Cell Membranes: Structure, Function, and Transport Mechanisms
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Phospholipid bilayer
Double layer of phospholipids forming cell membranes.
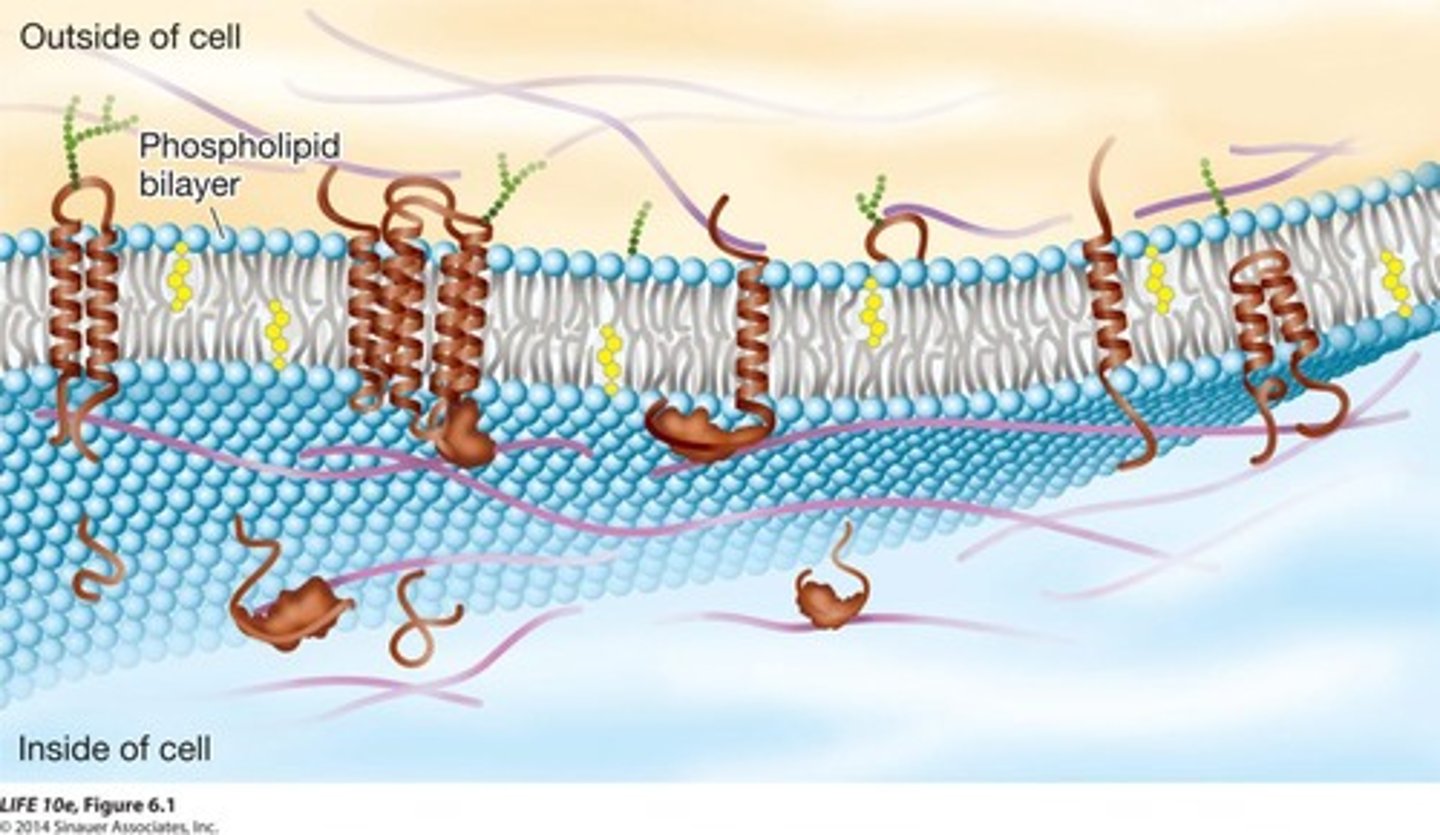
Fluid Mosaic model
Describes membrane structure with proteins in lipids.
