W13-Animal Development
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are the two ways animals can reproduce?
Asexually and sexually
Which type of reproduction is more common in animals?
sexually
What are the 3 mechanisms of Asexual reproduction?
Fission
Budding
Fragmentation
When does sexual reproduction begin?
Fertilization
Describe fertilization
Fusion of a haploid egg and sperm to produce a diploid zygote
Where can sexual reproduction occur?
Either internally or externally
What kind of fertilization does sea urchin go through?
External fertilization
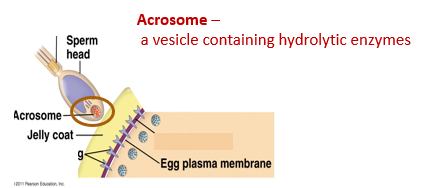
What is a acrosome?
A vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes found in the sperm head of a sea urchin
What is Fast block to polyspermy?
The fast block to polyspermy is a rapid electrical change in the egg's membrane that prevents multiple sperm from entering after the first sperm fuses with the egg
What occurs before an acrosomal reaction can begin of a sea urchin?
Sea urchin release eggs into the waters
The eggs releases attractants that can cause the sperm to swim towards the egg
As soon as the sperm reaches the jelly coat of the egg, molecules in the jelly coat trigger the acrosomal reaction in the sperm.
What does exocytosis of the acrosome of the sperm of a sea urchin lead to?
Exocytosis of the acrosome leads to release of the enzyme which results in partial digestion of the jelly coat
Describe the Acrosomal Reaction
Proteins on acrosomal proteins bind to sperm receptors
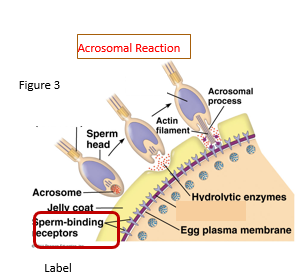
Importance for Acrosomal Reaction
Allows for species-species recognition
After proteins on acrosomal process bind to sperm receptors, what occurs?
Fusion of plasma membranes occur.
Fusion results in the opening of sodium channels in the egg’s plasma membrane
Na+ enters
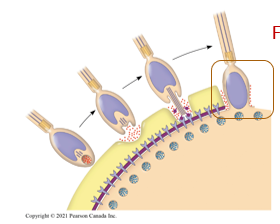
As sodium channels are opened in the egg’s plasma membrane, what occurs?
Na+ enters resulting in depolarization; a decrease in the membrane’s potential.
As Na+ enters the egg cell after fusion of the membranes of the sperm and egg cell, what are the resulting changes and what are their effects?
Negative result on the outside of the membrane and Positive on the inside of the membrane
Will result in the repulsion of any additional nearby sperm
Preventing polyspermy - acting as a fast block to polyspermy
What prevents fast block to poplyspermy?
A change in charge as Na+ enters the egg cell leading to the inner membrane to have a positive charge and the outer membrane to have a negative charge
Describe Polyspermy
More than one sperm nuclei in the egg
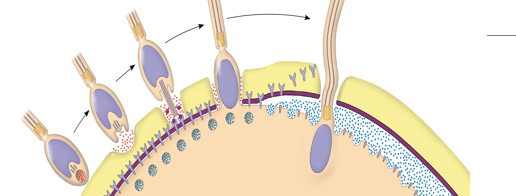
Describe the process illustrated int he picture
What is the longer-lasting change that occurs as well to prevent polyspermy?
Slow block to polyspermy
Define the Vitelline Layer
Layer of glycoprotein attached to the plasma membrane.
(THE PURPLE PART)
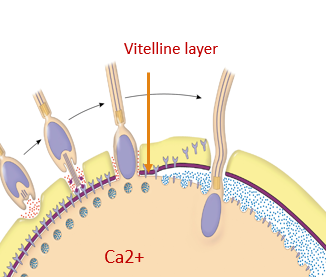
What is found underneath the plasma membrane of the egg cell of a sea urchin?
vesicles called Cortical Granules
What does binding of a sperm to an egg of a sea urchin cause?
