Chem- Unit 4: Organ systems and Clinical Correlation
1/252
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
253 Terms
play a role in blood formation and the destruction of cellular debris
(immune surveillance and homeostasis)
A: retinol (eye)
D: Calciferol (skeletal development and calcium uptake)
Accelerated hemolysis: sickle cell crisis, hemolytic anemia/destruction of transfused RBCs
Decreased delivery if unconjugated bilirubin to liver
decreased conjugation due to benign genetic mutation
(most common cause of hepatic jaundice)
liver conjugates, but body can't eliminate
Obstructive in nature
conjugated bilirubin found in blood bound to albumin (can cause problems with lab measurements)
(normally unconjugated bilirubin found in blood attaches to albumin carrier protein)
involves gall bladder and bile canal infrastructure
liver can conjugate but cannot excrete correctly
Physical obstructions prevent flow of conjugated bilirubin into bile canaliculi
Clay colored stools
rarely detected in early phases; when liver deteriorates signs and symptoms appear
Symptoms: fatigue, nausea, unexpected weight loss, jaundice
iron overload that accumulates in the liver
(stored iron can cause severe damage that may lead to organ failure and cirrhosis. Therapeutic phlebotomy is treatments)
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hepatoma
(80% of HCC cases caused by Hep B/C viral infections)
Moderate AST, ALT, GGT, and Alk phos elevations
(AST/ALT ratio >2)
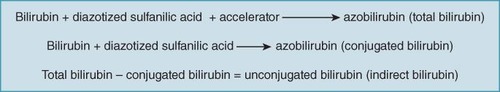
purple coloring of azobilirubin molecules (Mallow-Evelyn)
(intensity in purple color directly proportional to bilirubin concentration)
total bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin
Total bilirubin (aliquot #1): Tests for all unconjugated bilirubin, conjugated bilirubin, and delta bilirubin; reacted with diazo reagent after stabilization with caffeine-benzoate accelerator
Direct bilirubin only (aliquot #2): reacted directly with diazo reagent to measure only conjugated bilirubin
indirect bilirubin
Total bilirubin mins conjugated (direct) bilirubin = unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin
Tbil - BC = BU
blood or urine, more stable in blood
avoid hemolysis and protect from light