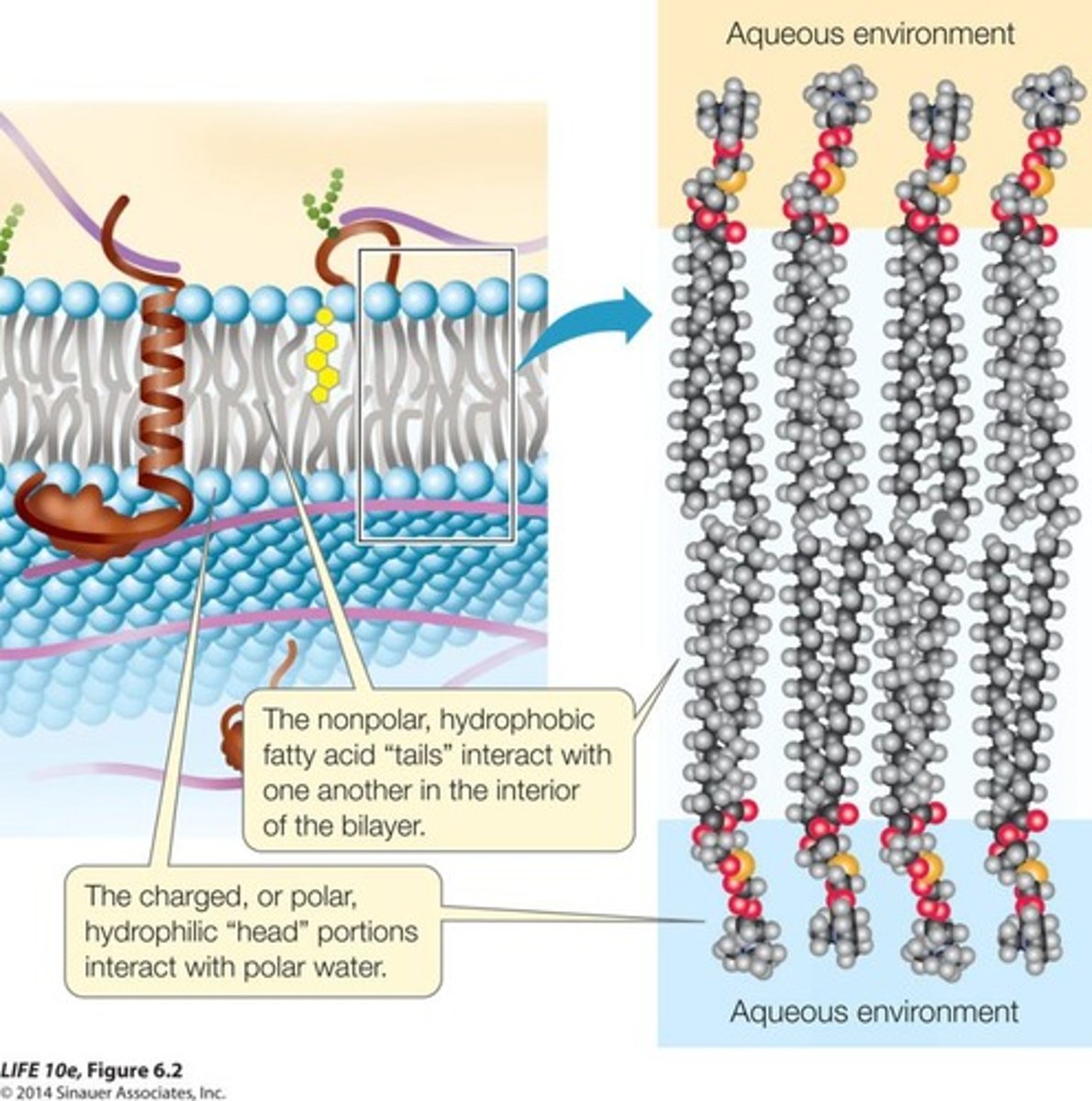
Hydrophobic interior
Nonpolar region of the membrane repels water.
Polar phospholipid heads
Hydrophilic parts facing water inside and outside.
Nonpolar phospholipid tails
Hydrophobic parts facing inward, away from water.
Transport proteins
Facilitate movement of substances across membranes.