Causes release of Ca2+ from the ER to the cytosol
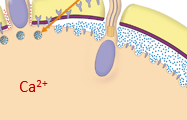
What does increase in Ca2+ causes on the sea urchin after sperm and egg cell binds?
Causes the cortical granules to release enzymes and other macromolecules into the space between the plasma membrane and the vitelline layer.
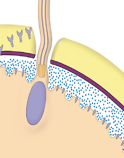
After cortical granules release enzymes and other macromolecules into the space, what does it trigger?
Triggers a cortical reaction, which lifts the vitelline layer away from the egg which is hardened to form a protective fertilization envelop.
What does the fertilization barrier do?
Provides a barrier against any additional sperm, leading to a slow block of polyspermy
After sperm enters the egg cell what occurs with the nuclei of both egg and sperm cell?
Sperm nucleus fuses with the egg nucleus which initiates and speeds up various metabolic reactions that will trigger embryonic development.
This process is called Egg ActivationW
What is egg activation?
A series of events that must occur in a fertilized egg to trigger it to initiate and speed up various metabolic reactions that will likely begin embryonic development
What is a difference between sea urchin and mammals in terms of fertilization?
No fast block to polyspermy has been observed in mammals.
List the ordered steps at which embryonic development occurs of a Sea Urchin.
Fertilization
Cleavage
Formation of Blastula
Gastrulation
Organogenesis
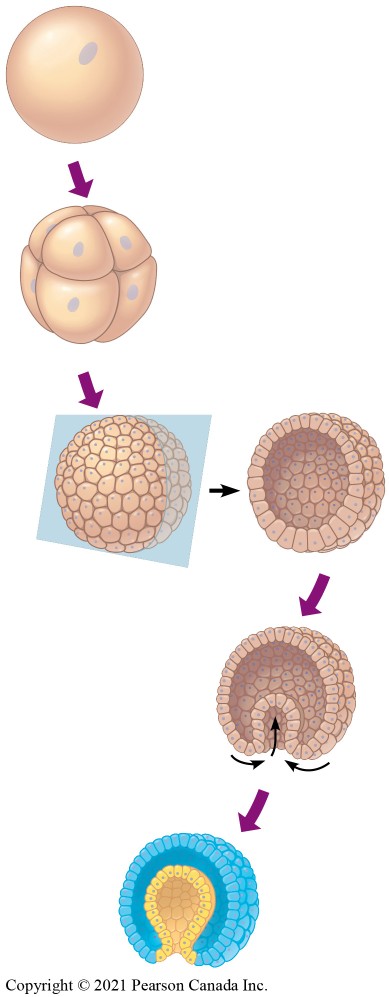
Describe the process of cleavage done by a sea urchin zygote.
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a succession of rapid cell divisions called cleavage. The large fertilized eggs is divided into many smaller cells called Blastomeres
Define Blastomeres
a type of cell produced by cell division (cleavage) of the zygote after fertilization
Describe the process of formation of the blastula done by a sea urchin zygote.
A blastula is a a hollow ball of cells that surrounds a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel, formed from blastomeres.
What are the factors that affect the variation in appearance of the blastula?
The blastula can vary in appearance depending upon the cleavage pattern of the animals and the amount of yolk
Describe the process of gastrulation done by a sea urchin zygote.
Process by which the blastula is changed into a two or three-layered embryo called a gastrula.
These cell layers are collectively called the germ layers.
What are the cell layers called after gastrulation of the sea urchin zygote has occured?
Germ layers
List the 3 germ layers
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm
True or False: Process of gastrulation differs among animals groups, but the end result is the same.
Yes, the end result being the Formation of Germ layers
Describe the process of Organogenesis done by a sea urchin zygote.
Process by which organs develop from the three germ layers of the gastrula.
Each germ layer contributes to a specific set of structures in the adult animal
What does the ectoderm germ layer mainly develop?
Skin and nervous system
What does the mesoderm germ layer mainly develop?
Skeletal and muscular systems
What does the Endoderm germ layer mainly develop?
Lining of the digestive tract
In general, describe the development of a zygote sea urchin?
