Cerebellum
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
The cerebellum is best known as a motor part of the brain, serving to maintain ___ and coordinate _____
equilibrium // muscle contractions
T/F: The cerebellum makes a special contribution to synergy of muscle action (i.e., to the synchronized contractions and relaxations of different muscles that make up a useful movement).
TRUE - ability to contract and relax at same time in synchronization
The _____ ensures that contraction of the proper muscles occurs at the appropriate time, each with the correct force
cerebellum
Classic Cerebellar Deficits
Ataxic, wide-based, unsteady gait
Dysdiadochokinesia
Difficulty with accurate movement
Decomposition of movement
Dysmetria (past-pointing)
Intention tremor
what is ataxia
not moving as one smooth movement
the ability to do rapid alternating movement back and forth that people with cerebellar deficits have issues with
Dysdiadochokinesia
Classic with Cerebellar Deficits is to have difficulty with accurate movement, including...(3)
•Decomposition of movement
•Dysmetria (past-pointing)
•Intention tremor (gets worse as they start to move - finger to nose)
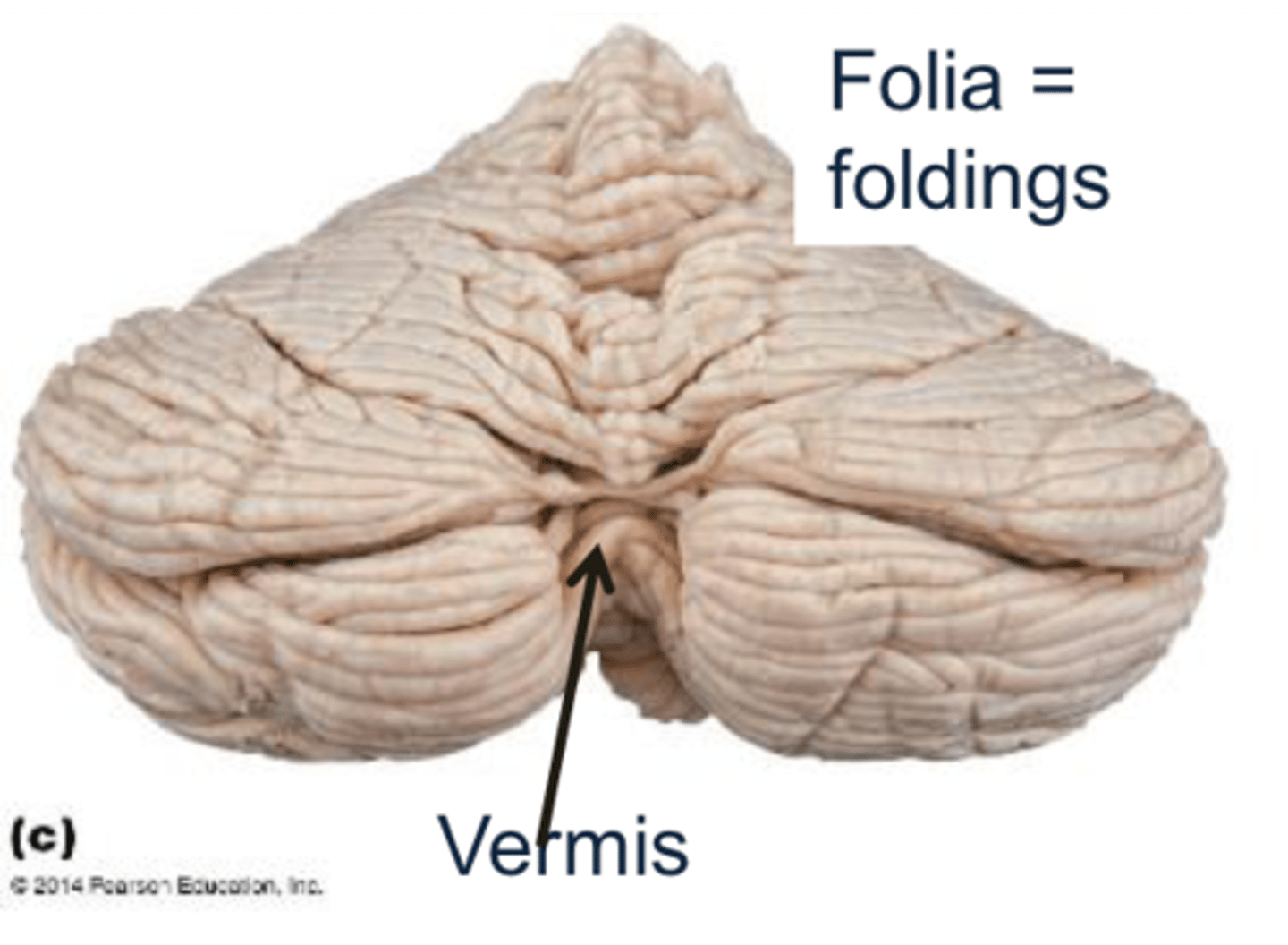
central bottom of cerebellum is called ____
inferior vermis
cerebellum contains ___ that have implications for timing and spatial awareness for limb movements; contain many nuclei
folia
does the cerebellum have a homonculus?
YES
The cerebellum consists of a _____, or surface layer, of gray matter contained in transverse folds called ____, plus a central body of ____ ____
cortex // folia // white matter
Don’t Eat Greasy Foods
dentate, emboliform, globuse, fastigial
(the 4 deep cerebellar nuclei, from lateral to medial)
___ pairs of central nuclei are embedded in the cerebellar white matter
FOUR (fastigial, globuse, dentate, emboliform)
4 deep cerebellar nuclei
-fastigial
-globose
-emboliform
-dentate
what two nuclei are interposed and tend to work together with axial/postural muscles?
globose and emboliform
where does most of the output from cerebellum come from?
deep nuclei
what ventricle lines up with cerebellum?
fourth
3 pairs of cerebellar peduncles, composed of myelinated axons, connect the _______ with the _______
cerebellum; brainstem
T/F: the cerebellar nuclei are always excited
true!
The 4 deep cerebellar nuclei receive ______ (glutamatergic) collateral input from all incoming sensory information before the signals are processed by the ______ cortex.