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates attached to lipids for cell recognition.
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrates attached to proteins for cell adhesion.
Semi-permeable barrier
Allows selective passage of substances through membrane.
Non-polar molecules
Easily cross membranes without assistance.
Polar molecules
Cannot diffuse across membranes without help.
Ions
Cannot cross membranes unaided, e.g., Na+.
Membrane composition
Varies among different cells and organelles.
Saturated fatty acids
Less fluidity in membranes, more stable.
Unsaturated fatty acids
Increase membrane fluidity, especially in cold.
Peripheral membrane proteins
Not embedded, interact with membrane surface.
Integral membrane proteins
Embedded in membrane, have hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts.
Transmembrane proteins
Span the membrane, protruding on both sides.
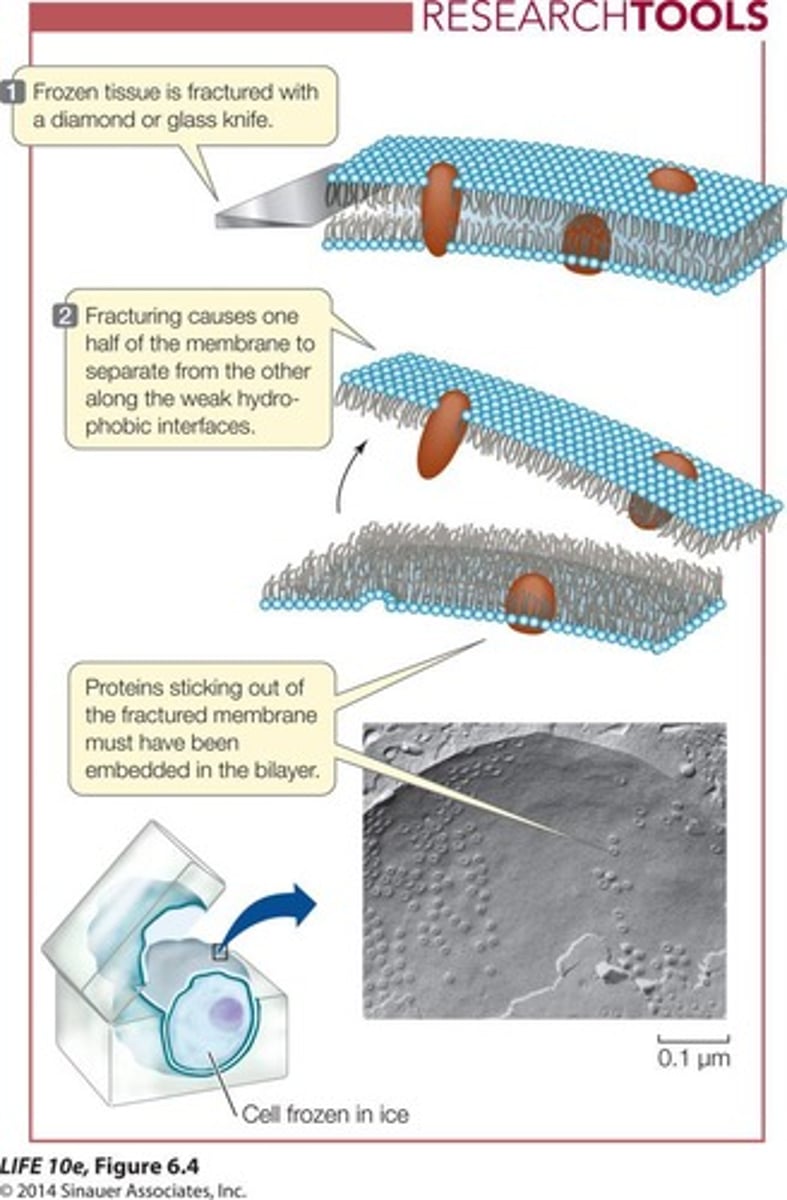
Freeze-fracture method
Technique to visualize membrane proteins.
Cell junctions
Structures that connect adjacent cells.
