IB Biology - 6.4. Gas exchange
5.0(1)Studied by 57 people
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:36 PM on 12/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
Ventilation
Exchange of air between the atmosphere and the lungs, activated by breathing.
2
New cards
Gas exchange
The exchange of oxygen and CO2 between bloodstream and the alveoli via passive diffusion.
3
New cards
Respiratory system diagram
You should be able to label it
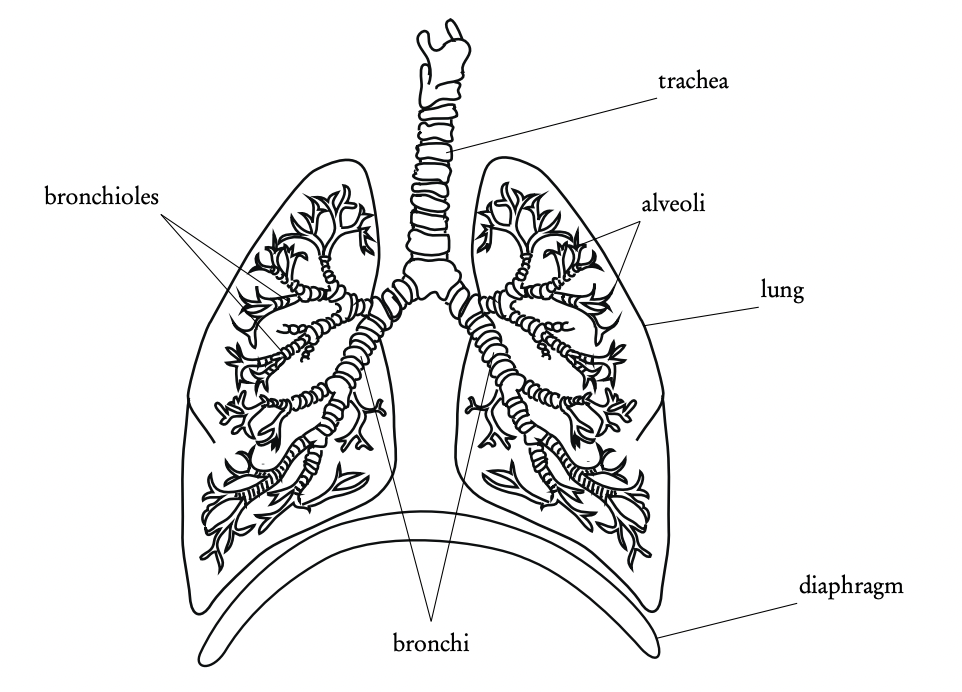
4
New cards
Alveoli
Are the body's gas exchange surfaces, formed in clusters at the ends of the smallest bronchioles.
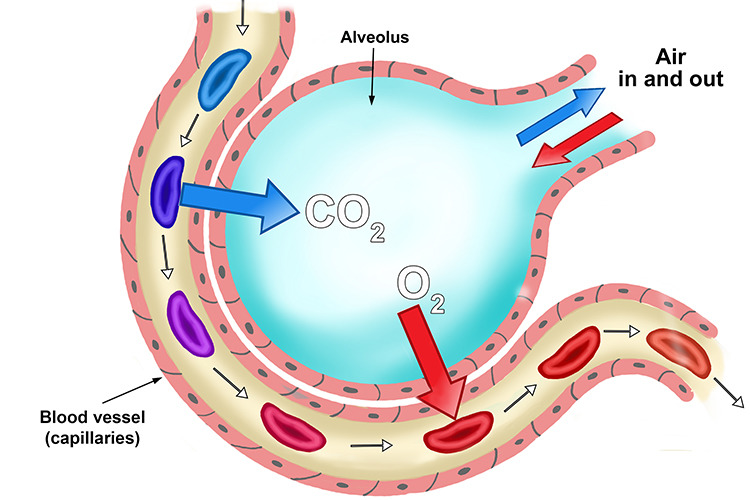
5
New cards
Pneumocytes type I
Extremely thin alveolar, permeable and adapted for gas exchange.