excitatory; cerebellar
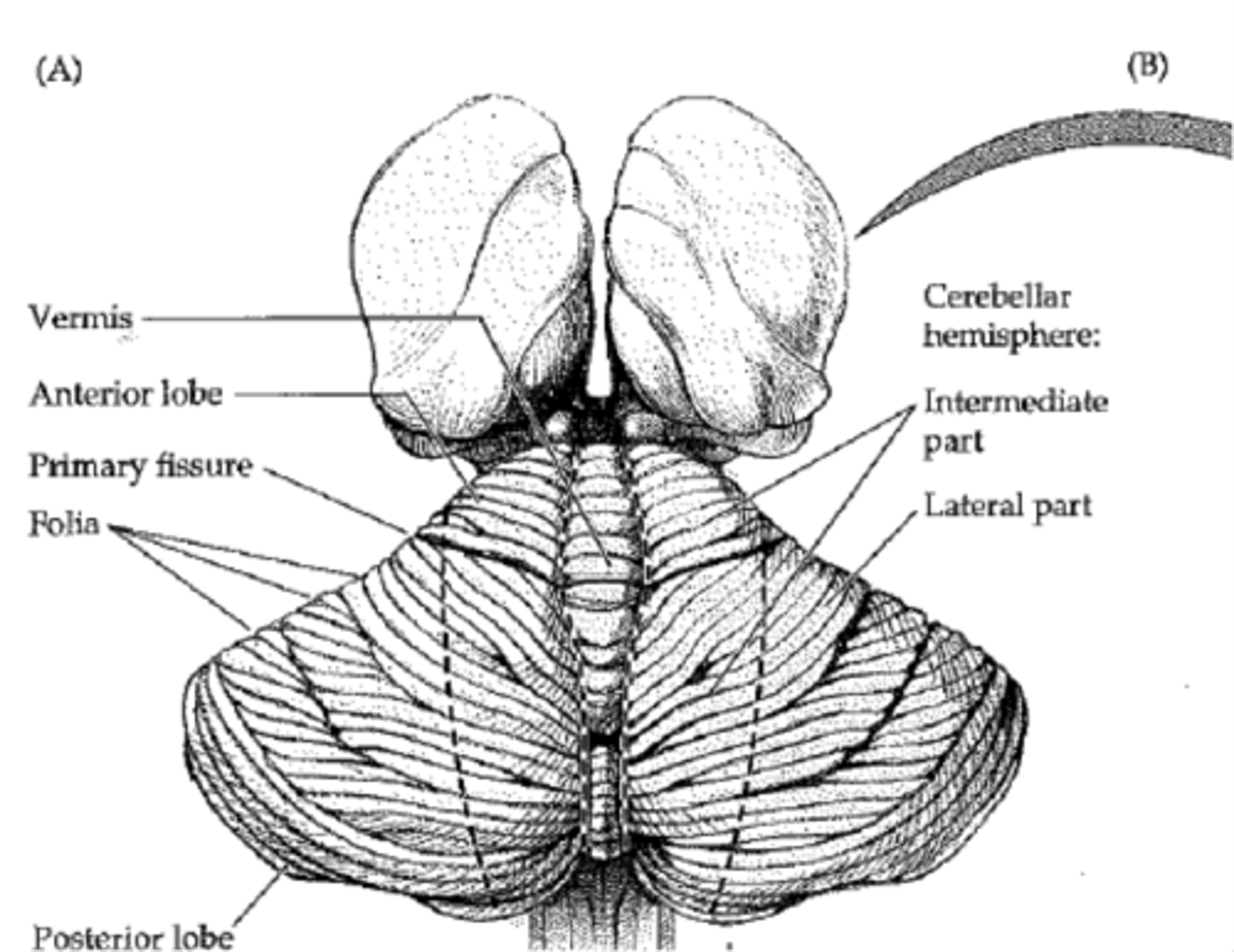
the region in and near the midline of the cerebellum is known as the _______
vermis
the region in and near the midline of the cerebellum is the vermis, and the remainder is the _______
hemisphere
The ____ vermis blends into the hemispheres, but the ____ vermis lies in a deep depression and is well delineated.
superior; inferior
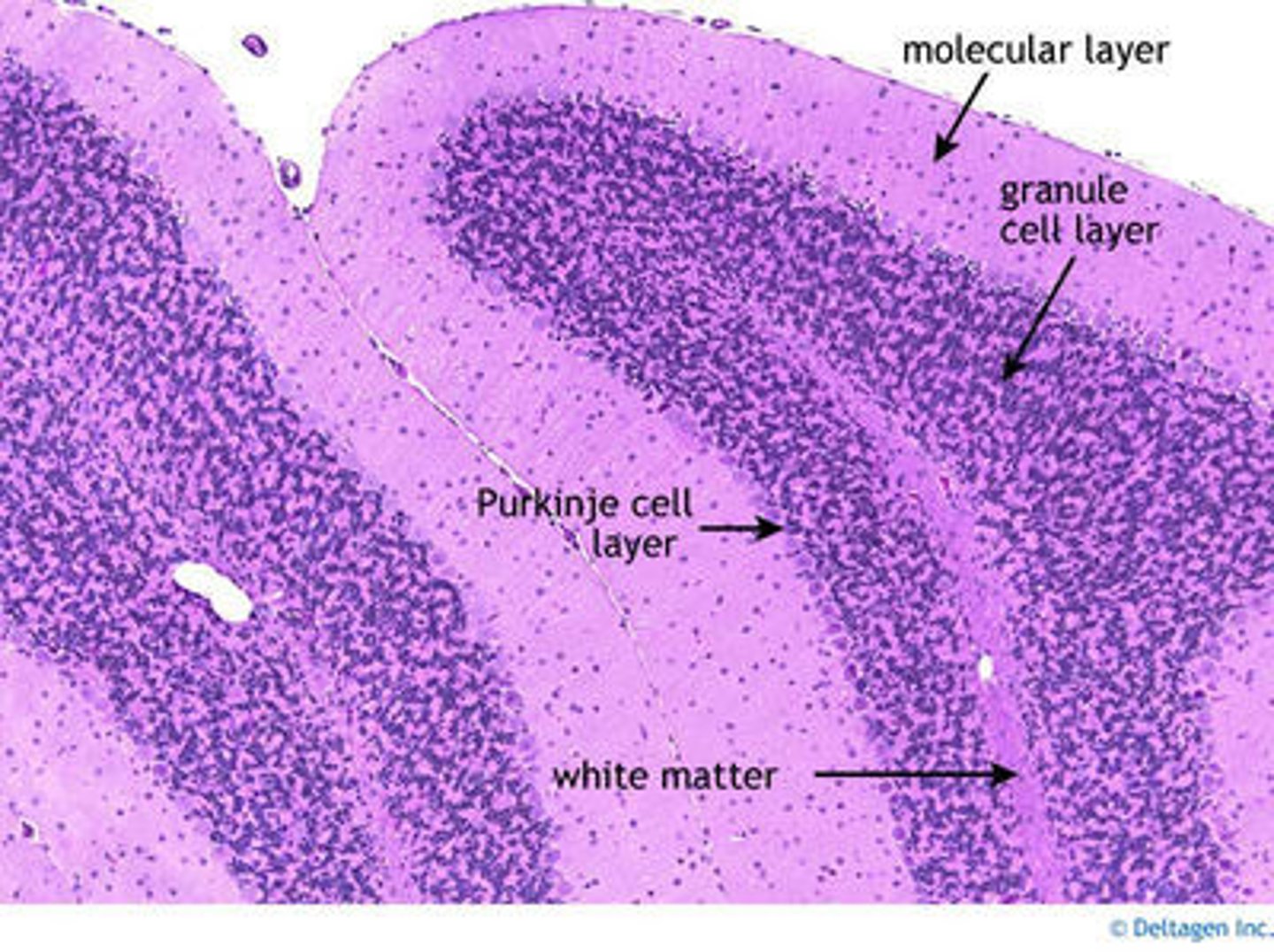
how many layers of cells does the cerebellum have? what are they?
