Nihen College Physics 2 Test 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Absolute Zero
Temperature at which particle motion is at a minimum (0 Kelvin)
Specific Heat
Amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of any substance by 1°C
Q into a substance equals?
Q out of a substance
Latent Heat of Fusion (Lf)
Solid to liquid, liquid to solid (334 J/g)
Latent Heat of Evaporation (Lv)
Vapor, steam (2256 J/g)
At the same temperature, will steam or water burn worse?
Steam, because of Lvapor
3 conditions of an ideal gas
- ideal gas particles have zero volume
- no attractive forces between each other
- have perfectly elastic collisions = no loss of energy/ momentum
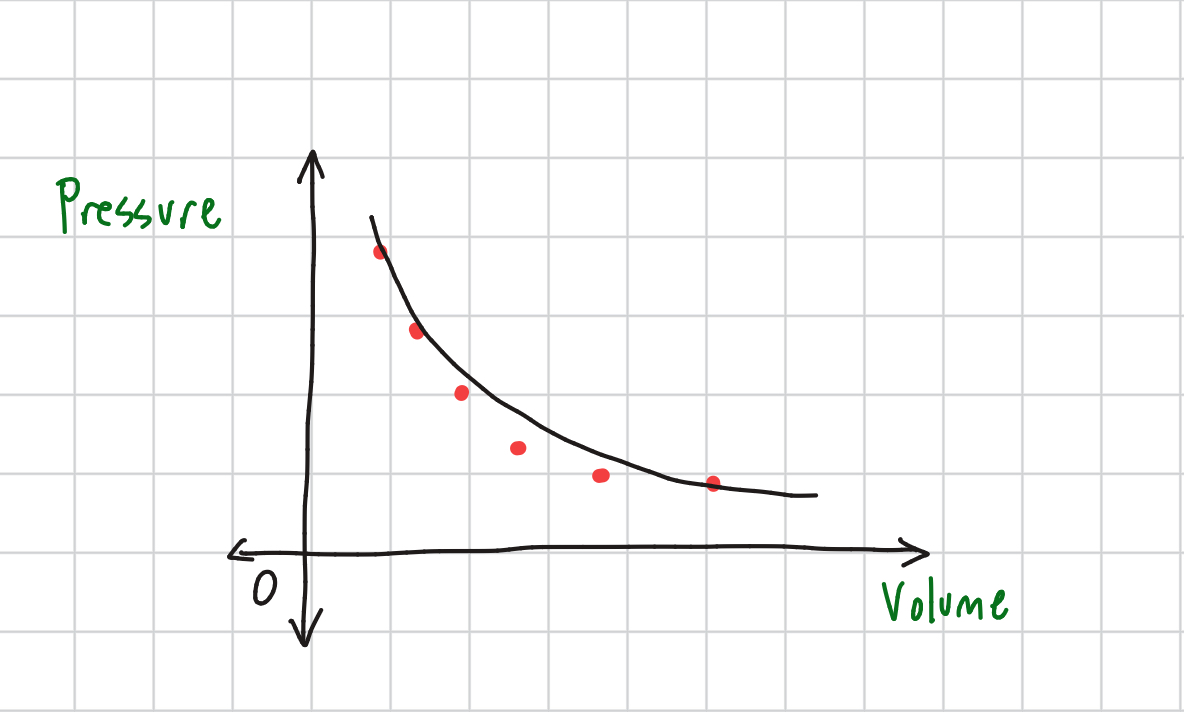
Boyle's Law Equation
P1/V1 = P2/V2 @ constant temperature: inversely proportional (as one increases, the other decreases)
