Earth Science Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 7-12 exam review
Last updated 4:02 AM on 4/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
Who came up with Continental drift?
Alfred Wegener
2
New cards
When did pangea break apart?
200 million yrs ago
3
New cards
When did pangea cone together?
300 million yrs ago
4
New cards
When Pangea came together what formed?
The Appalachian Mountains
5
New cards
How often does magnetic reversal happen?
Every 200 thousand yers
6
New cards
Is Hawaii a plate boundary?
No
7
New cards
What is Hawaii?
A Hot Spot
8
New cards
What is another example of a hot spot?
Yellow Stone
9
New cards

What type of wave is (a)?
P wave
10
New cards
What can P waves travel through?
Solids, liquids, and gases
11
New cards

What type of wave is (b)
S wave
12
New cards
What can S waves move through
Just Soilds
13
New cards
Which wave is faster and reaches the station first?
P wave
14
New cards
What is the majority of the oceaic crust made of?
Basalt
15
New cards
What is the majority of the crust made of?
Granite
16
New cards
What is the majority of the upper mantle made of?
Peridotite
17
New cards
Where does most of our knowledge of the earth’s interior come from?
From P and S waves
18
New cards
How old is the oldest rock ?
around 4 billion yrs old
19
New cards
What is the measure of a material’s resistance to flow?
Viscosity
20
New cards
What does it mean if magma has a high viscosity?
It is slow flowing and will cover a small area
21
New cards
What does it mean if magma has a low viscosity?
It is fast flowing and will cover large areas
22
New cards
What are the 3 types of Volcanoes?
Shield, Cinder, and Composite Volcanoes
23
New cards
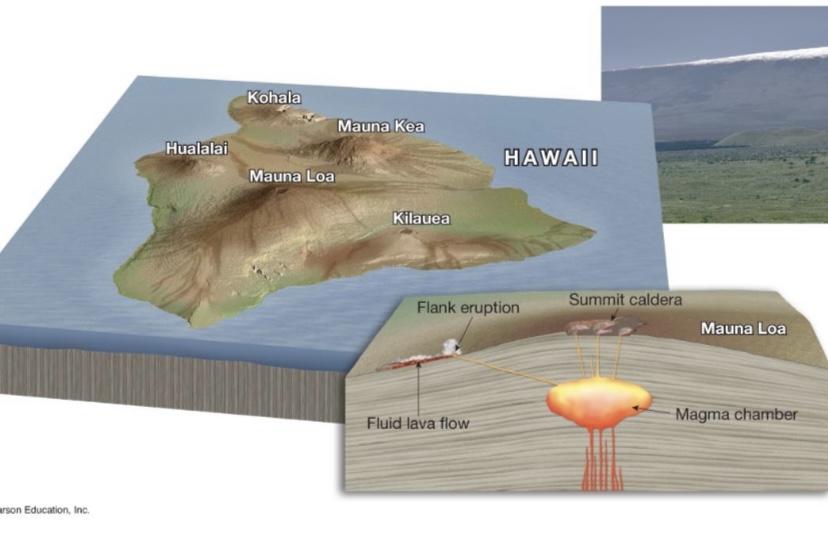
What are some feature of shield volcanos?
Broad, slightly domed,Primarily made of basaltic (fluid) lava,Generally large size
24
New cards
What is an example of a shield volcano?
Mauna Loa in Hawaii
25
New cards
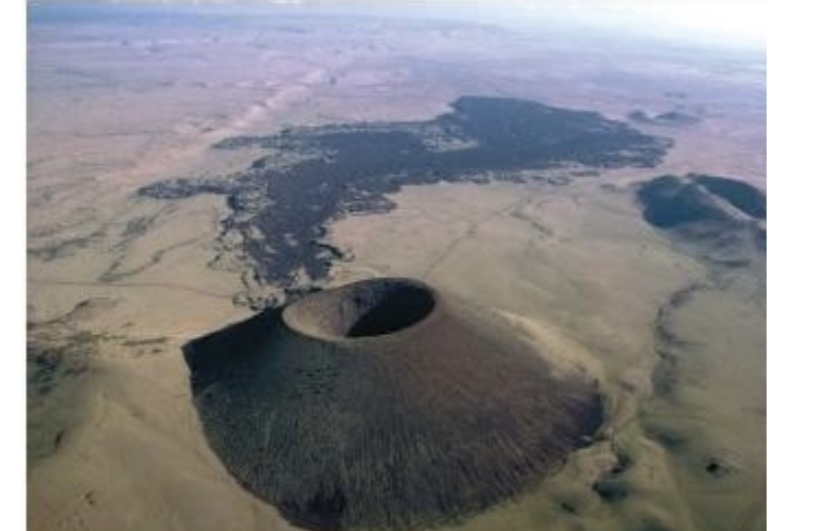

What are some features of a cinder volcano?
Steep slope angle, Rather small size, made of cinder
26
New cards
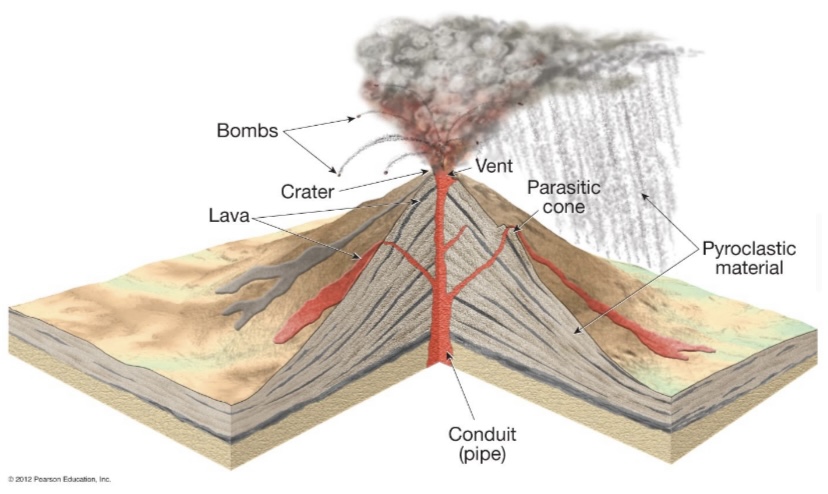
What are some feature of a composite volcano?
Large size, Interbedded lavas and pyroclastics, Most violent type of activity
27
New cards
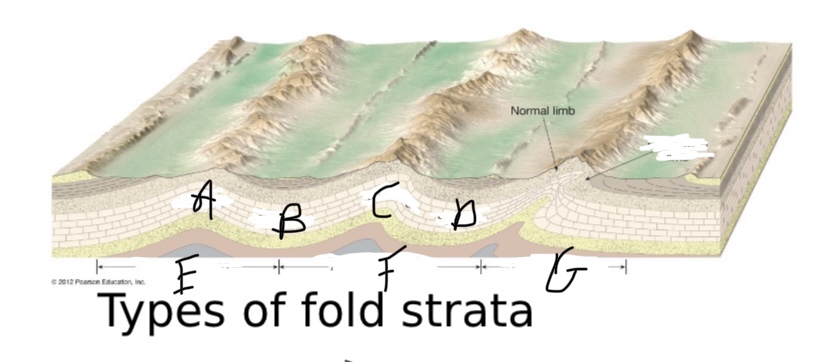
What type of fault is A?
Anticline
28
New cards
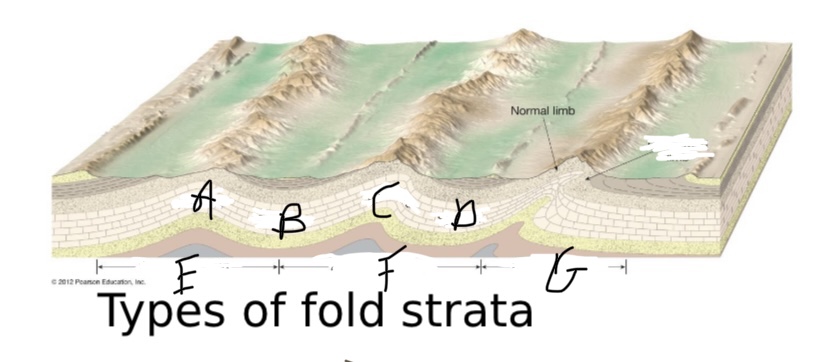
What type of fault is B?
