2.5 Active and Passive Transport
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is diffusion?
the net movement of molecules or ions from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, down a concentration gradient until there is a concentration equilibrium (they are evenly distributed)
Fill in the blank: (B)_____ (m)____ causes particles to randomly move around due to kinetic energy and bump into each other
Brownian motion
Why is diffusion a passive process?
it doesn’t require energy
True or false? when diffusion reaches equilibrium across a membrane the particles no longer move across it
False - the particles still move, just equally in both directions, so there is no net movement
What characteristics of molecules mean they can diffuse straight through a membrane?
small and non-polar
Give an example of a molecule that can diffuse straight across a membrane?
water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, steroid hormones, small ions
How do larger, charged particles diffuse through membranes? (just the name of the process)
facilitated diffusion
Give an example of a molecule that diffuses across membranes by facilitated diffusion
glucose and amino acids
What is facilitated diffusion?
the diffusion of large, polar molecules and ions across cell membranes with the help of certain proteins, which are highly specific
Is facilitated diffusion an active or a passive process?
passive - molecules are moving down a concentration gradient
What are the two types of protein that carry out facilitated diffusion?
channel and carrier proteins
Fill in the blanks and choose the correct words: Channel proteins are intrinsic/extrinsic proteins which contain a ____ (a hydrophilic/hydrophobic channel) which has a ___ shape. They may be (g)___ - ___ cause the proteins to change shape closing one side and opening the other
intrinsic, pore, hydrophilic, specific, gated, ions
Fill in the blanks: carrier proteins are intrinsic/extrinsic ___proteins with a ___ shape. The molecule binding to the protein causes a ___ shape change in the protein which delivers the molecule to the other side of the membrane.
intrinsic, glyco-, specific, conformational
Rank in terms of speed for diffusion: diffusion, facilitated diffusion by a carrier protein and facilitated diffusion by a channel protein
diffusion, channel, carrier
List the factors that affect the rate of diffusion
temperature, concentration gradient, surface area, size of molecule, distance/thickness, stirring/moving
How does the size of the molecule affect the rate of diffusion?
smaller molecules require less kinetic energy to move, so move and therefore diffuse faster. They are also move likely to be able to diffuse straight through the membrane, which is faster than larger molecules diffusing by facilitated diffusion
Fill in the blanks to compare active and passive transport:
in passive transport ___ isn’t needed but it active transport it is needed in the form of ___
passive transport transports molecules from a ___ to ___ concentration ___ a concentration gradient
active transport carries molecules ___ a concentration gradient, and requires ____ ____
energy, ATP, high, low, down, against, carrier proteins
True or false? active transport can occur if diffusion isn’t quick enough and cannot meet the needs of the cell
true
What is active transport?
the movement of molecules and ions through a cell from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, against a concentration gradient using energy from respiration/in the form of ATP
True or false? active transport for a specific molecule can happen both ways across a cell membrane
false - it only allows a one-way flow
In active transport, what do the molecules or ions bind to inside the carrier proteins and why is this possible?
bind to receptors due to their complementary shape
Fill in the blanks to describe the process of active transport:
the molecule/ion binds to the ____ of the carrier protein
ATP also binds and is ___ into ___ and a ___
the binding of the ____ causes the carrier protein to ___ ____
the molecule/ion is ___
the phosphate molecule is ____ and recombines with ___ to form ___
the carrier proteins return to its ___ ___
receptors
hydrolysed, ADP, phosphate
phosphate, change shape
released
released, ADP, ATP
original shape
Give an example of a use of active transport
reabsorption of useful molecules and ions into blood after filtration into kidney tubules
absorption of glucose and amino acids from digestion into the blood
absorption of mineral ions by the roots of plants
exchange of sodium and potassium ions in nerve impulses
What is bulk transport?
the movement of large quantities of materials into and out of cells
True or false? Bulk transport is a type of diffusion
false - it is a type of active transport
Do diffusion, osmosis and active transport transport large amounts of molecule or ions?
no - they only transport individual molecules or ions
Give an example of a substance that is moved by bulk transport?
hormones, enzymes, phagocytes
What is endocytosis?
the bulk transport of materials into cells
Compare the 2 types of endocytosis
phagocytosis is the bulk intake of solids by a cell whereas pinocytosis is the bulk intake of liquids
What type of cell specialises in phagocytosis?
phagocytes
When phagocytes intake a substance, what are the vacuoles formed?
phagocytic vacuoles
What is the term for the pinocytosis of a very small amount of a substance?
micropinocytosis
True or false? both phagocytosis and pinocytosis work in the same way
true
Fill in the blanks for the process of endocytosis: The cell surface ____ and the membrane ___ the material until the membrane ____, forming a ___. The vesicle ____ ___ and moved into the cytoplasm where it is further ____ by the cell
invaginates, enfolds, vesicle, pinches off, processed
What is exocytosis?
