AVS 472 Exam 2 Review - Male Reproductive Anatomy + Fertilization Processes
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
scrotum
External sac that contains the testes, functions of protection, thermosensor, and radiator
thermosenor function of scrotum
retraction/extension with weather
radiator functions of scrotum
5° cooler than the rest of the body
tunica dartos
smooth muscle which lines scrotal wall, androgen dependent to maintain tone, when environment I cold it will contract, forces testis closer to body cavity and vice versa
Gubernaculum
band of connective tissue that attaches testes to scrotum
parietal vaginal tunic
Thick outer layer
Forms a fibrous sac around each testis and spermatic cord
visceral vaginal tunic
lies directly on the testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens
parenchyma
functional tissues of any organ, such as the tissues of the bronchioles, alveoli, ducts, and sacs, that perform respiration
mediastinum
series of networks where all sperm being produced converge in the common area of mediastinum to go the rest of way through the system
tunica albuginea
fibrous capsule of the testes
rete testis
network of tubules between the seminiferous tubules and the epididymis
epididymis
A long, coiled duct on the outside of the testis in which sperm mature.
vas deferens
tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra
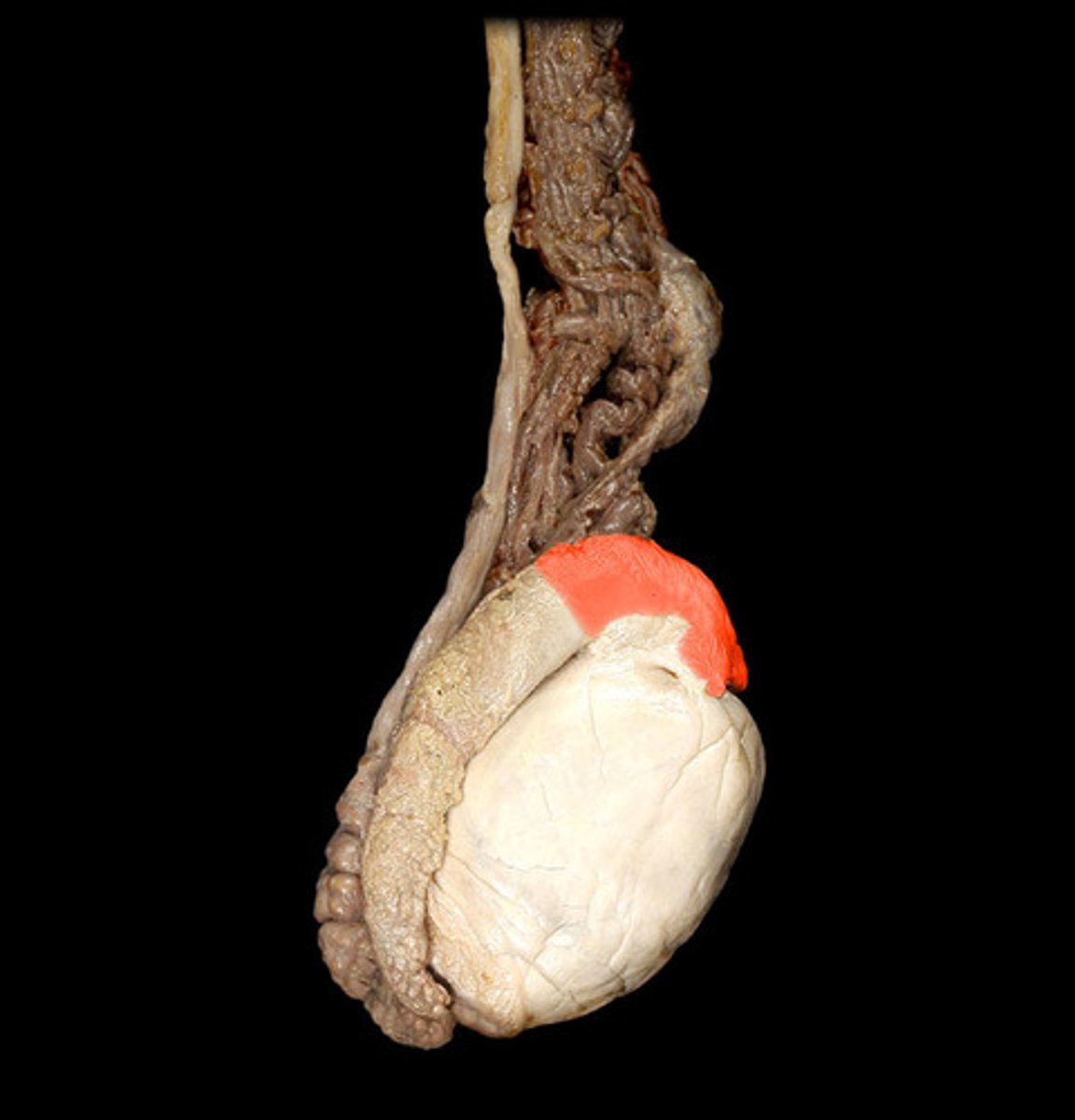
caput epididymis
head of epididymis
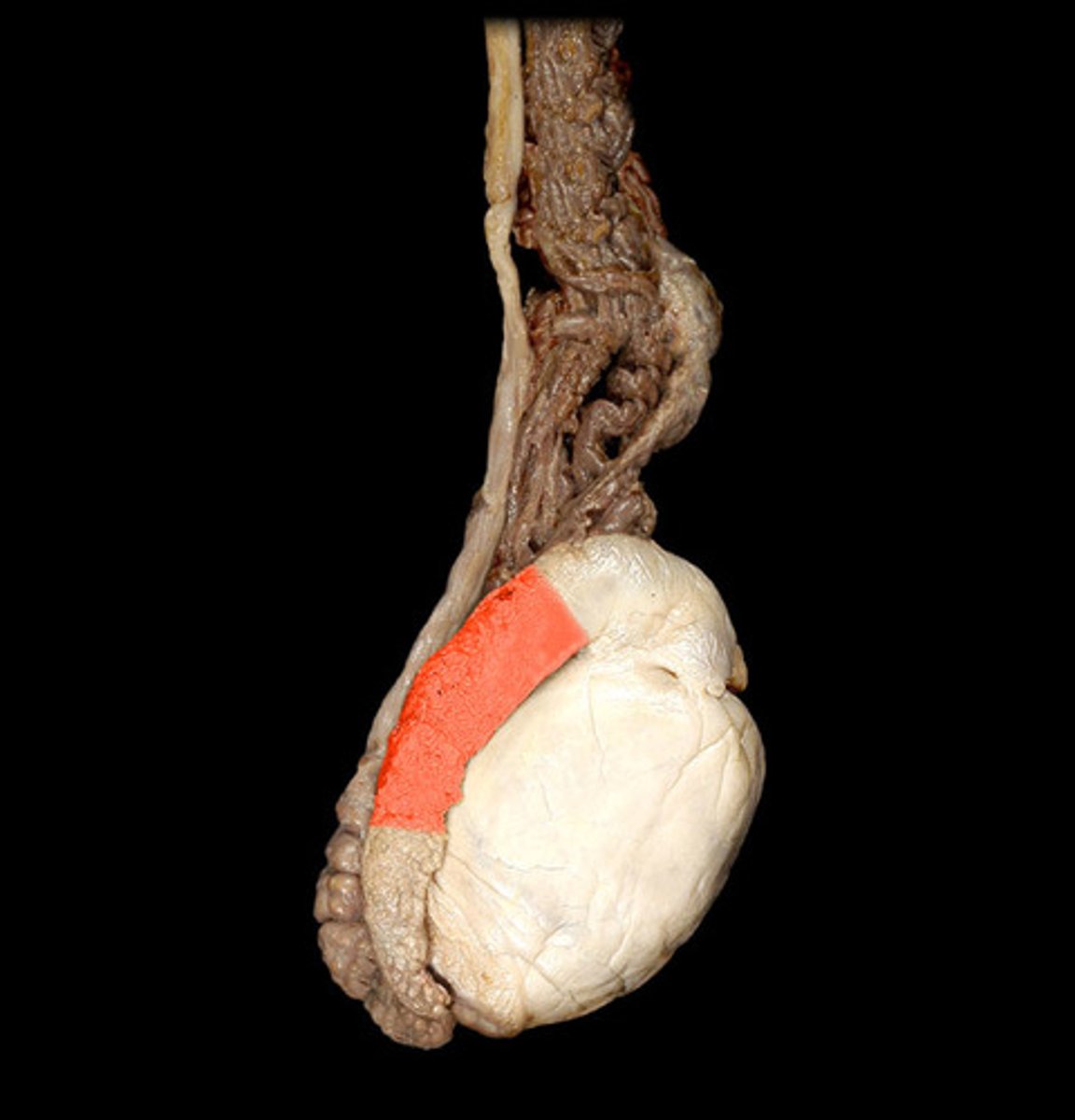
corpus epididymis
body of epididymis
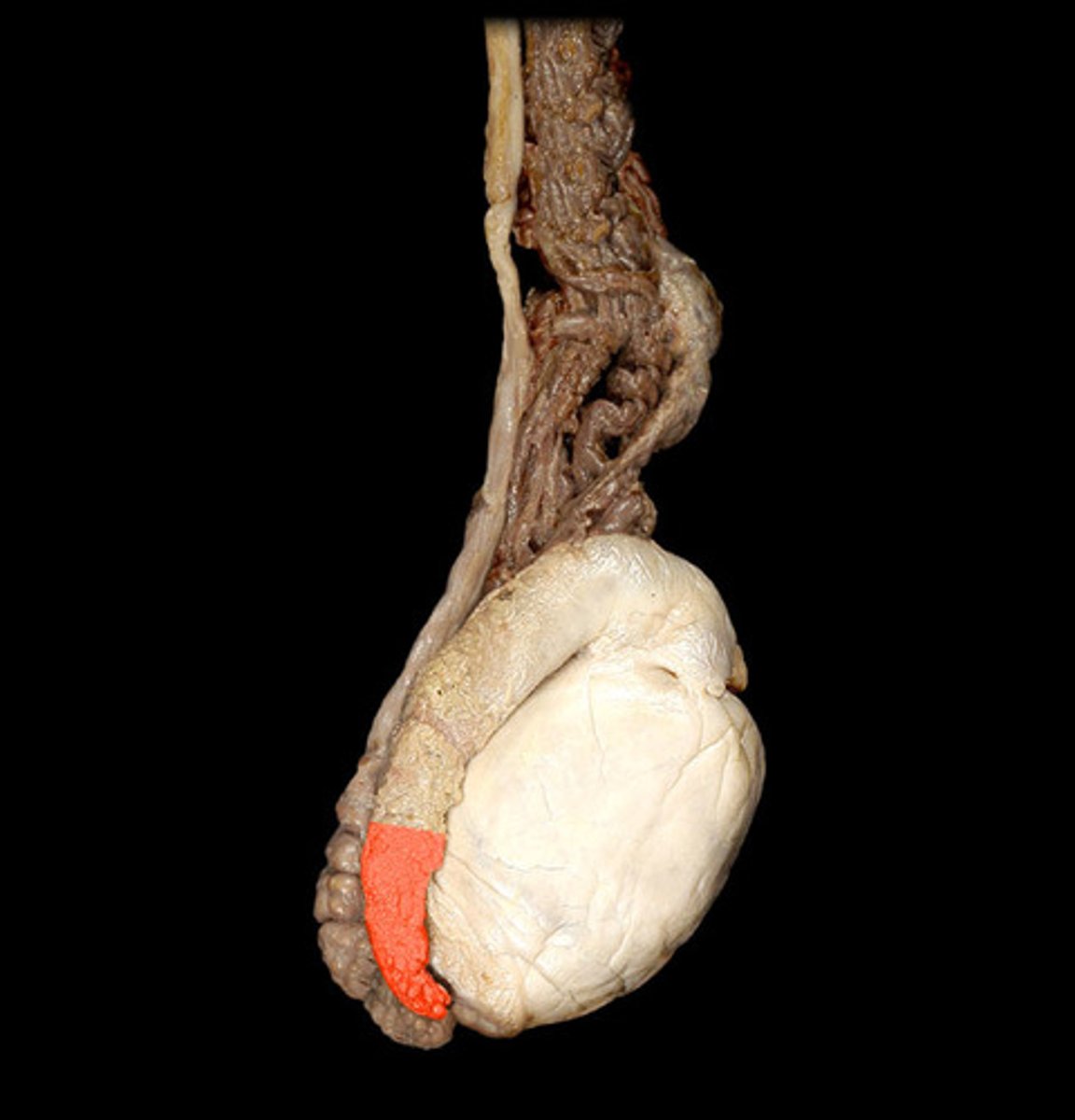
cauda epididymis
tail of the epididymis
vas efferentia
The tiny tubules that carry sperm to the head of the epididymis.