Zygote → Produces many cells by cleavage → Blastula → Gastrulation → Will produce 3 germ layers → Will form organs
What is determination, in terms of the development of a sea urchin?
When an embryonic cell has committed to particular cell type
How is determination done?
By Induction
By presence of Cytoplasmic determinants
What is Induction?
Process by which determination is done. It occurs when one cell or tissue sends out an extracellular signal which is received and responded to by neighboring cells.
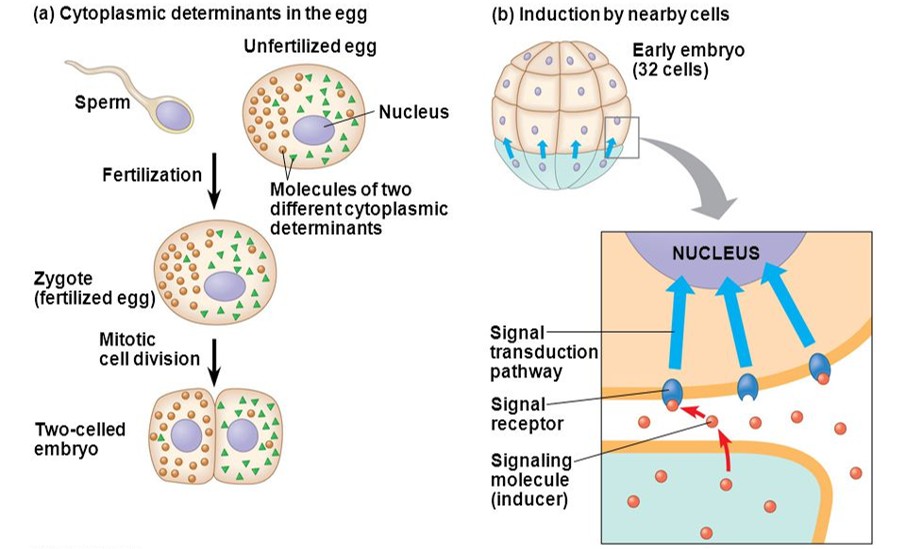
What is Cytoplasmic Determinants?
These are determinants found in the egg cytoplasm, that will ‘define’ what the cell will become
Upon cleavage, they will end up in different cells
Which cell receives which determinant, will predict its fate
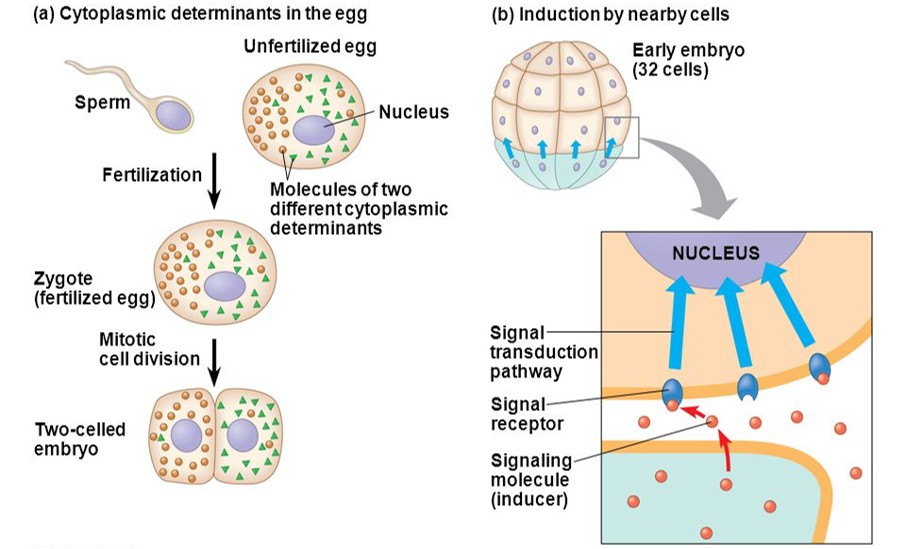
After cell fate has determined, what occurs of a sea urchin zygote?