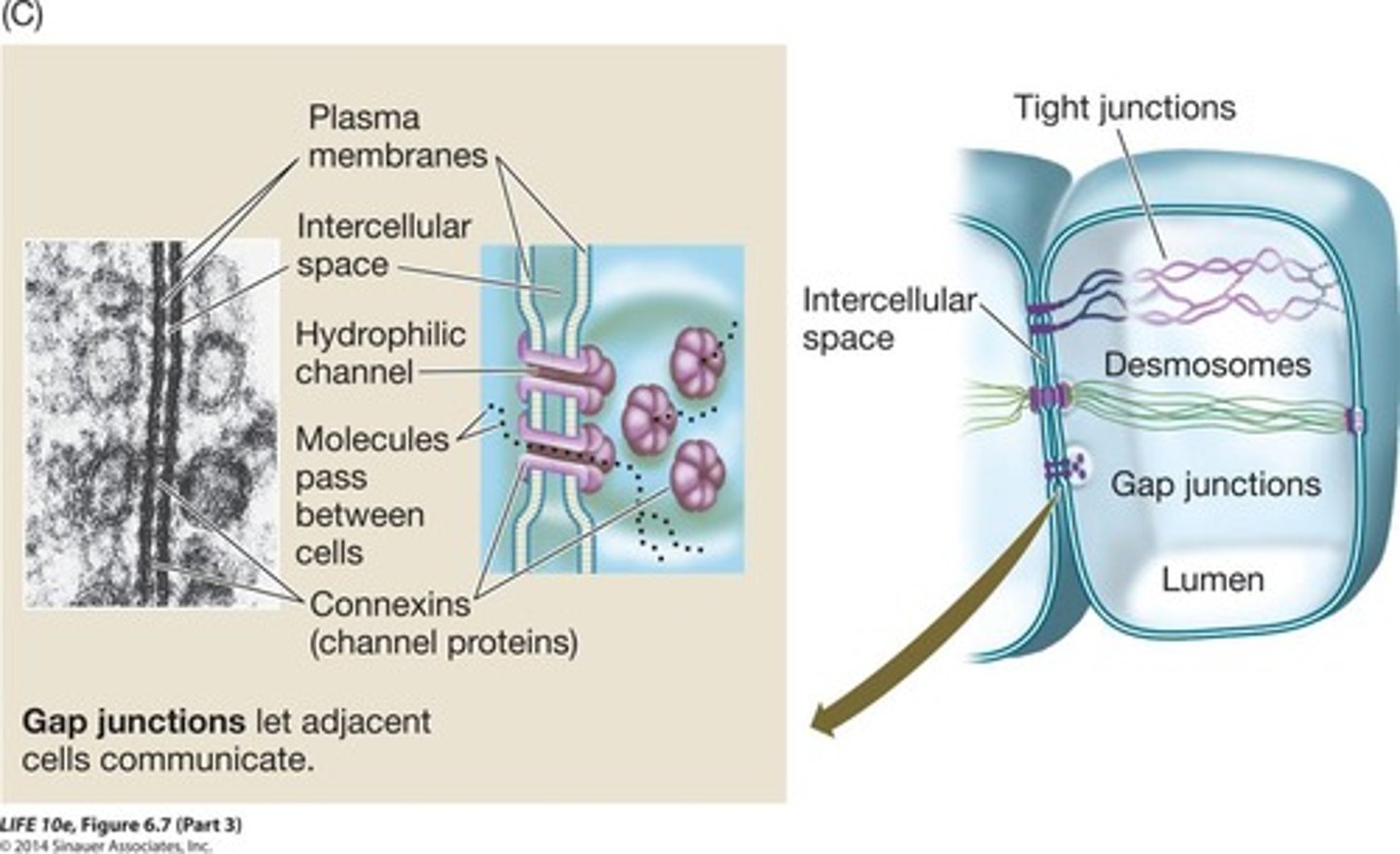
Tight junctions
Prevent leakage between cells, seal intercellular spaces.
