ACCOUNTING CHAPTER 9 - RECORDING AND ANALYZING LONG-LIVED ASSETS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:24 AM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
What are plant assets?
Resources that have 3 characteristics
* They have physical substance (a definite size and shape)
* They are used in the operations of the business
* They are not intended for sale to customers
* They have physical substance (a definite size and shape)
* They are used in the operations of the business
* They are not intended for sale to customers

2
New cards
What are plant assets also referred to as?
Property, plant, and equipment; plant and equipment; and fixed assets
3
New cards
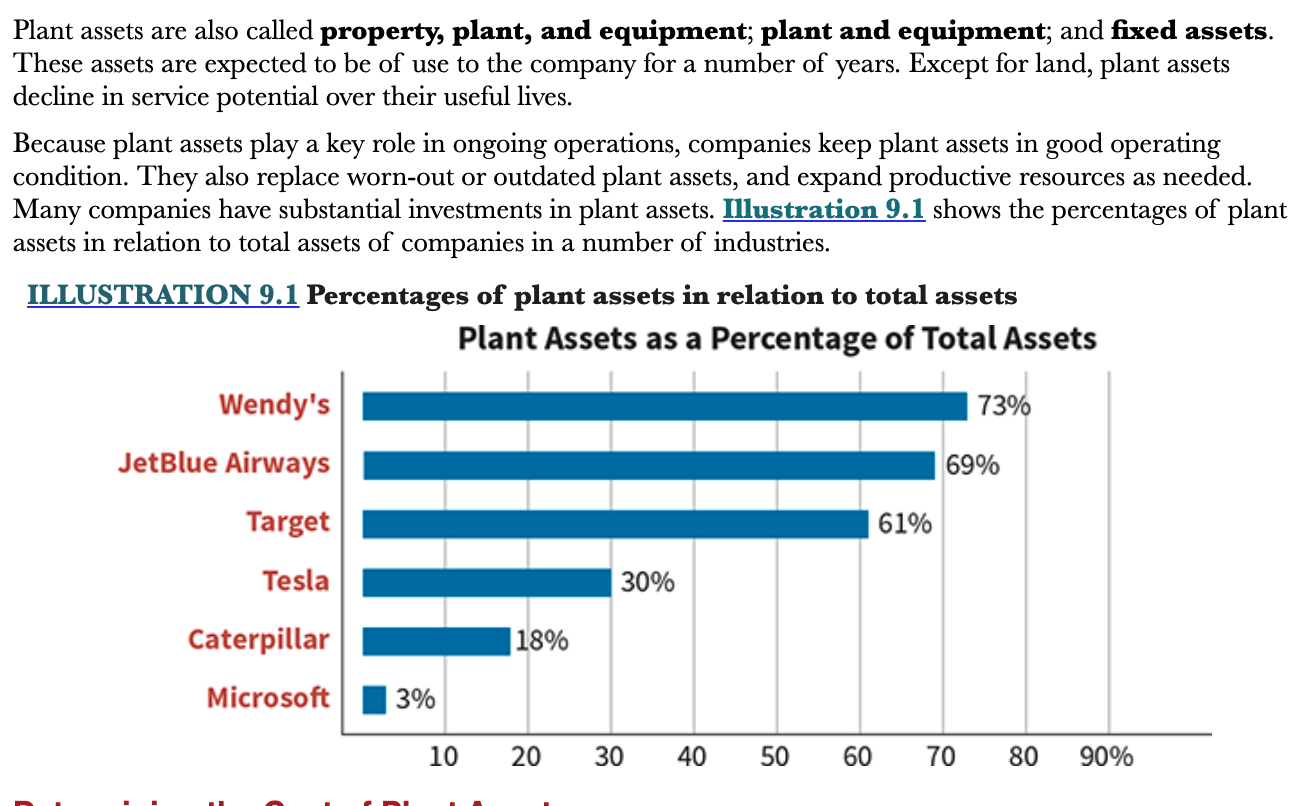
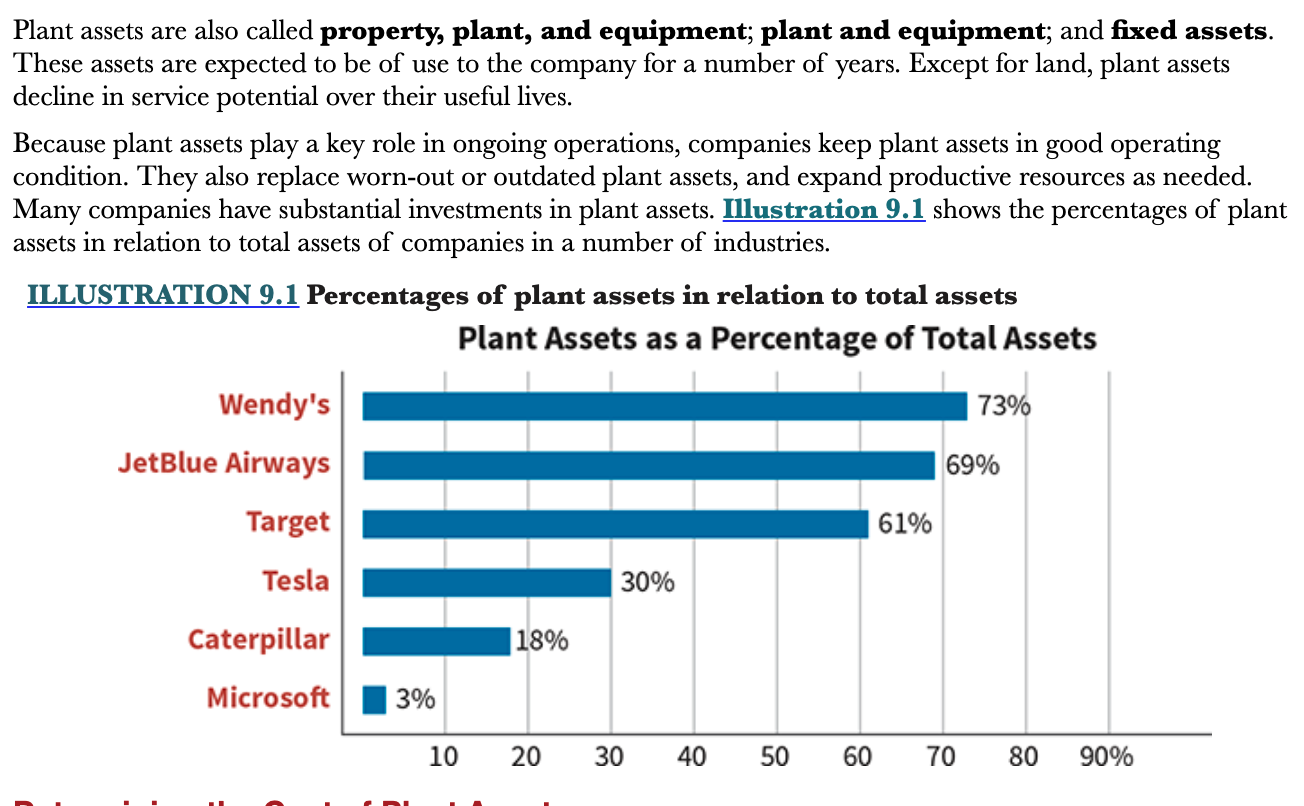
What is the expected life span of plant assets?
Plant assets are expected to be of use to the company for a number of years. Plant assets, except land, decline in service potential over their useful lives
4
New cards
How does the historical cost principle require companies to record plant assets?
They must record it as cost. Cost consists of all expenditures necessary to acquire an asset and make it ready for its intended use
* Purchase price, freight cost, installation costs, etc.
* Purchase price, freight cost, installation costs, etc.
5
New cards
What is the cash equivalent price?
Another way to record cost of a plant asset. It’s an amount equal to the fair value of the asset given up or the fair value of the asset received, whichever is more clearly determinable.

6
New cards
What is the cost of land?
* The cash purchase price
* Closing costs such as title and attorney fees
* Real estate broker commissions
* Accrued property taxes and other liens assumed by the purchaser
* Closing costs such as title and attorney fees
* Real estate broker commissions
* Accrued property taxes and other liens assumed by the purchaser

7
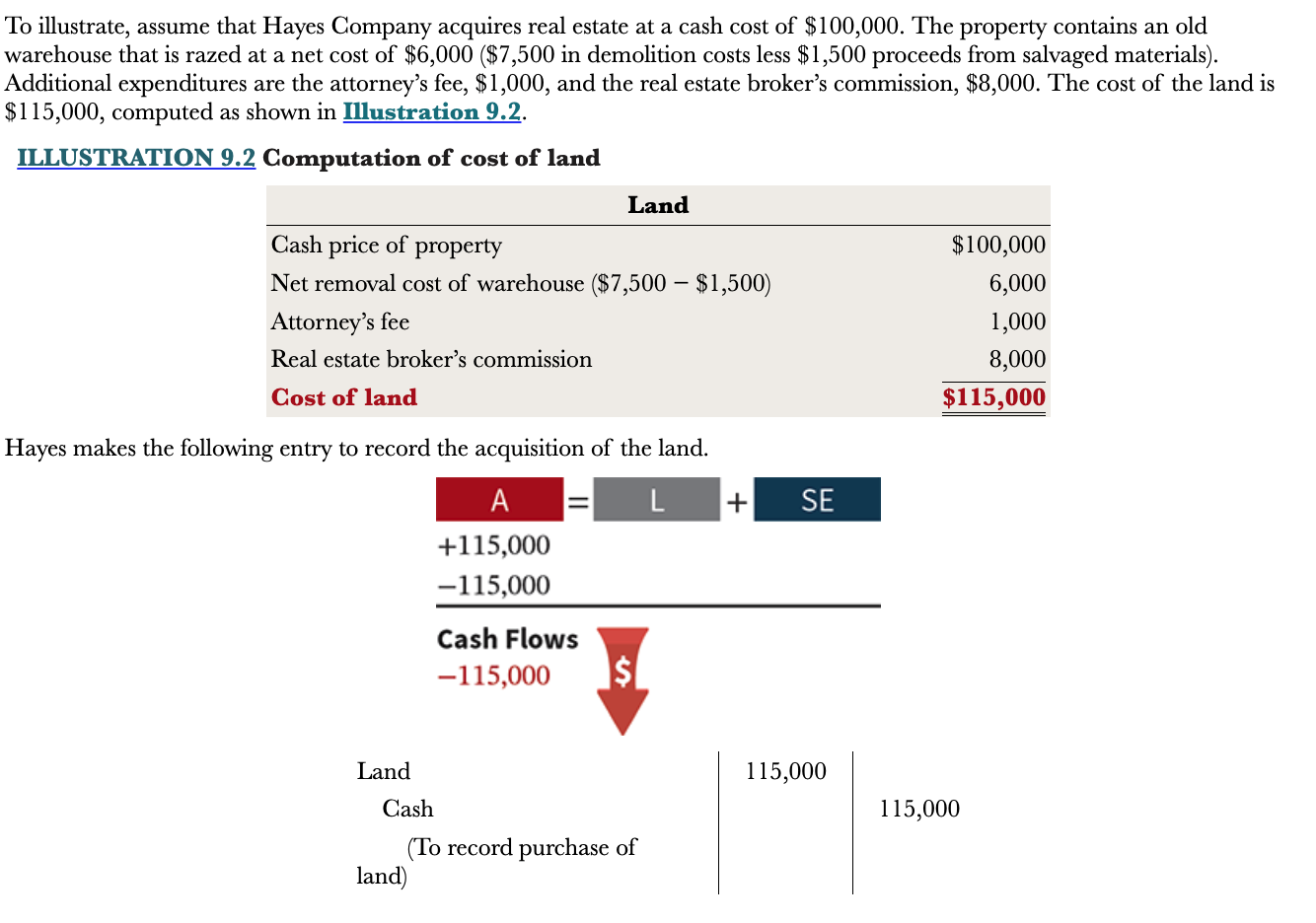
New cards
What entries are made for land?
A debit (increase) to the land account for all necessary costs incurred to make land ready for its intended use. And a credit (decrease) to cash
8
New cards
What are land improvements?
Structural additions with limited lives that are made to land
* Driveways, parking lots, and underground sprinklers
\
The cost of land improvements include all expenditures necessary to make the improvement ready for their intended use
* Driveways, parking lots, and underground sprinklers
\
The cost of land improvements include all expenditures necessary to make the improvement ready for their intended use