Syncline
29
New cards
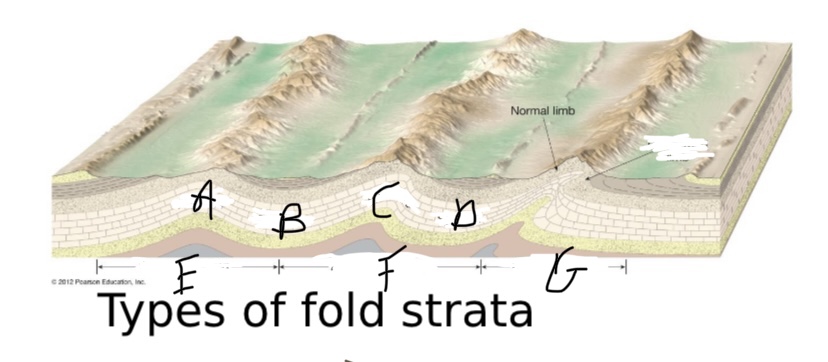
What type of fault is C?
Anticline
30
New cards
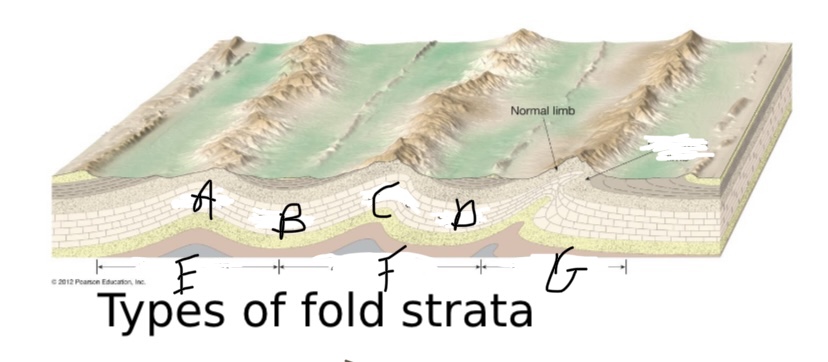
What type of fault is D?
Syncline
31
New cards
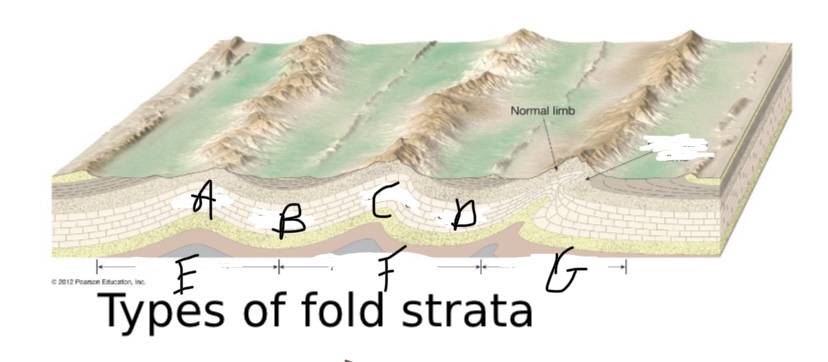
What type of symmetry is happening at E?
Symmetric fold
32
New cards
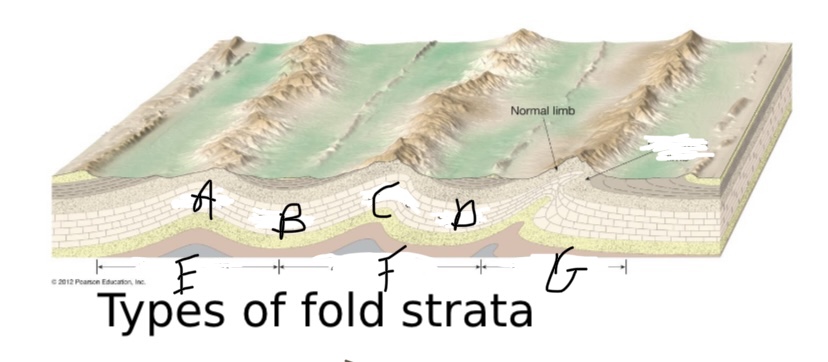
What type of symmetry is happening at F?
Asymmetric
33
New cards
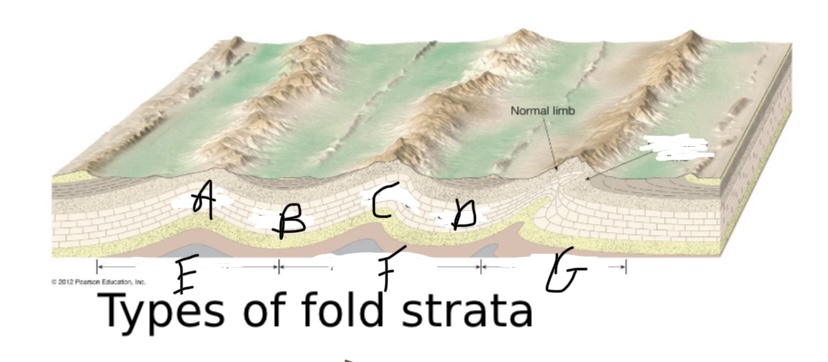
What type of symmetry is happening at G?
Overturned
34
New cards
What are the types of dip slip faults?
Normal and Reverse
35
New cards
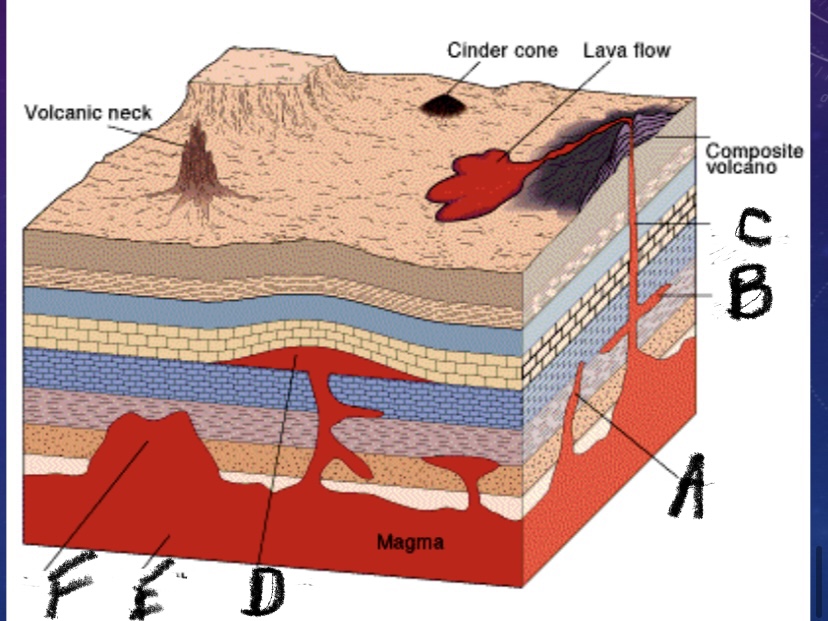
What is this a picture of
Intrusive igneous activity
36
New cards
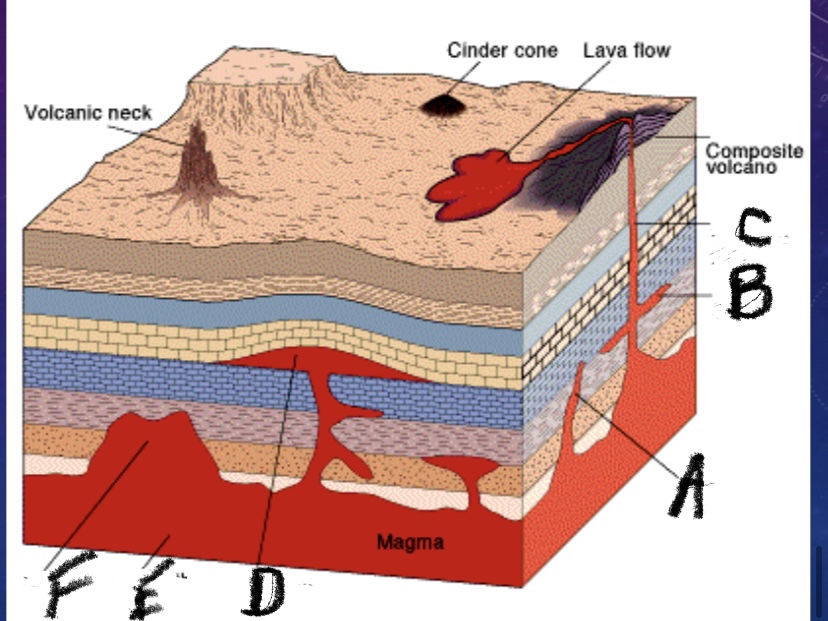
What is feature A?