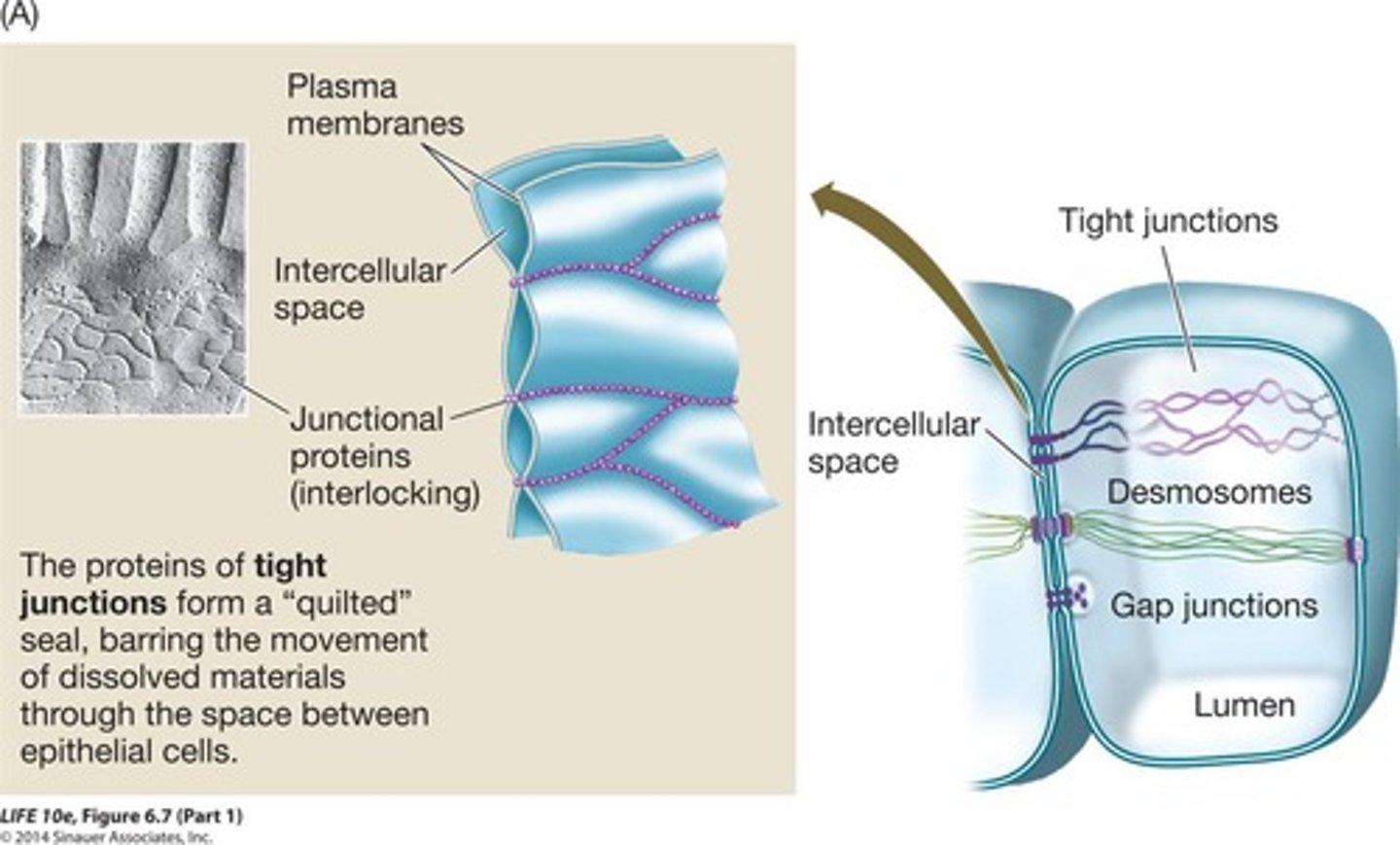
Desmosomes
Provide mechanical stability, hold cells together.