3 - molecular layer, purkinje layer, granular layer
____ pairs of cerebellar peduncles, composed of myelinated axons, connect the cerebellum with the brainstem
3 - middle, inferior, superior
cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum with what?
brainstem
middle cerebellar peduncle contains ____ fibers
pontocerebellar (afferent, coming from pontine nuclei)
restiform body is part of which cerebellar peduncle?
inferior
every bit of sensory info coming into cerebellum, axons synapse and send collaterals to all 4 deep nuclei and excite them via what NT?
glutamate (excitatory!) - deep nuclei are excited ALL the time --- this means cerebellar cortex has to inhibit it via outflow
what cranial fossa is cerebellum in?
posterior cranial fossa
what separates cerebellum from occipital lobe?
tentorium cerebelli
The region in and near the midline of cerebellum is known as the ____, the remainder is known as the ___
vermis // hemisphere
The ____ vermis blends into the hemispheres, but the ____ vermis lies in a deep depression and is well delineated
superior // inferior
The main mass of the cerebellum (all but the focculonodular lobe) consists of ____ and ___ lobes
anterior & posterior
The anterior lobe is the part of the superior surface rostral to the ____.
(+ describe what rostral means in this context)
primary fissure.
(here rostral = anterior to/in front of)
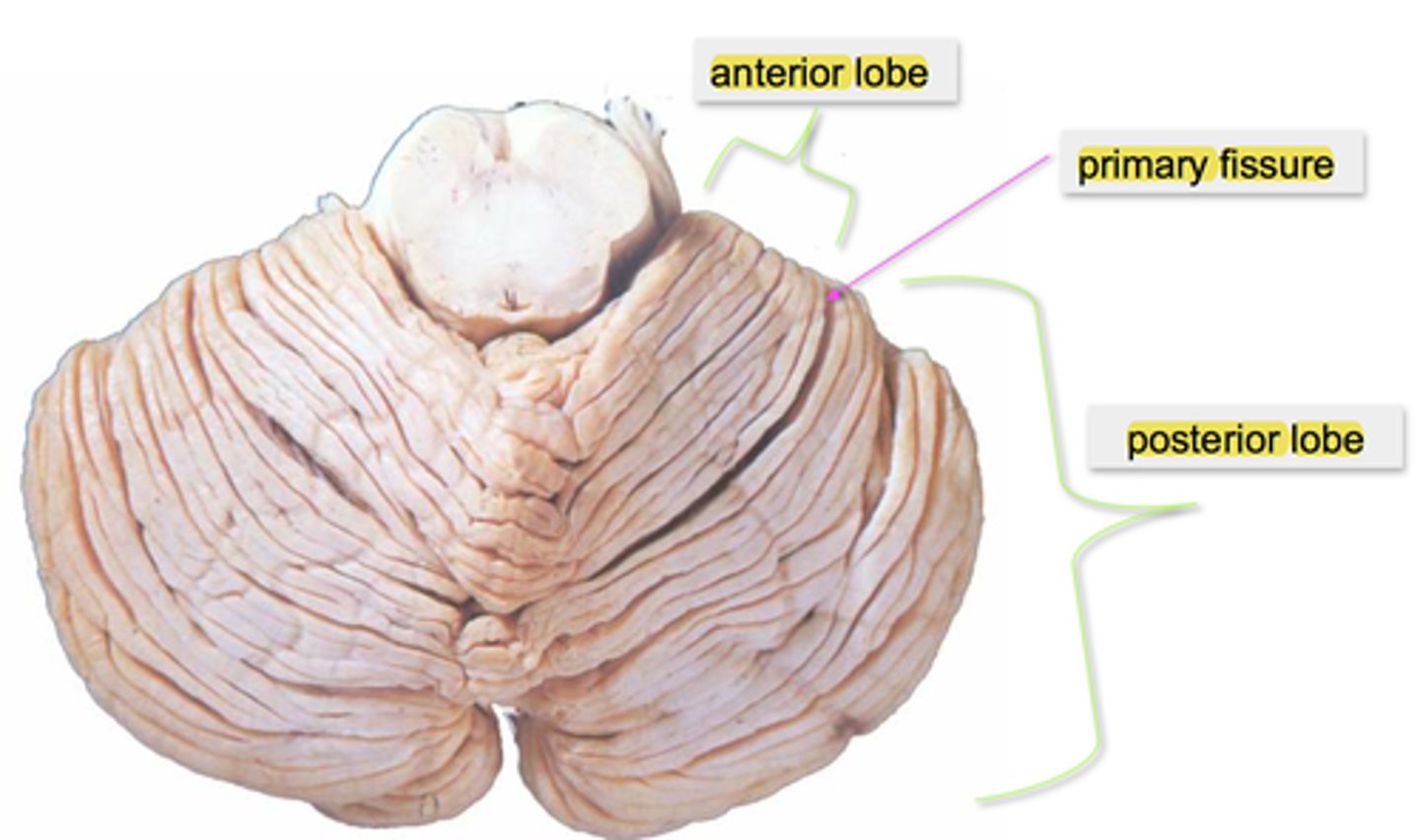
anterior lobe is ___ to primary fissure
rostral (anterior/in front of)
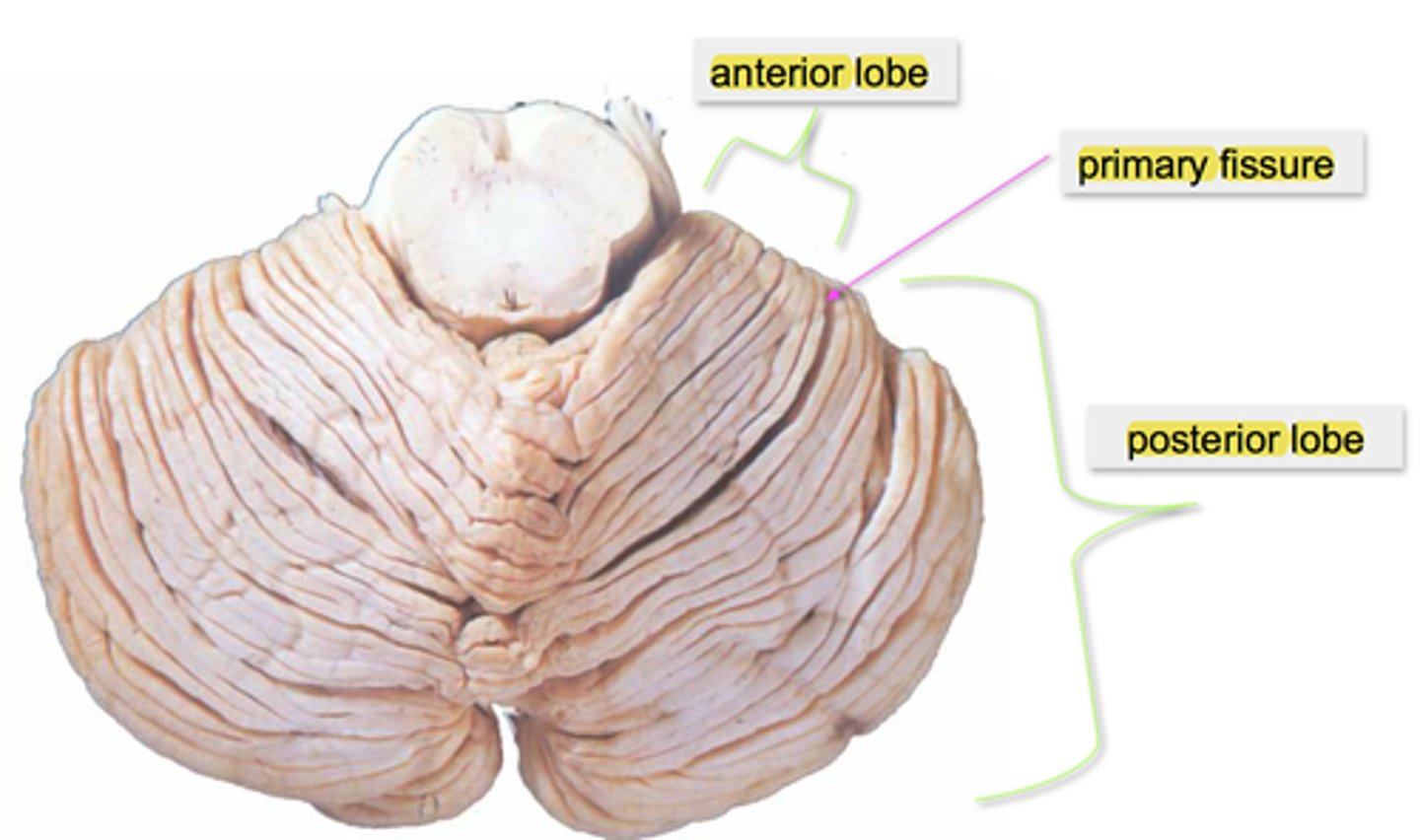
this fissure separates the flocculonodular lobe
posterolateral fissure
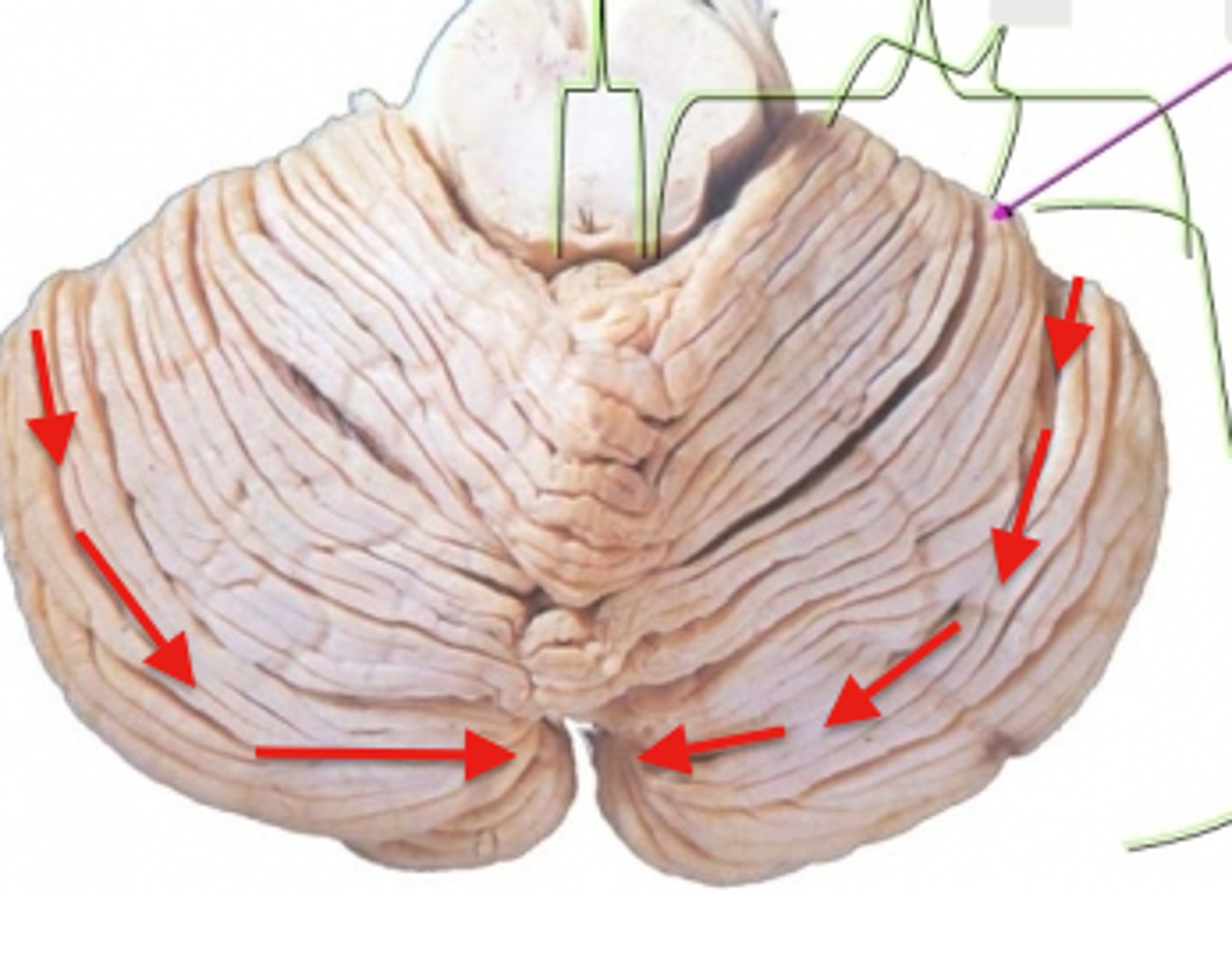
The cerebellar surface is folded into many narrow folia, with ___% of the cortical surface concealed in the intervening sulci
85%
the cerebellar cortex is about ___ the size of the cerebral cortex
3/4
the cortical area of the cerebellum is about ___ the cortical area of the cerebrum
3/4
The ____ cell layer consists of a single row of bodies of ____ cells, the large principal cells of the cerebellar cortex
purkinje; purkinje