Dike
37
New cards
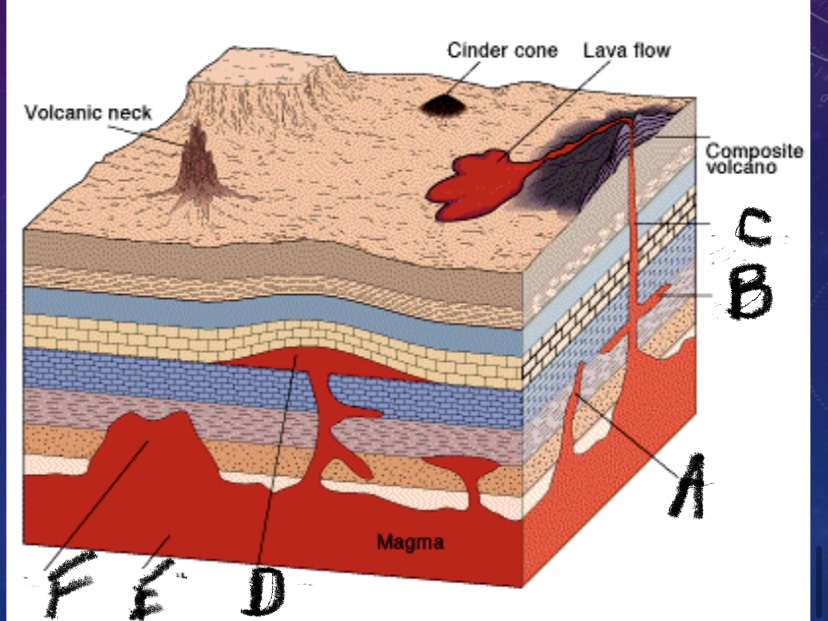
What is feature B
Sill
38
New cards
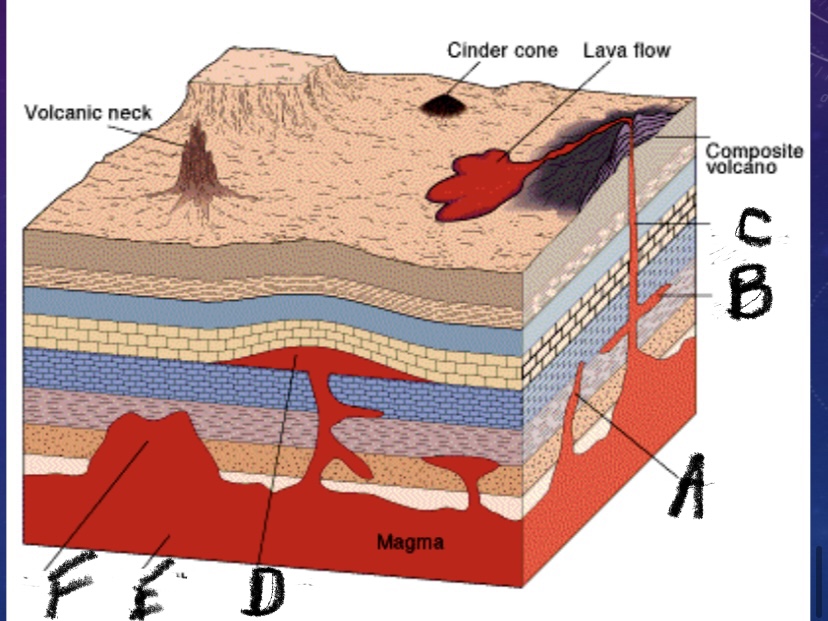
What is feature C?
Volcanic pipe
39
New cards
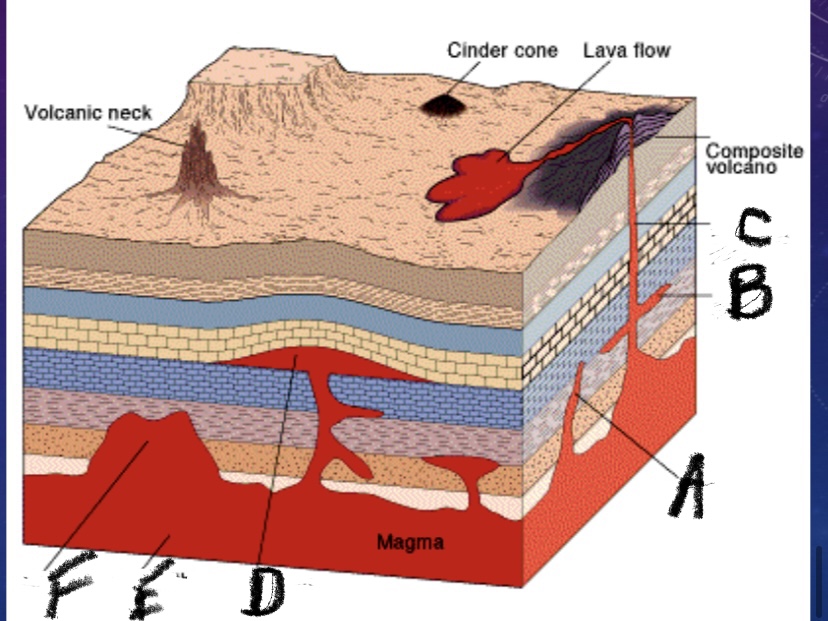
What is feature D
Laccolith
40
New cards
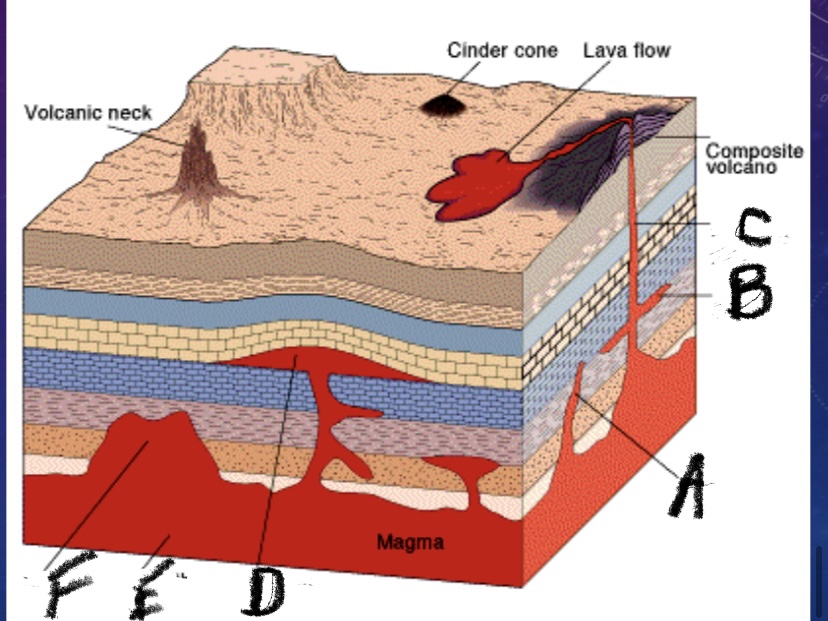
What is feature E
Batholith
41
New cards
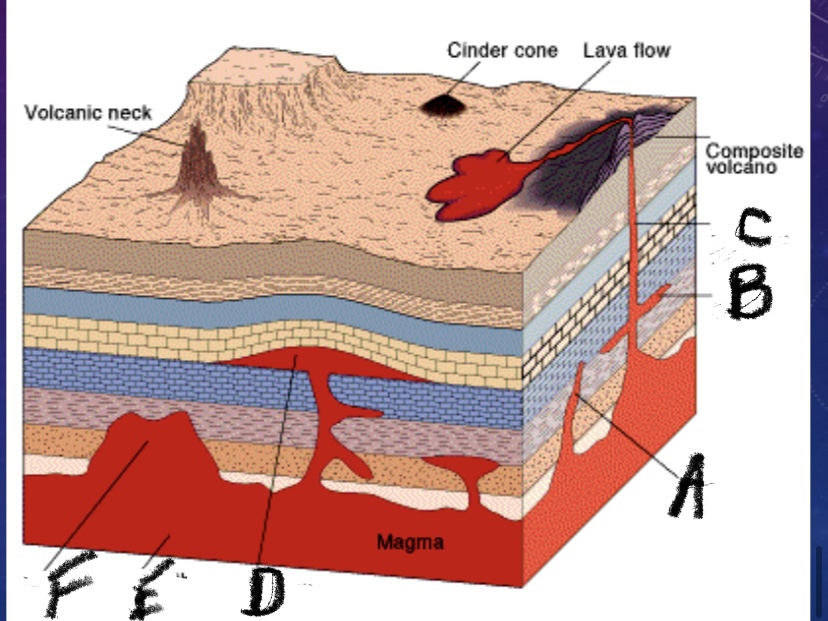
What is feature F
Stock
42
New cards
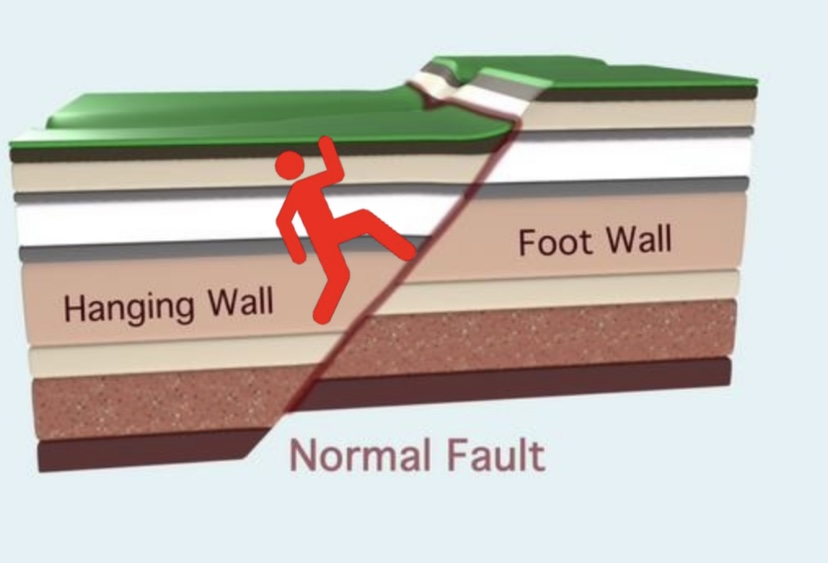
What causes a normal fault?
tensional forces
43
New cards
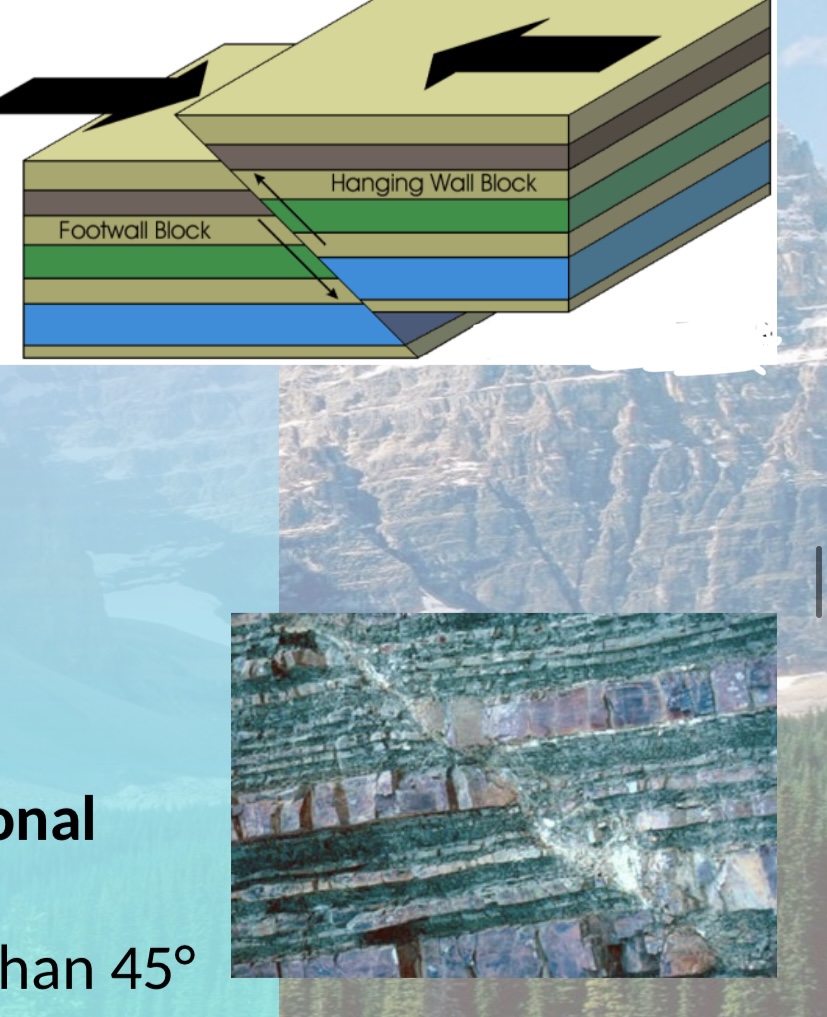
What causes a reverse fault?
strong compressional stresses
44
New cards
What is the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt?
Orogenesis
45
New cards
What is Uniformitism?
“The present is the key to the past”
46
New cards
What is the Spontaneous breaking apart (decay) of atomic nuclei?
Radioactivty
47
New cards
What are 3 types of Radioactive decay?
Alpha emission, Beta emission, Electron capture
48
New cards
What is princeaple that states the oldest rocks are on the bottom?
Law of superposition
49
New cards
What is the principle that states sediment is deposited horizontally
Principle of original horizontality
50
New cards
What is the principle that states that younger feature cuts through an older feature?
