[PT11] Mechanical Principles
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
1
New cards
force
that which alters the state of rest of a body or its uniform motion in a straight line
2
New cards
direction and magnitude of force
what is the composition of forces?
3
New cards
causes movement in the direction of the force
the effect of the application of a single force applied to a body
4
New cards
equivalent to a single force acting at a common point but with the magnitude equal to the sum of their forces
the effect of two forces acting in the same direction and at a common point
5
New cards
a state of equilibrium
the effects of two equal forces acting at a common point, and in opposite directions
6
New cards
movement in the direction of the greater force
the effect of two unequal forces acting at a common point and in opposite directions
7
New cards
their forces compound producing a desired effect
the effect of two forces acting at an angle to each other
8
New cards
rotation of the body
the effect of two unequal forces acting at different points and in opposite directions
9
New cards
tension
a system of forces tending to separate parts of the body with equal and opposite forces which hold the parts together; used synonymously with force
10
New cards
gravity
the force by which all bodies are attracted to the earth
11
New cards
force of gravity
acts continuously upon the human body, and if unopposed the body will fall to the ground
12
New cards
anti-gravity muscles
erect position is maintained by the integrated contraction of these muscles
13
New cards
center of gravity
the point through which the line of action of the weight acts
14
New cards
the body of the 2nd sacral vertebra
where the center of gravity of the human body is located
15
New cards
line of gravity
a vertical line through the center of gravity
16
New cards
the vertex of the skull, body of the 2nd sacral vertebra, and between the feet
where does the line of gravity of a human pass through?
17
New cards
base of support
the area by which a body is supported
18
New cards
the area between the feet
where is the base support in humans?
19
New cards
stable equilibrium
the body restore to its original position after being displaces
20
New cards
unstable equilibrium
the body tend to displace after application of a force, the body falls on the ground
21
New cards
neutral equilibrium
there is a displacement of the body but the height and position of the center of gravity remain (e.g. a ball moves on a flat surface)
22
New cards
in a lying position
when is the stability of a human greatest?
23
New cards
it becomes less stable as the center of gravity is raised and base of support is reduced
how does the human body become less stable?
24
New cards
kinetics
concentrates on the forces that produce or resist the movement
25
New cards
kinematics
deals with types of motion or movement without regard for the forces that produce motion (type, direction, and quantity of motion)
26
New cards
osteokinematics & arthrokinematics
subdivisions of kinematics
27
New cards
axis
a line about which movement takes place
28
New cards
plane
the surface which a movement takes place
29
New cards
axes & planes
these are used to describe movement
30
New cards
sagittal axis
in an anterior-posterior direction
31
New cards
frontal axis
in the side-to-side direction
32
New cards
vertical axis
is parallel to the line of gravity
33
New cards
horizontal plane
a surface that divides the body into upper and lower
34
New cards
frontal plane
a surface that divides body into anterior and posterior aspect
35
New cards
sagittal plane
a surface that divides the body into right and left
36
New cards
horizontal plane
which plane is trunk rotation performed?
37
New cards
frontal plane
which plane is shoulder adduction performed?
38
New cards
sagittal plane
which plane is shoulder flexion performed?
39
New cards
horizontal plane
which plane is supination-pronation performed?
40
New cards
frontal plane
which plane is hip abduction performed?
41
New cards
sagittal plane
which plane is elbow flexion performed?
42
New cards
sagittal plane
which plane is hip flexion performed?
43
New cards
speed
the rate at which the body moves
44
New cards
velocity
the rate of motion which incorporates direction
45
New cards
work
the product of force and distance
46
New cards
energy
the capacity of a body for doing work
47
New cards
potential energy
the capacity for doing work by virtue of position
48
New cards
kinetic energy
capacity for doing work because of its velocity
49
New cards
power
the rate of doing work or the rate of energy expenditure; (force*distance/time)
50
New cards
joules/second or ergs/second
the unit of power
51
New cards
acceleration
the rate of change in velocity
52
New cards
acceleration
increase in velocity
53
New cards
decceleration
decrease in velocity
54
New cards
momentum
the quantity of motion it possesses
55
New cards
mass x velocity
how do you calculate momentum?
56
New cards
inertia
the resistance of a body to any change in its state of rest or motion; Newton's first law of motion
57
New cards
friction
the force which opposes motion when one surface slides upon another
58
New cards
lever
a rigid bar which is capable of movement about a fixed point called fulcrum
59
New cards
when a force or effort (E) applied at one point in the lever, acts upon another force or weight (W) acting at a second point on the lever (F) - fulcrum
how is work done in a lever?