6
New cards
Pneumocytes type II
Secrete a solution containing surfactant, which creates a moist surface inside the alveoli to prevent the sides of the alveolus adhering to
each other by reducing surface tension.
each other by reducing surface tension.
7
New cards
Lung cancer causes
Smoking, passive smoking, air pollution, radon gas, asbestos and silica.
8
New cards
Lung cancer consequences
Difficulties with breathing, chest pain, persistent coughing, loss of appetite, weight loss, coughing blood, fatigue, death.
9
New cards
Emphysema
Respiratory disease, caused by smoking or air pollution. Consequences are loss of elasticity in lungs, reduced surface area for gas exchange and difficulty to exhale air. Inflammatory response.
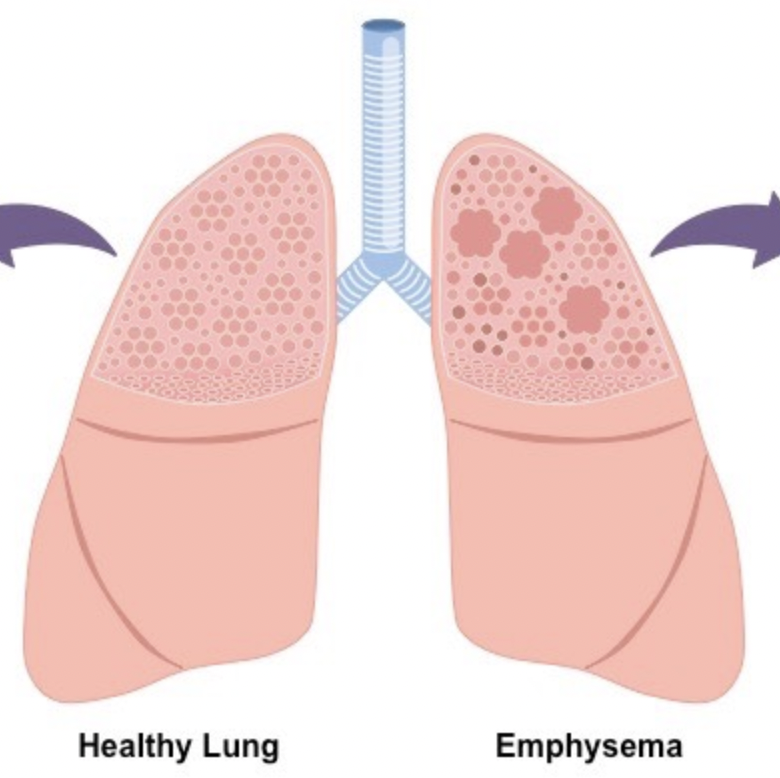
10
New cards
Cell respiration
Production of ATP at the cellular level.
11
New cards
Necessity of a ventilation system
We are large organisms, we are land-borne, large concentration gradient.