9
New cards
What is the costs for buildings that are purchased?
* Purchase price
* Closing costs (attorney’s fee, title insurance, etc.), and the real estate broker’s commission
* Costs to make the building ready for use (remodeling and replacing or repairing the roof, floors ,electrical wiring, and plumbing)
* Closing costs (attorney’s fee, title insurance, etc.), and the real estate broker’s commission
* Costs to make the building ready for use (remodeling and replacing or repairing the roof, floors ,electrical wiring, and plumbing)

10
New cards
What is the costs of constructed buildings?
* Contract price plus payments for architect’s fees
* Building permits
* Excavation costs
* Building permits
* Excavation costs

11
New cards
How do interest cost come into play for purchased and constructed buildings?
Interest cost incurred to finance the projects are included in the cost of the building when a significant period of time is required to get the building ready for use
\
The inclusion of interest costs in the cost of a constructed building is limited to interest costs incurred during the constructed period
\
The inclusion of interest costs in the cost of a constructed building is limited to interest costs incurred during the constructed period

12
New cards
What entries are made for buidlings?
Debit (increase) to building account and debit (increase) to interest expense

13
New cards
What are the costs of equipment?
* Cash purchase price
* Sales taxes
* Freight charges
* Insurance during transit paid by the purchaser
* Expenditures required in assembling, installing, and testing the equipment
* Sales taxes
* Freight charges
* Insurance during transit paid by the purchaser
* Expenditures required in assembling, installing, and testing the equipment

14
New cards
What are the 2 criteria for determining the cost of equipment?
* The frequency of the cost (one time or recurring)
* The benefit period (the life of the asset or one year)
* The benefit period (the life of the asset or one year)

15
New cards
Example of entries for equipment
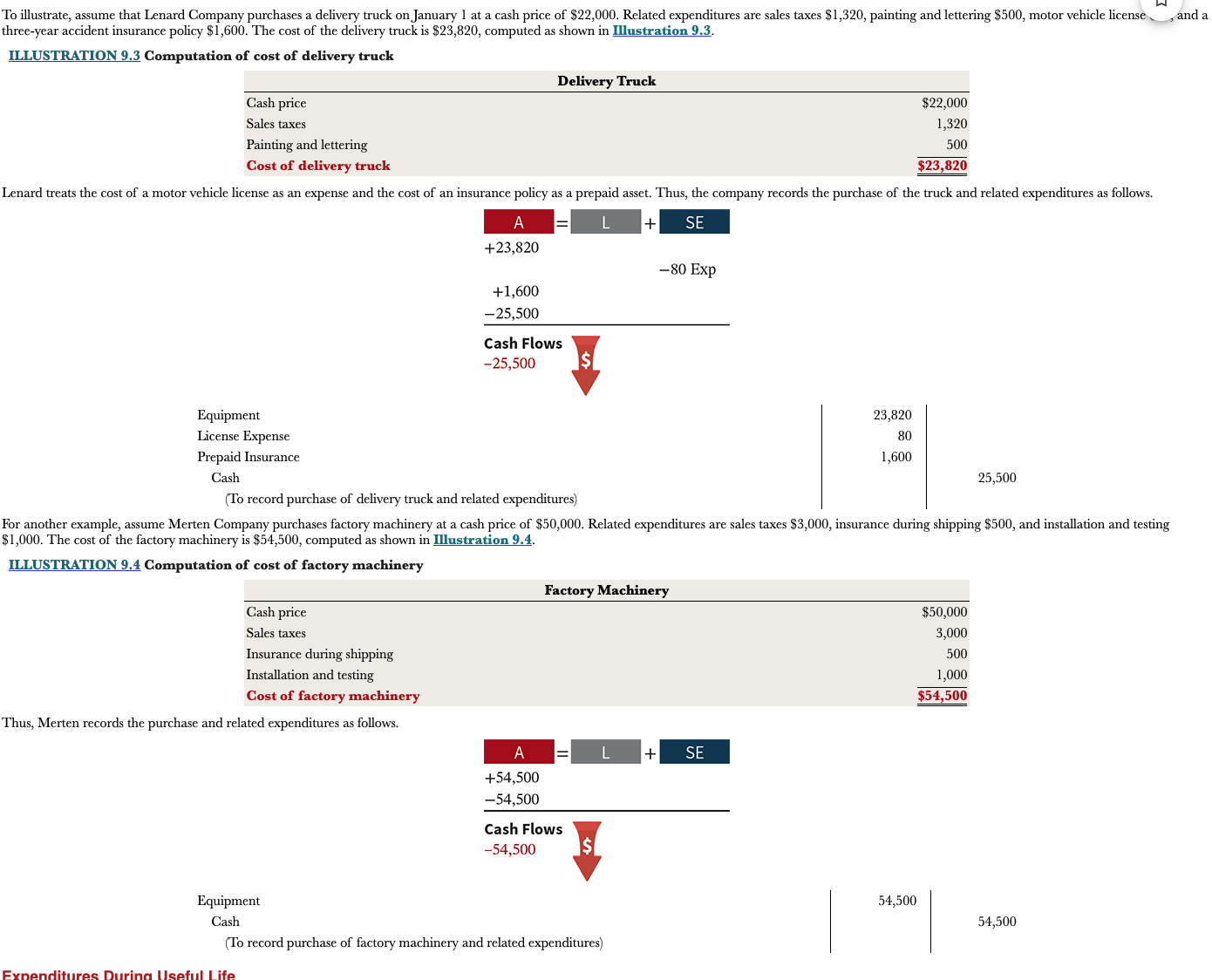
16
New cards
What are ordinary repairs?
Expenditures to maintain the operating efficiency and productive life of the asset
* Motor tune-ups and oil changes, the painting of buildings, and the replacing of worn-out gears on machinery
* Motor tune-ups and oil changes, the painting of buildings, and the replacing of worn-out gears on machinery

17
New cards
What are revenue expenditures?
Expenditures that are immediately charged against revenues as expenses

18
New cards
What are additions and improvements?
Cost incurred to increase the operating efficiency, productive capacity, or useful life of a plant asset

19
New cards
What are capital expenditures?
Expenditures that increase the company’s investment in plant assets

20
New cards
What is a lease?
A contractual agreement in which the owner of an asset (the lessor) allows another party (the lessee) to use the asset for a period of time at an agreed price

21
New cards
What are the advantages of leasing?
* Reduced risk of obsolescence
* Little or no down payment
* Shared tax advantages
* Little or no down payment
* Shared tax advantages

