Topic 15 - Dynamic Earth Part 2: Earthquakes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Why do we study earthquakes?
To guide us where to build, to avoid tsunamis, to interpret Earth history
What is an earthquake?
Strong vibrations that travel through the ground, due to a release of energy
What happens when the ground breaks (ruptures)?
When the ground breaks (ruptures), the energy is released
What are the waves of energy called?
the waves of energy are called seismic waves
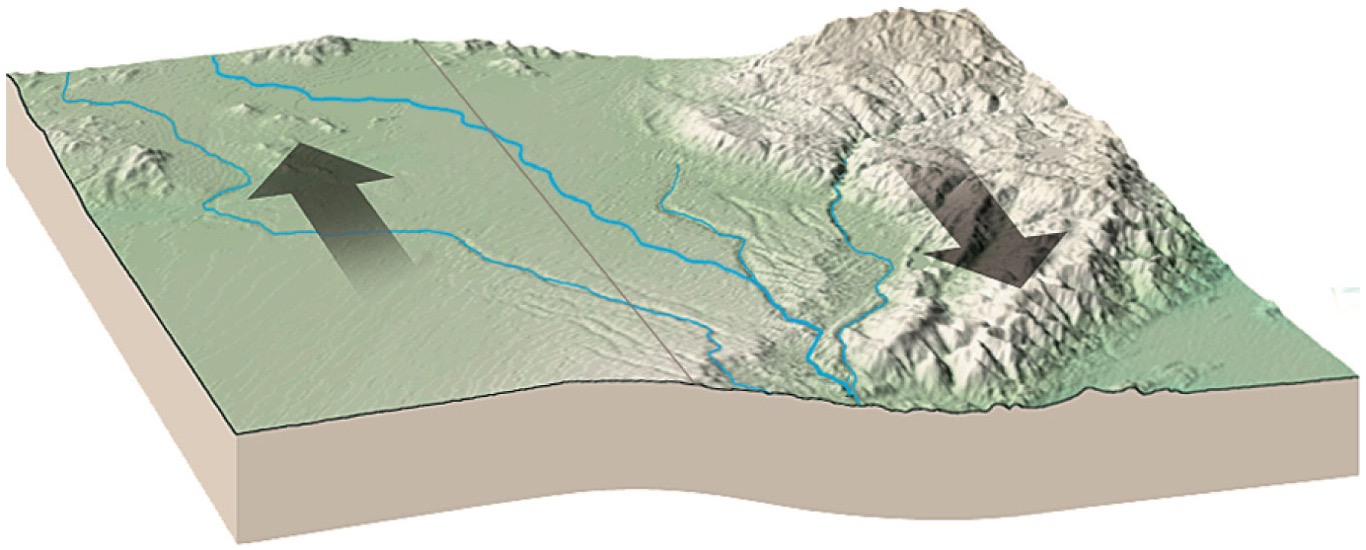
What is a fault?
