respiratory and cardiovascular
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
heart rate definition
the heart contracts and relaxes in a rhythm which produces a heart beat. it is the number of heartbeats in a minute (BPM)
cardiac output definition
the amount of blood ejected from the heart (left ventricle) in one minute. measurement = litres/min
stroke volume definition
the volume of blood pumped out of the heart by each ventricle during one contraction. measurement = ml per beat
tidal volume definition
the volume of air inspired or expired per breath.
breathing rate definition
the number of breaths per minute. it is typically 12-20 breaths per minute on a healthy adult
minute ventilation definition
amount of air a person breaths in a minute. this is calculated by : tidal volume x breathing rate
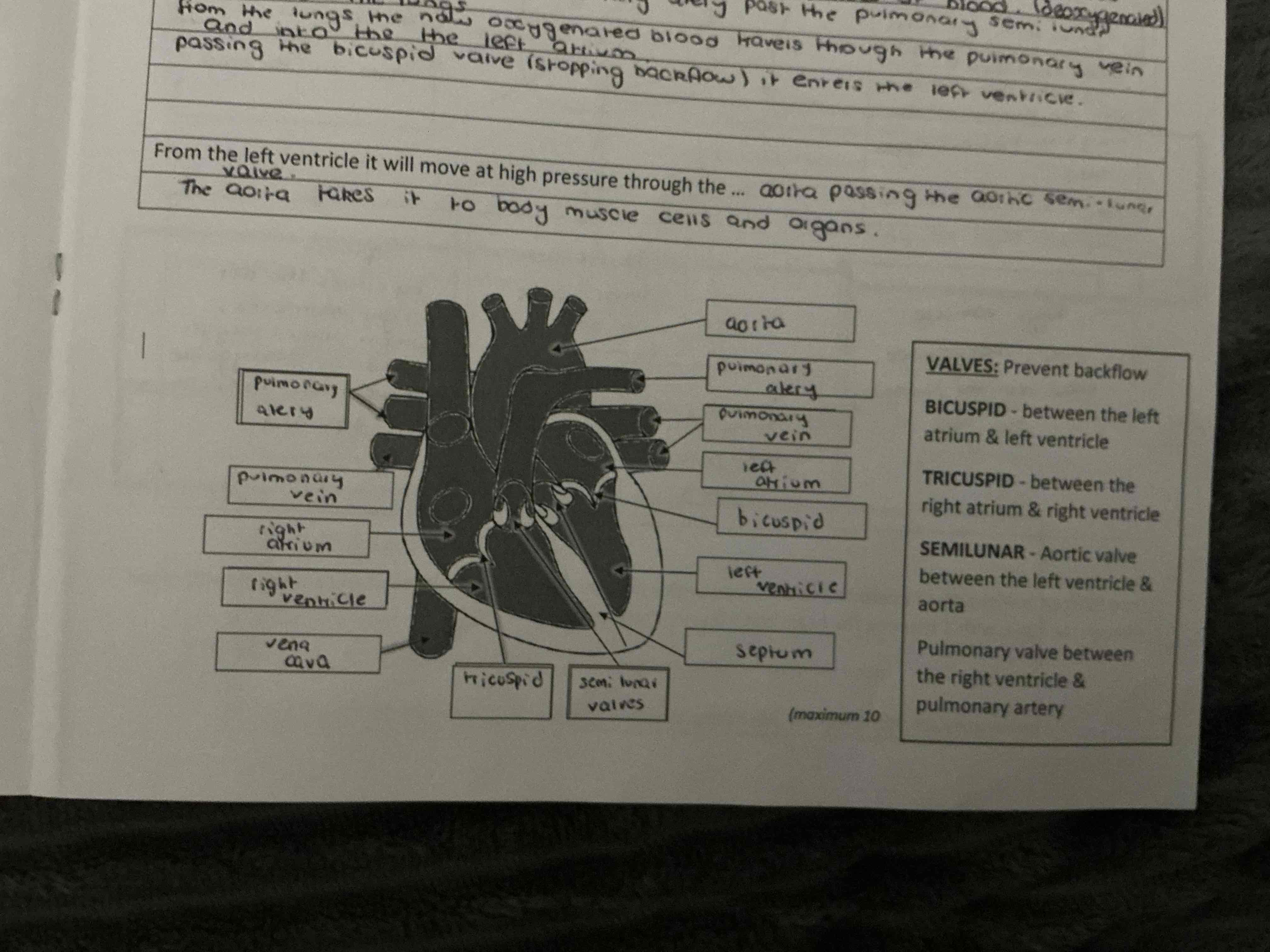
label the heart
what is inspiration?