Where are sperm stored?
cauda epididmyis
how is movement through the epididymis conducted?
peristalsis
spermatic cord
extends upward from the epididymis and is attached to each testicle, contains vascular, lymphatic, nervous tissue, pampiniform plexus, and cremaster muscle
pampiniform plexus
an extensive network of veins from the testes that surrounds the testicular artery and spermatic cord. Reduced heat, concentrates tester one, and reduced amplitude and arterial pulses
Testosterone concentration of the testis
70ng T/mL
testosterone concentration in the body
4.8 ng T/mL
cremaster muscle
skeletal muscle that arises from the internal obliques; elevates testes
ampulla
The ampulla of vas deferens is an enlargement of the vas deferens near the bladder. It contributes secretions to the semen, including fructose and ergothioneine.
seminal vesicles
two small glands that secrete a fluid rich in sugar that nourishes and helps sperm move
body of prostate
The prostate gland, a walnut-sized organ in the male reproductive system, produces fluid that becomes part of semen, which nourishes and carries sperm during ejaculation.
disseminate prostate
Glandular tissue distributed along the dorsal and lateral walls of the pelvic urethra
Cowper's gland
either of a pair of small glands that open into the urethra at the base of the penis and secrete a constituent of seminal fluid. illicitness a preejaculate upon erection, doesn't contain sperm, cleans urethra of urine and bacteria
bulbourethral glands
Cowper's glands
sigmoid flexure
"S" shape in urethra allows for extension of penis outside of body for reproduction
retractor penis muscle
attached to the sacral vertebra. Relaxes during sexual excitement
corpus cavernosum
Pair of spongy tissue regions full of blood during erection
corpus spongiosum
surrounds the urethra
large veins in corpus cavernous
collapse during erection to allow for blood to pool, port to leave
raphe
vestige of where the prepuce extended when its unsheathed during sexual maturity
which animals have vertical orientation of testis
bull, ram, rabbit, human
which animals have oblique orientation of testis
boar, dog
what animal has horizontal orientation of testis
stallion
ram anatomy feature
no body of prostate (smaller amount of seminal fluid)
boar anatomy features
no ampulla, but large Cowper's gland (large amount of seminal fluid)
stallion anatomy features
no disseminate prostate, enlarged seminal vesicles
dog anatomy features
no seminal vesicles, disseminate prostate, or Cowper's glands
tom anatomy features
no seminal vesicles or disseminate prostate