this is the crack in the ground, along which the ground moves
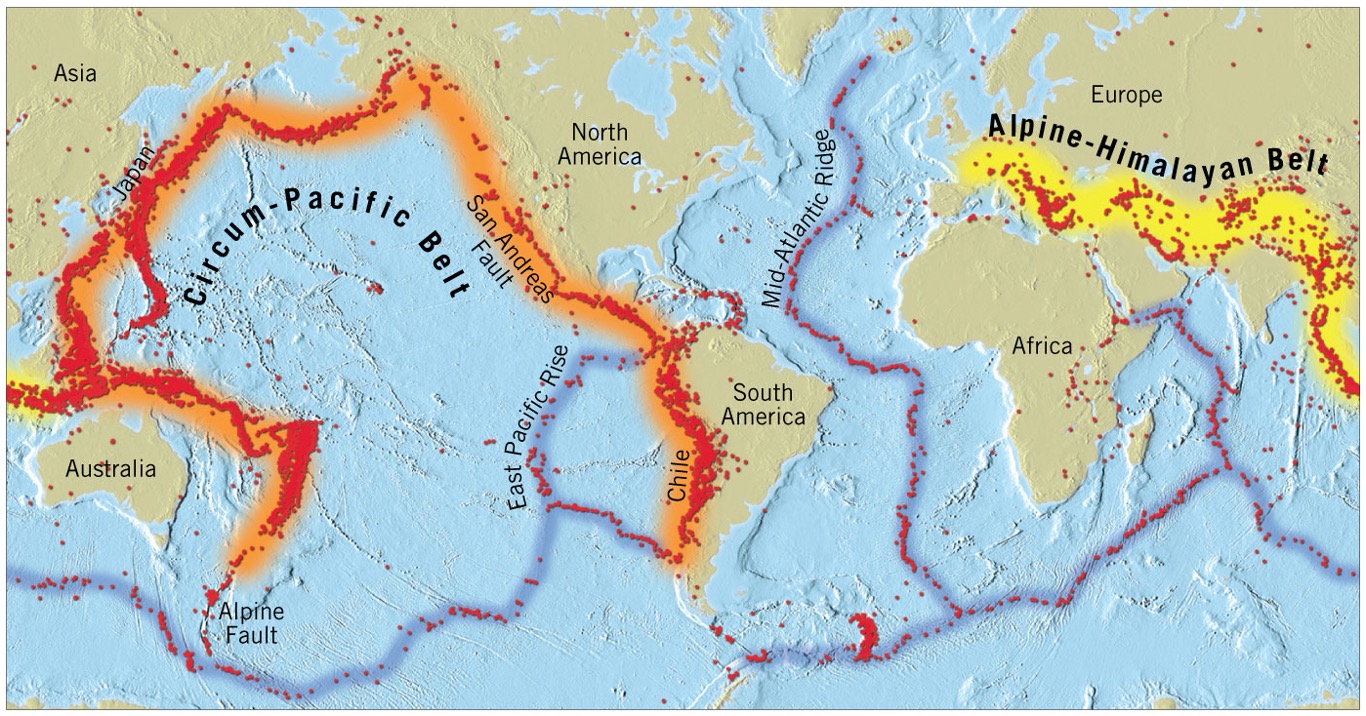
What is the relationship between earthquakes and volcanoes?
they often occur near or in the same locations
What are other causes of earthquakes?