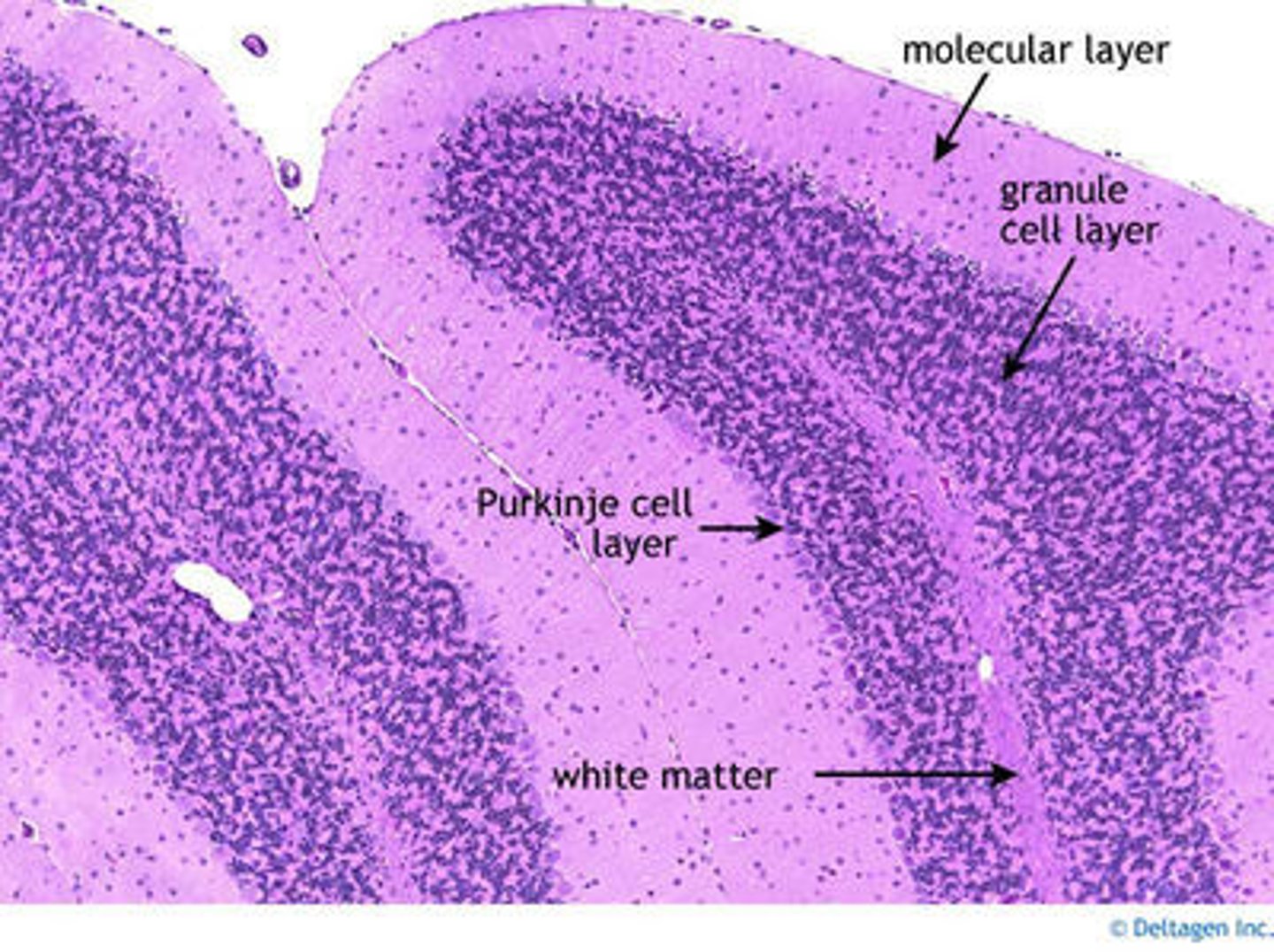
this is the most superficial layer which is a synaptic zone and contains dendrites of the purkinje cells which branch profusely in a plane perpendicular to the long axis of the folium (remember folium refers to the narrow folds of the cerebellar cortex)
molecular layer
this layer is deep to the purkinje cell layer and contains closely packed interneurons with axons that extend into the molecular layer
granule layer
types of cells in granule layer (2)
granule cell, golgi cell
purkinje cells have dendrites that go into ___ layer in a perpendicular direction (sagittal plane) and axons that go into the ___ layer
molecular // granule
purkinje cells have _______ that go into molecular layer in a perpendicular direction (sagittal plane) and ____ that go into the granule cell layer
dendrites; axons
output of cerebellar cortex travels via what?
axons of purkinje cells to deep cerebellar nuclei
what NT does purkinje cell use?
GABA (inhibitory)
what are the small inhibitory interneurons located in molecular layer? (2)
basket and stellate cells
cells found in molecular layer (be specific)
axons of granule cells, dendrites of purkinje cells, basket cells, stellate cells
what is the ONLY excitatory cell in the cortex?
GRANULE!!!
output of cortex via purkinje cell is ____
INHIBITORY
axons of granule cells travel up to ____ layer and become known as ____ fibers
molecular // parallel ("telephone wire")
T/F: Purkinje cells have their dendritic arbor in a plane perpendicular to the folium and therefore each parallel fiber (granule cell) is in a position to contact several Purkinje cells
TRUE
The ____ cell is the primary excitatory (glutamatergic) cell of the cortex
granule
___ cells have dendrites that branch in molecular layer & have an axon that is inhibitory (GABA) to granule cell
golgi cells
fibers containing input to the deep cerebellar nuclei of the cerebellum are known as ___ or ___ fibers
climbing or mossy
climbing fibers are neurons that originate in the ____ and send their axons to the cerebellum to synapse on ____ cell dendrites