22
New cards
What is depreciation?
The process of allocating to expense the cost of a plant asset over its useful (service) life in a rational and systematic manner. Such cost allocations are designed to properly record expenses (efforts) with associated revenues (results)
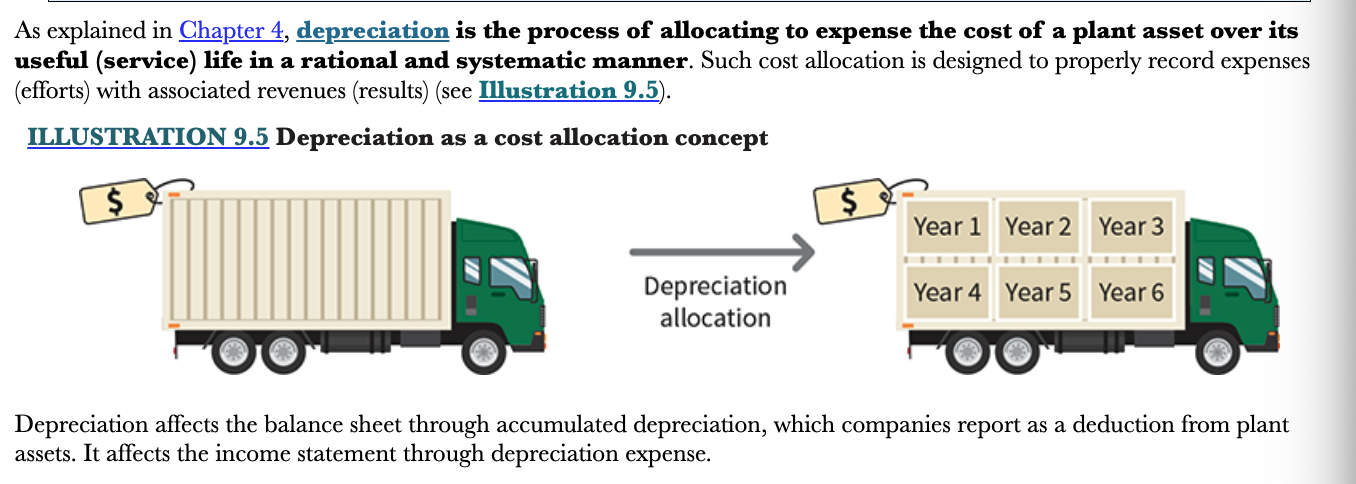
23
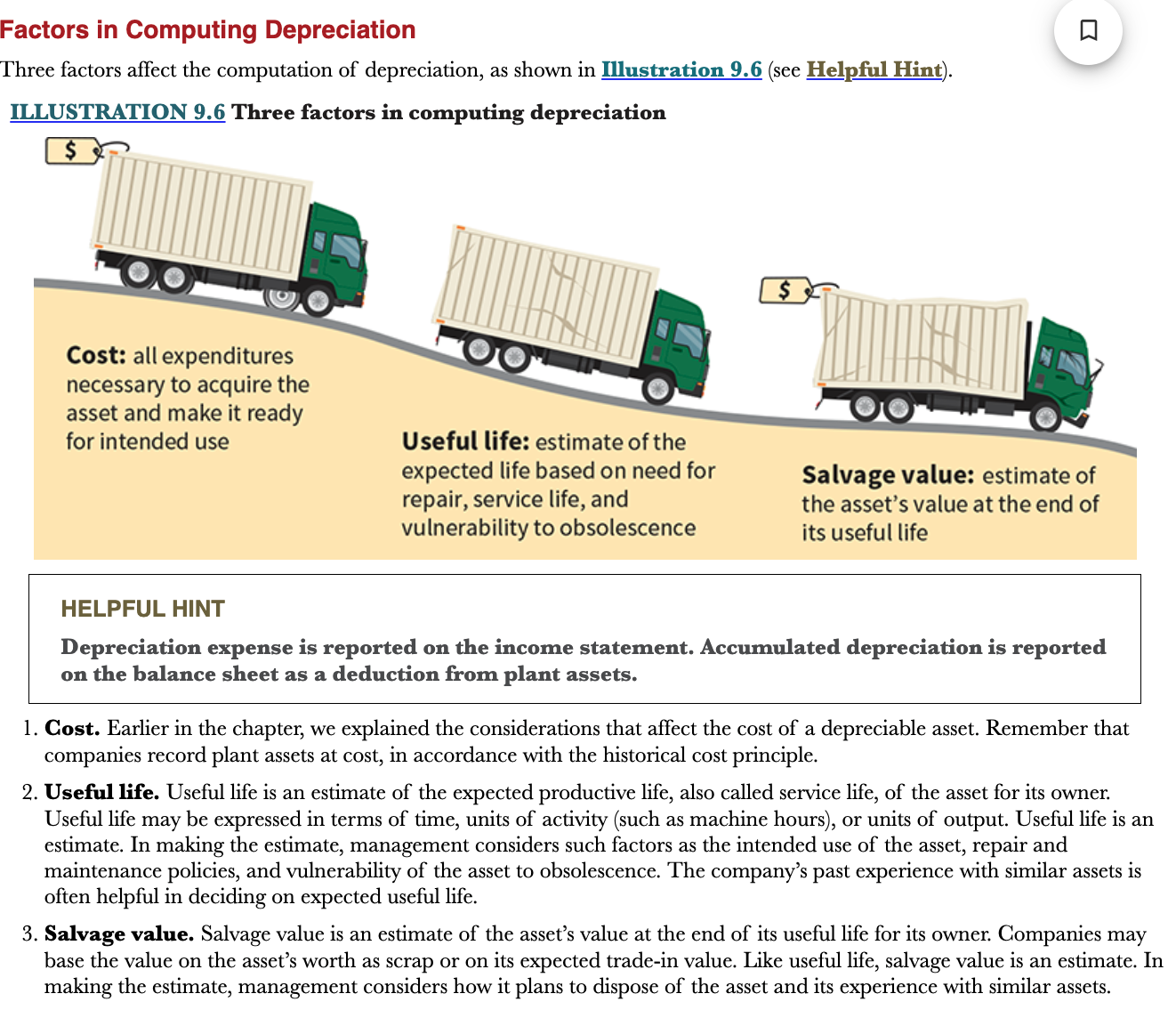
New cards
What are the 3 factors in computing depreciation?
* Costs
* Useful life
* Salvage value
* Useful life
* Salvage value
24
New cards
What is the factor costs?
The historical cost principle
25
New cards
What is the factor useful life?
Estimate of the expected productive life, also called service life, of the asset for its owner. Can be expressed in terms of time, units of activity (such as machine hours), or units of output.
26
New cards
What is the salvage value?
The estimate of the asset’s value at the end of its useful life for its owner
27
New cards
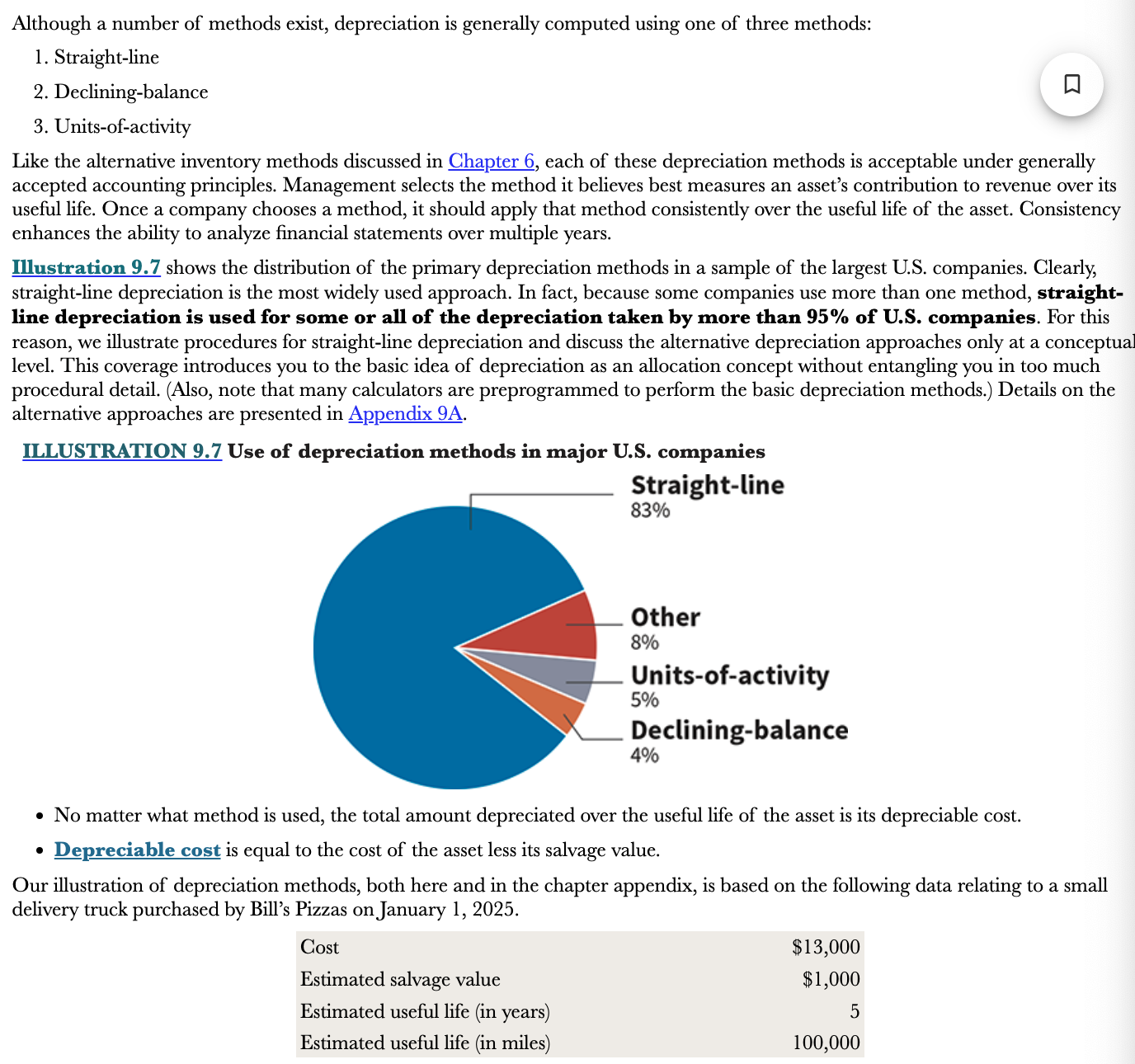
What are the 3 depreciation methods?
* Straight-line
* Declining-balance
* Units-of-activity
\
83% of major U.S. companies use the straight-line method