the process by which materials are removed from/transported away from the cell
Fill in the blanks for the process of exocytosis: (s)___ vesicles are transported from the ___ ___ along (m)____ in the ____. The vesicle becomes linked and pulled into contact with the ___ ___ _____, with which the (p)___ ___ begin to merge. In (c)___ (f)___ the vesicle membrane fully ___ with the cell surface membrane, which creates a (f)___ (p)____ allowing the contents of the vesicle to leave the cell
secretory, Golgi apparatus, microtubules, cytoskeleton, cell surface membrane, phospholipid bilayers, complete fusion, fuses, fusion pore
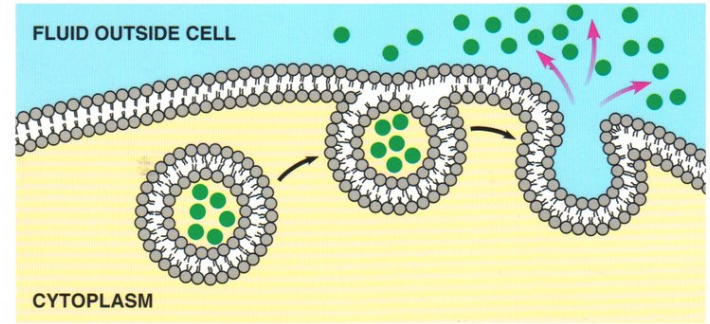
exocytosis
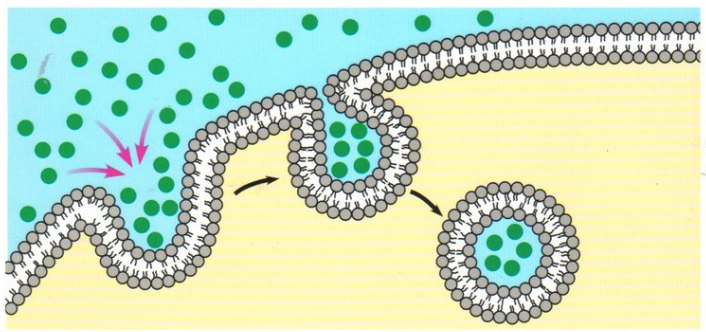
endocytosis
What is osmosis?
The net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential through a selectively permeable membrane until the water potential is in equilibrium
What is water potential?
the pressure exerted by water molecules as they collide with a membrane or container
Fill in the blanks: water potential is a measure of the water molecule potential for ___ in a solution and the ___ created by water molecules.
movement, pressure
What is the symbol for water potential?
Ψ (Greek letter psi)
What are the units of water potential?
pascals (Pa)
What is the water potential of pure water under standard conditions of temperature and pressure?
0
What are the standard conditions of temperature and pressure?
25ºC and 100kPa
What happens to the water potential in the presence of a solute?
it lowers as water molecules cluster around the solute particles, so are no longer free to move
True or false? water potential is always a positive value
false - it is always a negative value (or 0)
Does a dilute or concentrated solution have a higher water potential?
dilute
Solution A has a water potential of -2Pa and solution B has a water potential of -6Pa. Which is more concentrated?
solution B
True or false? solutions with different concentrations have different water potentials
true
Is a solution with a higher water potential more or less concentrated?
less
When solutions of different concentrations are separated by a partially permeable membrane, does the water or the solute move between solutions to create equilibrium?
water
Fill in the blanks: In a closed system such as a cell, the diffusion of water molecules into it will cause an increase in the ____ and therefore also increase the ____
volume, pressure
What is the name of the pressure caused by the diffusion of water molecules into a cell, increasing its volume?
hydrostatic pressure
What could happen if there is a large increase in hydrostatic pressure in an animal cell?
the cell would swell and burst
Why can too large of an increase in hydrostatic pressure cause an animals cell to burst?
animals cells have thin cell membranes which can easily break and no cell walls for extra support
What is the term used to describe the bursting of an animal cell due to osmosis?
cytolysis
Describe what happens during the crenation of an animal cell
water moves out of the cell by osmosis causing it to shrink and the plasma membrane to pucker
What is osmotic pressure?
the ‘pulling’ pressure where water is pulled into an area of low water potential by osmosis
What is a hypertonic environment around a cell?
the water potential of the external environment is higher than inside the cell
What is a hypotonic environment around a cell?
the water potential of the external environment is lower than inside the cell
What is a isotonic environment around a cell?
the water potential of the external environment is equal to the inside the cell
Describe what happens when a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution
water moves into the cell by osmosis, so the hypotonic pressure increases, pushing the membrane against the cell wall, creating turgor pressure
What has happened to a plant cell if it is in a state of plasmolysis?
it is in a hypotonic solution, so water moves out of the plant cell by osmosis, reducing the volume of the cytoplasm which causes it to pull the cell-surface membrane away from the cell
How would you describe the state of a plant cell if it was in an isotonic solution?
incipient plasmolysis
What happens to the movement of water by osmosis in an animal cell in an isotonic solution?
water constantly leaves and enters the cell at a constant rate
Why don’t plant cells burst? Give 2 reasons
the cell wall is made of cellulose so is rigid, so creates turgor pressure, which increasingly resists the entry of more water
What is the term that describes a swollen plant cell?
turgid
Describe the appearance of a red blood cell that has undergone cytolysis
a pale broken cell membrane remains, as the cell has burst an released its haemoglobin
Describe the appearance of a red blood cell that has undergone crenation
a shrunken, shrivelled cell with a darker colour to due the haemoglobin being more concentrated
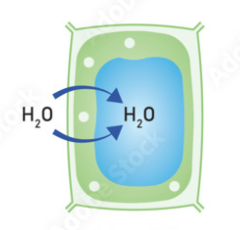
turgid
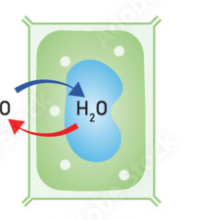
incipient plasmolysis
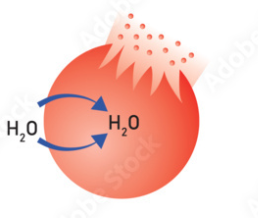
cytolysis
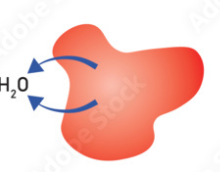
crenation
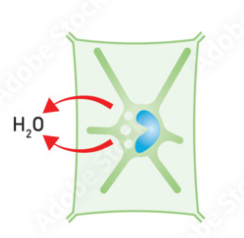
plasmolysis