fracking (hydraulic fracturing), bomb testing, blasting in a quarry
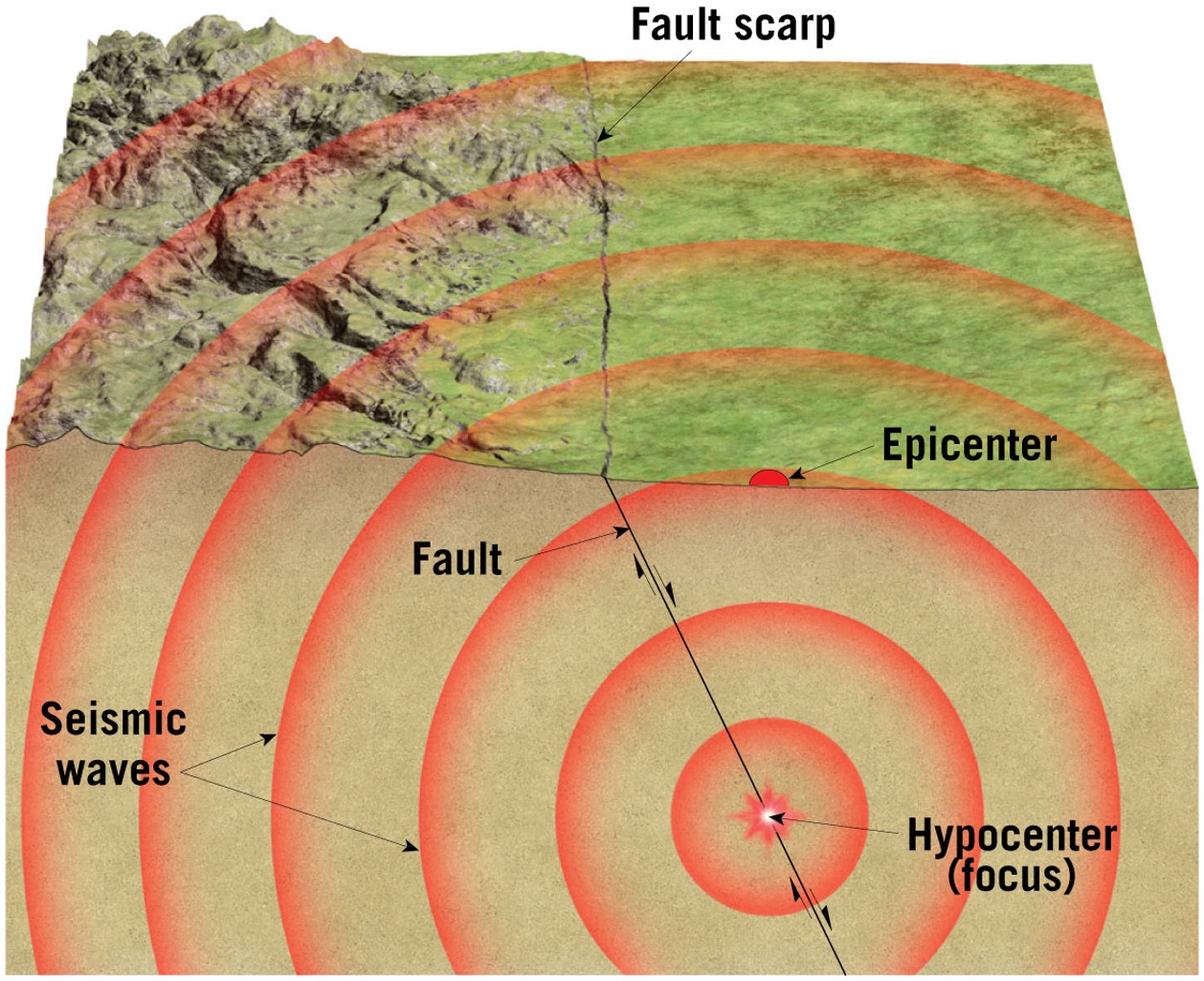
what are seismic waves?
energy released during an earthquake. They show up as three distinct wave forms. The ground actually moves
what is a P-wave?