\
Total depreciation expense is the same no matter what method you use
* Declining-balance
* Units-of-activity
\
83% of major U.S. companies use the straight-line method
\
Total depreciation expense is the same no matter what method you use
28
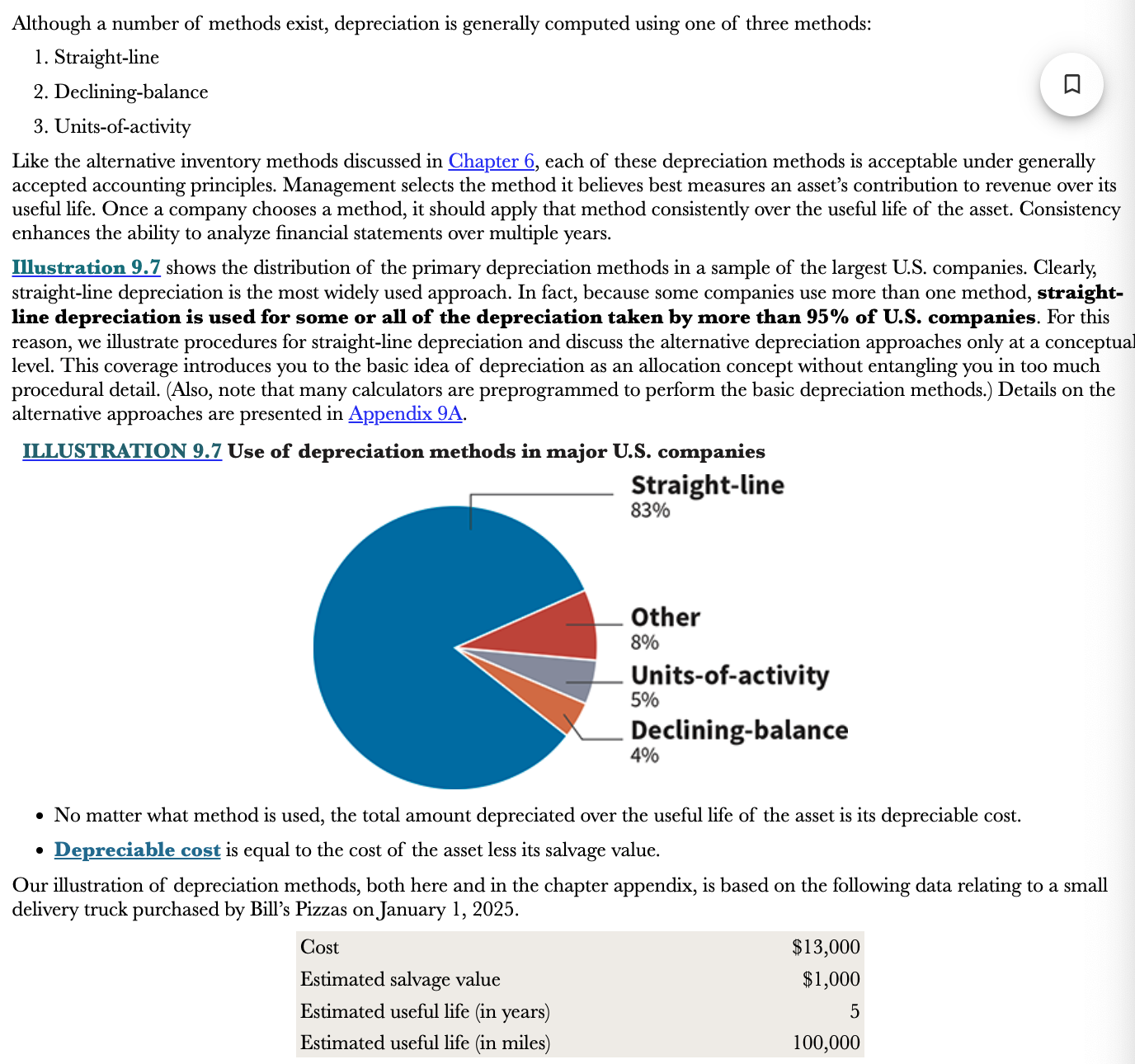
New cards
What is depreciable cost?
It is equal to the cost of the asset less its salvage value
29
New cards
\
What is the straight-line method?
What is the straight-line method?
Companies expense an equal amount of depreciation each year of the asset’s useful life. Management must choose the useful life of an asset based on its own expectations and experience
30
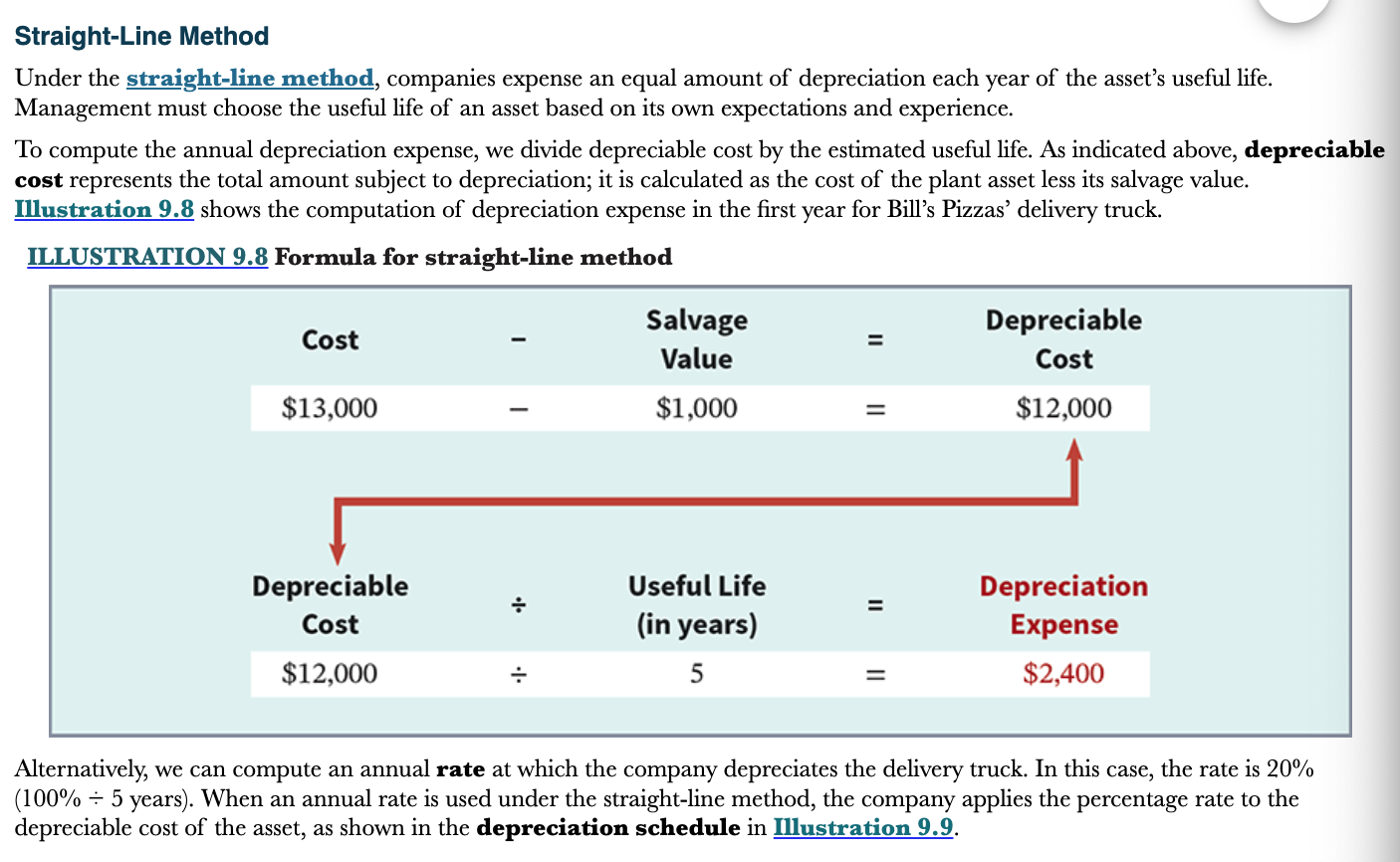
New cards
How is the annual depreciation expense calculated in the straight line method?
Take the depreciable cost and divide it by the useful life (annual rate)
31
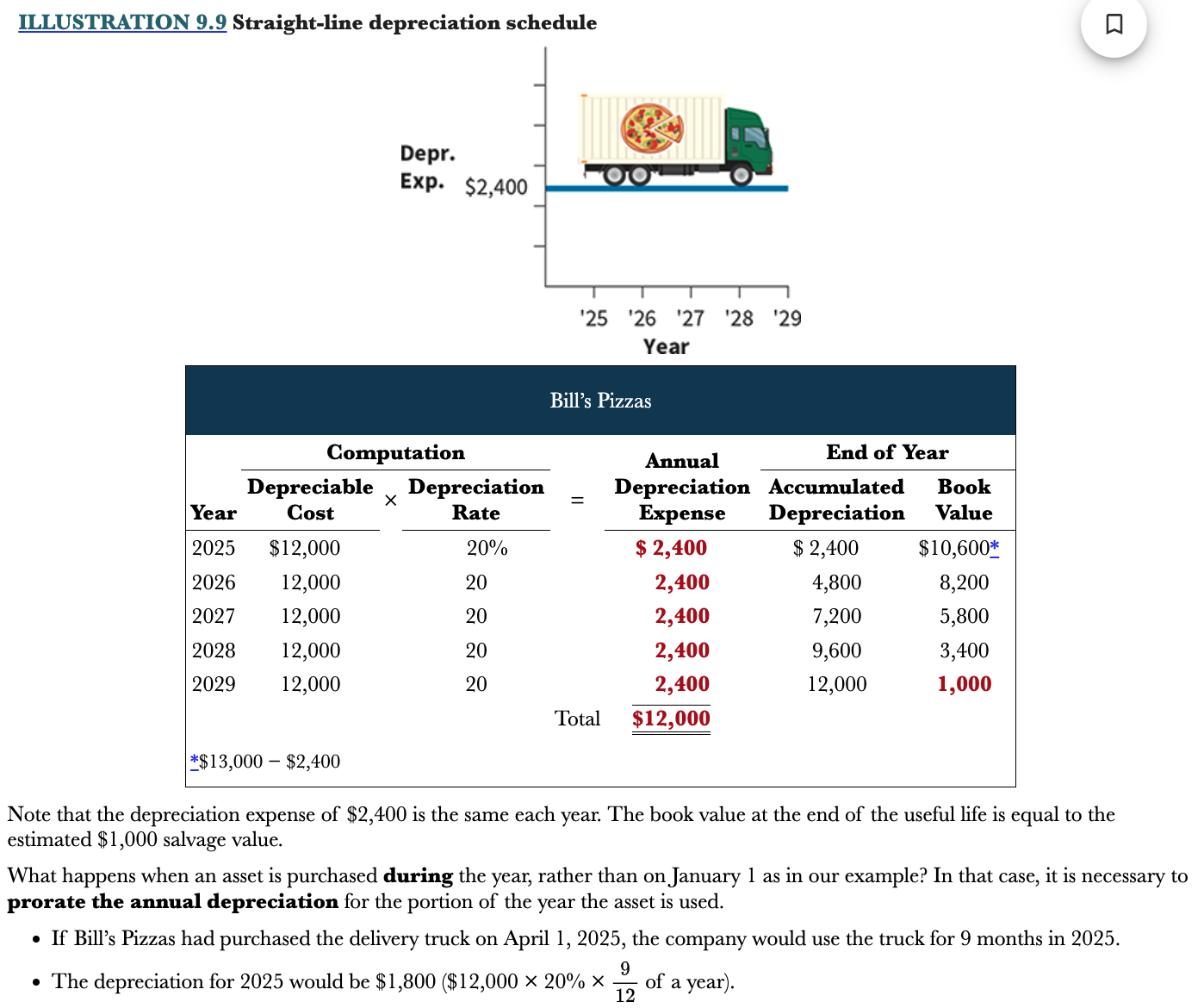
New cards
Example of straight line method
32
New cards
What is prorating the annual depreciation?
Taking into account depreciation of a plant asset that was purchased later in the year
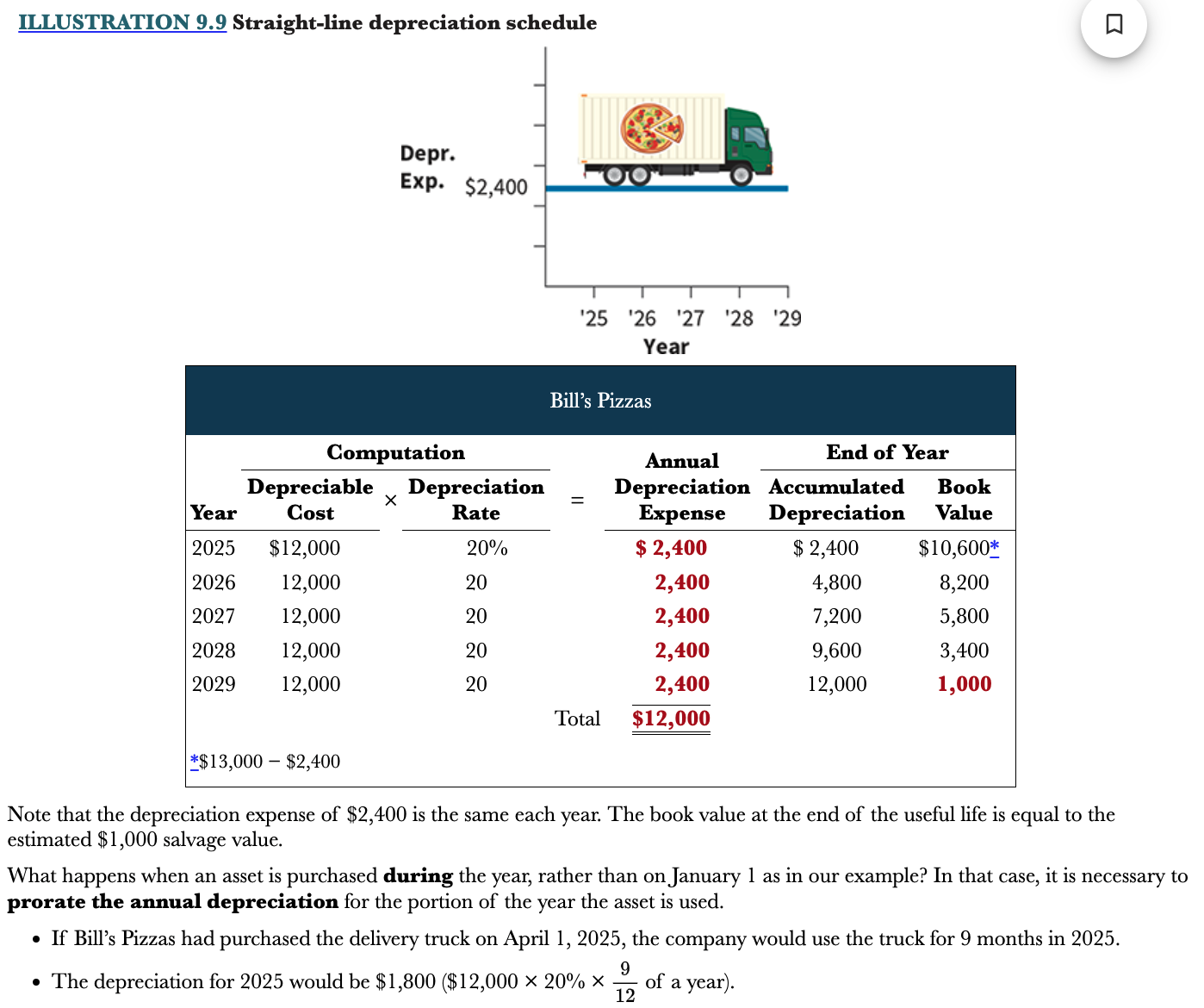