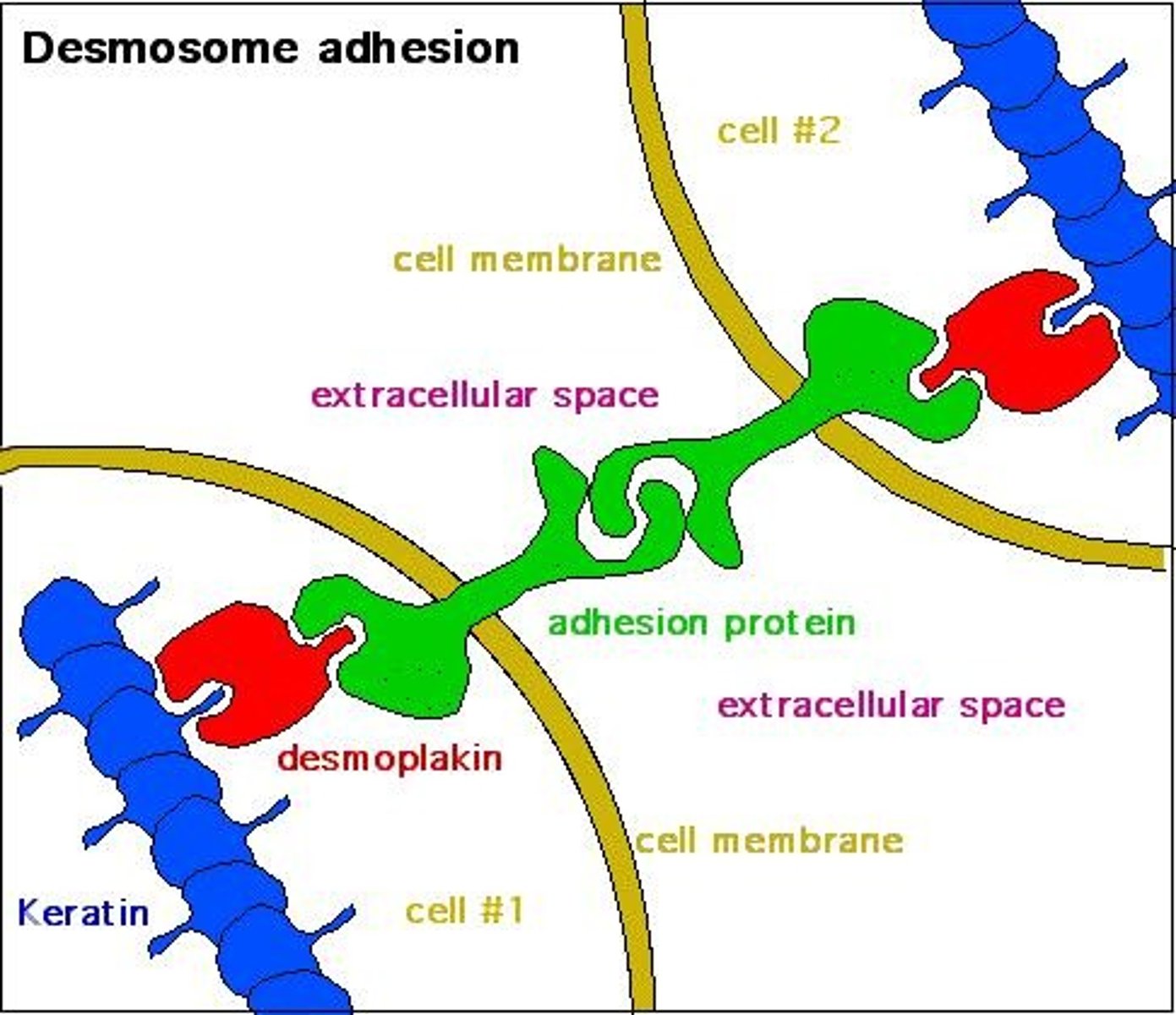
Gap junctions
Channels for communication between adjacent cells.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Protein mix surrounding cells, aiding communication.