inferior olivary nucleus (located in the medulla oblongata);
purkinje
___ cells are located in molecular layer; their axons form a "basket" around the Purkinje cell bodies; inhibitory (GABA).
basket
____ fibers originate in the inferior olivary nucleus and synapse with the proximal dendrites of Purkinje cells.
CLIMBING
climbing fibers (excite/inhibit) purkinje cells and nuclei
EXCITE
Cerebellar afferents from other sources end as ____ fibers, each synapsing with the neurons in the granular layer in a formation known as a glomerulus - excite Granule and Golgi cells.
MOSSY
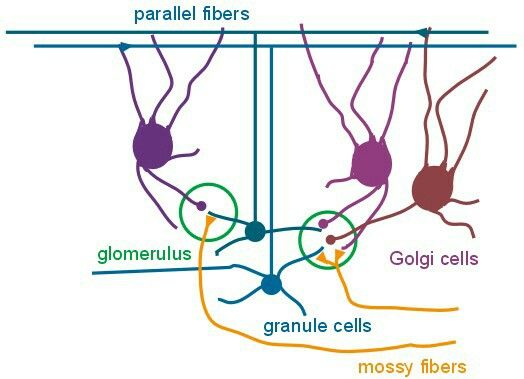
mossy fibers synapse with the neurons in the ___ layer in a formation known as a ____
granule // glomerulus
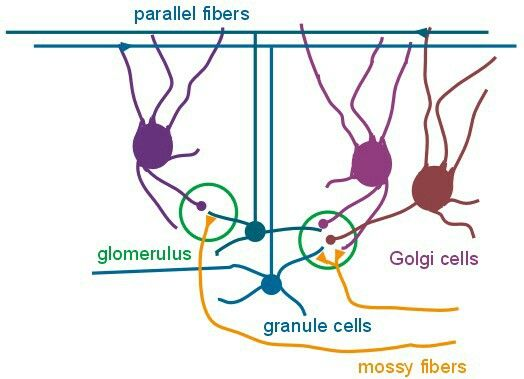
____ fibers excite granule and golgi cells
mossy
mossy fibers excite ___ & __ cells // climbing fibers excite ___ cells
granule & golgi // purkinje
mossy fibers and climbing fibers each send collaterals to the ____ nuclei and are (excitatory/inhibitory)
central cerebellar nuclei // excitatory
Four pairs of nuclei are embedded deep in the cerebellar white matter; in a lateral to medial direction, they are:
Dentate
Emboliform
Globuse
Fastigial
(Don’t Eat Greasy Foods)
The input to the cerebellar nuclei is from: (2)
•Sources outside the cerebellum
•The Purkinje cells of the cortex
extrinsic input from outside the cerebellum to the cerebellar nuclei comes from what fibers? (3)
pontocerebellar, spinocerebellar, and olivocerebellar
BOLD AND IN COLOR:
Whereas the input to the central nuclei from outside the cerebellum is ____; the input from Purkinje cells, which use ____ as their transmitter, is ____
excitatory // GABA // inhibitory
Crudely processed information in the central nuclei is refined by the ____ signals received from the cortex
INHIBITORY
T/F: the combination of the two inputs (extrinsic and intrinsic) to the cerebellar nuclei maintains a tonic discharge from the central nuclei to the brainstem and thalamus
TRUE - combo of inhibitory and excitatory output
which circuits contain more synapses: inhibitory or excitatory?