33
New cards
What is the declining-balance method?
Computes depreciation expense using a constant rate applied to a declining book value. Produces a decreasing annual depreciation expense over the asset’s useful life
\
Also referred to as the accelerated-depreciation method because it results in higher depreciation in the early years of an assets life compared to straight-line approach
\
In early years, declining-balance depreciation expense will exceed straight-line. In later years, it will be less than straight line
\
Also referred to as the accelerated-depreciation method because it results in higher depreciation in the early years of an assets life compared to straight-line approach
\
In early years, declining-balance depreciation expense will exceed straight-line. In later years, it will be less than straight line
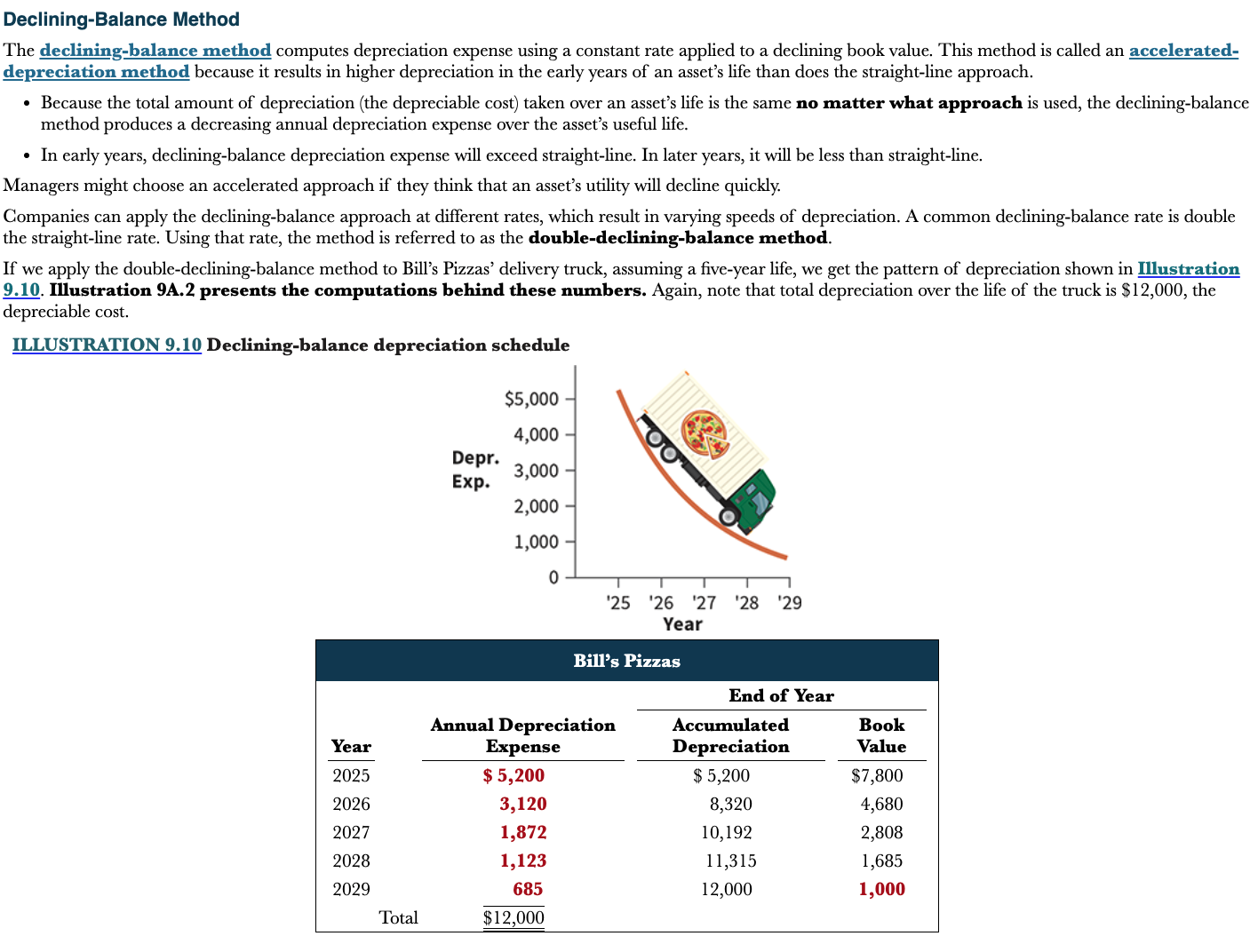
34
New cards
How can you calculate the rate for declining-balance>
A common declining balance rate is double the straight line rate
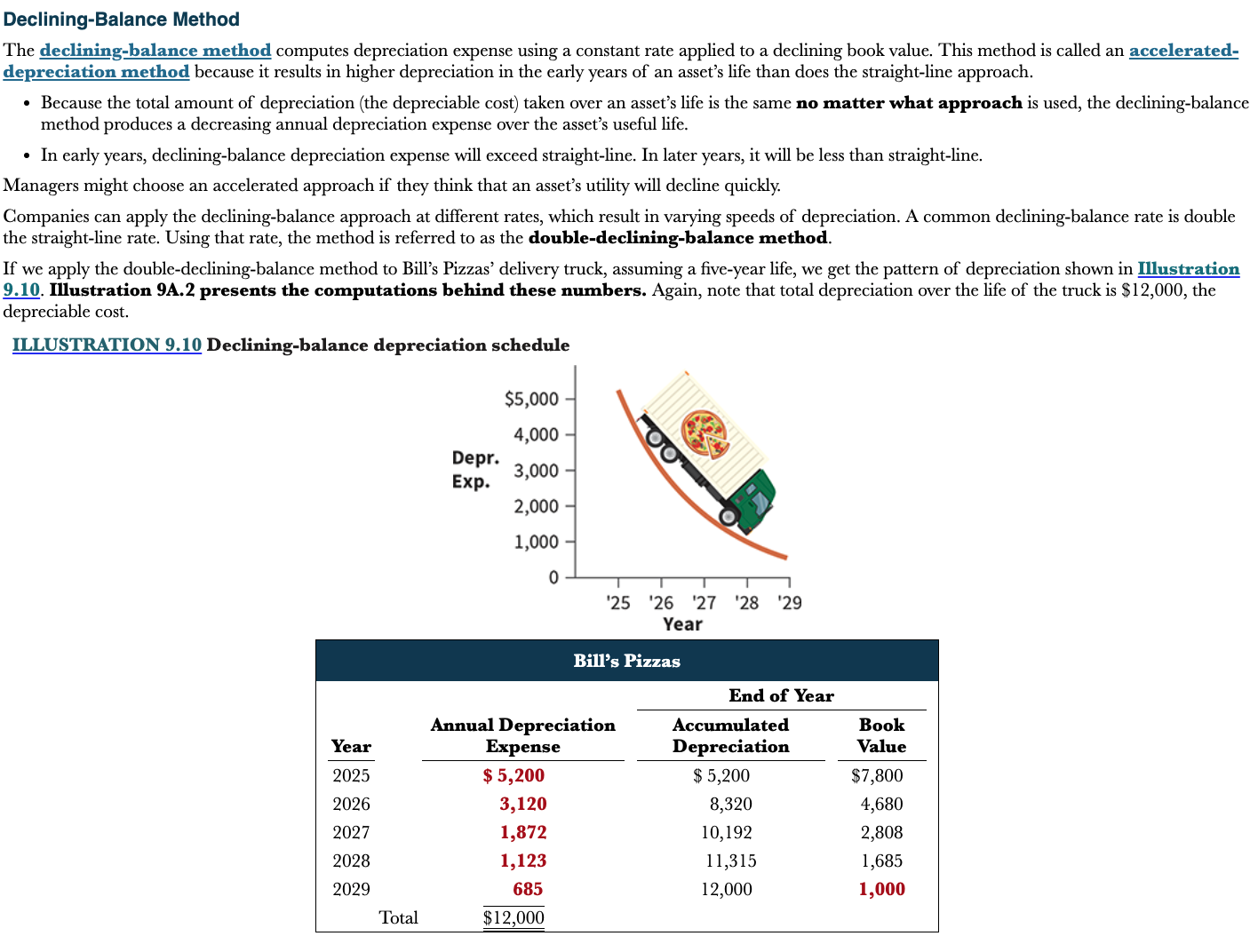
35
New cards
What is the units-of-activity method?