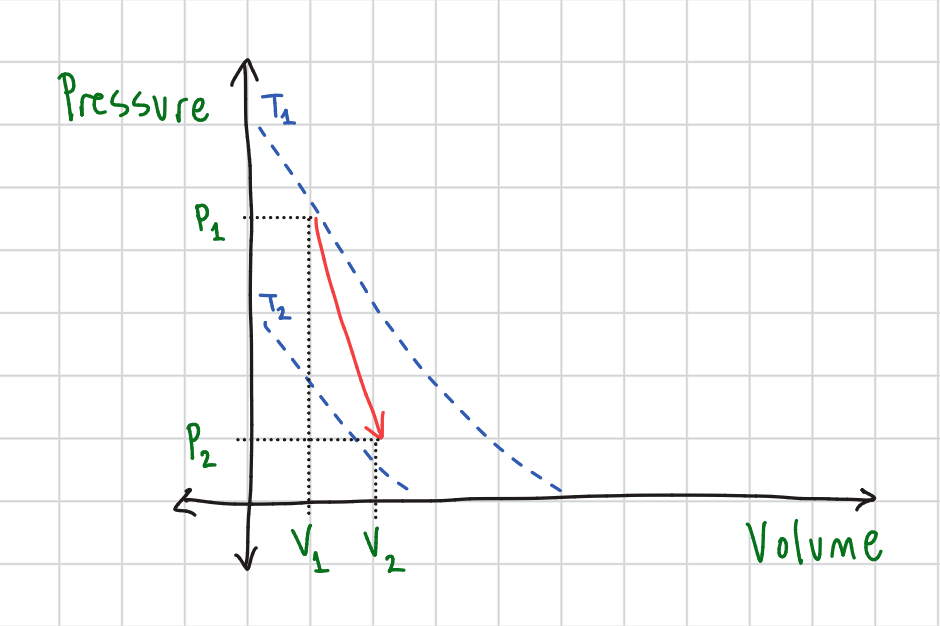
Boyle’s Law Graph
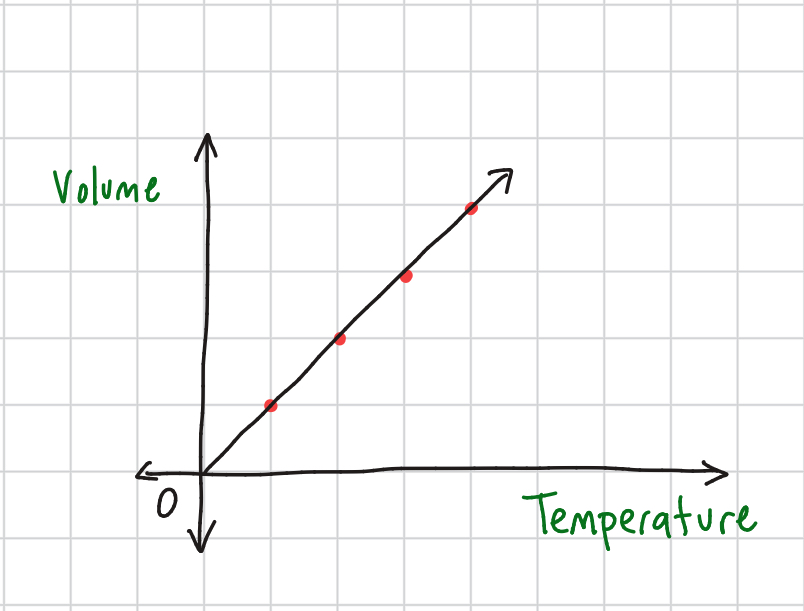
Charles' Law Equation
V1/V2 = T1/T2 @ constant pressure: directly proportional (one increases, so does the other)
Charles’ Law Graph
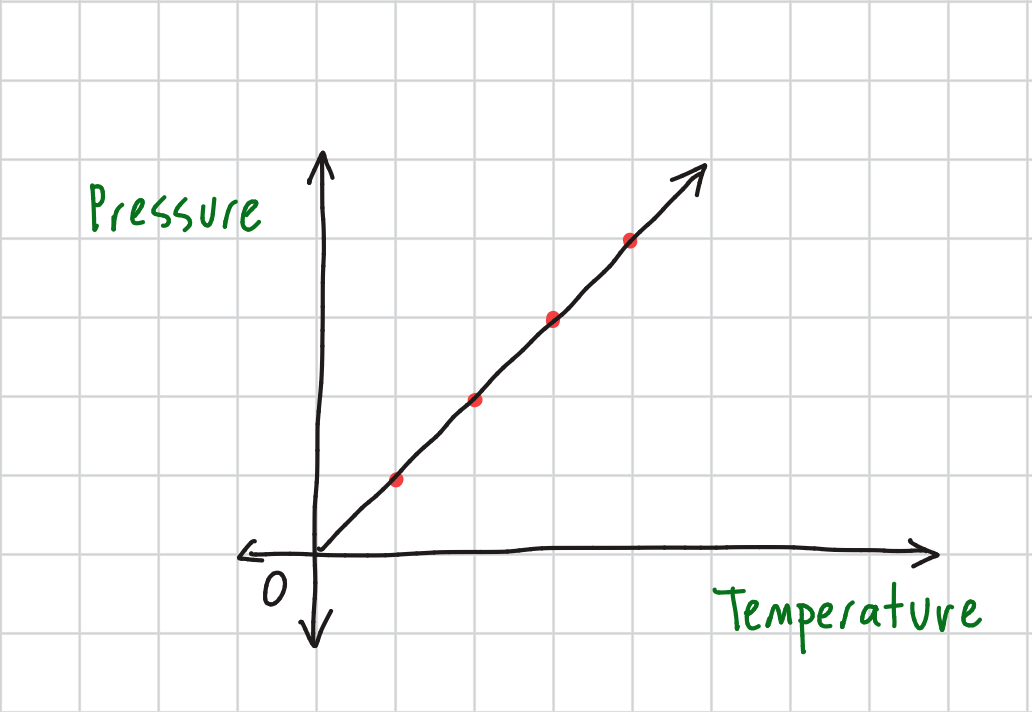
Gay-Lussac's Law Equation
P1/P2 = T1/T2 @ constant volume: directly proportional (as one increases, so does the other)
Gay-Lussac’s Law Graph