human anatomy features
no disseminante prostate
muscular-vascular penis
engorged in length and diameter, stallion, humans, cats, and dogs
fibroelastic penis
engorged in length only, bull, ram, and boar
seminiferous tubules
Narrow, coiled tubules that produce sperm in the testes.
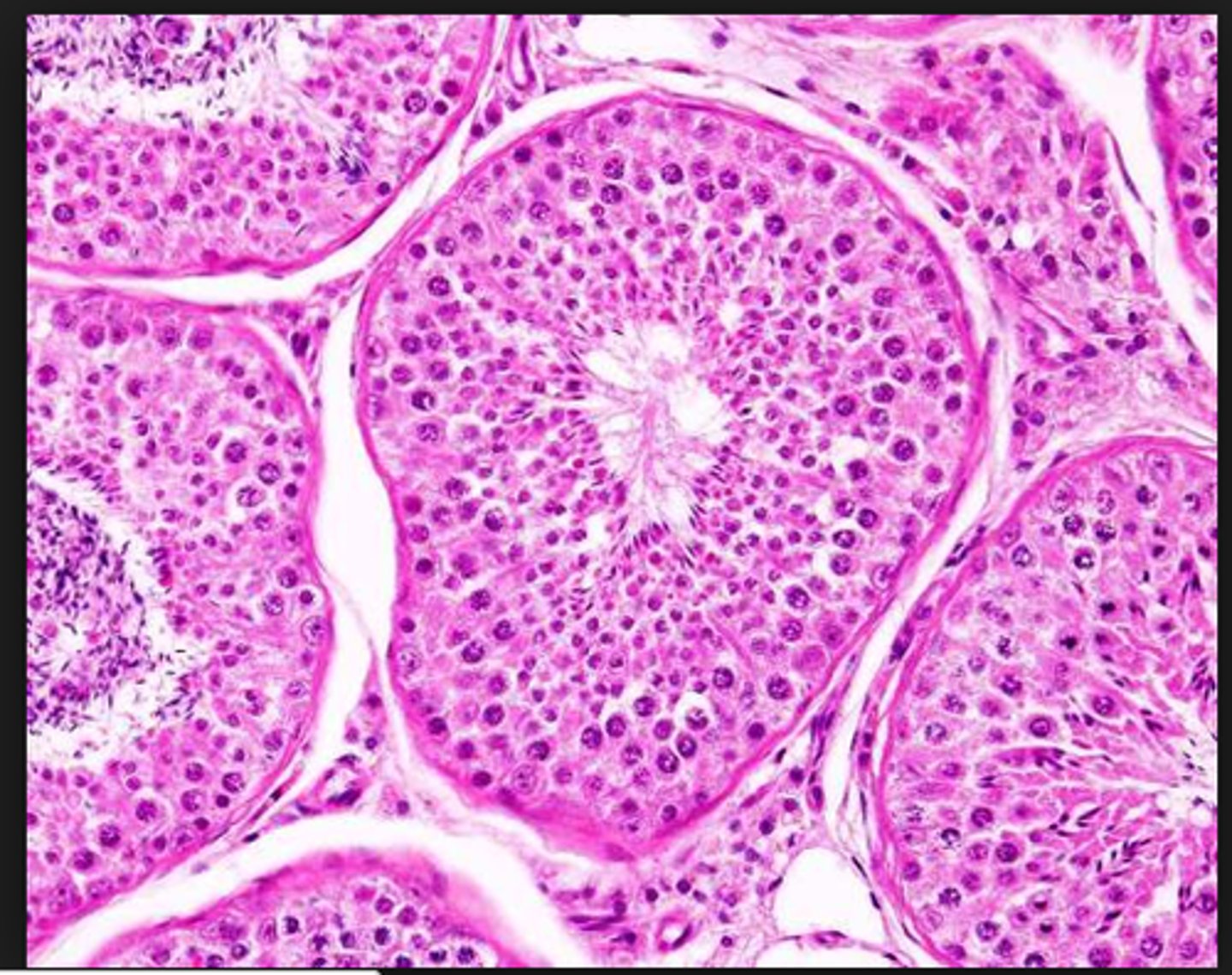
spermatogonium
A diploid cell that can undergo mitosis to form more spermatogonium, and can also be triggered to undergo meiosis to form sperm.
myoid cells
smooth muscle-like cells surrounding seminiferous tubule that contract to squeeze sperm and testicular fluid through tubules
secondary spermatocytes
Haploid cells resulting from the first meiotic division of spermatogenesis. Secondary spermatocytes are ready to enter meiosis II.
primary spermatocyte
specialized cell that undergoes meiosis to ultimately form sperm
round spermatids
Found closer to the centre of the seminiferous tubules. First stage of differentiation in spermatogenic cycle
spermatid
an immature male sex cell formed from a spermatocyte that can develop into a spermatozoon without further division.
Sertoli cells
cells found within the seminiferous tubules that provide metabolic support for the spermatids, responds to FSH
Leydig cells
A cell that produces testosterone and other androgens and is located between the seminiferous tubules of the testes, responds to LH , have blood supply access
spermatozoa
a mature sperm cell
primary sex cords in fetal testis
monocytes are precursors to spermatogonia, bulk of cord is made up of pre-sertoli cells secreting AMH (determines sex), fetal leydig cells secrete tester one as well, additionally suppressing female tract. The lending cell will support development of the male track
FSH on Sertoli cells
1. stimulates spermatogenesis by synthesizing and secreting growth factors
2. stim synthesis and secretion of ABP which concentrates testosterone in the lumen of the seminiferous tubules and brings tester one to epididymis
3. Sertoli cells produce inhibit which inhibits FSH secretion from the ant pituitary (negative feedback)
4. Produces estradiol
5. aids tight junctions which separate diploid from haploid cells
bulbus glandis
enlargement toward the rear of the glans of dogs, inflates to allow penis to "lock" into vaginal canal of bitch
what species have sigmoid flexures
bull, ram, boar
Spermatocytogenesis
differentiation of spermatogonia into primary spermatocytes
spermiogensis
maturation of spermatids into sperm cells
how long does the production of sperm take
about 2 months
How many pulses of LH/FSH/GnRH are in a 24 hour period of a male?