Expresses useful life in terms of total units of production or the use expected from the asset
* Amount of depreciation is proportional to the activity that took place during that period
* Ideally suited to factory machinery
* Also possible to use on items such as delivery equipment (miles driven) and airplanes (hours in use)
* Amount of depreciation is proportional to the activity that took place during that period
* Ideally suited to factory machinery
* Also possible to use on items such as delivery equipment (miles driven) and airplanes (hours in use)
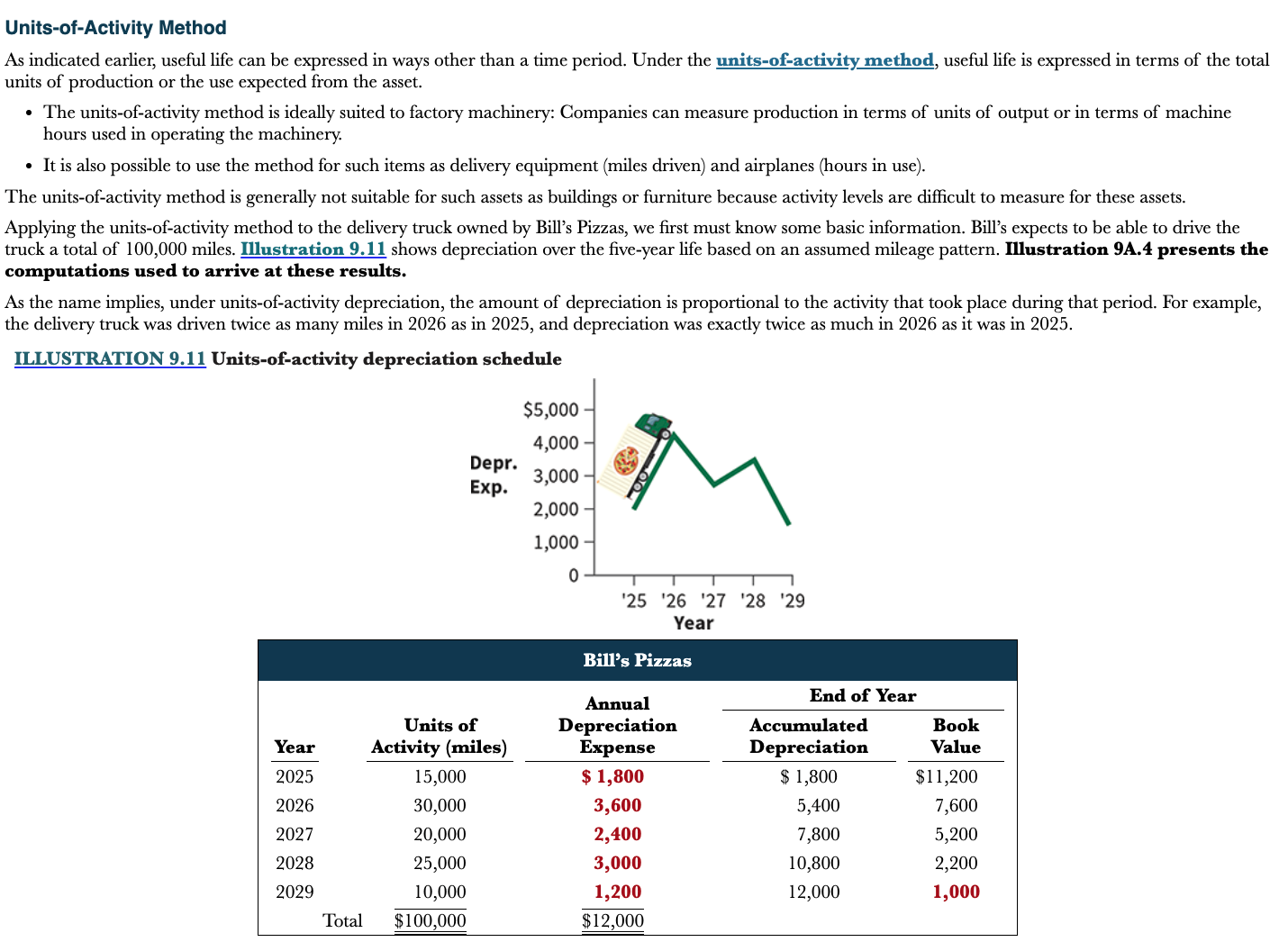
36
New cards
When should management revise the depreciation expense amount?
When the annual depreciation is either inadequate or excessive.
\
When a change in estimate is required, the company makes changes to current and future years, but not to prior periods
\
When a change in estimate is required, the company makes changes to current and future years, but not to prior periods
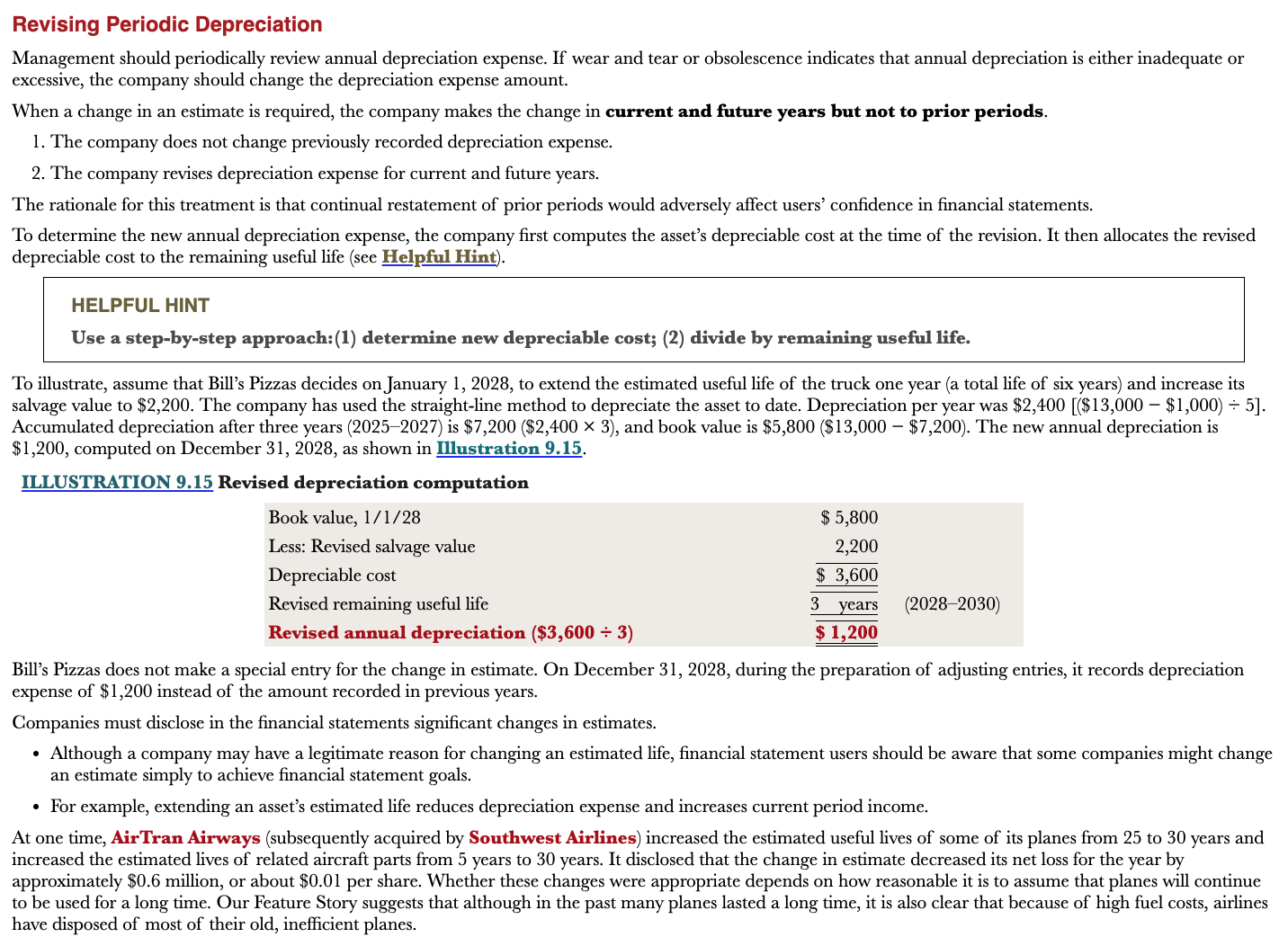
37
New cards
What is an impairment?
A permanent decline in the fair value of an asset