Principle of cross-cutting relationships
51
New cards
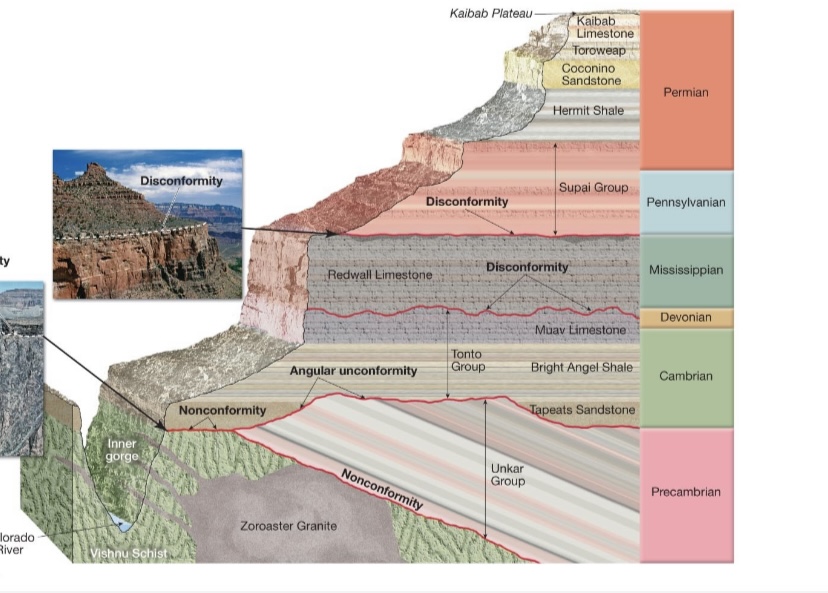
Know the Unconformaties in this picture
Nonconformaty, Angular, and disconformity
52
New cards
What type of fossils are cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter
Petrified
53
New cards
What type of fossils are shells or other structures that are buried and then dissolved by underground water
Mold
54
New cards
What type of fossils is a hollow space of a mold that is filled with mineral matter
cast
55
New cards
What type of fossils does organic matter become a thin residue of carbon?
Carbonization
56
New cards
What type of fossils are replica of the fossil’s surface preserved in fine-grained sediment
Impression
57
New cards
What type of fossils are hardened resin of ancient trees surrounds an organism ?
Preservation in amber
58
New cards
What keeps soft parts perserved in a fossil?
**Amber**, Ice, and tar
59
New cards
(true or false) Pangea was the only supercontinent
False
60
New cards
What created earth atmosphere and oceans?
Outgassing of volcanoes
61
New cards
What is the oldest fossil?