primary wave, arrives 1st
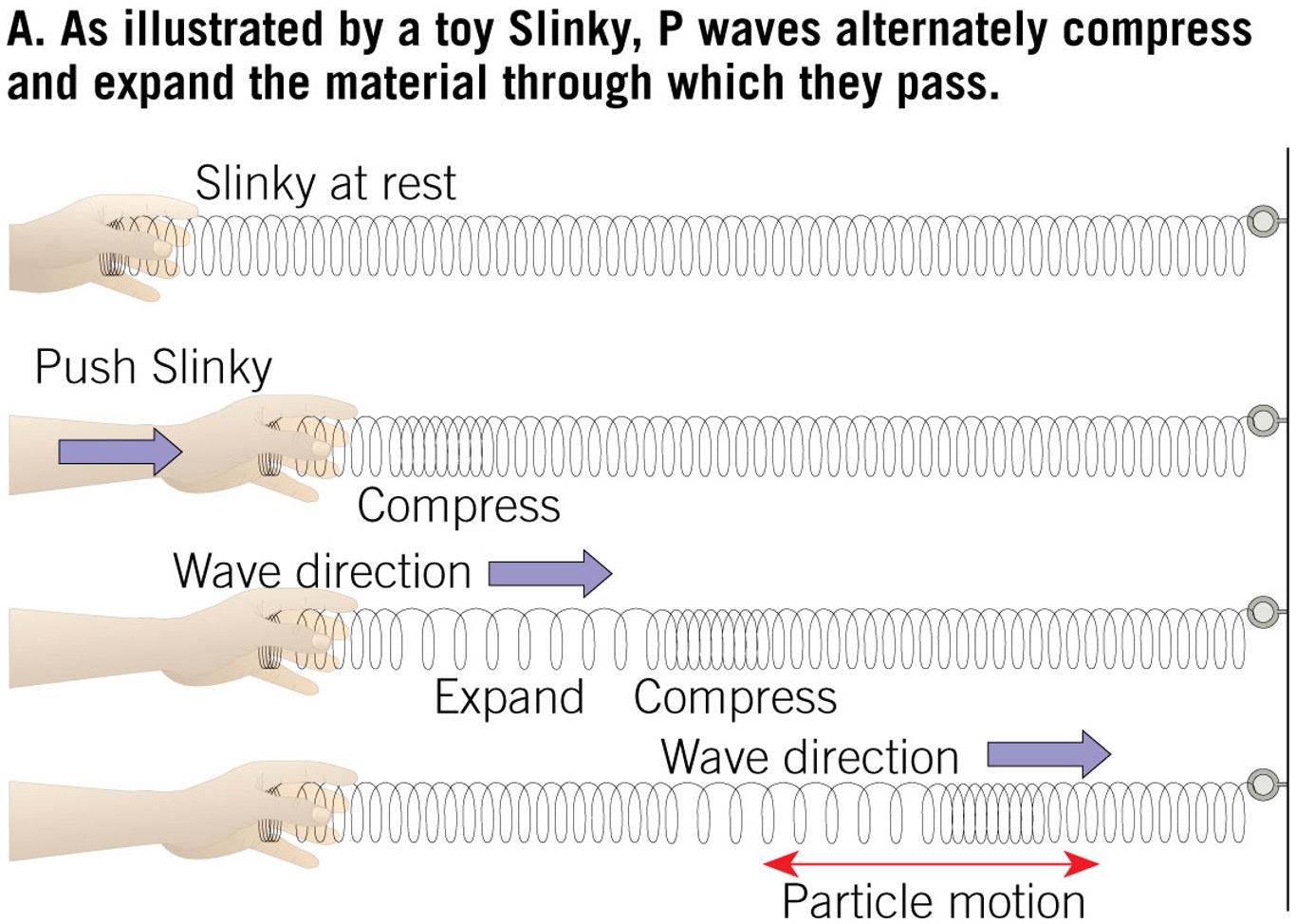
how does a p-wave move?
Push pull, like a spring, this is a sound wave
Through what kind of materials can a p-wave move through?
solid, gas and liquids
what is a S-wave?
secondary wave, arrives 2nd