12
New cards
Mechanics of ventilation
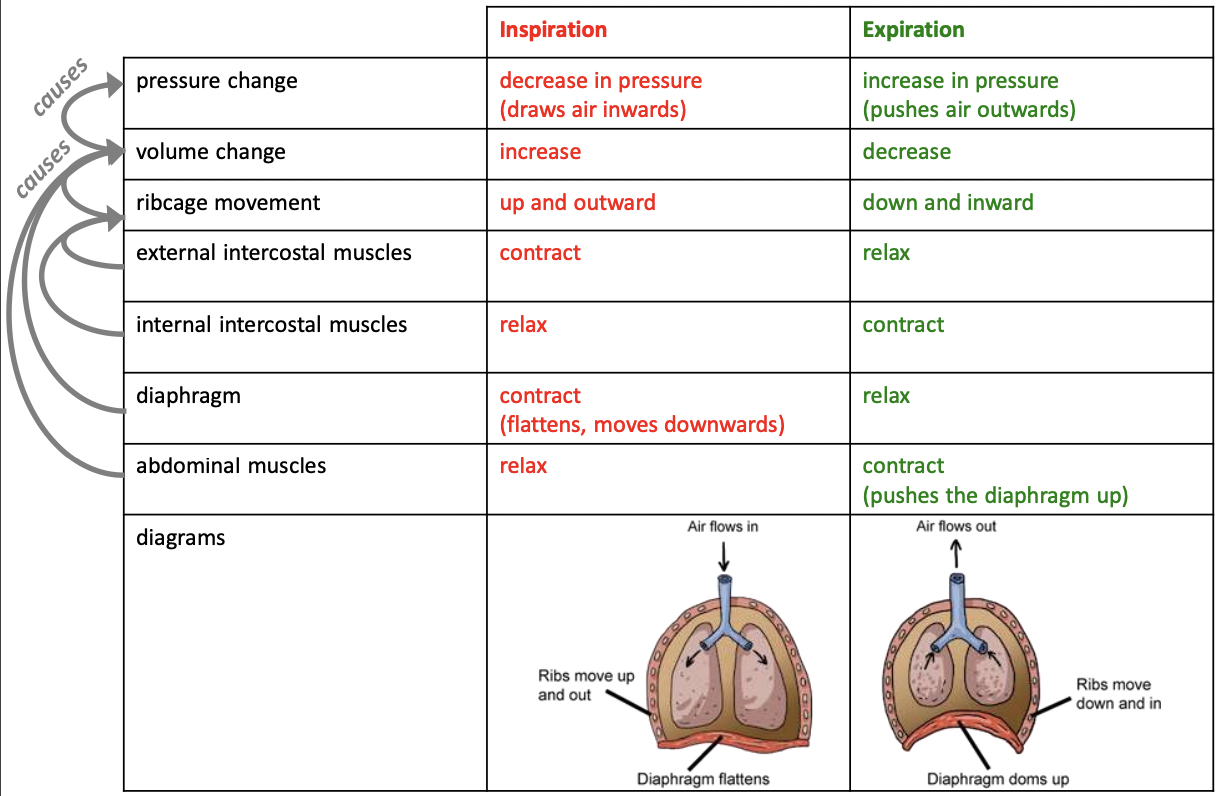
13
New cards
Tumor
Abnormal growth of tissue that develop at any stage of life in any part of the body.
14
New cards
Physiological respiration
Involves the transport of oxygen to cells within the tissues, where energy production occurs.
15
New cards
Pneumocytes
Alveolar cells. Are the cells that line the alveoli and comprise of the majority of the inner surface of the lungs
16
New cards
Surface tension
The elastic force created by a fluid surface that minimizes the surface area (via cohesion of liquid molecules)
17
New cards
Breathing
Active movement of respiratory muscles that enables the passage of air into and out of the lungs. Boyle's law.
18
New cards
Inspiration
Increase volume of the chest.
19
New cards
Expiration
Decrease the volume of the chest.
20
New cards
Diaphragm
Muscles contract, causing the diaphragm to flatten and increase the volume of the thoracic cavity.
21
New cards
External intercostals
Contract, pulling ribs upwards and outwards (expanding chest).
22
New cards
Influence of exercise
Increase ventilation rate and tidal volume.
23
New cards
Spirometry
Measuring the amount (volume) and speed (flow) at which air can be inhaled or exhaled.
24
New cards
Total lung capacity
Volume of air in the lungs after a maximal inhalation.
25
New cards
Vital capacity
Volume of air that can be exchanged by the lungs via a maximal inhalation and exhalation.
26
New cards
Residual volume
Volume of air that is always present in the lungs (20% of total lung capacity).
27
New cards
Tidal volume
Volume of air that is exchanged via normal breathing.
28
New cards
Asthma
Chronic inflammation of the airways to the lungs.
29
New cards
Pneumothorax
Abnormal collection of gas in the pleural space that causes an uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall