Science Final
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Erosion
The process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity transports sediment from one location to another.
Lava
Magma that reaches Earth's surface.
Magma
Molten rock beneath Earth's surface.
Compaction
The process that presses sediments together.
Cementation
The process by which dissolved minerals crystallize and "glue" particles of sediment together into one mass.
Weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
Sediments
Weathered rock fragments.
Sedimentary Rock
A rock that forms from compacted and cemented layers of sediment.
Metamorphic Rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
Igneous Rock
A type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface.
Clastic Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rock that forms when fragments of preexisting rocks are compacted or cemented together.
Chemical Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rock that forms when minerals precipitate from a solution.
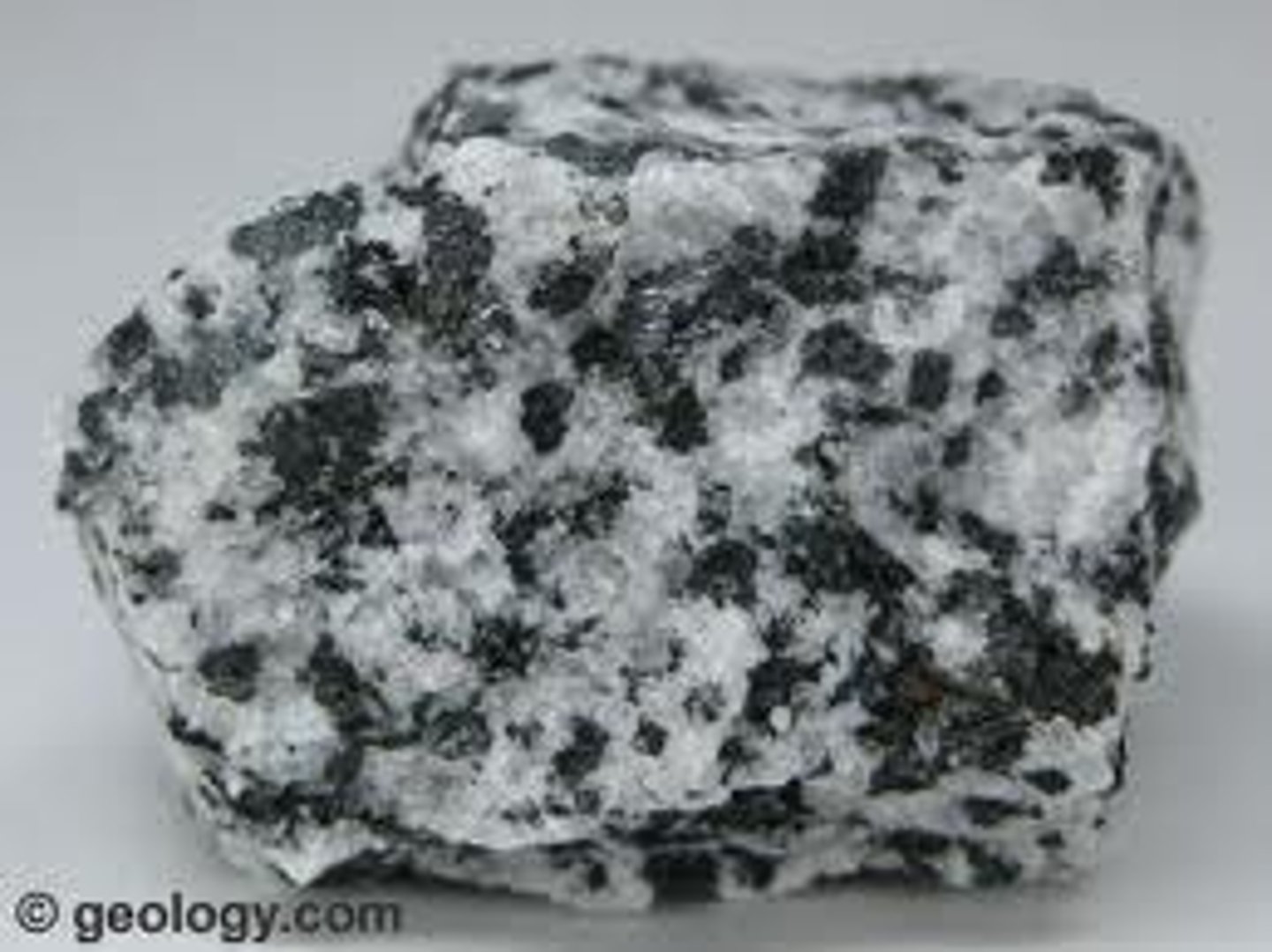
Intrusive Igneous Rock
Rock formed from the cooling and solidification of magma beneath Earth's surface. Coarse grained (large minerals, see image), and long cooling time.