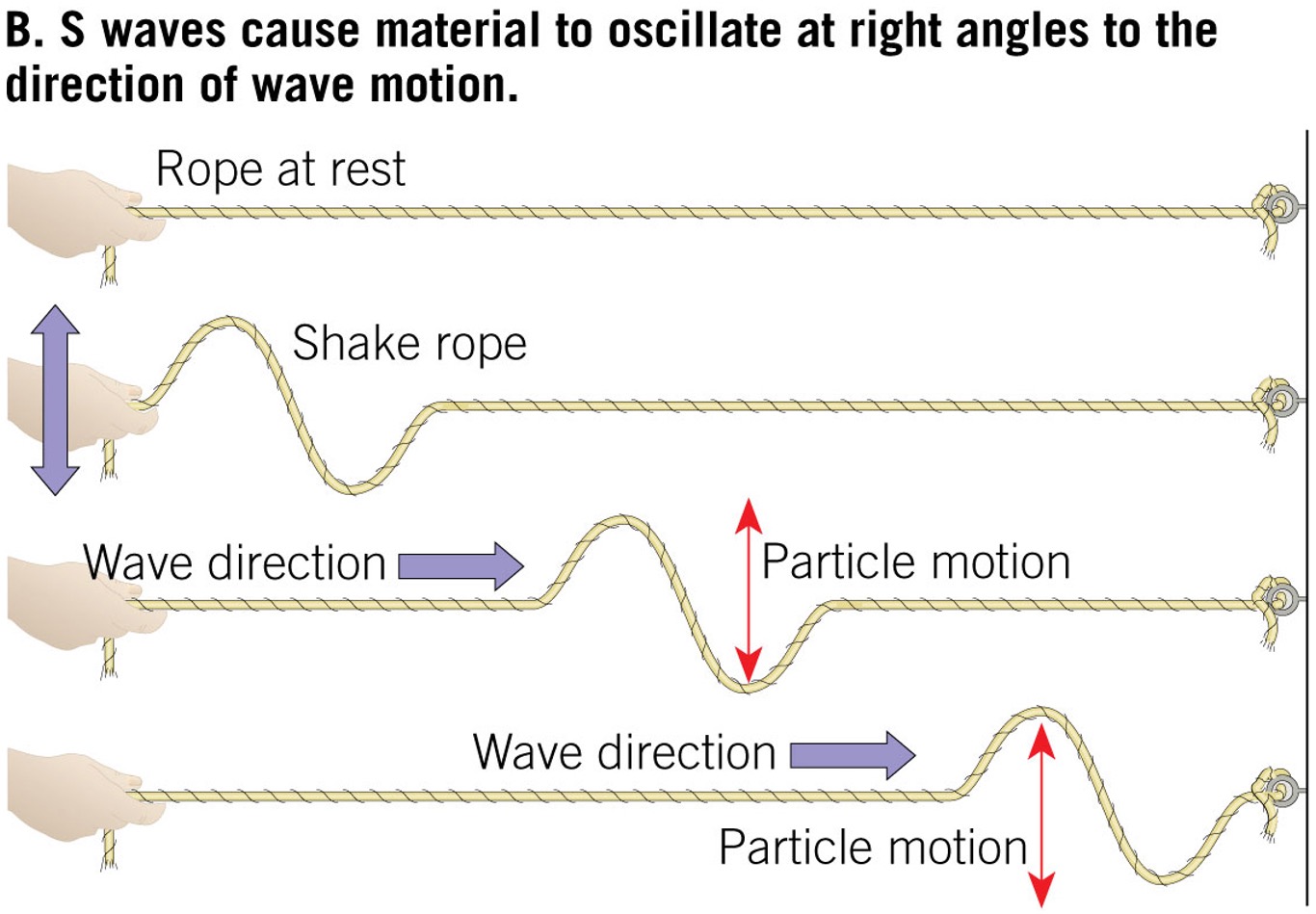
how does a s-wave move?
Up and down, side to side
Through what kind of materials can a s-wave move through?
only solids
what is a L-wave?
long waves, arrive 3rd
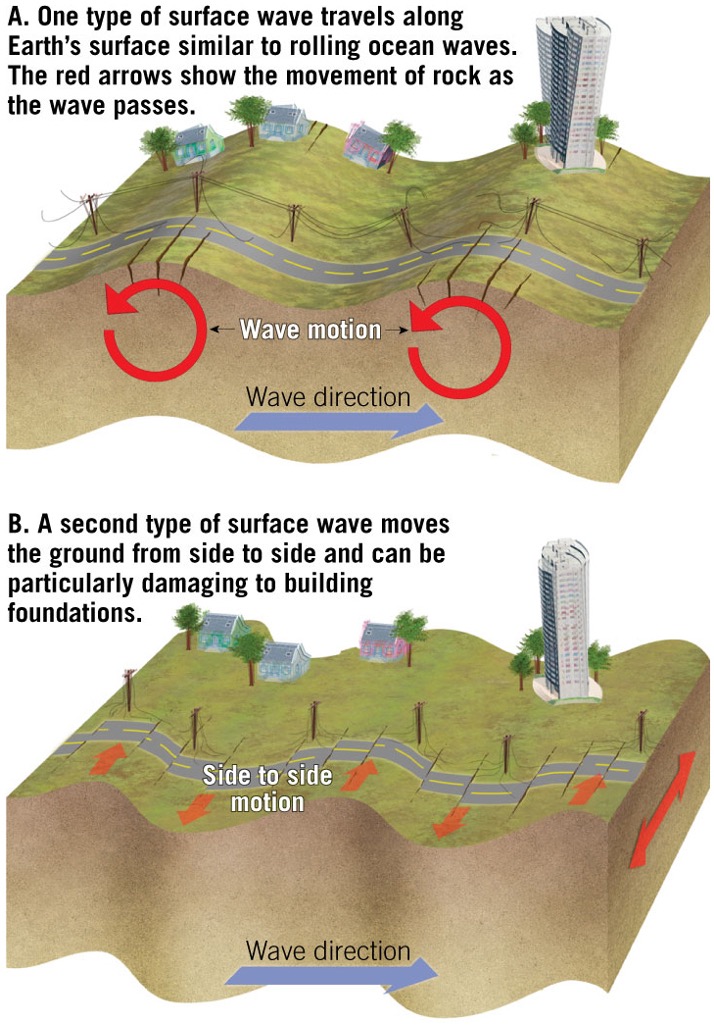
how does a l-wave move?