4-5
Why are pulses important?
to keep Leydig cells sensitive to LH, excess t4 can suppress Sertoli cell function, a high amount of t4 is needed for spermatogenesis
3 phases of spermatogenesis
proliferation, meiotic, differentiation
proliferation
mitotic division near basement membrane, goal of generating a large number of spermatogonia (three types A,I, and B)
meiotic phase of spermatogenesis
spermatocytes undergo meiosis to generate haploid spermatids, between 2-6 divisions, cytoplasmic bridges form between daughter cells, apoptosis can occur at rates as high as 75% meiosis one for primary and meiosis two for secondary
things that can affect apoptosis of spermatogonia
normal part, season, disease, trauma or heat, hormone levels
Differentiation phase of spermiogenesis
transformation of round spermatid to elongated spermatozoa, four phases ( golgi, cap, acrosomal, and maturation phases)
Golgi phase of differentiation
*Initial acrosome formation
*Initial tail development
*translocation of centrioles
cap phase of differentiation
acrosome membrane formed, produce hydrolytic enzymes, flagellum elongates
Acrosomal phase of differentiation
*Large acrosome
*nucleus elongates
*manchette forms
*Neck and annuls form
maturation phase of differentiation
Final sperm assembly
*Spermatid becomes spermatozoon
*Mitochondria surround mid-piece as helix
*Completion of tail
*golgi removed
*Spermiation
cytoplasmic droplet
a remnant of cytoplasm located either at the neck of the spermatozoon (proximal) or just posterior to the midpiece of the spermatozoon (distal), as the migration of the sperm to the nail of epididymus it will migrate towards the end and be removed, can be used as a way to determine if you are overworking a male
stages of spermatogenesis
1-8 stages per cycle, each stage represents a window of time of and a snapshot as to what that tubules may look like at a given time , differ in duration
duration of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium
time required to complete a from a spermatogonia to spermatozoon
how many cycles must a somniferous tubule must go through to complete sperm production completely
4.5 - 5
spermatogenic wave
the sequential ordering of stages along the length of the seminiferous tubule
blood testis barrier
prevents antibodies in the blood from getting to the germ cells, first appear at puberty and induced by FSH targeting Sertoli cells
what can destroy tight junctions of Sertoli cells
heat, heavy metals, endocrine disruptors, lack of FSH or testosterone
variation of sperm production
*testis size
*efficiency of spermatogenesis
-mitotic division
-degeneration of germ cells
*length of spermatogenesis
sperm metabolism biochemistry
can be anaerobic (glycolysis) or aerobic, glucose will be phosphorated to glucose-6-phosphate by hexokinase, and fructose in seminal plasma will be phosphorated to fructose-6-phostate by hexokinase
phosphatase in sperm
futile cycle as a short term fix to maintain glucose levels in sperm, turns glucose-6-phosphate back to glucose
ATP utilization in sperm
- motility (60%)
- substrate cycling (40%) [wasted]
- maintenance of ionic gradients [very small amount]
- transcription and translation [none after condensation of nucleus and loss of residual body]
sperm metabolism
•Temperature dependent
-ATP production increases as temperature increases
•ATP dependent processes are temperature dependent
-motility increases with increasing temperature
how does sperm transport in the seminiferous tubules
bulk fluid flow, contraction of myoid cells
how does sperm transport in the rate testis
fluid flow, rete testis secretion
how does sperm transport in the epididymis
contraction
how does sperm transport in the vas efferent
fluid flow and cilia
epididymal functions
maturation, concentration, secretion, transport, storage
maturation function of epididymis
change in fertility (changes in protein on surface of sperm head), develop motility, nuclear condensation, cytoplasmic droplet
concentration function of epididymis
remove water (vas efferens, caput)
secretion function of epididymis
turns testerone to dihydrotesterone, the enzyme that converts this is 5-alphareductase, energy substrates (GPC, free fatty acids, carntitine) and glycoproteins, lipids, and enzymes
5-alphareductase
Converts testosterone to 5-alpha
hormonal control of epididymis
-absolute need for androgen
-caput- tubal testosterone
-corpus- tubal DHT, vascular testosterone
-cauda- tubal DHT, vascular testosterone
EEE=PSP
erection, emission, ejaculation is regulated by intervention of parasympathetic, sympathetic, and parasympathetic
which species have a fractionated composition of ejaculate
boar, stallion, human
components of semen
water, sperm, substrates , inorganic salts, proteins