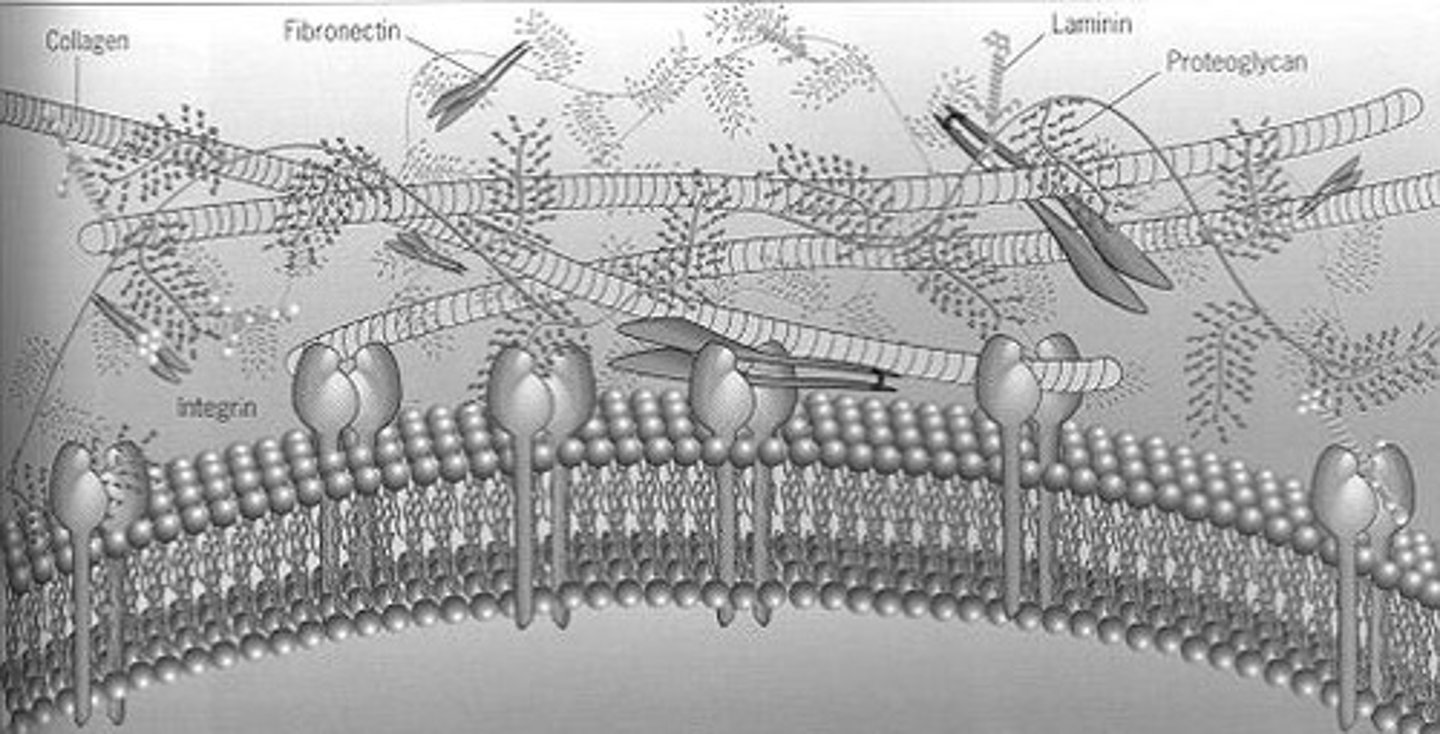
Integrin
Protein mediating cell attachment to ECM.
Passive transport
Movement of substances without energy input.
Diffusion
Movement from high to low concentration.
Simple diffusion
Nonpolar molecules cross membranes unaided.
Facilitated diffusion
Polar molecules use proteins to cross membranes.
Carrier proteins
Transport molecules across membranes, limited speed.
Active transport
Movement against concentration gradient, requires ATP.
Sodium-potassium pump
Moves Na+ out and K+ into cells.
Primary active transport
Direct use of ATP for transport.
Secondary active transport
Uses established gradients for energy.
Endocytosis
Process of bringing substances into the cell.
Exocytosis
Process of expelling substances from the cell.
Phagocytosis
Cell engulfs large particles or cells.
Pinocytosis
Cell takes in fluids and dissolved substances.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Specific uptake of substances via receptors.
Clathrin
Protein aiding in vesicle formation during endocytosis.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable barrier.
Tonicity
Comparison of solute concentrations in solutions.
Hypertonic solution
Higher solute concentration, water moves toward it.
Hypotonic solution
Lower solute concentration, water moves away from it.
Cell-cell recognition
Cells identify and bind to each other.
Cell adhesion
Cells stick together to maintain tissue structure.
Cell junction types
Include tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions.
Membrane fluidity
Affected by lipid composition and temperature.
Cold-blooded animals adaptation
Change fatty acids to maintain membrane fluidity.