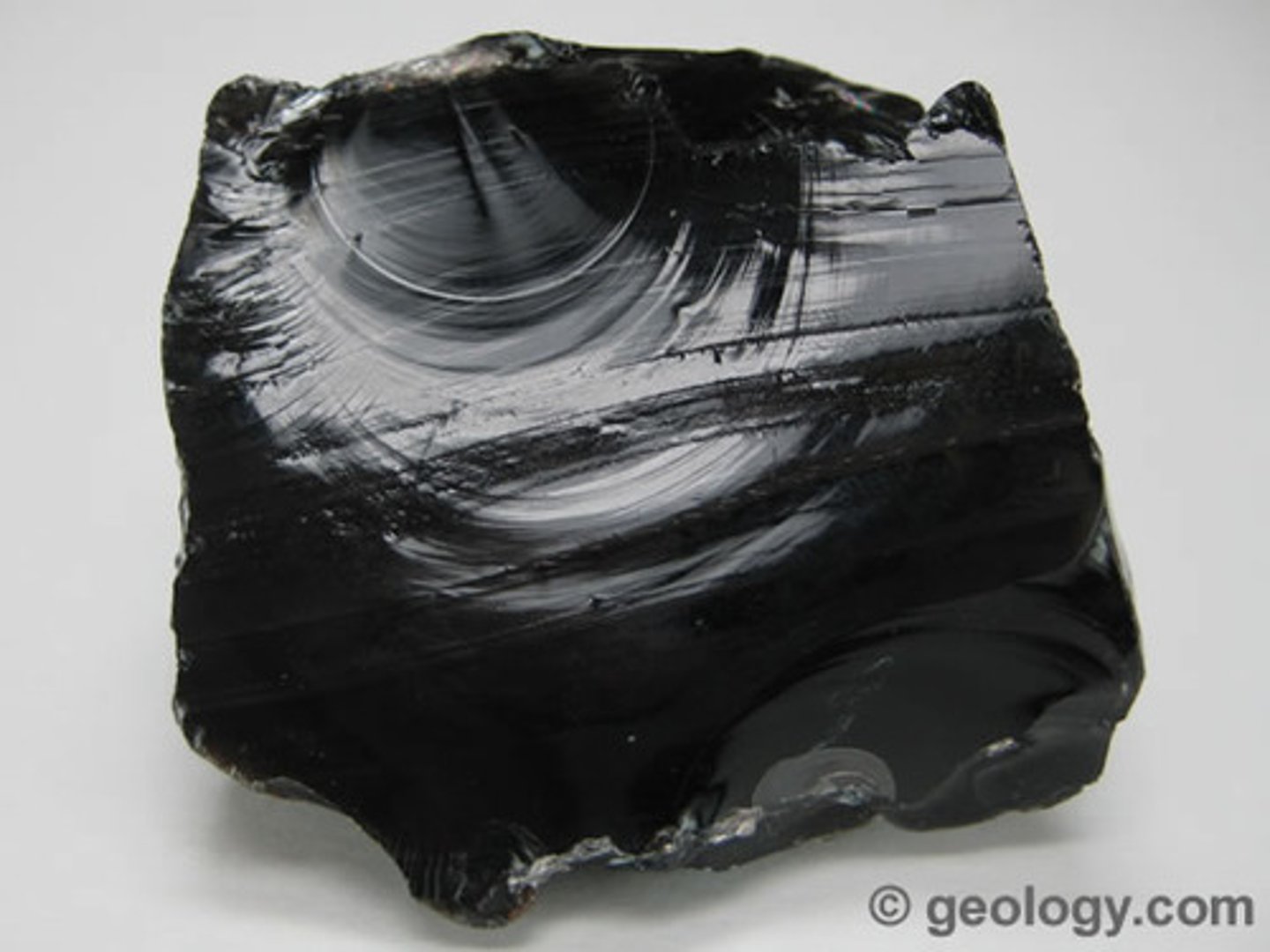
Extrusive Igneous Rock
Rock that forms from the cooling and solidification of lava at Earth's surface. If it cools fast, it is fine grained, and if it cools very fast, it is glassy. See image.