side to side, roll like waves across the surface
Through what kind of materials can a l-wave move through?
only solids
How are earthquakes detected ?
use seismographs

what is a seismograph?
This is the machine that detects seismic waves
what does a seismograph do?
Use the arrival times of the different waves to calculate and determine the location of an earthquake
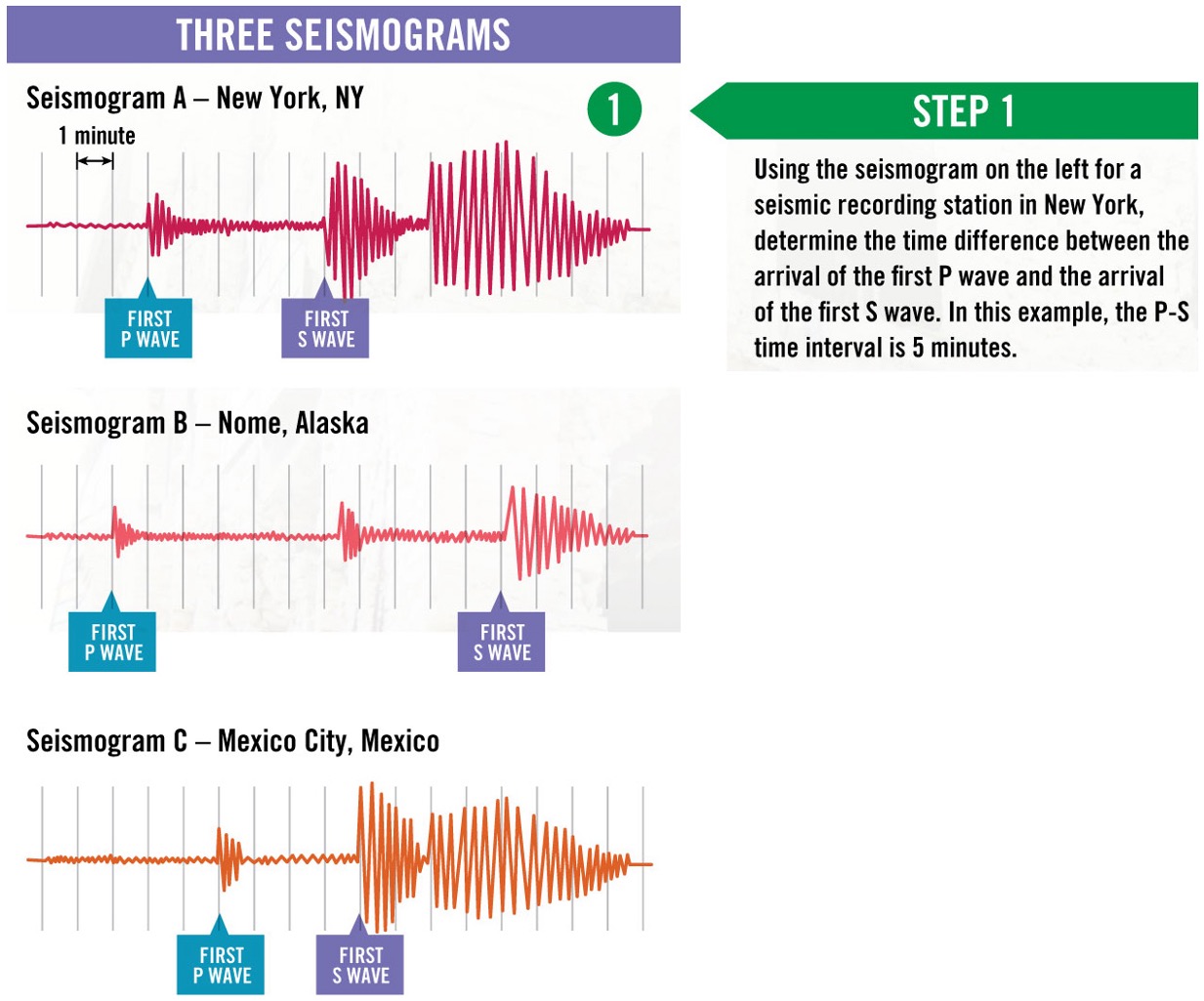
what is a seismogram?