Differentiation - A process that causes the cell to become specialized to its structure and function
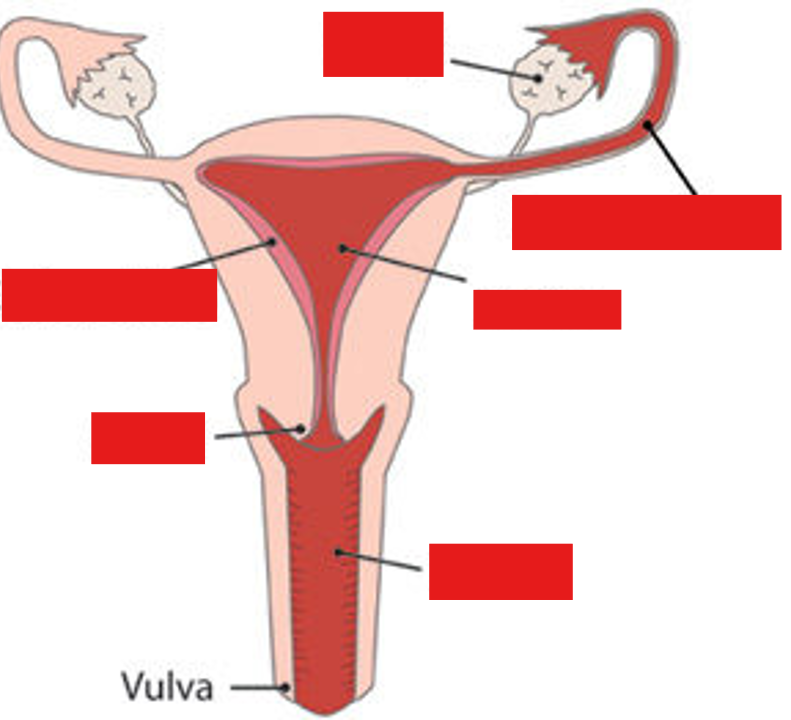
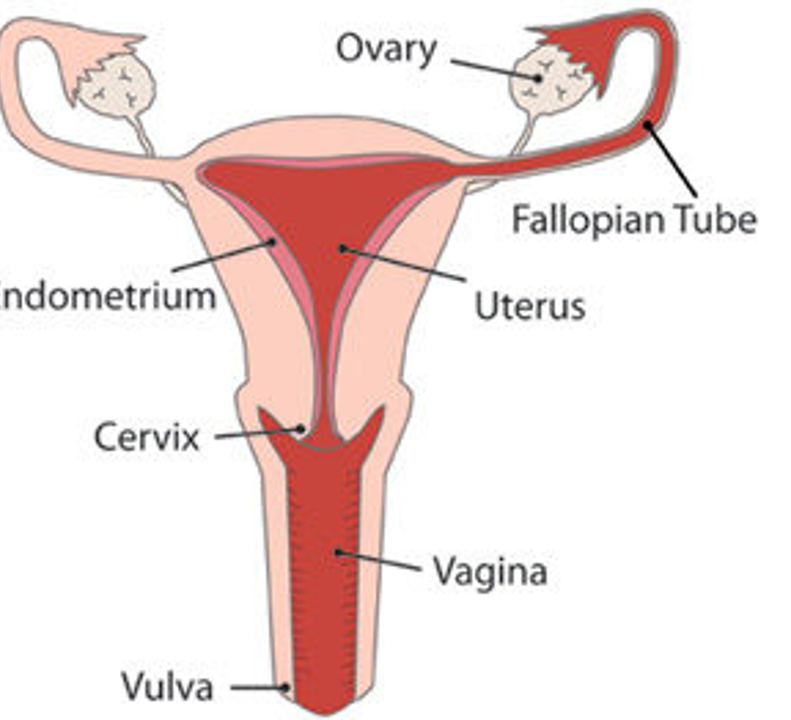
In which location does fertilization usually take place in a human female?
Oviduct
List the stages if the early embryonic development in the human
Ovulation
Fertilization
Cleavage
Implantation into endometrium
Once the egg cell is fertilized, what is it called in humans?
