Chapter 11- Liquids and Ch 12- Solids
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Solids have ___ Kinetic energy
low
Solids have ___ attraction
high
liquids have ___ kinetic energy
an equilibrium of

liquids have ___ attraction
an equilibrium of

gases have ____ kinetic energy
high

gases have ___ attraction
low

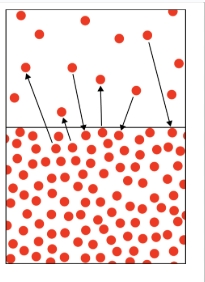
what must molecules do for a liquid to boil?
they must overcome the attraction from nearby molecules
high attraction = ____ boiling point = _____ for the molecules to break free
high; harder
Intramolecular bonds
covalent bonds
intramolecular bonds have _____ attraction
stronger
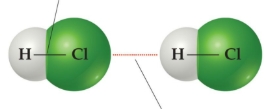
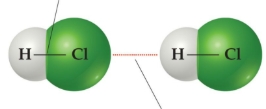
intermolecular bonds
between separate molecules
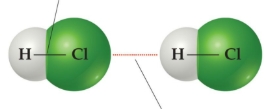
intermolecular bonds have _____ attraction
weaker
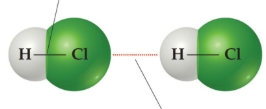
from coulomb’s law, we can tell this about intramolecular forces
stronger, shorter distances, usually full charges or strong electron sharing
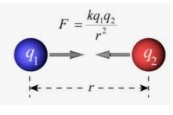
from coulomb’s law, we can tell this about intermolecular forces
weaker, longer distances, usually partial charges
Van der Waals IMFs include
London dispersion force and dipole-dipole force
order the IMFs from weakest to strongest
LDF (london dispersion)
D-D (dipole-dipole)
Hbond (hydrogen bond)
I-d (ion-dipole)
which force(s) can only be associated with ionic or non-neutral particles?
ion-dipole
which force is found in all molecules/atoms?
LDF
an LDF can best be described as
a temporary imbalance in the e- cloud
how does LDF create a dipole?
it’s instantaneous and occurs when the e-’s just so happens to be on the same side, causing a slightly more negative side and the nearby atom/molecule’s protons to be attracted to it
True or false: LDF’s can occur at long distances
false; only at short distances!
what is polarizability?
the distortion of the e- cloud
the _____ e-, the ____LDF
more; more
T/F: a molecule with a larger mass has a greater LDF compared to one with a smaller mass
True!
a molecule has a stretched-out (linear) shape! what happens to its LDF?
greater LDF
a molecule has a spherical shape! what happens to its LDF?
lesser LDF
which has a higher boiling point? butane (C4H10) or hexane (C6H14)?
hexane!
why does hexane have a higher bp than butane?
more mass!
isomers share
the same formula
isomers differ in
arrangement and properties
what’s true about an isomer/s molecular weight?
they’re the same!
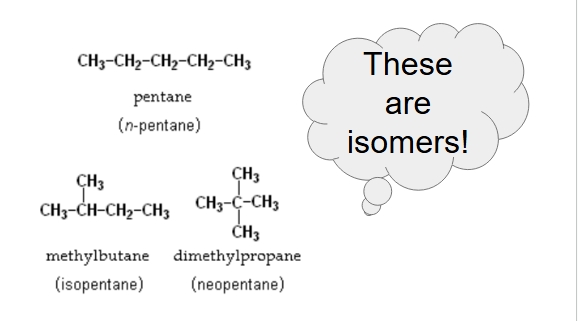
rank from lowest to highest bp
dimethylpropane, methyl butane, pentane
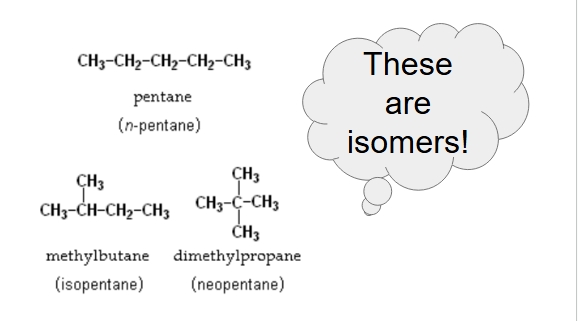