Regional Metamorphism
Formation of metamorphic rock bodies that are hundreds of square kilometers in size, usually caused by plate tectonics.
Contact Metamorphism
Small scale metamorphism, close to magma.
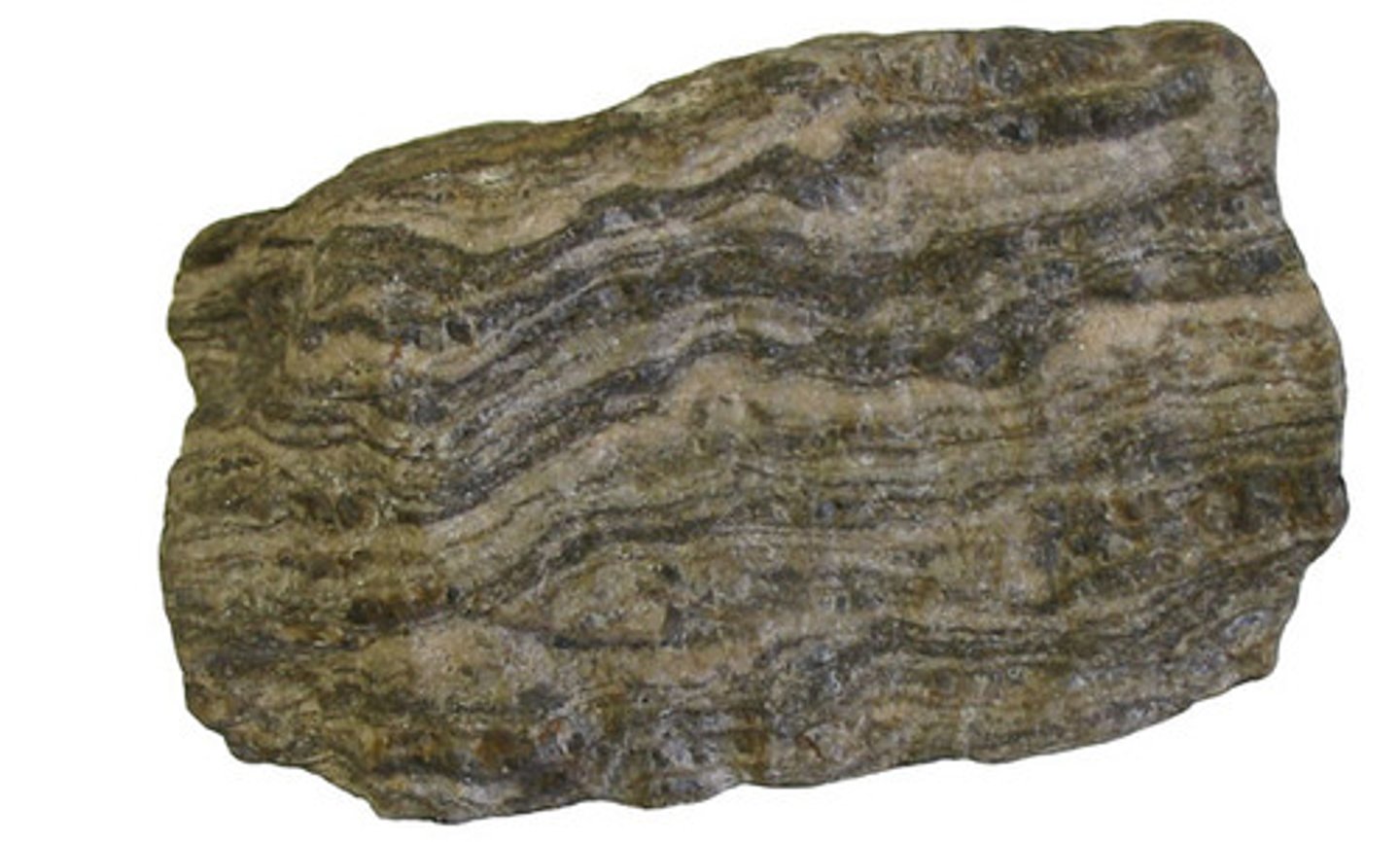
Foliated Metamorphic Rock
A metamorphic rock with a texture that gives the rock a banded pattern (see image).