the drawing in of breath, inhaling.
what is expiration?
releasing breath, exhaling
what is the equation for tidal volume, minute ventilation and breathing rate?
minute ventilation = tidal volume x breathing rate
what is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
what is the word equation for anaerobic respiration?
glucose → lactic acid + energy
what is a sporting example for aerobic respiration?
marathon running
what is a sporting example for anaerobic respiration?
sprinting
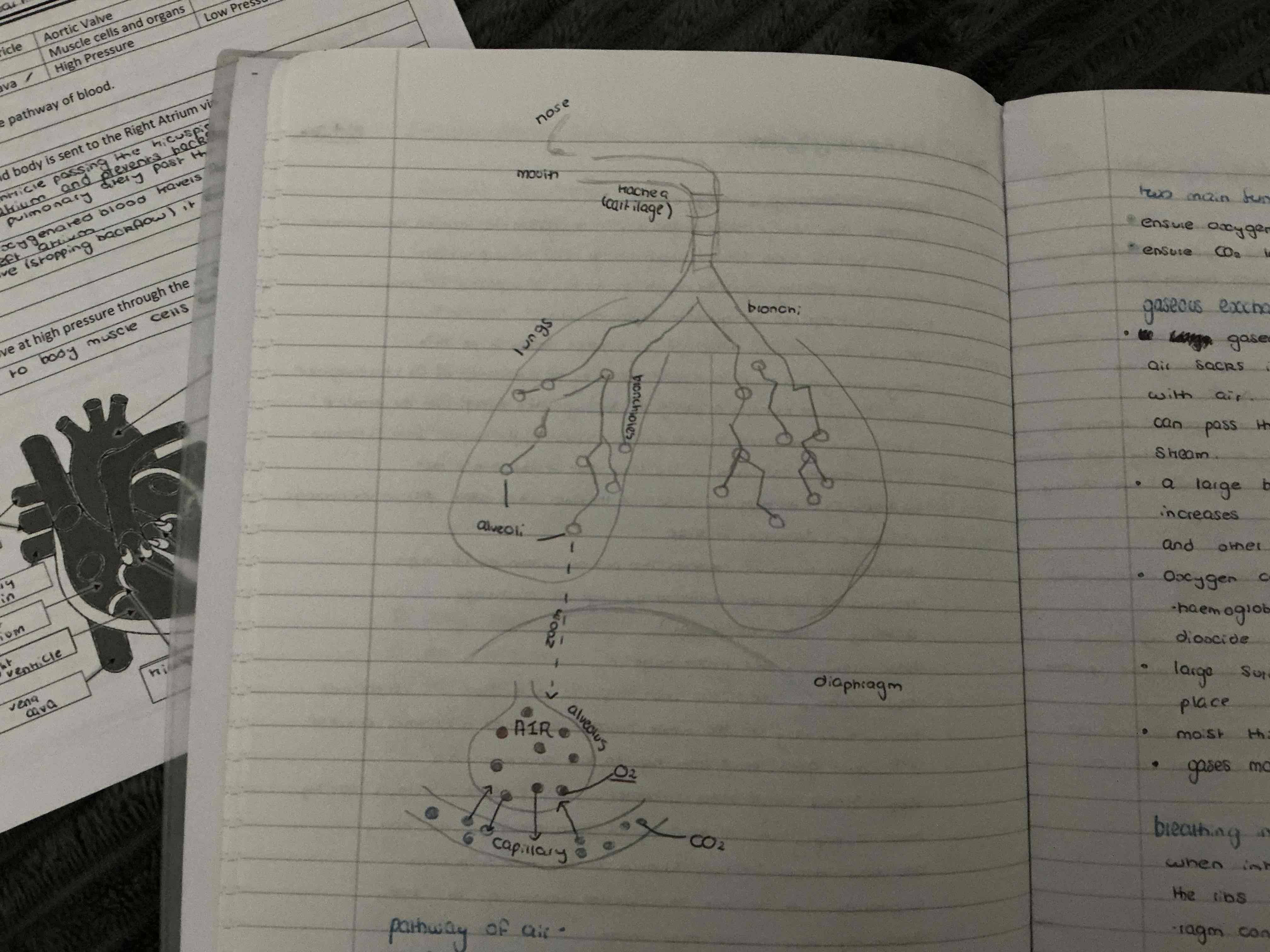
label the respiratory system
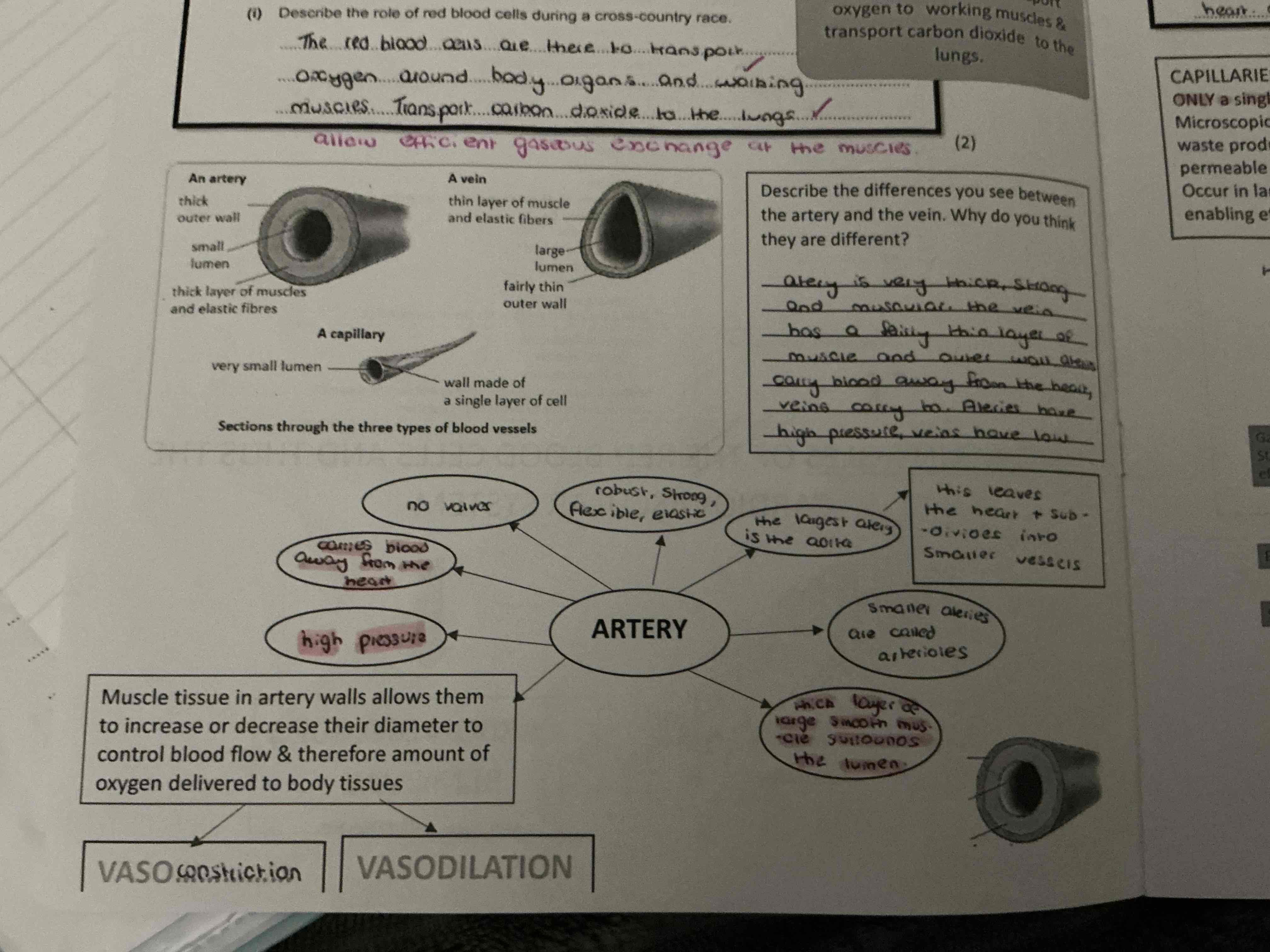
what are the functions of red blood cells
carry oxygen from the lungs and deliver it throughout the body
carry carbon dioxide away from the body and back to the lungs
allow efficient gaseous exchange at the muscles
how does a footballer use aerobic and anaerobic respiration in a match?
aerobic - lasting the whole duration of a match
anaerobic - sprinting to make an interception
how is inspiration and expiration used in exercise ?
Inspiration- The diaphragm contracts and moves downwards. The intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upwards and outwards. This increases the size of the chest and decreases the air pressure inside it which sucks air into the lungs. The rate of inspiration increases during exercise because there is a higher demand for oxygen by the working muscles.