the printout of the wave history, reminds you of an EKG
what is a focus?
the place where the ground ruptured, this is the start of the earthquake
what is the epicenter?
The location on the surface directly above the focus
Earthquake strength and severity is defined by?
defined by intensity and magnitude
Intensity is very ?
subjective
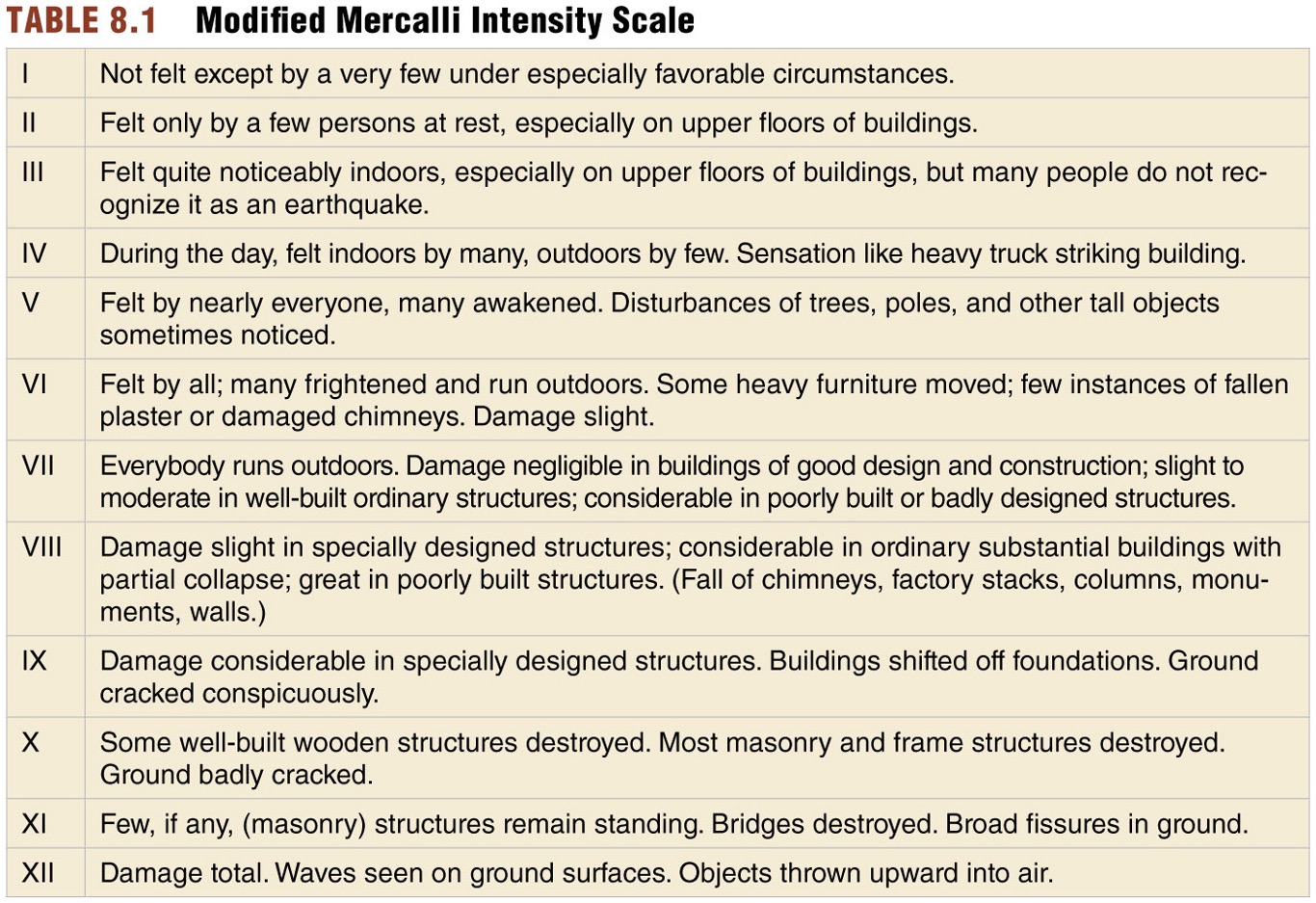
Intensity is measured with ?
modified mercalli scale
The modified mercalli scale is a function of?