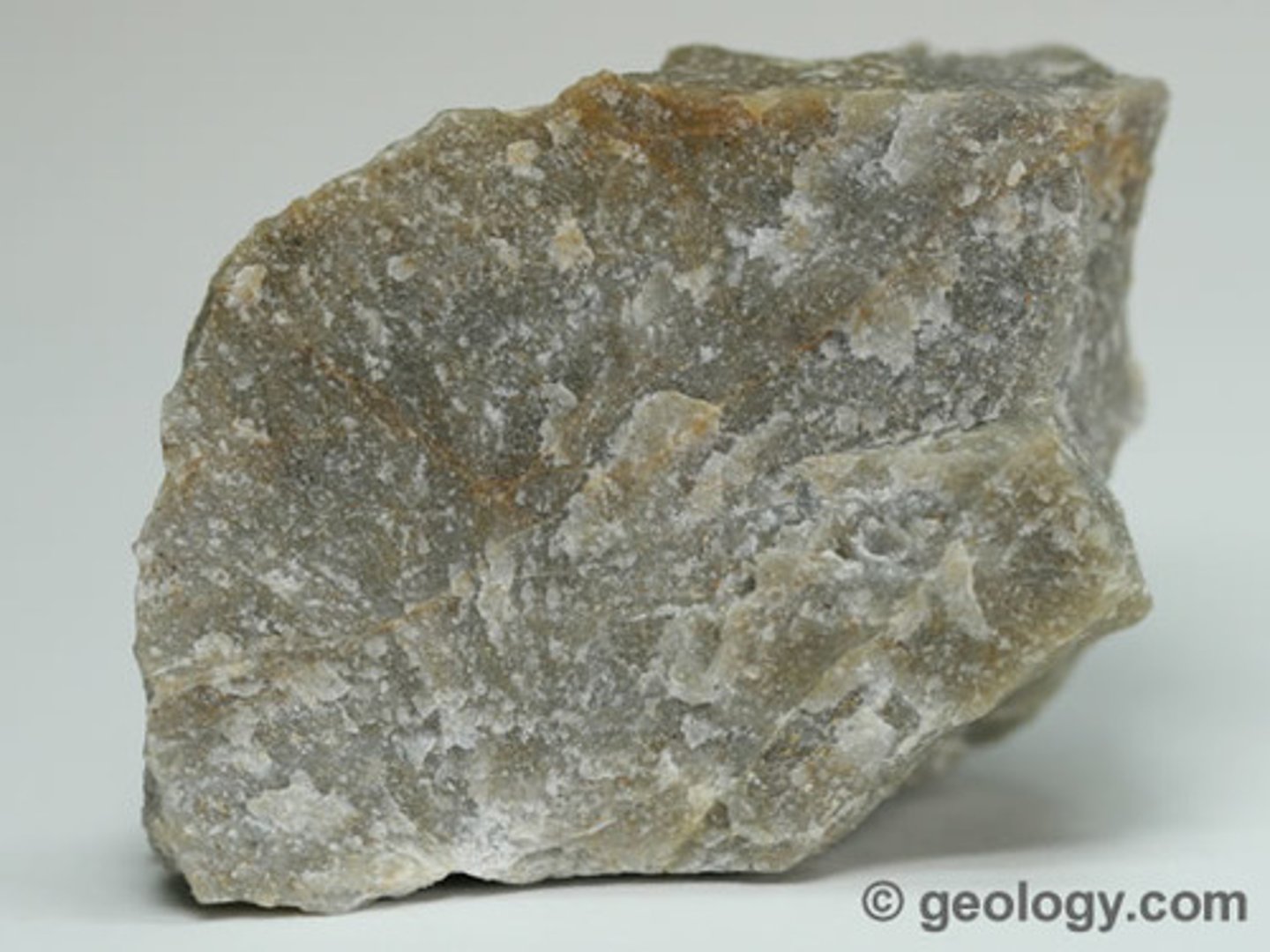
Nonfoliated Metamorphic Rock
A metamorphic rock with a texture that gives the rock a scattered appearance (see image).

True
True or False; metamorphic rocks form many miles underground.
Organic
Fossil fuels come from ______ matter.
Plants, Fossil
Earth's heat and pressure turns ______ from long ago into ______ fuels.
Rock
Consolidated mixture of minerals.
Renewable Resource
Resource that is virtually inexhaustible and/or replenishes very quickly.
Nonrenewable Resource
Resource that takes millions of years to form and is clearly limited.
Hydrocarbon
What is used as fuel for fossil fuels?
Ore
Material from which useful mineral or minerals can be mined for a profit.
Hydroelectric Power
Power generated by falling water.