Blastocyst (blastula)
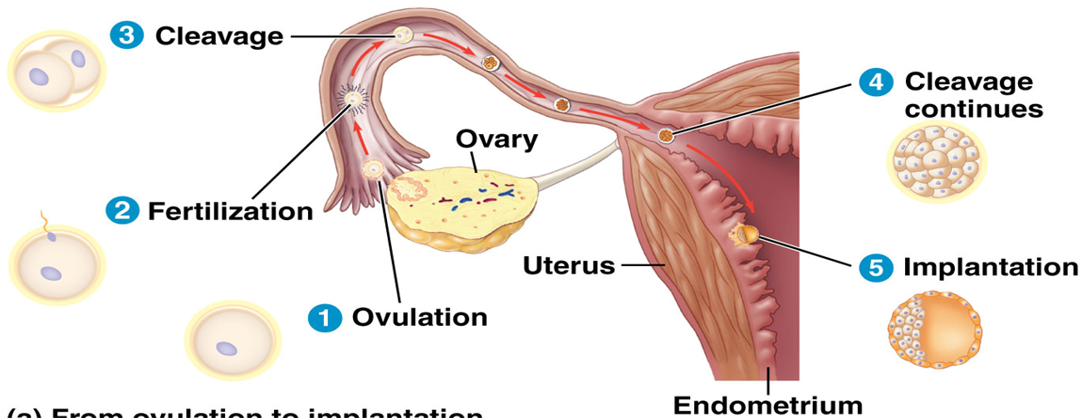
What occurs after the blastocyst is formed in humans?
Outer layers if the blastocyst grow into the endometrium.
Days after fertilization, extraembryonic membranes form
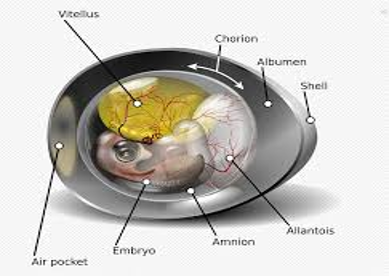
What are amniotes?
Mammals and reptiles produce amniotic egg that consists of extraembryonic membranes
List the 4 extraembryonic membranes.
Chorion
Amnion
Allantois
Yolk sac
What does Chorion do?
One of the four extraembryonic membranes which plays a role in gas exchange
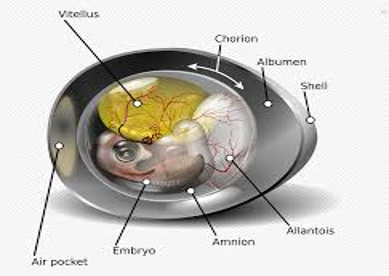
What does Amnion do?
One of the four extraembryonic membranes. It is a membrane that encloses fluid that helps to cushion the embryo.
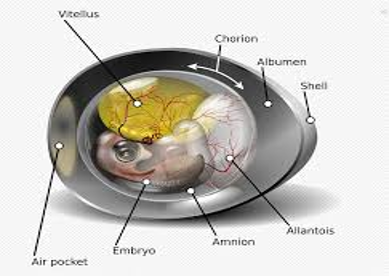
What is Allantois?
One of the four extraembryonic membranes which gets rids of wastes and in mammals it becomes a part of the umbilical cord.
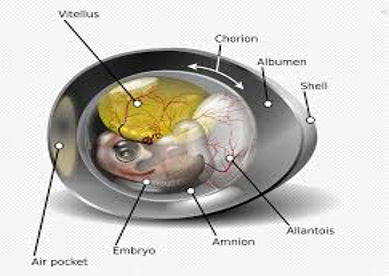
What is a yolk sac?
One of the four extraembryonic membranes which transfers nutrients to the embryo and in mammals it is a site of early blood formation.
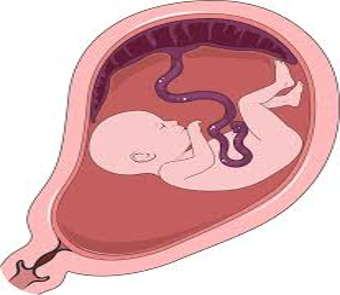
As the embryo develops, what organ develops within the uterus?