stromatolites
62
New cards
What are the core of continent?
Cratons
63
New cards
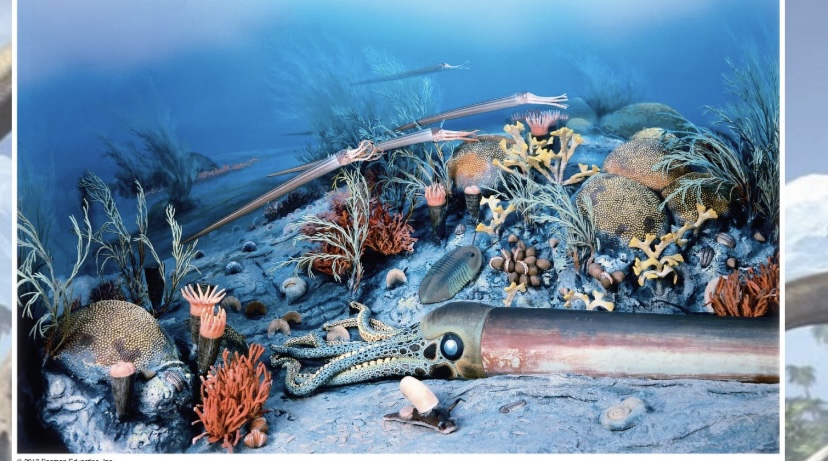

What era does this represnt?
Paleozoic
64
New cards
What is the era of dinosaurs?
Paleozoic
65
New cards
What is the era of mammals?
Cenozoic
66
New cards
What are unconformities?
A skip in time
67
New cards
Name 3 descrutive things that come from earthquakes
ground shaking, surface faulting, ground failure
68
New cards
Draw a slip strike fault
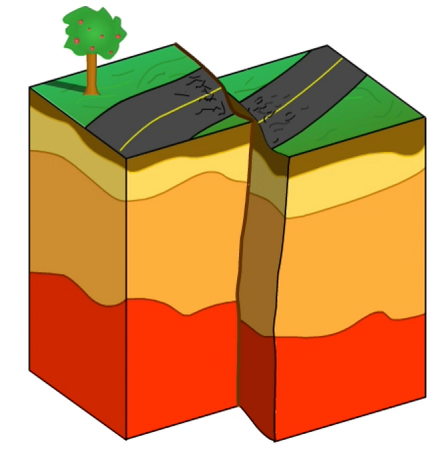
69
New cards
Draw a normal dip slip fault
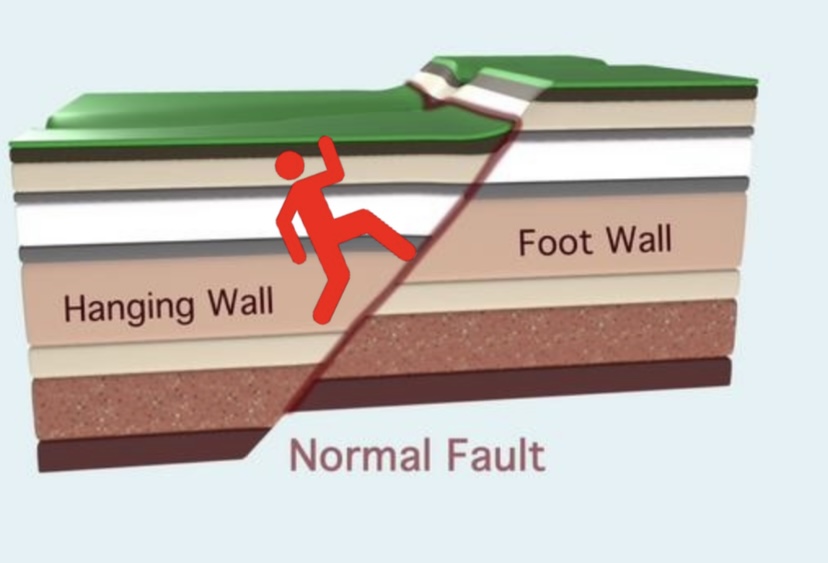
70
New cards
Draw a reverse dip slip fault
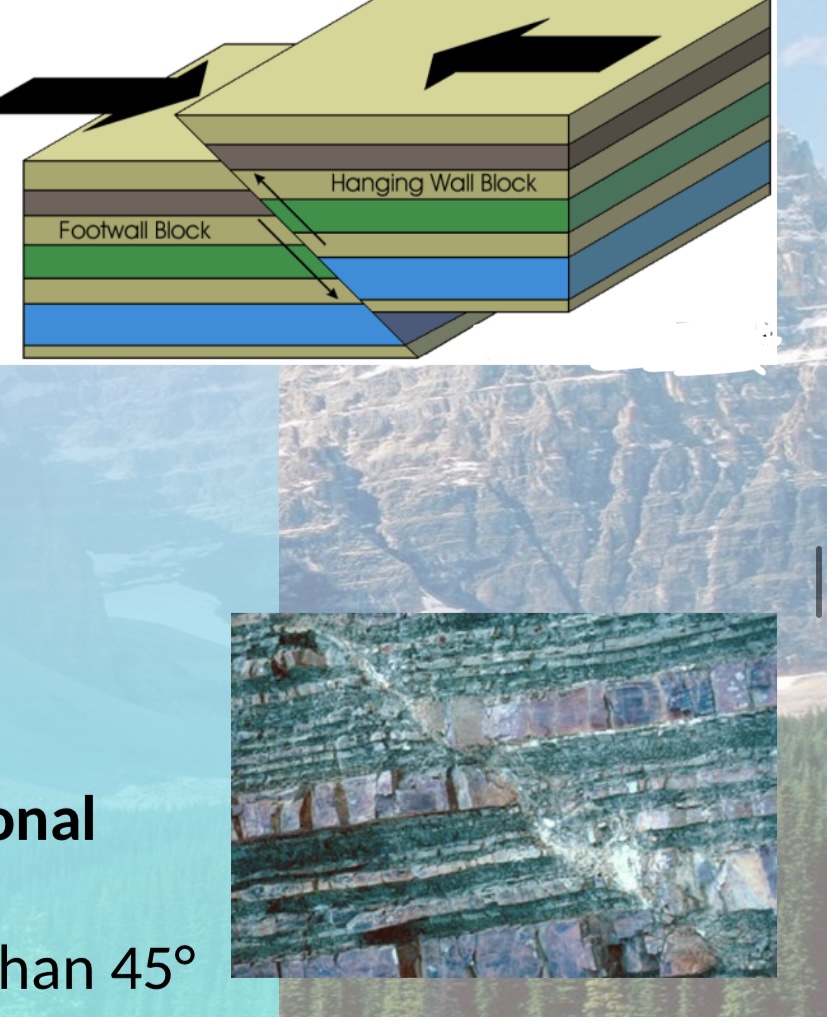
71
New cards
Draw a divergent boundary
label the feature,label crust, movement with arrows
give an example of a divergent boundary
label the feature,label crust, movement with arrows
give an example of a divergent boundary
This example picture is oceanic-oceanic
example of this divergent boundary is the __**mid atlanic ridge**__
example of this divergent boundary is the __**mid atlanic ridge**__
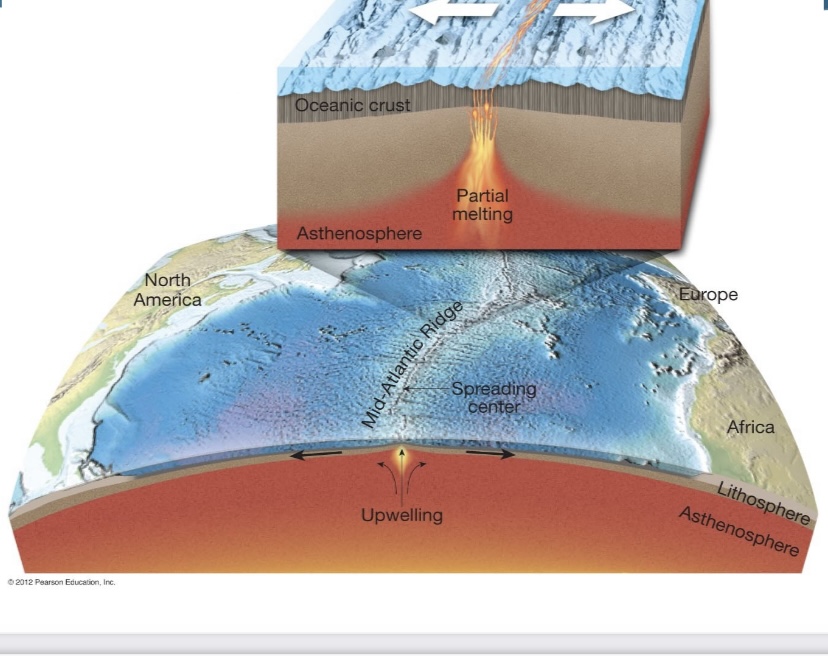
72