Geothermal Energy
Energy that can be extracted from Earth's internal heat.
Point Source Pollution
Water pollution, from a specific, known source.
Nonpoint Source Pollution
Water pollution, no known source.
Runoff
When water flows over the ground instead of into it.
Global Warming
A gradual increase in average global temperature in part due to high CO2 levels.
Compost
Decayed organic material used as a plant fertilizer.
Recycling
Collection and processing of used material for new products.
Sun, Gravity
Two forces that drive the rock cycle.
Coarse, Fine, Glassy
_____ grain igneous rocks cooled slow, ______ grain igneous rocks cooled fast, and igneous rocks with a ______ texture cooled very fast.
Granitic Igneous Rock
Mostly quartz and feldspar.
Basaltic Igneous Rock
Darker silicates, iron rich, darker in color.
Fire
What is the meaning of the Latin word ignis?
Deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.
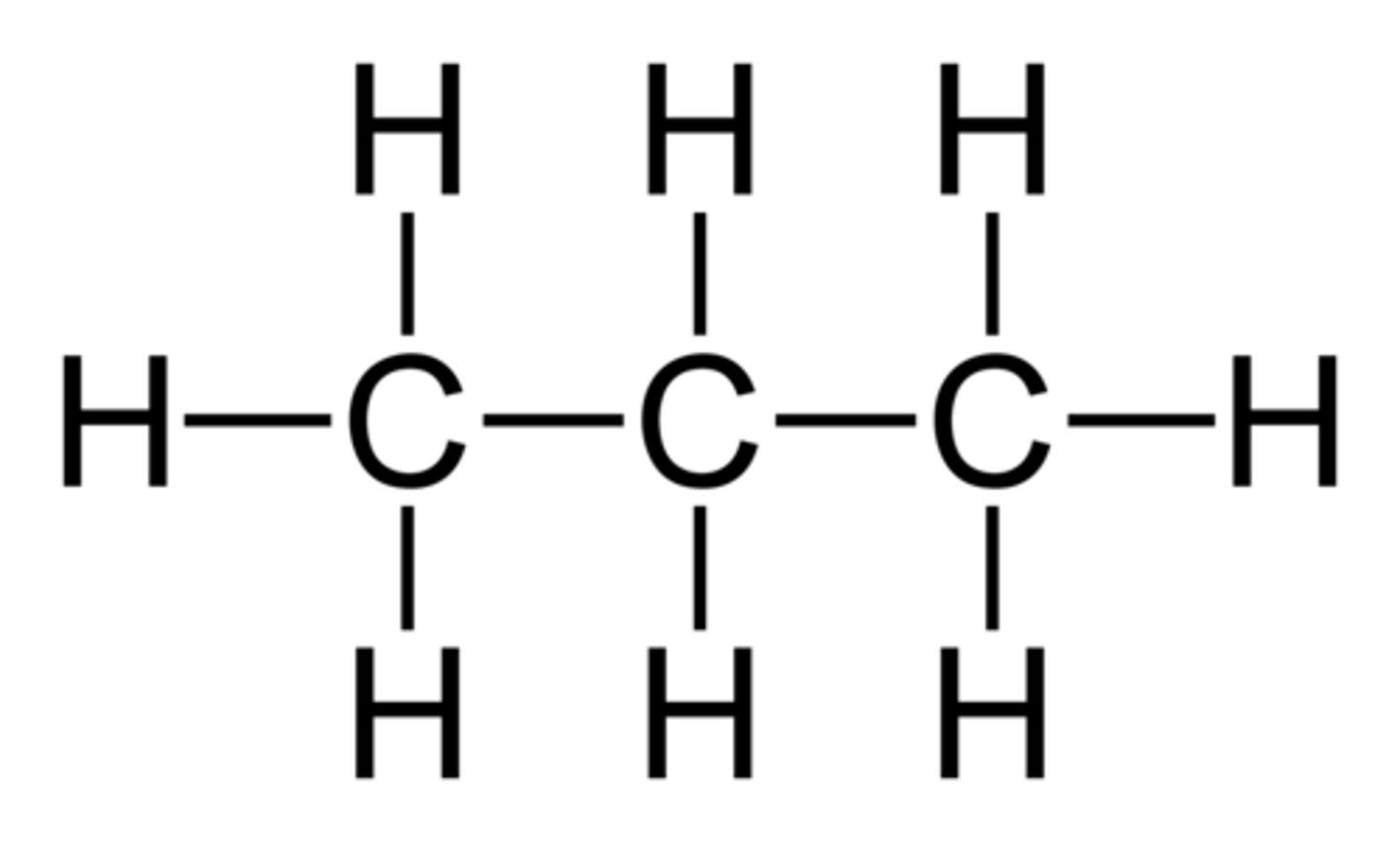
A
Chemical structure and formula for propane (see image). Type "A" to get this question right.
