Suicide
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
ancient rome
lucieta was assaulted by dong og king of rome
sign of beauty
Was suicides acceptable
not for slaves because they technically devoted themselves to the empire
altruistic suicide
sacrifice for the greater “good”
suicide attempt
effort to die by suicide that may or may nor result in death
suicicde ideation
recurrent thoughts of dying
very common
Joiner’s interpersonal theory
people who die by suicide stand out or those with ideation or attempts
perceived burdensomeness
belief that one’s existence poses significant hardships to family friends or society
thwarted belongingness
feeling alienated from and a lack of connection or acceptance with others
aquired capability
people are born with intrinsic desire towards self-preservation
acting on suicidal behavior requited overcome their inherent drive to stay alive
acquired through repeated exposure to painful experiences that result in high levels of pain and tolerance and a fearlessness or lack of sensitivity to possibility of death
How does stigma affect people with suicide?
they don’t seek for treatment
preventive interventions
educational
risks, what you should watch for
attempts to destigmatize have been backfired and suggest it is understandable response to a stressful circumstance
Crisis interventions
hotlines and crisis centers
Non-suicidal self injury
any act that deliberately harms or damages one’s body but without the explicit desire to die by..
chronic NSSI
people cite numerous reasons:
to allevitae negative emotions
self punishment
to feel something when feeling numb
influence others
resist urge to harm self further— anti -suicide
sensation seeking, to generate excitement
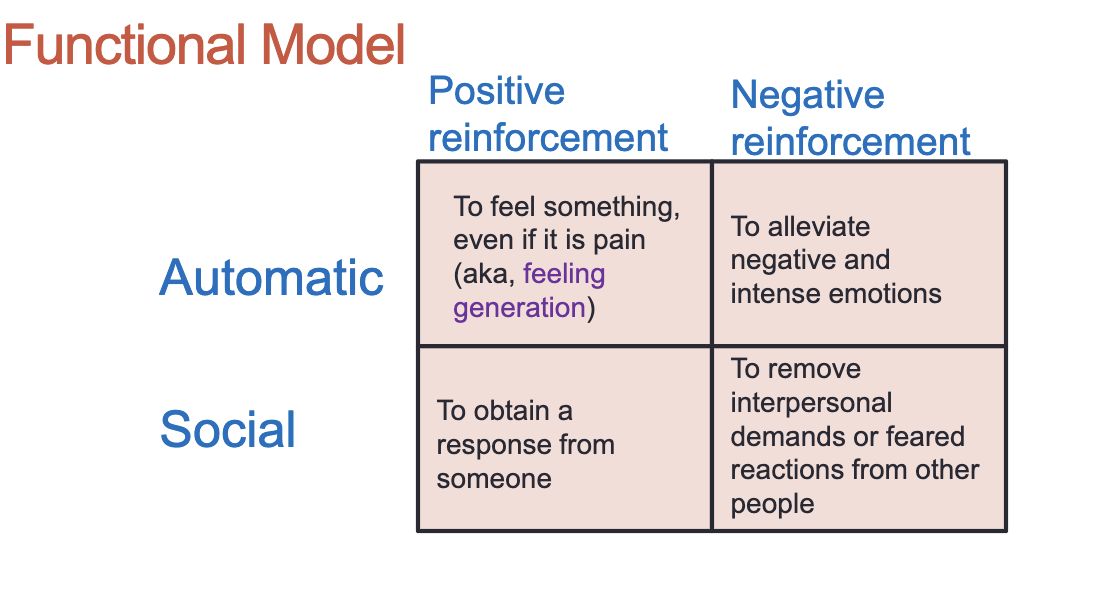
Nock & Prinstein’s Functional Model: why people self harm
automatic: to gain reinforcement by accomplishing something within oneself
social: to gain reinforcement by accomplishing something in relation to another person
the most common is automatic negative reinforcment
what is a way to alleviate change
self harm seems to be a strategy to regulate emotions
they do this because they cannot otherwise seem to change how they are feeling
What do individuals that chronically self injury show compared to those who don’t ?
differences in interoceptive awareness
How is pain processed in the brain?
the ACC acts as an “alarm system’
the insula perceives “how wrong” something is and the degree of it
Pain and the Brain
brain activates ACC and insula
surgeons used to remove sections of the ACC to alleviate chronic pain
people who are more sensitive to physical pain show greater activations of ACC and insula in brain scans
Is Sadness a pain in the ACC and insula?
yes
emotionally painful experiences are shown
same brain regions responsible for the sensation of physical pain are responsible for the processing of emotional pain
True or False: chromic self-injurers can withstand even more pain than usual when they are upset
TRUE
what happens when we expose chronic self-injurers to intense physical pain?
we see decreased activations in the ACC and insula (which is the opposite of what most have)
this effect is accentuated if we first induce distress of some kind in participants
suggests that NSSI alleviates rather than increases pain for some people
Treating NSSI
DBT was developed to address chronic self-injury
can be adapted to address NSSI in populations without borderline personality disorder
CBT and SSRIs are also effective