New cards
Draw a convergent boundary
label the feature,label crust, movement with arrows
give an example of a convergent boundary
label the feature,label crust, movement with arrows
give an example of a convergent boundary
photo is oceanic-continental
example-Andes Mountains
make sure to draw and label partial melting and volcanoes
example-Andes Mountains
make sure to draw and label partial melting and volcanoes
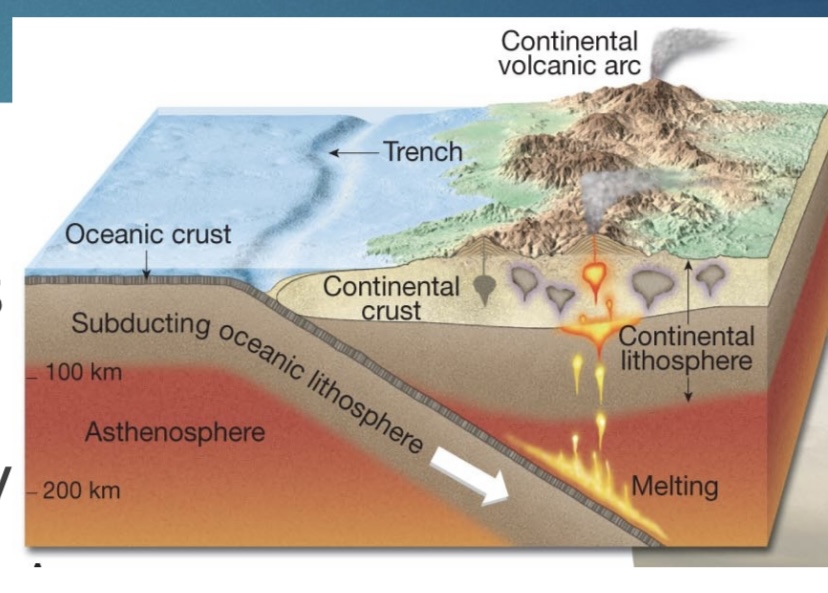
73
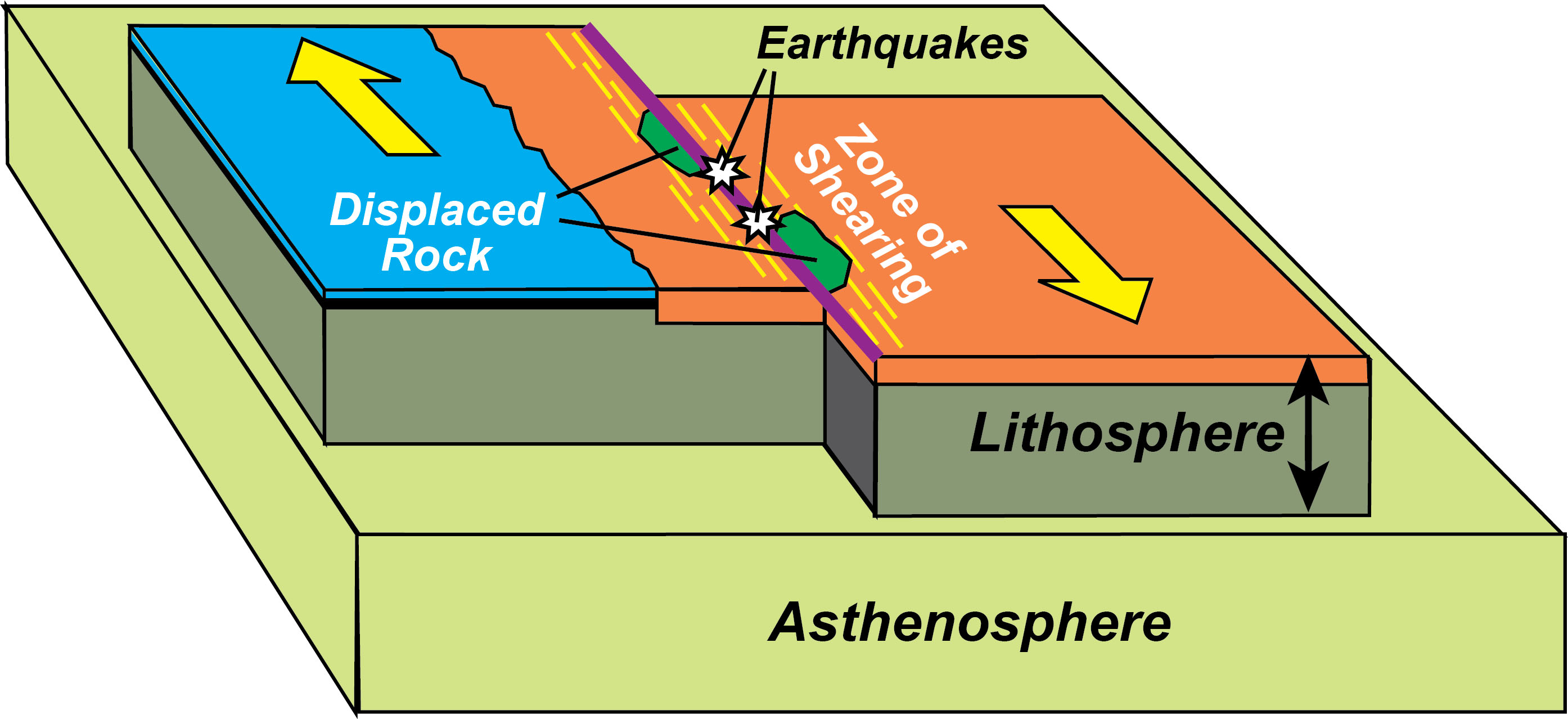
New cards
Draw a transform boundary
label the feature,label crust, movement with arrows
give an example of a transform boundary
label the feature,label crust, movement with arrows
give an example of a transform boundary
example-san andres fault
74
New cards
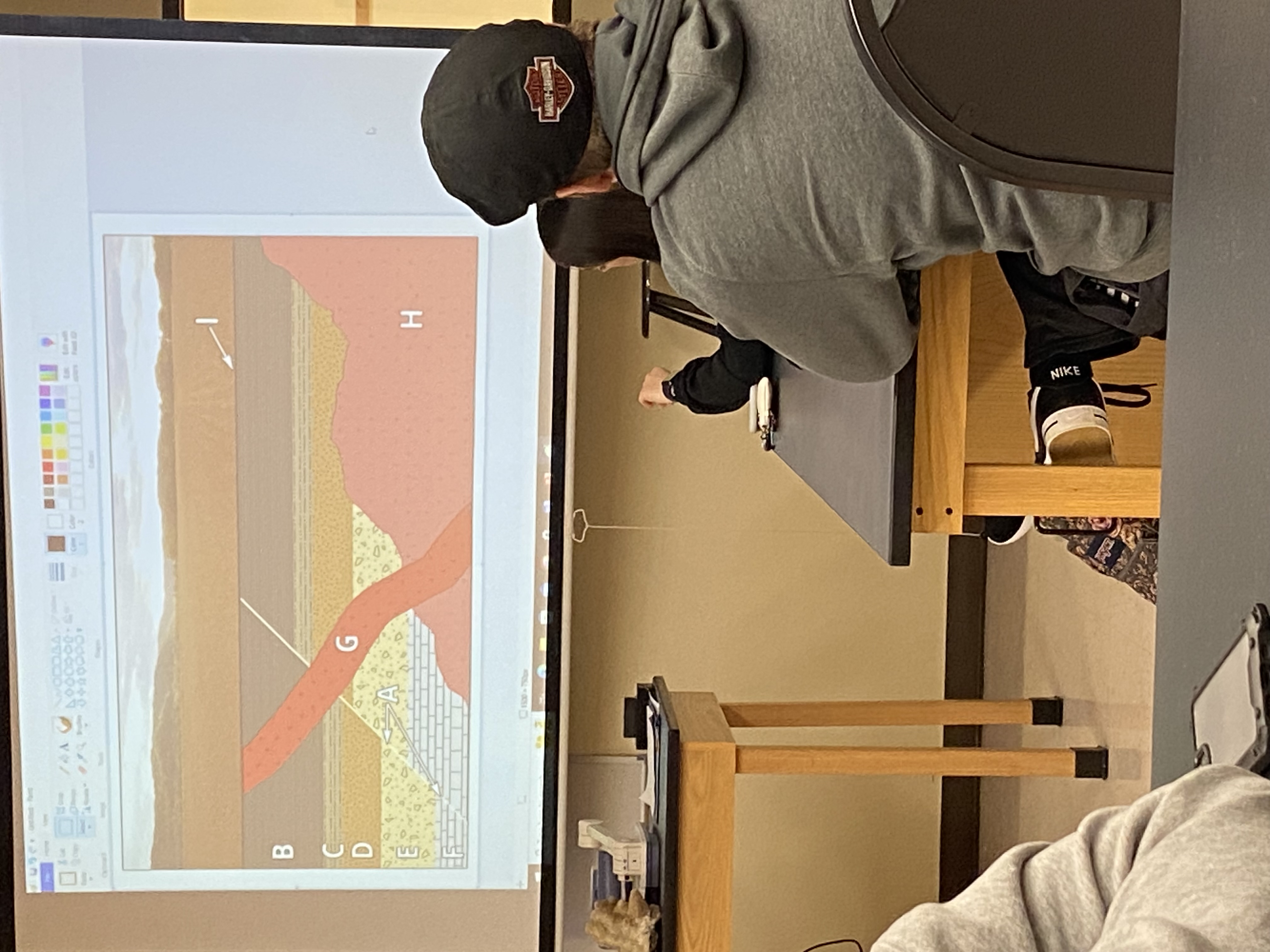
Put these in order from oldest to youngest
F,E,D,C,B,A,H, G, I

75
New cards
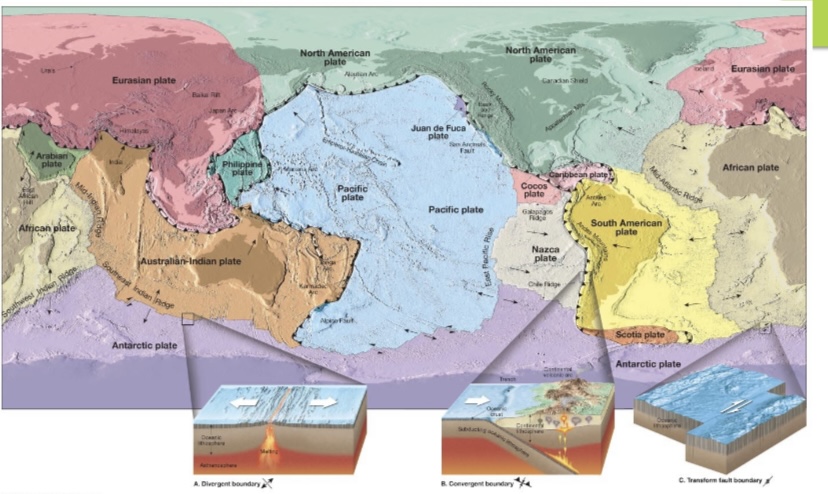
Label the 7 major plate boundries
African, Antarctic, Eurasian, Indo-Australian, North American, Pacific and South American.
76
New cards
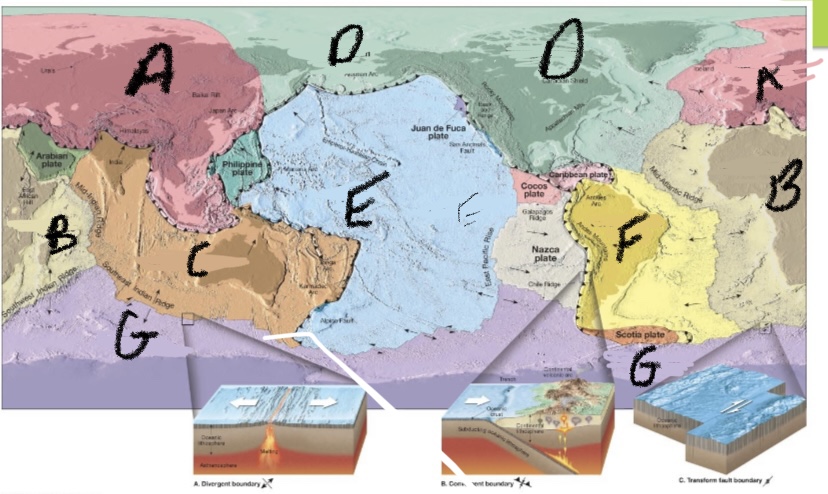
What plate is A. ?