38
New cards
What are the 3 methods of plant asset disposal?
Sale, retirement, exchange

39
New cards
What must companies due in their books in order to dispose of plant assets?
They must determine the book value (difference between the cost of plant asset and accumulated depreciation to date) of the plant asset at the time of disposal in order to determine the gain or loss.
\
The company eliminates the book value by reducing (debiting) accumulated depreciation for the total depreciation association with that asset to the date of disposal and reducing (crediting) the asset account for the cost of the asset
\
The company eliminates the book value by reducing (debiting) accumulated depreciation for the total depreciation association with that asset to the date of disposal and reducing (crediting) the asset account for the cost of the asset

40
New cards
What is the sale of plant assets method?
Equipment is sold to another party
\
In a disposal by sale, the company compares the book value of the asset with the proceeds received from the sale
* If proceeds from sale exceed book value, a gain on disposal occurs
* If proceeds from sale are less than book value, a lose on disposal occurs
\
In a disposal by sale, the company compares the book value of the asset with the proceeds received from the sale
* If proceeds from sale exceed book value, a gain on disposal occurs
* If proceeds from sale are less than book value, a lose on disposal occurs
41
New cards
Example of gain on sale
1) Record updated depreciation expense
2) Determine the gain on disposal
3) Record sale of office furniture at a gain
\
Gain on disposal of plant asset is a credit
2) Determine the gain on disposal
3) Record sale of office furniture at a gain
\
Gain on disposal of plant asset is a credit
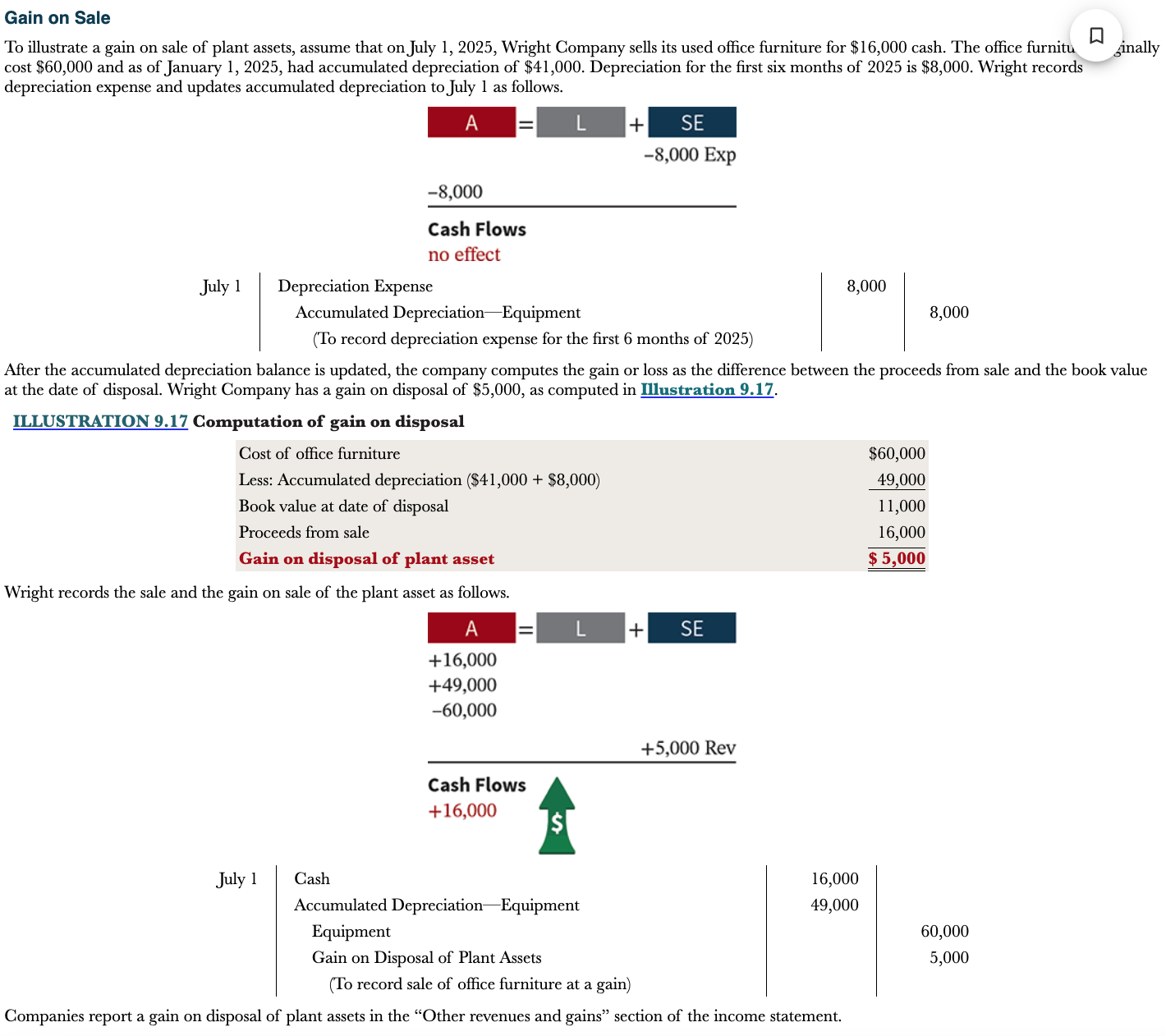
42
New cards
Example of lose on sale
1) Record updated depreciation expense
2) Determine the lose on disposal
3) Record sale of office furniture at a lose
2) Determine the lose on disposal
3) Record sale of office furniture at a lose
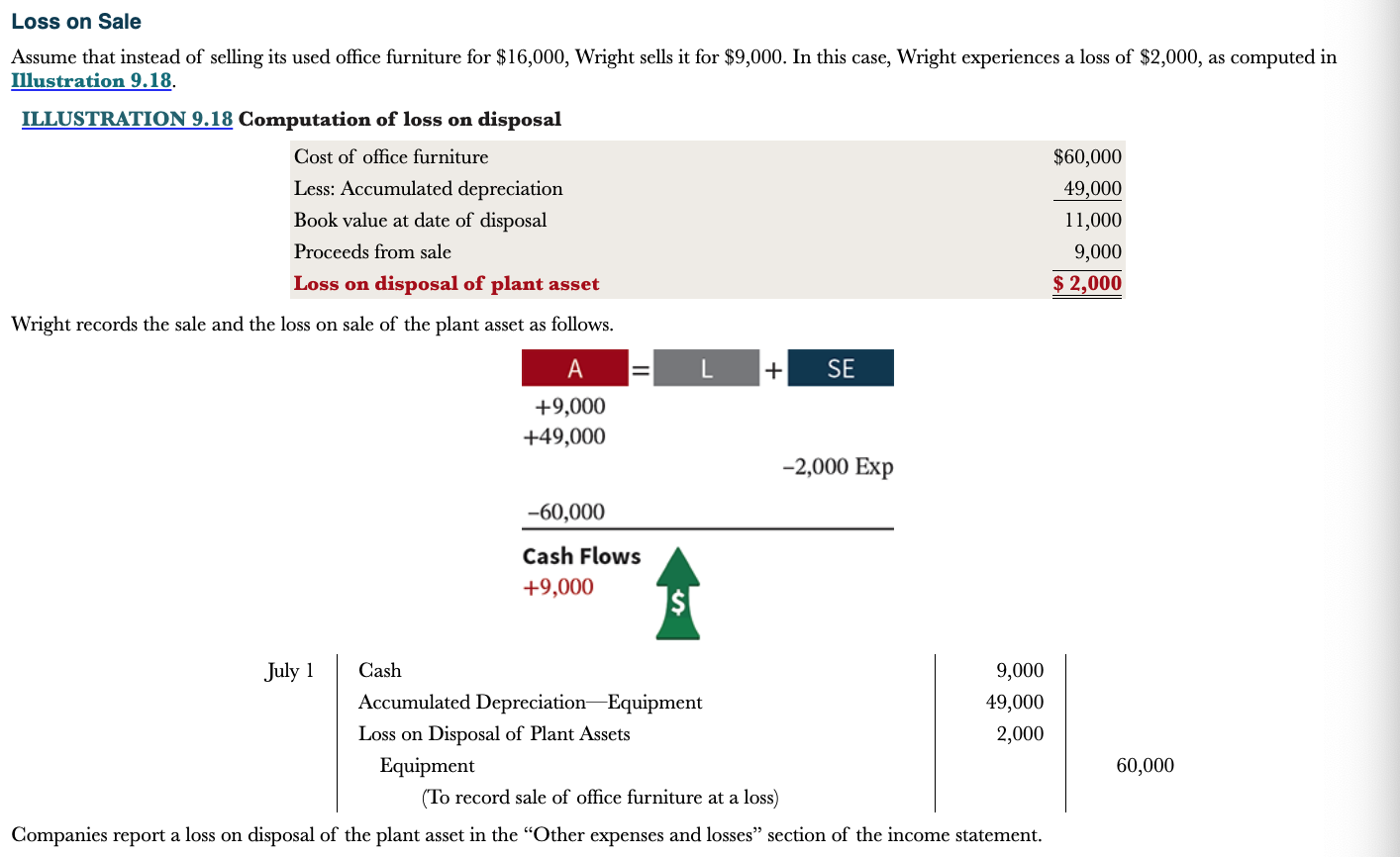
43
New cards
What is the retirement of plant assets method?
Equipment is scrapped or discarded. Companies record retirement of an asset as a special case of disposal where no cash is received
\
They decrease (debit) accumulated depreciation for the full amount of depreciation taken over the lief of the asset and decrease (credit) the asset account for the original cost of the asset
\
They decrease (debit) accumulated depreciation for the full amount of depreciation taken over the lief of the asset and decrease (credit) the asset account for the original cost of the asset

44
New cards
What are intangible assets?
Rights, privileges, and competitive advantages, that is, without physical , that result from ownership of long-lived assets

45
New cards
How do companies record intangible assets?
Companies record intangible assets at cost. This cost consists of all expenditures necessary for the company to acquire the right, privilege, or competitive advantage. Intangibles are categorized as having either a limited life or an indefinite life

46
New cards
What do companies do if an intangible asset has a limited life and indefinite?
The company allocates its cost over the asset’s useful life using a process similar to depreciation. The process on allocating the cost of intangibles is referred to as amortization
\
Indefinite intangibles should not be amortized
\
Indefinite intangibles should not be amortized

47
New cards
How do you record amortization of intangible assets?
Company increases (debits) amortization expense and decreases (credits) the specific intangible asset
\
Companies amortize the cost of a patent over its 20-year life or its useful life, whichever is shorter
\
Companies amortize the cost of a patent over its 20-year life or its useful life, whichever is shorter
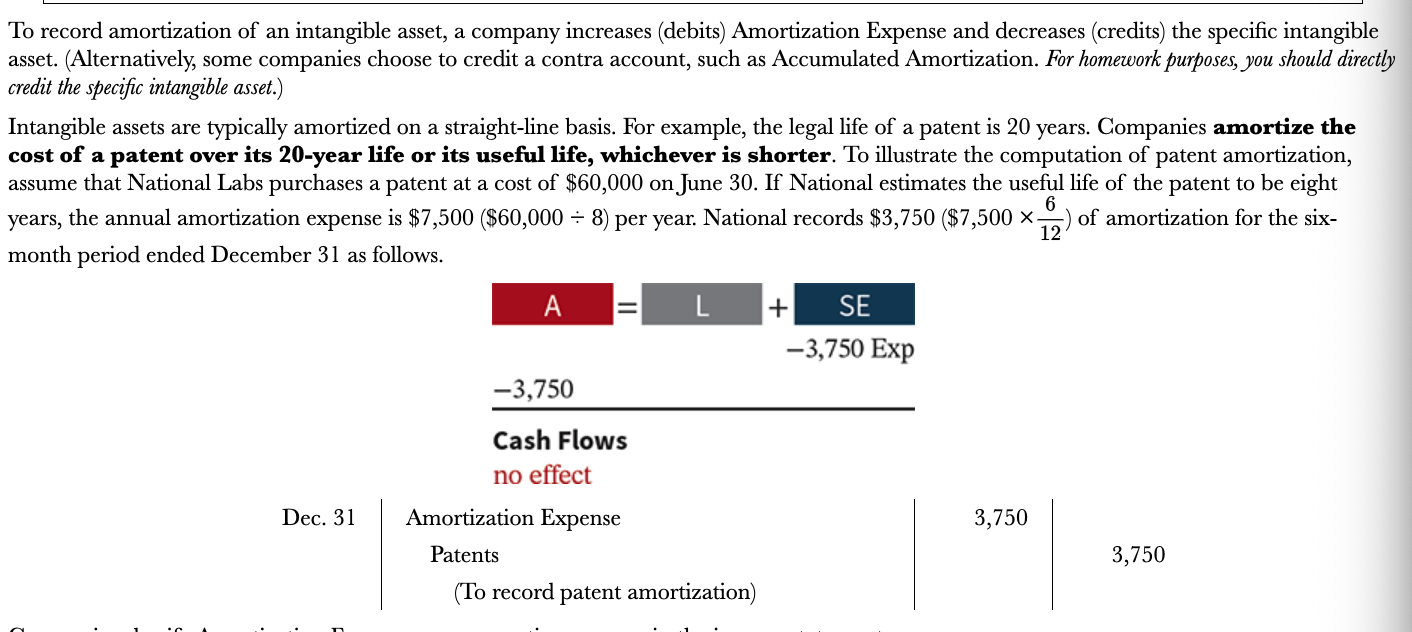
48
New cards
What is the difference between intangible and plant assets in determining cost?
Plant asset cost includes the purchase price and the costs incurred in designing and constructing the asset
\
Intangible assets only include the purchase price
\
Intangible assets only include the purchase price

49
New cards
What is a patent?
An intangible asset that represents an exclusive right issued by the U.S. Patent Office that enables the recipient to manufacture, sell, or otherwise control an invention for a period of 20 years from the date of the grant.
* The initial cost of a patent is the cash or cash equivalent price paid to acquire the patent
* The owner adds legal costs of successfully defending a patent to the patents account and amortizes them over the remaining life of the patent (cost of unsuccessful defenses are expensed)
* Patent holders amortizes the cost of a patent over its 20-year legal life or its useful life
* The initial cost of a patent is the cash or cash equivalent price paid to acquire the patent
* The owner adds legal costs of successfully defending a patent to the patents account and amortizes them over the remaining life of the patent (cost of unsuccessful defenses are expensed)
* Patent holders amortizes the cost of a patent over its 20-year legal life or its useful life

50
New cards
What is a copyright?
Copyrights give the owner the exclusive right to reproduce and sell an artistic or published work. Copyrights last for the life of the creator plus 70 years.
* Cost of copyright is cost of acquiring and successfully defending it
* Cost can vary
Useful life of a copyright generally is significantly shorter than its legal life
* Cost of copyright is cost of acquiring and successfully defending it
* Cost can vary
Useful life of a copyright generally is significantly shorter than its legal life

51
New cards
What are trademarks and trade names?
A trademark or trade name is a word, phrase, jingle, or symbol that identifies a particular enterprise or product
* Cost is the purchase price
* Any cost related to developing and maintaining the trademark are expensed as incurred
Trademarks have indefinite lives so they are note amortized
* Cost is the purchase price
* Any cost related to developing and maintaining the trademark are expensed as incurred
Trademarks have indefinite lives so they are note amortized