INHIBITORY
____ circuits, which include more synapses than do the ____ relays, serve to limit the area of cortex excited and the degree of excitation resulting from a volley of impulses delivered by a ____ fiber
inhibitory // excitatory // mossy
Mossy and Climbing fibers first excite neurons in the where before continuing to the cortex?
deep nuclei
purkinje cells inhibited = ____ deep cerebellar nuclei
exciting
(bc you’re inhibiting the inhibition of purkinje cells)
inferior peduncle cerebellar afferents
•Olivocerebellar fibers (Climbing fibers)
•Dorsal Spinocerebellar tract (Mossy fibers)
•Cuneocerebellar tract (Mossy fibers)
•Vestibulocerebellar fibers (Mossy fibers)
•Trigeminal sensory nuclei (Mossy fibers)
inferior peduncle cerebellar efferents (outflow)
•Cerebellar corticovestibular fibers (vestibular nuclei)
•Cerebelloreticular fibers
most efferent fibers come from what cerebellar peduncles?
superior
middle peduncle cerebellar afferents
Pontocerebellar fibers (Mossy fibers)
is there anything coming OUT of the middle peduncle?
NO!
superior peduncle cerebellar afferents
•Anterior Spinocerebellar tract (Mossy fibers)
•Trigeminothalamic (mesencephalic) (Mossy)
•Rostral Spinocerebellar tract (Mossy fibers)
superior peduncle cerebellar efferents
•Cerebellothalamic fibers (from cerebellar nuclei to VL of contralateral thalamus)
•Cerebellorubral fibers to ipsilateral red nucleus
memory tricks—
superior peduncle afferents: ART
middle peduncle afferents: the middle is PC
inferior peduncle afferents: x5
superior peduncle efferents: red thalamus
middle peduncle efferents: none!
inferior peduncle efferents: correct
superior peduncle afferents: ART
anterior spinocerebellar
rostral spinocerebellar
trigeminothalamic (mesencephalic)
middle peduncle afferents: the middle is PC
pontocerebellar fibers
inferior peduncle afferents: x5
olivocerebellar
cuneocerebellar
dorsal spinocerebellar
trigeminal sensory nuclei
vestibulocerebellar
superior peduncle efferents: red thalamus
cerebellorubral fibers (to ipsi red nucleus)
cerebellothalamic fibers
middle peduncle efferents: none!
none!
inferior peduncle efferents: correct
cerebellar CORticovestibular
cerebelloRETicular
output from superior cerebellar peduncle goes to ___ in the thalamus and then to cerebral cortex
VL
what is the blood supply of deep nuclei?
superior cerebellar artery
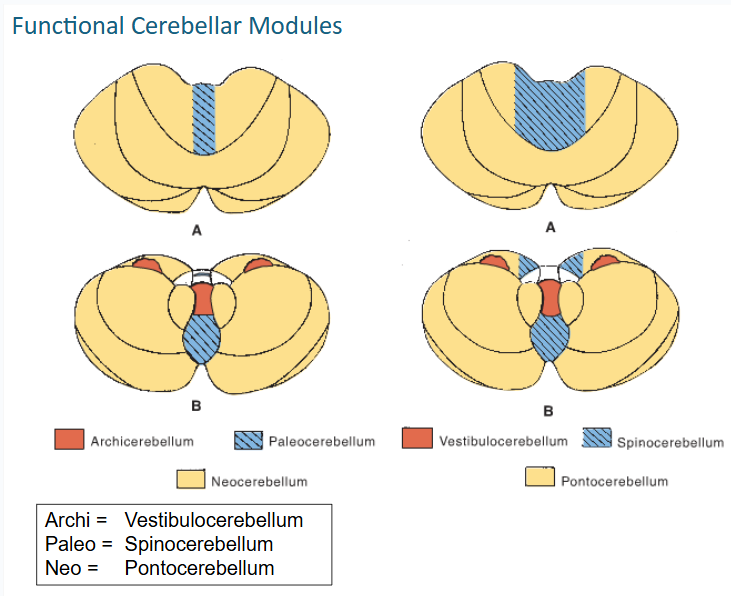
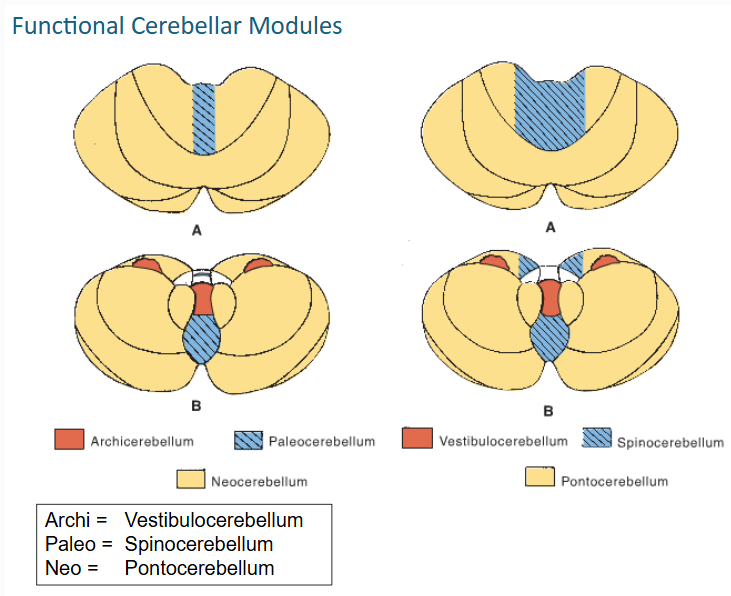
functional cerebellar modules (3)
-Vestibulocerebellum
-Spinocerebellum
-Pontocerebellum
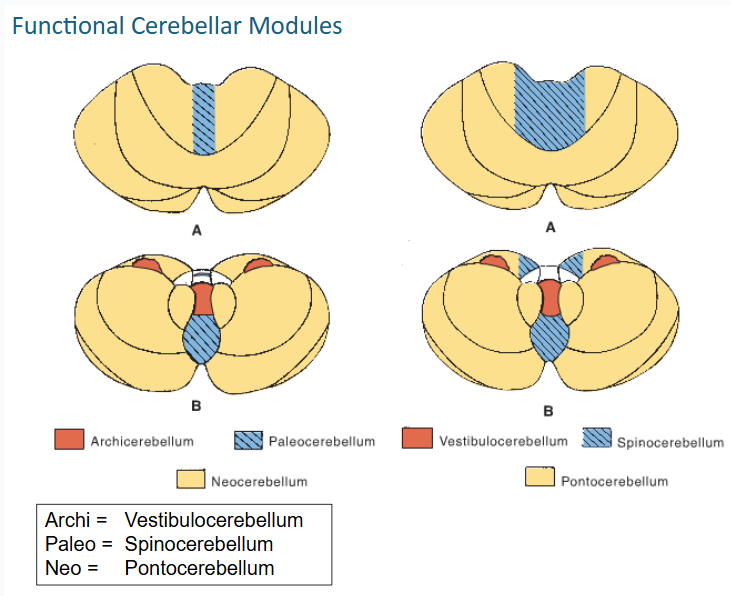
what lobe is the vestibulocerebellum in?