Eurasian
77
New cards
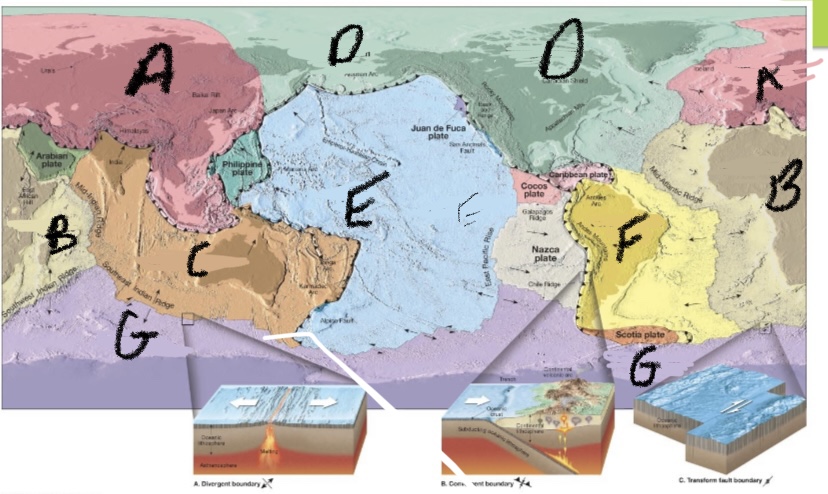
What plate is B?
African
78
New cards
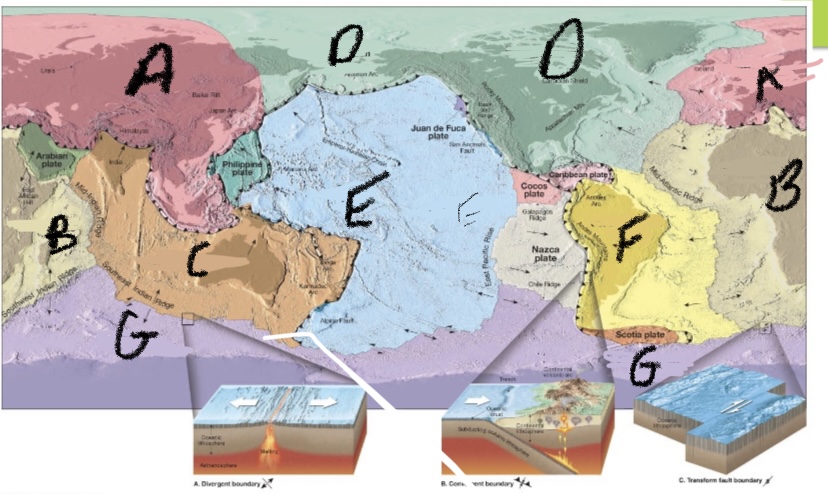
What plate is C?
Australlian- Indian
79
New cards
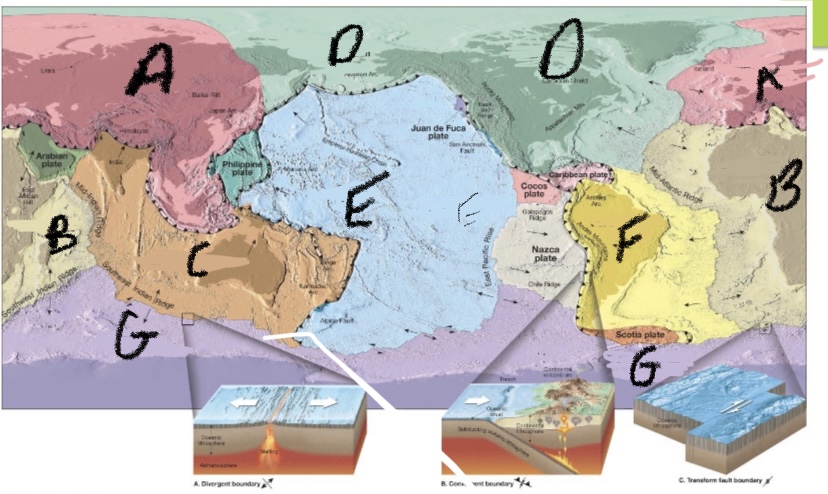
What is plate D?
North America
80
New cards
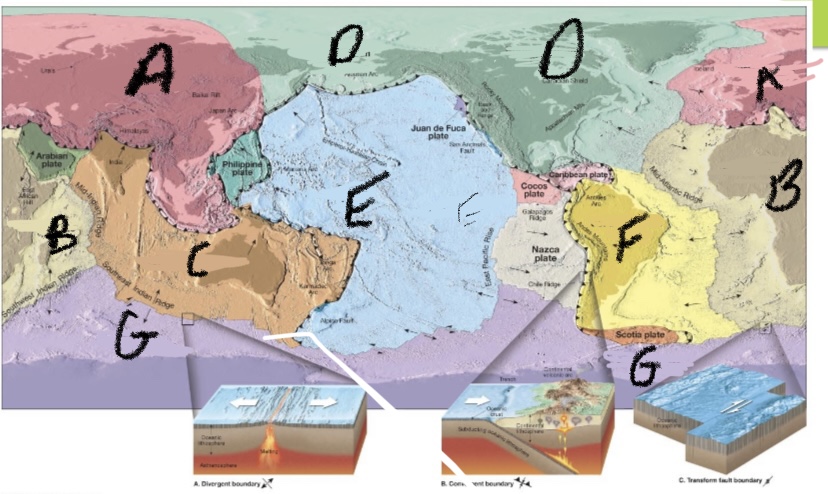
What is plate E?
Pacific
81
New cards
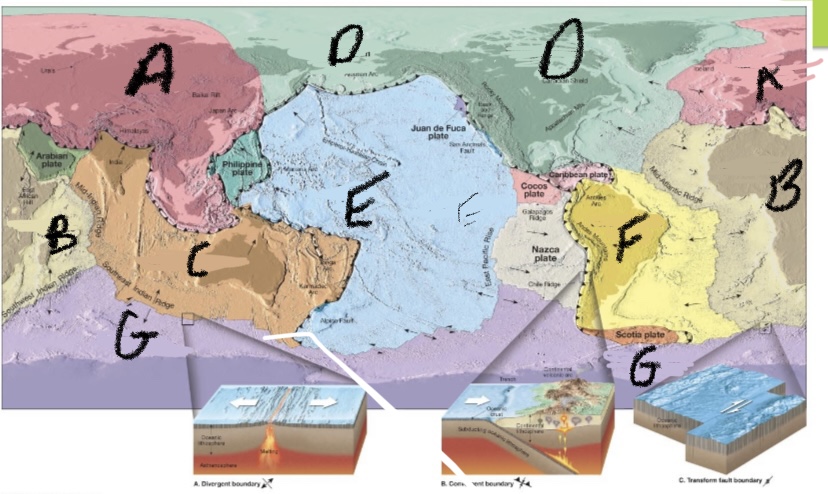
What plate is F?
South American
82
New cards
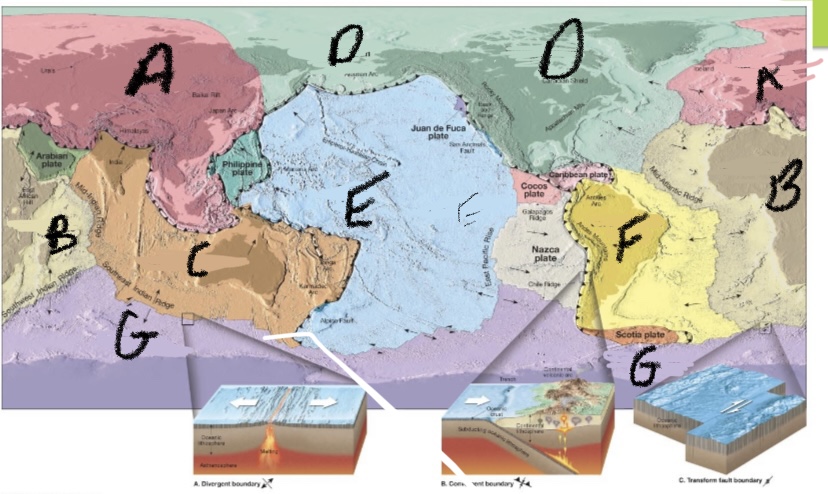
What plate is G?
Antarctic