52
New cards
What is a franchise?
A contractual arrangement between a franchisor and a franchise. The franchisor grants the franchisee the right to sell certain products, to perform certain services, or to use certain trademarks or trade names, usually within a designated geographic area
\
Another type of franchise is a license. A license granted by a governmental body permits a company to use public property in performing its services
* License for the use of city streets for a bus line or taxi service
\
Companies record as operating expenses annual payments made under a franchise agreement in the period in which they are incurred
* In the case of a limited life, a company amortizes the cost of a franchise (or license) as an operating expense over the useful life
\
Another type of franchise is a license. A license granted by a governmental body permits a company to use public property in performing its services
* License for the use of city streets for a bus line or taxi service
\
Companies record as operating expenses annual payments made under a franchise agreement in the period in which they are incurred
* In the case of a limited life, a company amortizes the cost of a franchise (or license) as an operating expense over the useful life

53
New cards
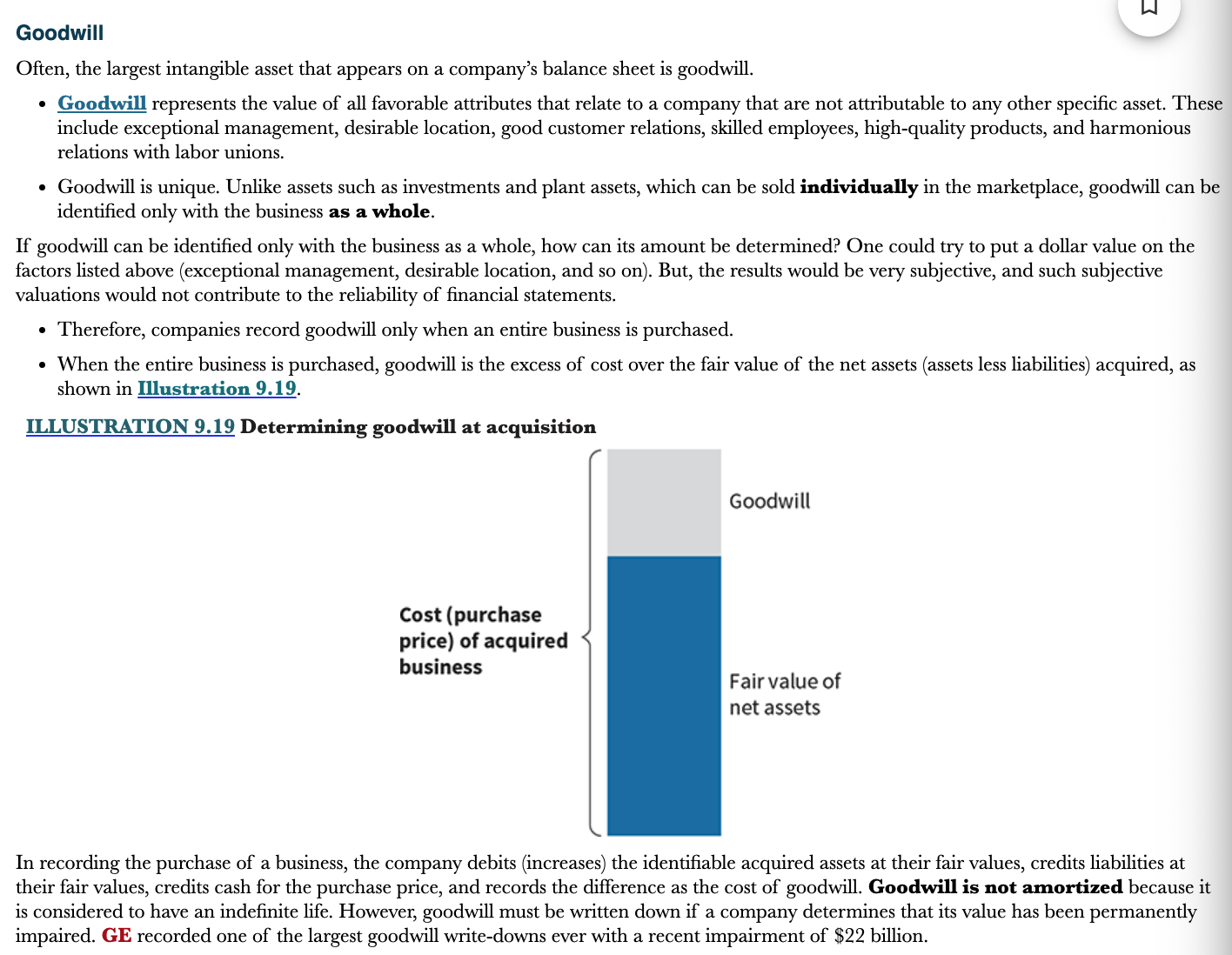
What is goodwill?
Goodwill represents the value of all favorable attributes that relate to a company that are not attributable to any other specific asset. These include exceptional management, desirable location, good customer relations, skilled employees, high-quality products, and harmonious relations with labor unions
* Good will is recorded only when an entire business is purchased because it can only be identified with the business as a whole
* When the entire business is purchased, goodwill is the excess of cost over the fair value of the net assets (Assets less liabilities) acquired
\
Goodwill is not amortized because it is considered to have an indefinite life
Goodwill must be written down if its value has been permanently impaired
* Good will is recorded only when an entire business is purchased because it can only be identified with the business as a whole
* When the entire business is purchased, goodwill is the excess of cost over the fair value of the net assets (Assets less liabilities) acquired
\
Goodwill is not amortized because it is considered to have an indefinite life
Goodwill must be written down if its value has been permanently impaired
54
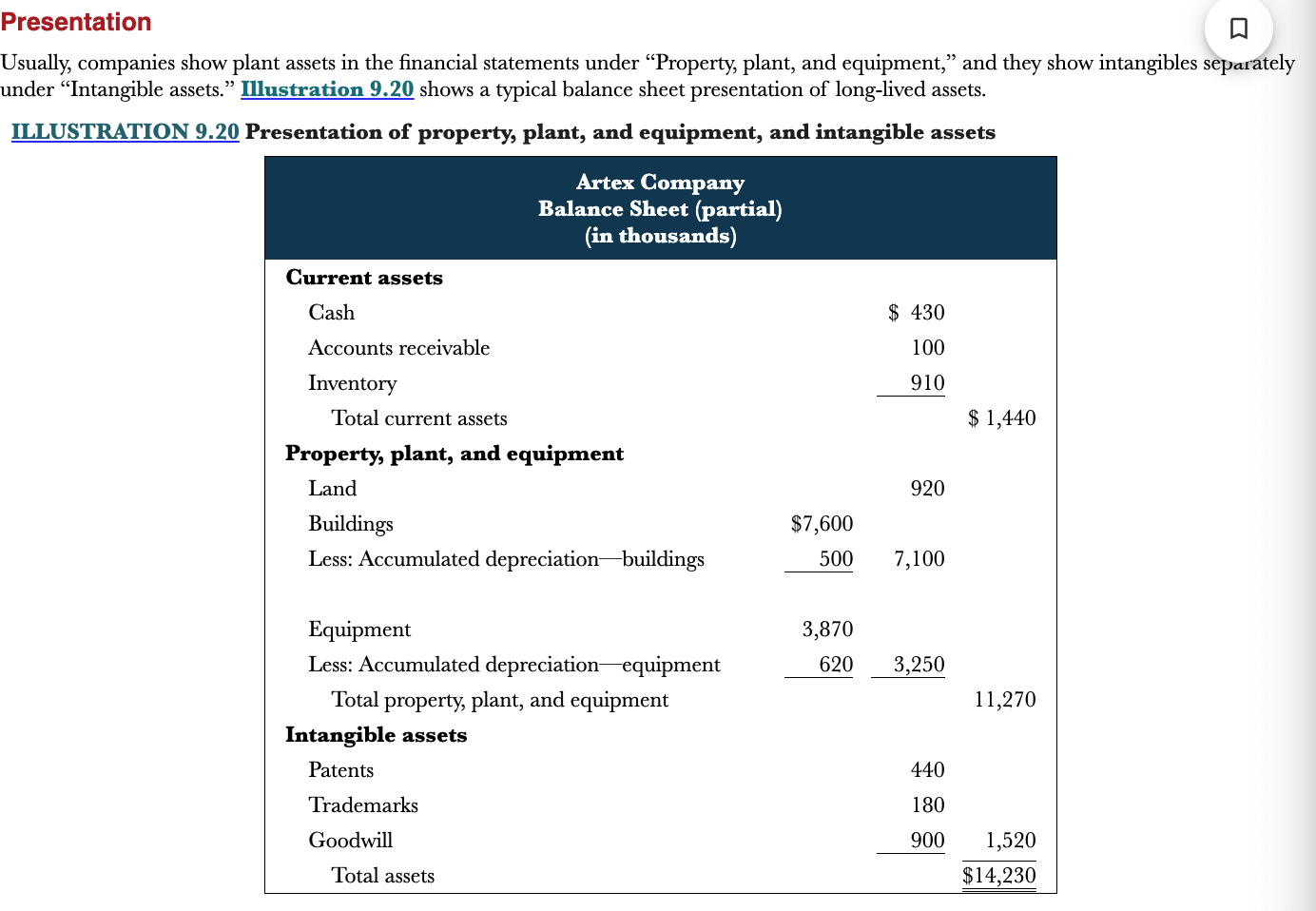
New cards
How are intangible assets shown in a typical balance sheet?
They are listed separately under “Intangible assets”
55
New cards
What are 2 measures to analyze plant assets?
Return on assets and asset turnovers

56
New cards
What is return on assets and how is it calculated?
An overall measure of probability
\
Computed by dividing net income by average total assets
* Average assets are calculated by adding the beginning and ending values of assets and dividing by 2
* Return on assets show the amount of net income generated by each dollar of assets. Thus, the higher the return on assets, the more profitable the company
\
Computed by dividing net income by average total assets
* Average assets are calculated by adding the beginning and ending values of assets and dividing by 2
* Return on assets show the amount of net income generated by each dollar of assets. Thus, the higher the return on assets, the more profitable the company

57
New cards
What are asset turnovers?
Indicates how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales, that is, how many dollars of sales a company generates for each dollar invested in assets
* Calculated by dividing net sales by average total assets
* Higher asset turnover means a company is generating more sales per dollar invested in assets
* Calculated by dividing net sales by average total assets
* Higher asset turnover means a company is generating more sales per dollar invested in assets

58
New cards
What is profit margin?
Measures the percentage of each dollar of sales that result in net income
* Calculated by dividing net income by net sales
\
Profit margin can be used to find return on assets by multiplying it with asset turnover
* Calculated by dividing net income by net sales
\
Profit margin can be used to find return on assets by multiplying it with asset turnover

59
New cards
How does the relationship with profit margin and asset turnover to increase return on assets?
1) Increase the margin it generates from each dollar of goods that is sells (the profit margin)
2) Increase the volume of goods that it sells (the asset turnover)
2) Increase the volume of goods that it sells (the asset turnover)