flocculondolar
vestibulocerebellum recieves input from the ___ nerve & nuclei
vestibular
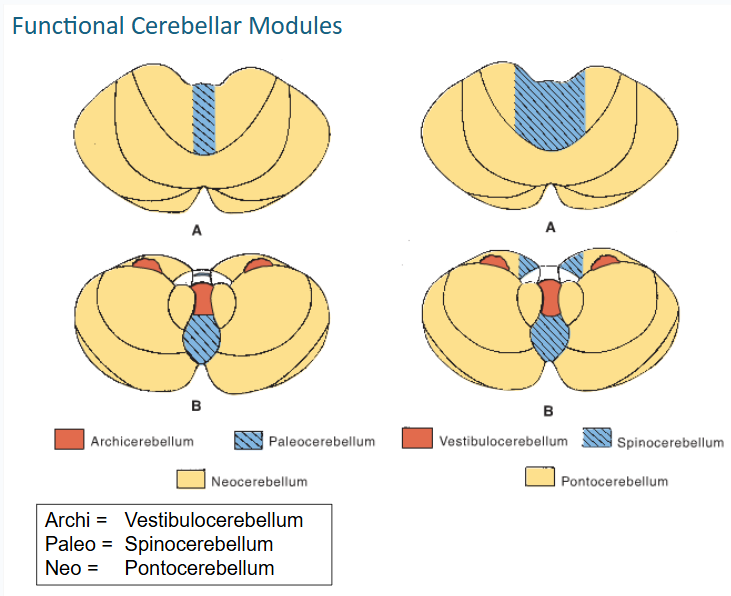
some afferents as they enter the vestibulocerebellum they synapse on the ___ nucleus
fastigial
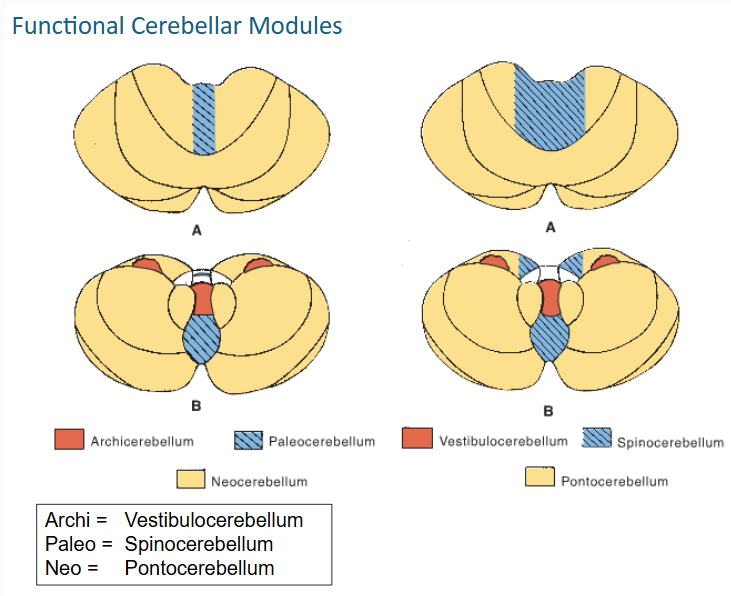
The Vestibulocerebellum influences motor neurons through (3)
•vestibulospinal tract
•medial longitudinal fasciculus
•reticulospinal fibers
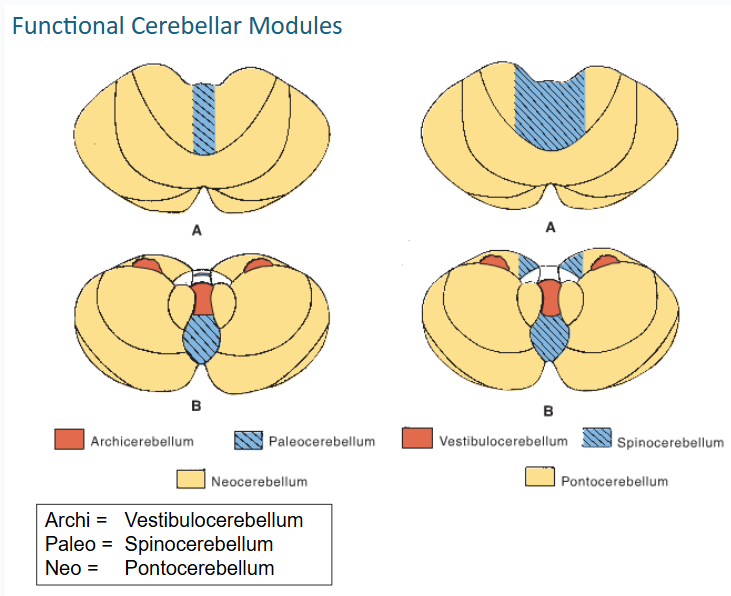
vestibulocerebellum is concerned with the adjustment of ___ in response to ____
muscle tone // vestibular stimuli
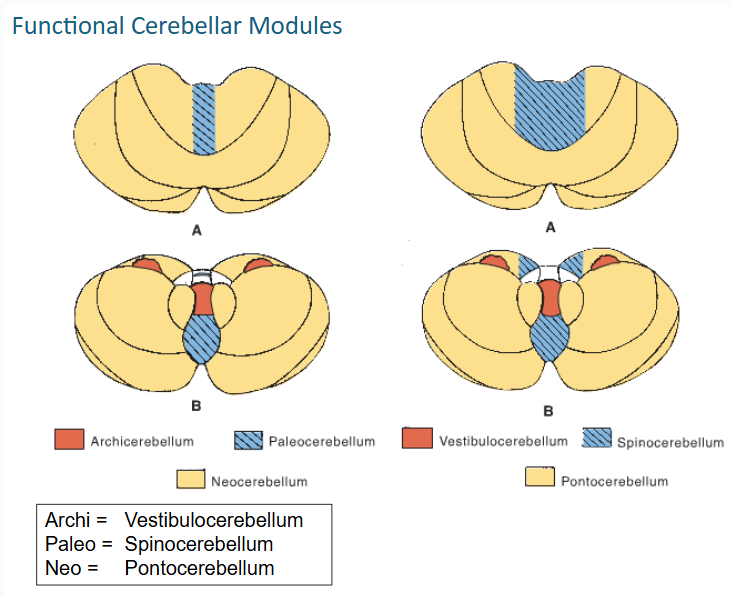
this functional cerebellar module coordinates the actions of muscles that maintain equilibrium and participates in other motor responses, including those of the eyes
vestibulocerebellum
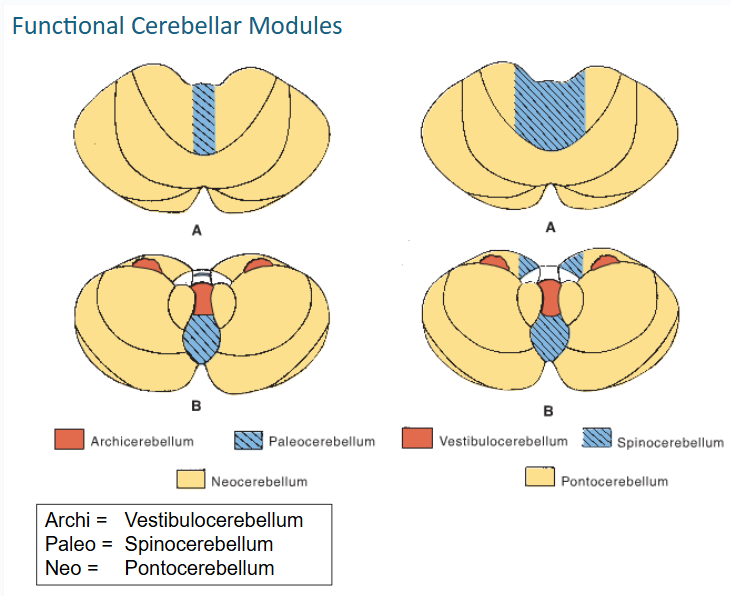
The Spinocerebellum consists of the ____ of the ____ lobe together with the adjacent medial or paravermal zones of the hemispheres