Number of moles
"n"
Molar mass
"M" BIG M (g/mol on periodic table)
Mass of gas
"m" little m (grams)
Avogadro's Number
NA = 6.022 * 10^23 particles
Root Mean Square Velocity
Average velocity of gas particles: √(3kT/m) & √(3RT/M)
First Law of Thermodynamics
Change in the internal energy (transitional, rotational, vibrational motion of gas particles) of a system
First Law of Thermodynamics Equation
ΔU = Q - W
Internal Energy
U = (3/2)nRT
Adiabatic Process Equation
@ Q = 0, ΔU = -W
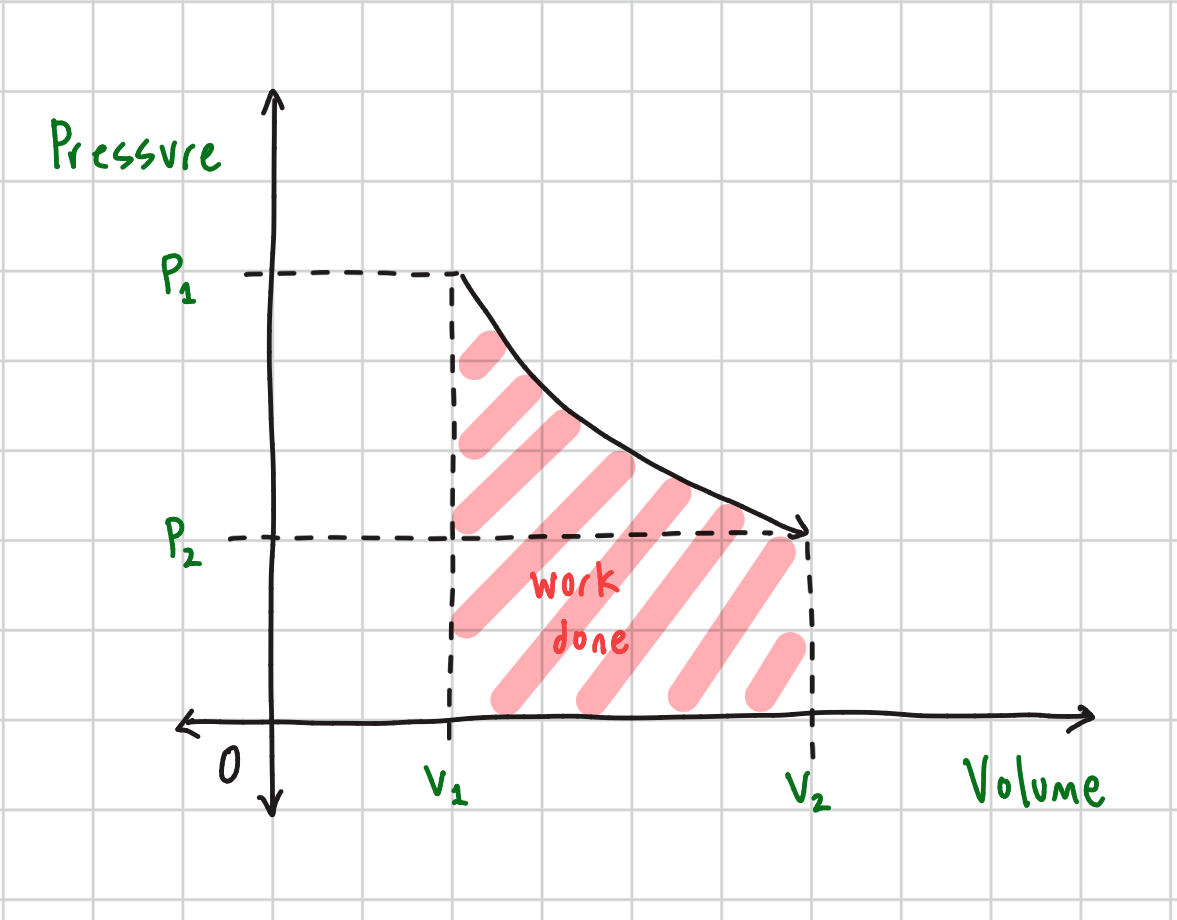
Adiabatic Process Graph
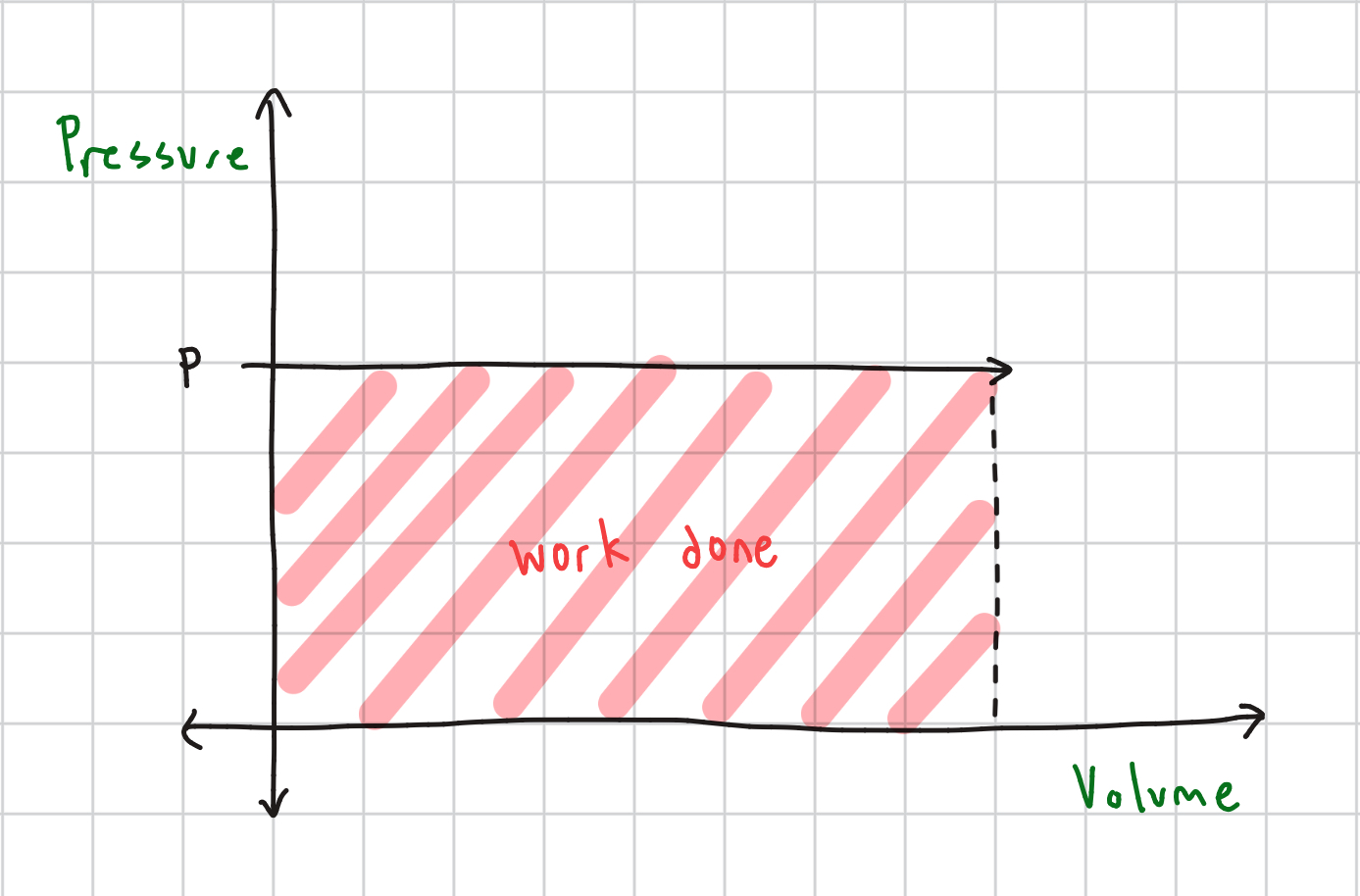
Isobaric Process Equation
ΔU = Q - PΔV
Isobaric Process Graph
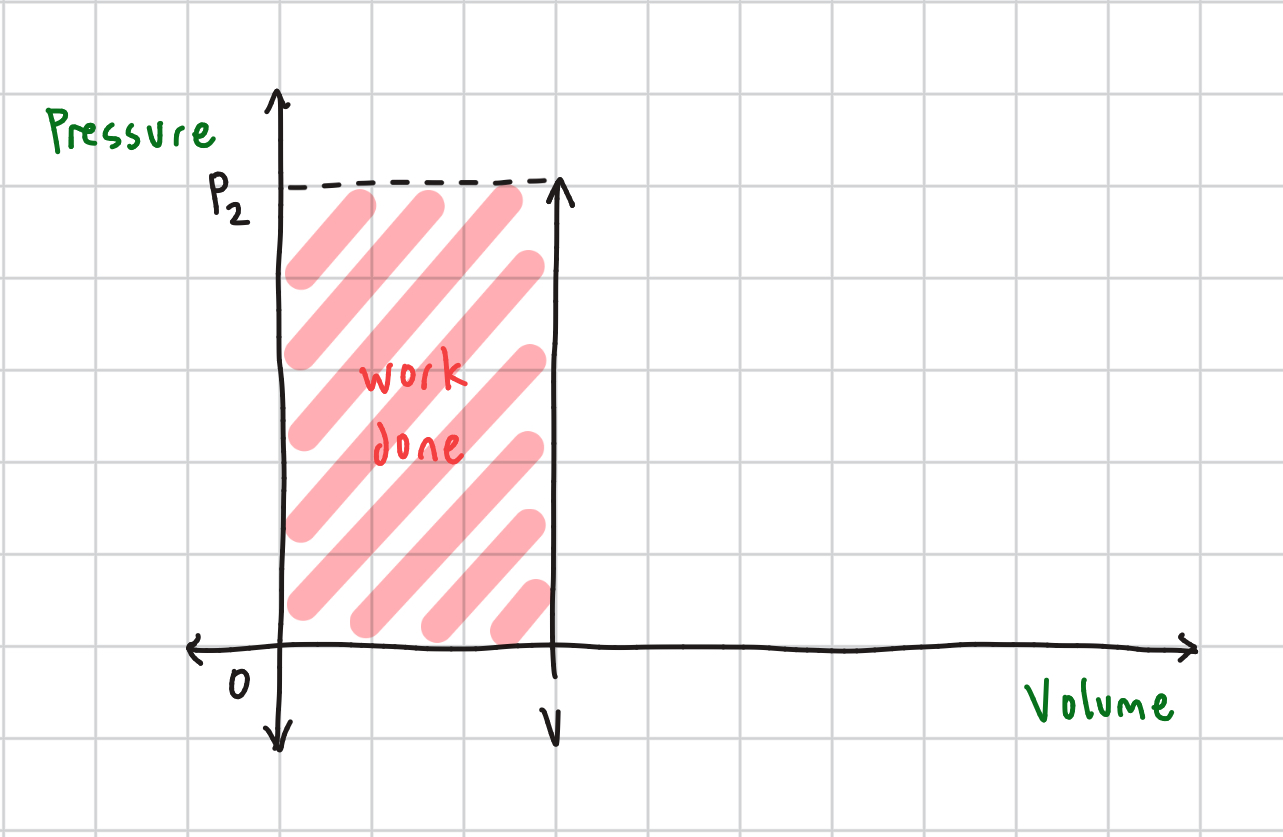
Isochoric/Isovolumetric Process Equation
ΔU = Q
Isochoric/Isovolumetric Process Graph
Isothermal Process Equation
Q = W
Isothermal Process Graph