Placenta
What is the role of the placenta?
Via the umbilical cord:
Provides the embryo with nutrients
Removes waste from the embryo
After fertilization, what stage occurs in mammals?
Gastrulation
What occurs at the end of the gastrulation stage for mammals?
An embryo with four extraembryonic membranes and three germ layers has been produced
What occurs after gastrulation stages in mammals?
Organogenesis which occurs during the first trimester
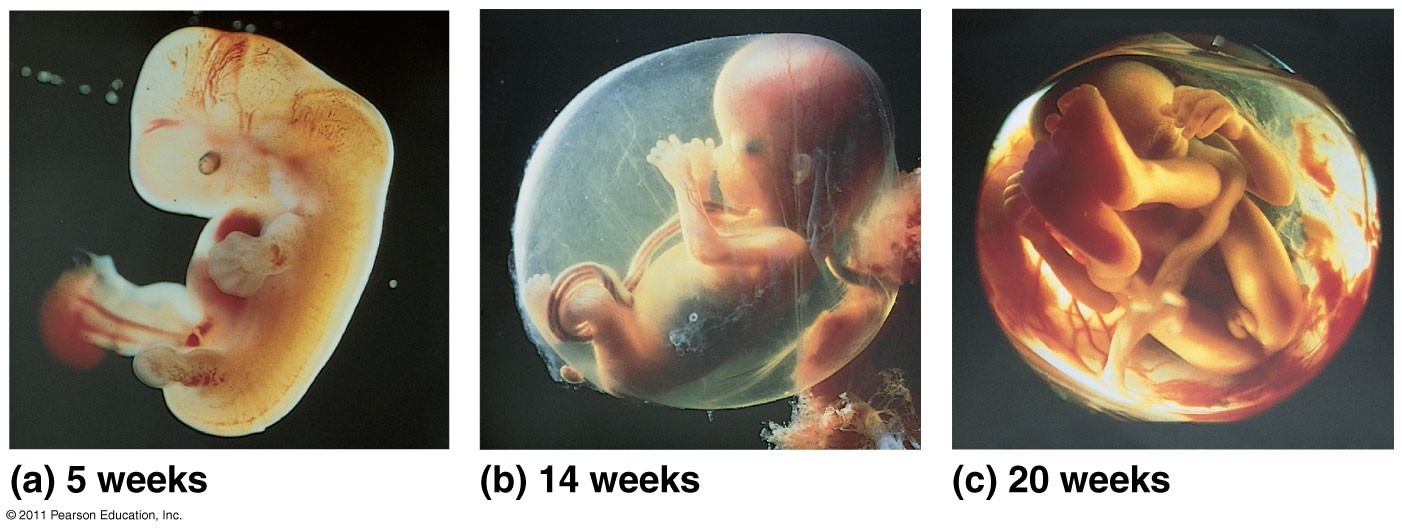
At what week is the embryo referred to as a Fetus?
At 8 weeks old
What is the type of pattern humans exhibit after birth?
Continuous Pattern of Development

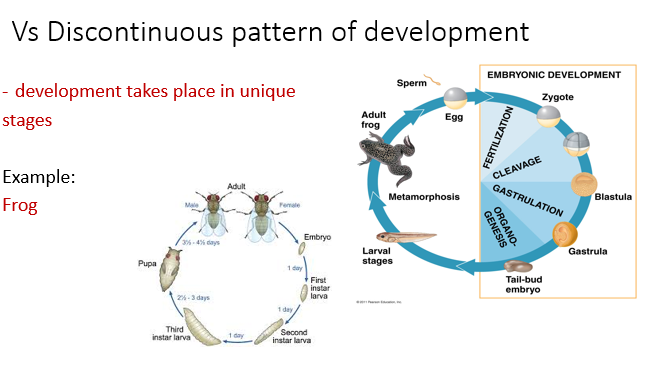
What is discontinuous pattern of development?
Development takes place in unique stages
Examples of animals that exhibit Discontinuous pattern of development.
Frog and fruit fly