vermis // anterior lobe
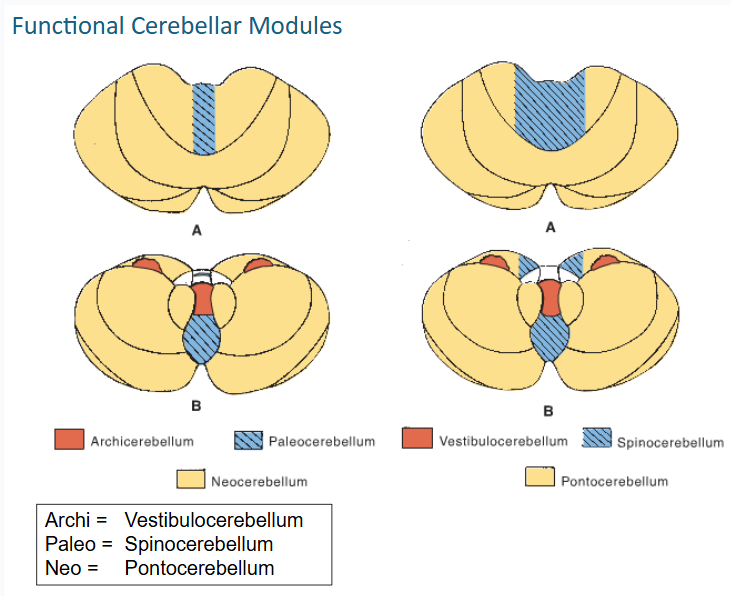
what tracts that convey proprioceptive and other sensory information terminate on the spinocerebellum? (2)
Spinocerebellar and Cuneocerebellar
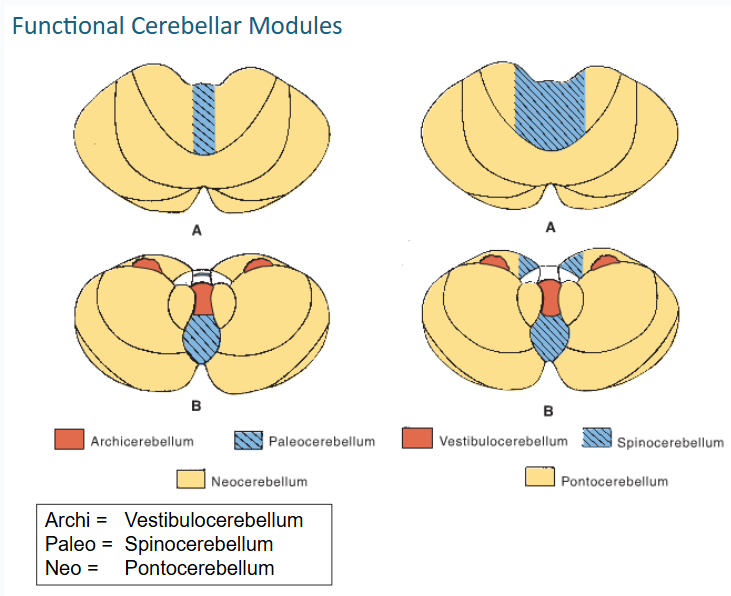
The Spinocerebellum gets input from these tracts (3)
•Ant & post spinocerebellar tracts
•Cuneocerebellar tract
•Olivocerebellar tract
tracts that give input to spinocerebellum synapse on what deep nuclei on their way to cerebral cortex? (3)
fastigial, globose, and emboliform
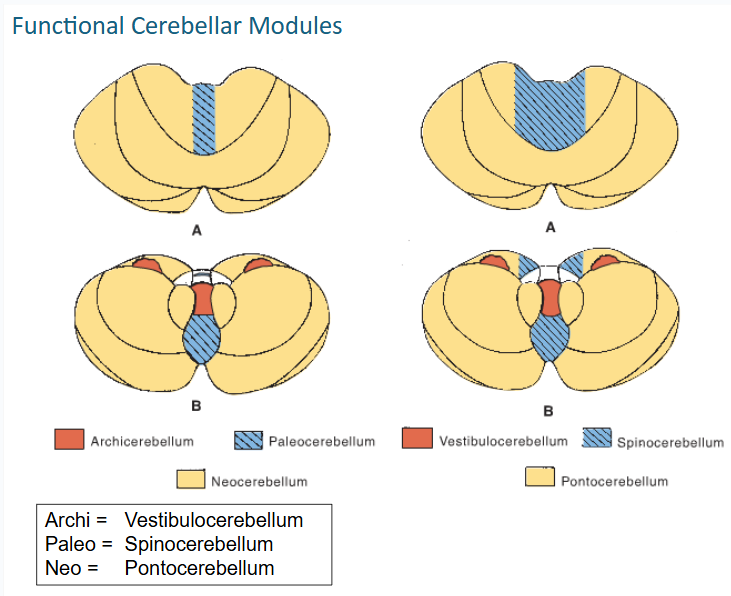
The output of the spinocerebellum is focused primarily on the control of ___ musculature through vermal cortex and ____ nucleus for postural corrections
axial // fastigial
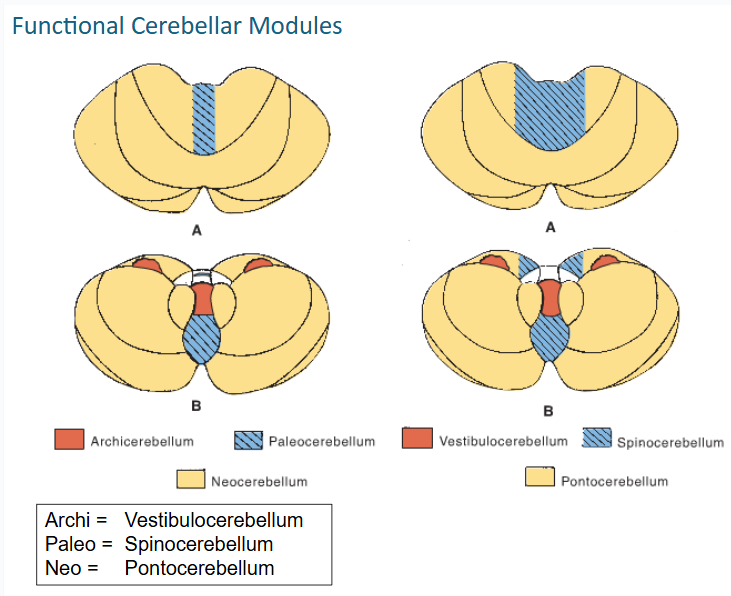
The output of the spinocerebellum is focused primarily on the control of ___ musculature through efferents of ___ & ___ nuclei for locomotion
limb // globose & emboliform