Peat, Lignite, Bituminous, Anthracite
Four steps in coal formation.
Igneous Process
A large magma body cools and minerals crystallize and settle at the bottom.
Hydrothermal Solutions
Mineral rich hot water seeps into fractures and cracks between rocks, cools and leave mineral deposits.
Placer Deposits
Eroded minerals settle out of moving water.
Oil Shale
Rock containing kerogen.
Tar Sands
Mixture of bitumen, water, clay, and sand.
Sun
Most abundant energy resource on Earth (one word).
False
True or False; solar energy is cheap.
True
True or False; solar energy is not always reliable.
Nuclear Fission
The nuclei of heavy atoms are bombarded with neutrons and that causes this to split, creating energy. The way by which nuclear reactors create energy.
5-10%
What percentage of energy could wind power provide in the next 50 years?
Dam
The stored energy in hydroelectric power is water held behind the ______.
Sediments
Dams have a limited lifespan because the reservoir fills with ______.
True
True or False; drawbacks of hydroelectric power, geothermal energy, and tidal power is that they are all limited to suitable sites.
Geothermal Energy
Water heated in underground reservoirs by volcanic forces and the steam is used to turn turbines.
Neutron
What type of particle is fired to create fission?
Uranium 235
An unstable, fissionable isotope of uranium.
71%
What percent of the earth's surface is covered by water?
Atmosphere
The chemical composition of the ______ helps maintain life by providing oxygen, protecting from harmful radiation, and maintaining surface temperature.
Greenhouse Gases
Maintains a warm temperature on Earth's surface.
Warming
Burning fossil fuels can contribute to global ______.
Conservation
The careful use of resources.
Clean Air Act
1970 law that established air pollution standards for private industry.
Clean Water Act
1972 law that was passed to reduce point source pollution.
Rock Cycle
The series of processes that changes one type of rock into another type of rock (most of the time).
Earth Science
A branch of sciences that study earth and space.
Meteorology
A kind of earth science that studies the climate and weather.
Oceonography
A kind of earth science that studies the ocean.
Astronomy
A kind of earth science that studies space.
Geology
A kind of earth science that can be divided into two groups, studying a timeline of earth and a study of our planet's processes.
Timeline
Historical geology tries to create a ______ of the earth.
Processes
Physical geology studies the ______ of the earth.
Atmosphere
Which sphere encompasses air?
Geosphere
Which sphere encompasses rocks, the crust, the mantle, and the core.
Biosphere
Which sphere encompasses all living things?
Hydrosphere
Which sphere encompasses water?
Hydrogen, Helium, Gravity, Collapse, Heat, Nuclear, Sun, Particles, Planets
The Nebular Hypothesis states that the solar system started as a cloud of dust and gas, made mostly of ______ and ______. ______ caused the cloud to ______, generating ______. ______ fusion occurred, forming the ______. ______ combined, forming the ______.
Atom
What is the smallest particle of matter that has properties of an element?
False
True or False; electrons have +1 mass.
True
True or False; electrons have a negative charge.
Electron
Which subatomic particle is in charge of bonding?
Proton
Which subatomic particle's number in an atom's nucleus decides the atomic number?
True
True or False; protons add +1 mass.
False
True or False; protons add -1 charge.
True
True or False; neutrons are located in the nucleus.
1
Neturons add +__ mass.
0
Neutrons add +__ charge.
False
True or False; electrons are located in the nucleus.
0
Electrons add +__ mass.
1
Electrons add-__ charge.
Isotope
An ______ is when two of the same kind of element have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
Bonding
Electrons are in charge of ______.
2, 8
Atom's bond to fill out their energy rings. The first ring has __ spaces, and the next has __.
Topographical, Contour
______ maps show elevation through ______ lines.
Equator
Latitude of 0 = ______.
Prime Meridian
Longitude of 0 = ______ ______.
False
True or False; a mineral can be organic.
Chemical Composition
Minerals must have a definite ______ ______.
True
True or False; a mineral has to be solid.