60
New cards
effort's arm
perpendicular distance from the fulcrum (F) to the effort (E)
61
New cards
weight's arm
perpendicular distance from the fulcrum (F) to the weight (W)
62
New cards
1st class lever
class of lever in which the fulcrum is in the middle of the weight and effort
63
New cards
2nd class lever
class of lever in which the weight is in the middle of the fulcrum and effort
64
New cards
3rd class lever
class of lever in which the effort is in the middle of the fulcrum and weight
65
New cards
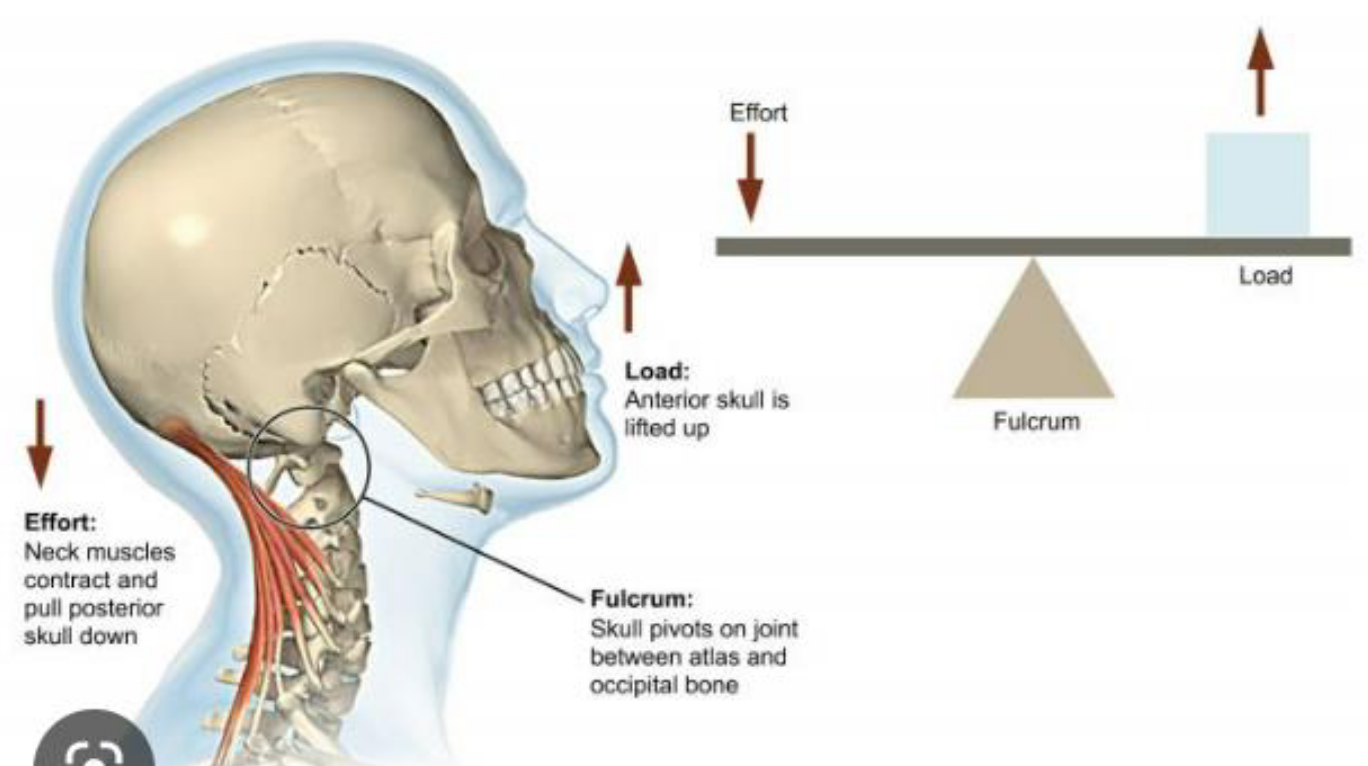
example of 1st class lever
66
New cards
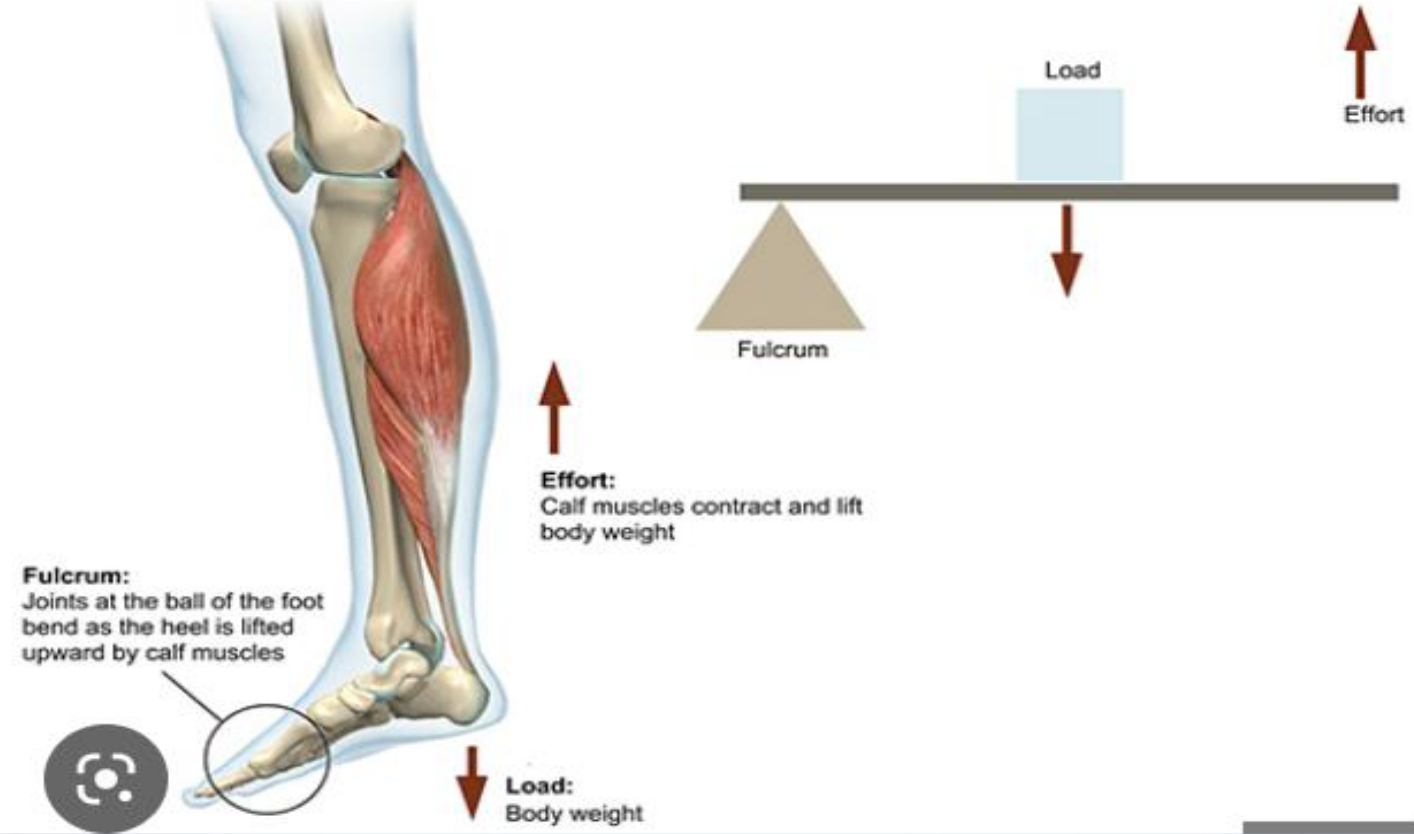
example of 2nd class lever
67
New cards
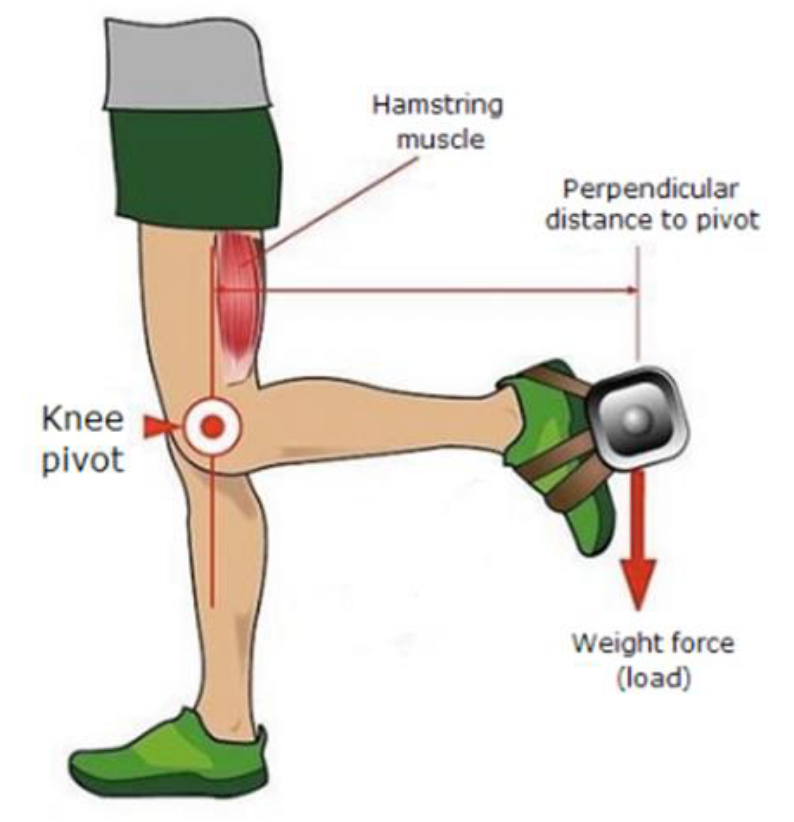
example of 3rd class lever
68
New cards
horizontal/transverse plane
a movement in the vertical axis would occur in which plane?
69
New cards
sagittal plane
a movement in the frontal axis would occur in which sagittal?
70
New cards
frontal plane
a movement in the sagittal axis would occur in which plane?
71
New cards
sagittal plane, frontal axis
which plane and axis does cervical forward flexion occur in?
72
New cards
horizontal/transverse plane, vertical axis
which plane and axis does internal rotation of the shoulder occur in?
73
New cards
horizontal/transverse plane, vertical axis
which plane and axis does circumduction occur in?
74
New cards
sagittal plane, frontal axis
which plane and axis does hip extension occur in?
75
New cards
frontal plane, sagittal axis
which plane and axis does neck lateral flexion occur in?