Expiration-The diaphragm relaxes and moves back to its domed shape. The intercostal muscles relax so the ribs move inwards and downwards under their own weight. This decreases the size of the chest and increases the air pressure in the chest so air is forced out of the lungs.The rate of expiration increases when exercising because more CO2 needs to leave the body in order for more oxygen to get to the working muscles.
what are the main differences between the veins and arteries ?
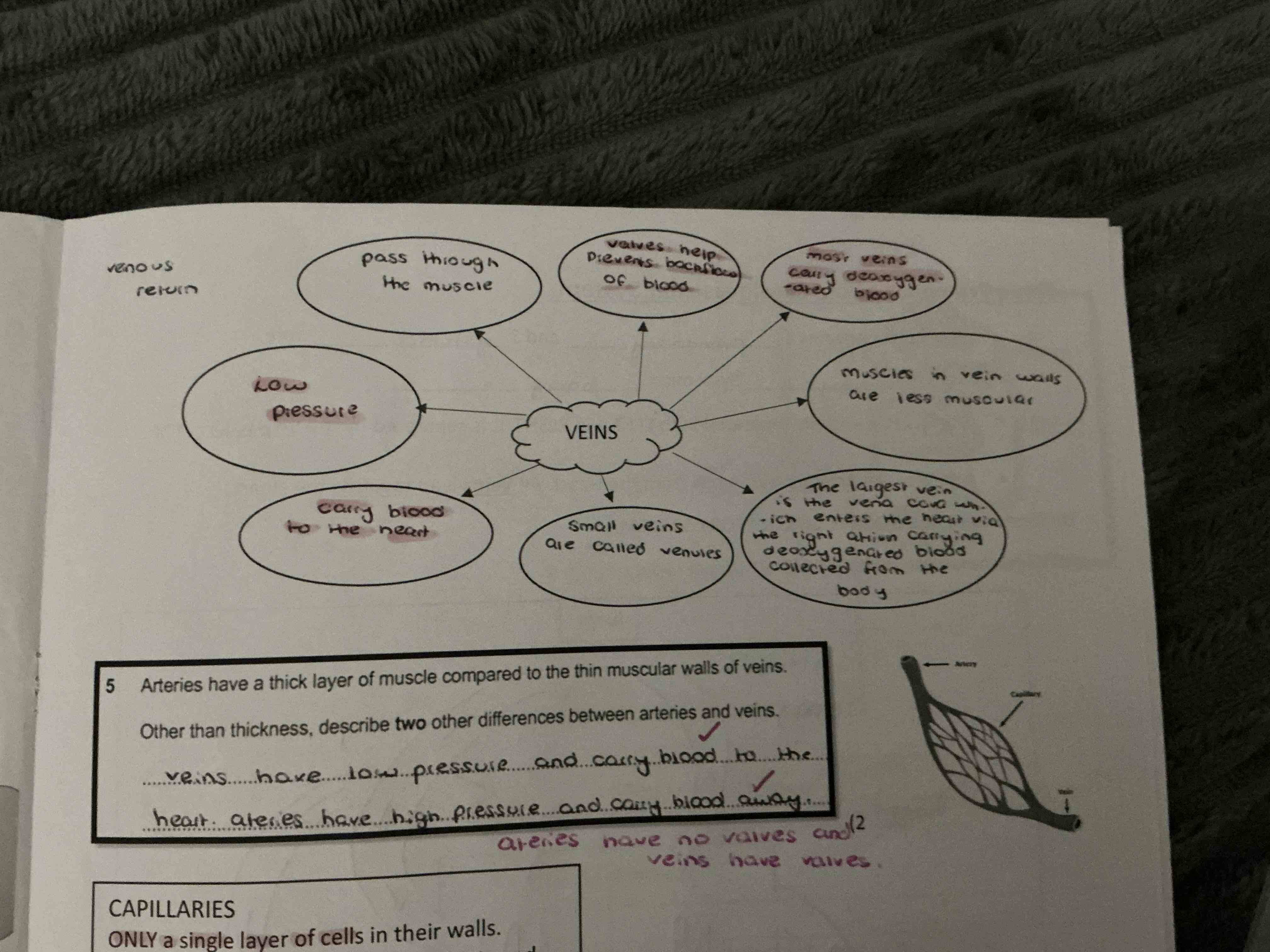
what are the main differences between the veins and arteries?