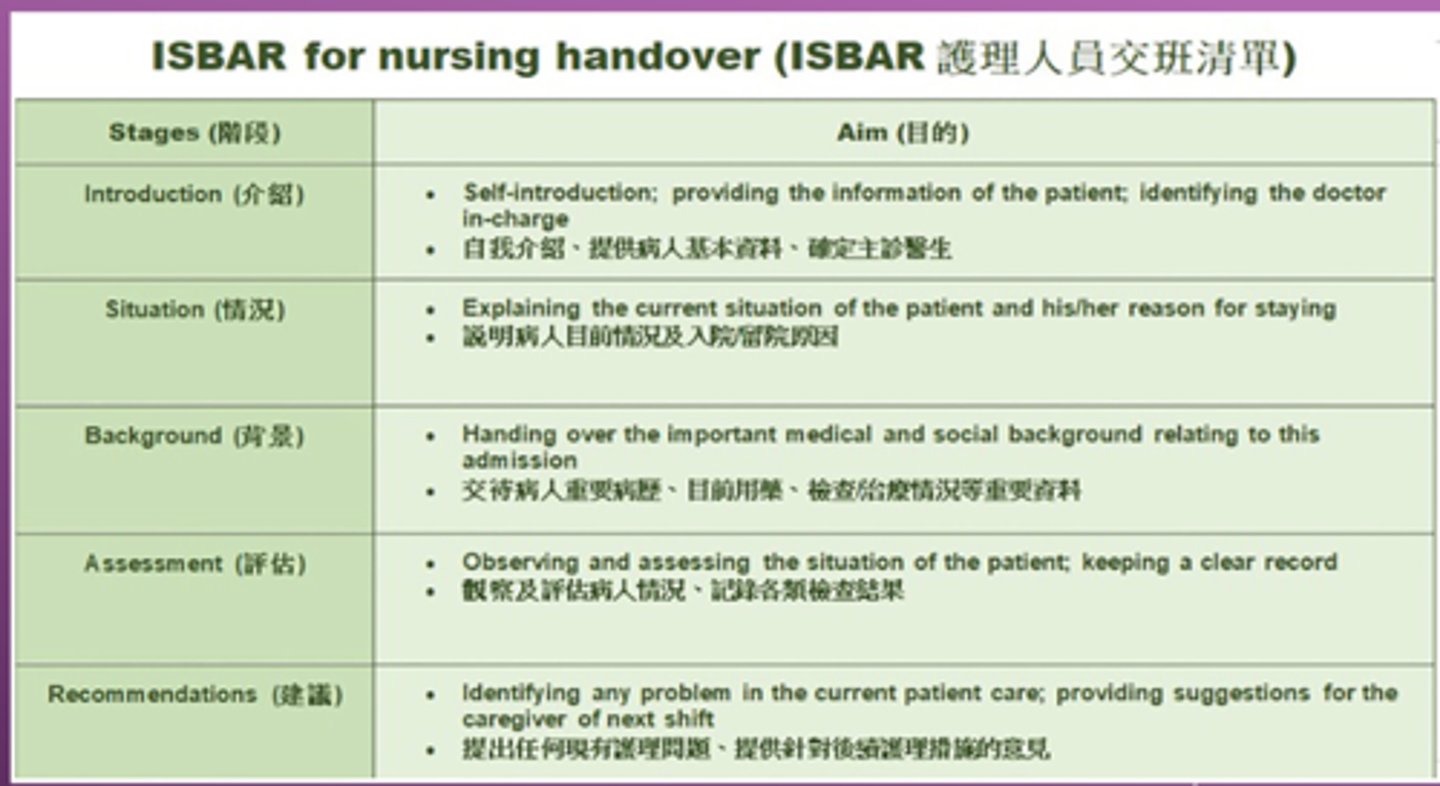
-introduction
-situation
-background
-assessment
-recommendation
what does ISBAR stand for
leadership
leadership
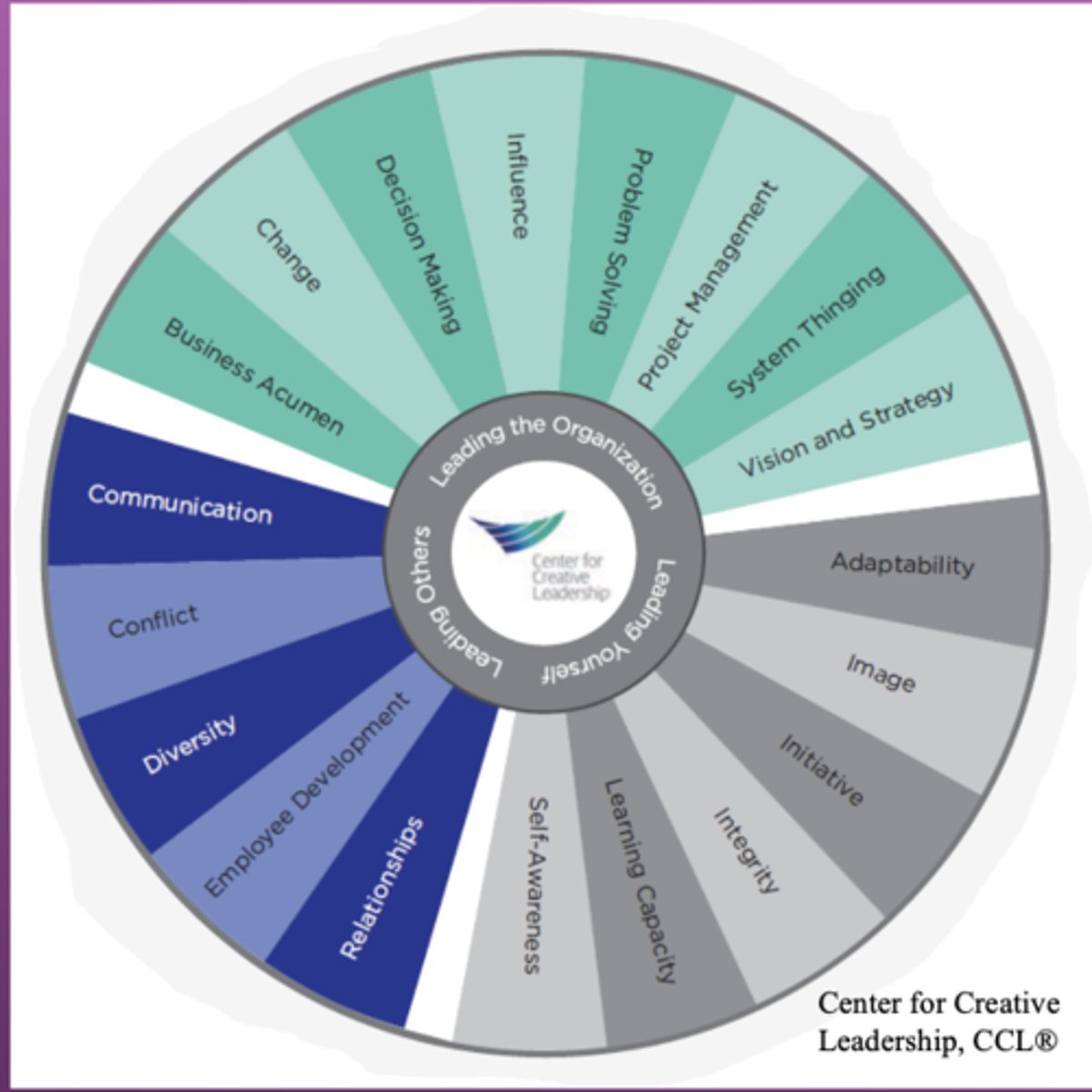
ANA
_____ developed the ANA Leadership for the nurse interested in excelling in a career path,
a leader within a health care organization who represents the interests of the nursing profession,
a seasoned nurse or health care administrator interested in refining skills to differentiate them from the competition or to advance to the next level of leadership.