strength of the quake, building materials, building design, type of ground material - how people perceive the quake
what is magnitude?
measures the amount of energy released
Magnitude is measured by?
Richter Scale
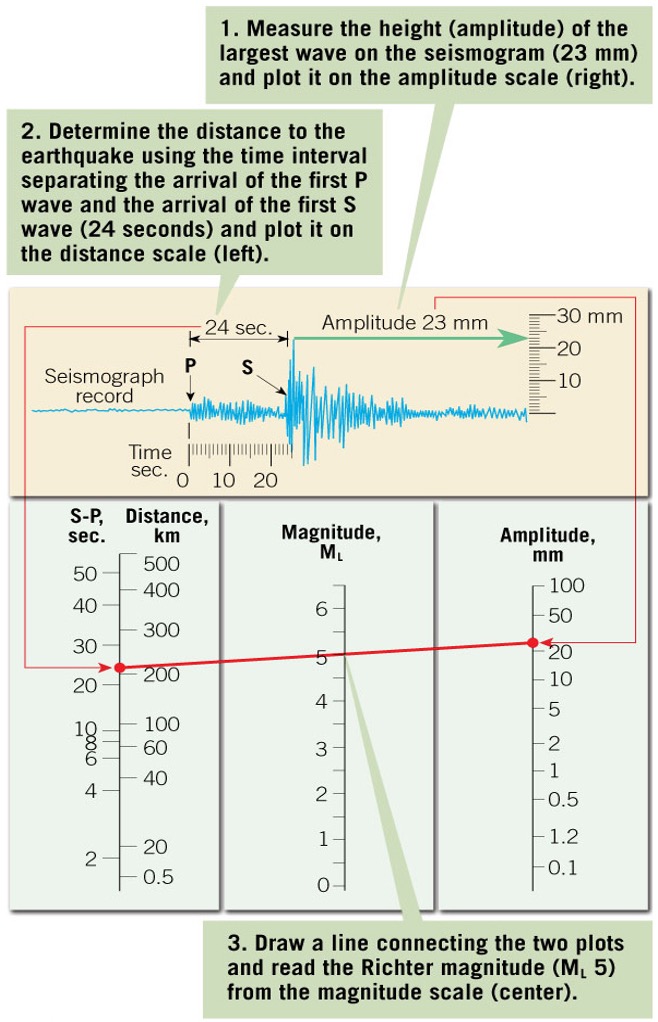
How do you measure the amount of energy released with the Richter scale?
Using a seismogram - the scale measures the amplitude (height) of the largest wave recorded
what is the relationship of the # on the scale to energy released?
10X increase in wave amplitude = increase of 1 on the scale