why does methyl butane have a higher bp than dimethylpropane although they have a similar molar mass?
it has a more linear shape
in dipole-dipole interactions, what is true about a dipole?
they are polar molecules with a more negative and a more positive end
negative and positive ends of a dipole are repelled or attracted?
attracted
the same charges of a dipole are repelled or attracted?
repelled
in D-D interactions, molecules with a similar mass and molar size/shape (LDF factors) have a higher bp when they are more
polar
what’s more important in considering IMFs: D-D or LDFs?
D-D if molecules are roughly the same size/shape; LDF if molecule is much larger than the other
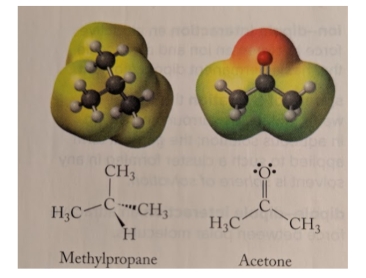
These two molecules have the same molar mass and roughly similar shapes. Which has a higher boiling point, and why?
acetone; it is more polar than methylpropane
which has a higher bp and why: ClCH2CH2Cl or CHCl2CH3
CHCl2CH3 because it has a greater dipole shift
in Hbonds, what will hydrogen be attracted to?
N, O, F
why do Hbonds form highly polar bonds?
due to the high electronegativities of N, O, and F
T/F: in order for a hydrogen bond to happen, F-H, O-H, or N-H bond in one molecule forms a H bond with F, O, or N in another molecule
true!
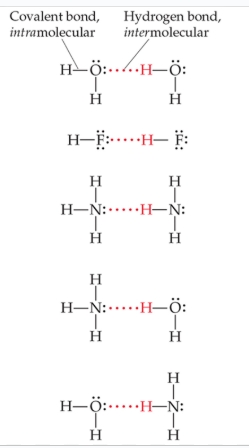
in an Hbond, what does the H on the first molecule have to interact with on the second molecule?
a lone pair of the second molecule
real-life examples of how Hbonds are important!
stabilize protein structures
forms ice rings
forms DNA double helix
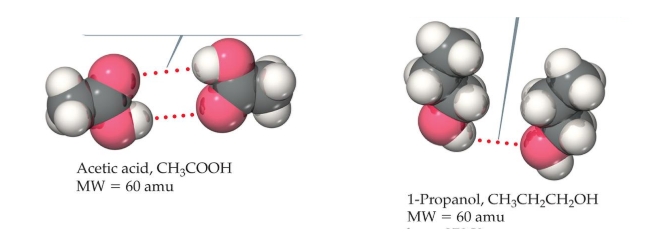
Which will have a higher boiling point, and why?
acetic acid; has more hydrogen bonds
Which of these will have a higher BP? Why?
CH3Cl or CH3Br
CH3Br; higher molar mass
Which of these will have a higher BP? Why?
CH3CH2OH or CH3OH
CH3CH2OH; molar mass, more spread out
(CH3)2NH or (CH3)3N, what has the higher bp?
(CH3)2NH; can form a hydrogen bond
Which of the following substances experiences…
The strongest dipole-dipole interactions?
H2NNH2
H2CCH2
Ne
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
H2NNH2
Which of the following substances experiences…
The largest London dispersion forces?
H2NNH2
H2CCH2
Ne
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
Which of the following substances experiences…
The lowest boiling point?
H2NNH2
H2CCH2
Ne
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
Ne; smallest mass, single atom
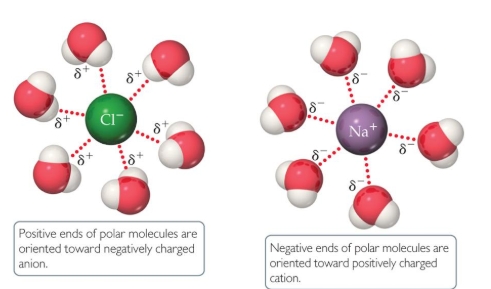
ion-dipole forces give good insight on how…
ionic compounds dissolve in water
ion-dipole explained
negative end of polar liquid is attracted to positive end of ion; positive end of polar liquid is attracted to negative end of ion