Earth Interior - The Earth and the Environment
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are Earth’s layers defined by composition?
Crust, Mantle, & Core
What are Earth’s layers defined by Physical Property?
Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer Core, & Inner Core
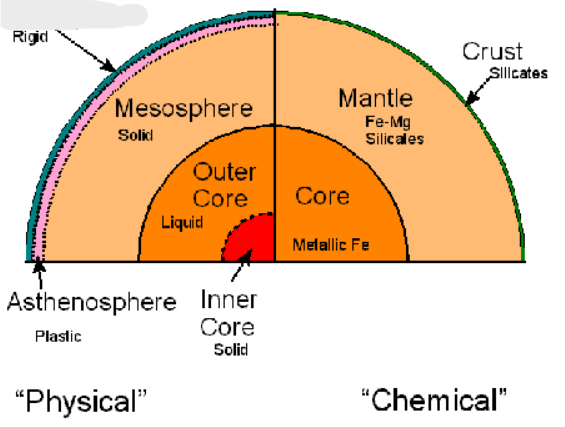
What is the first layer of the Earth’s Physical layers
Lithosphere
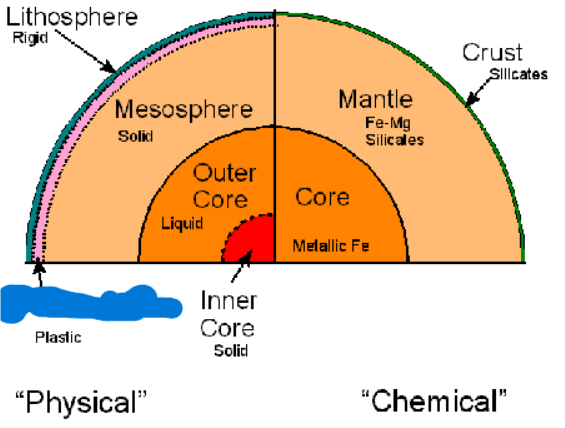
What is the third layer of the Earth’s Physical layers? It is at 660-2900 km. It is a rigid layer due to increased pressure.
Mesosphere
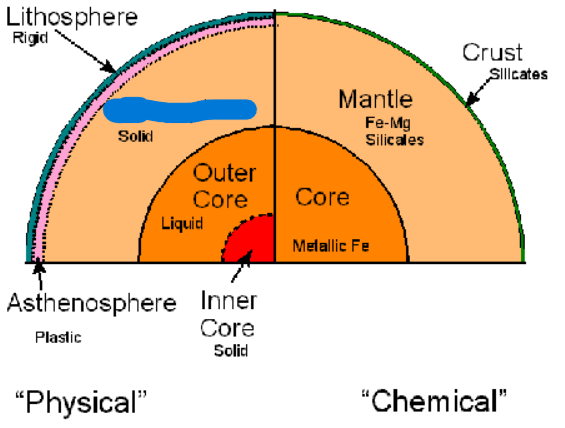
What is the second layer of the Earth’s Physical layers? It is at a depth of roughly 600 km. It is a softer and weaker layer.
Asthenosphere
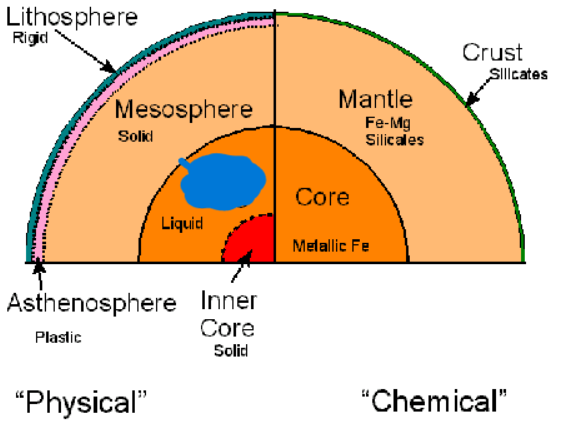
What is the fourth layer of the Earth’s Physical layers? It is 2,300 km thick. It is a liquid layer composed of an iron-nickel alloy and generates the magnetic field around the Earth.
Outer Core
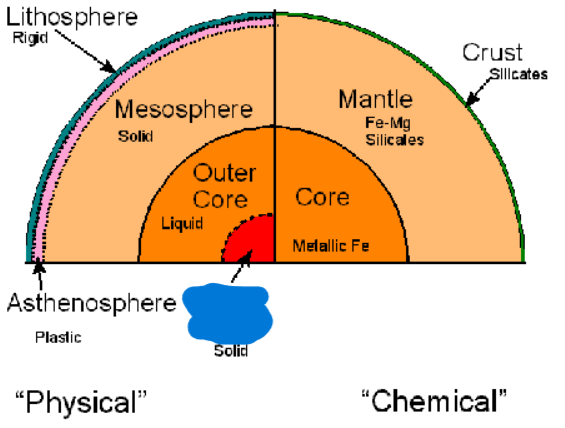
What is the lowest layer of the Earth’s Physical layers? It is 1,200 km thick. It is a solid layer of iron.
Inner Core
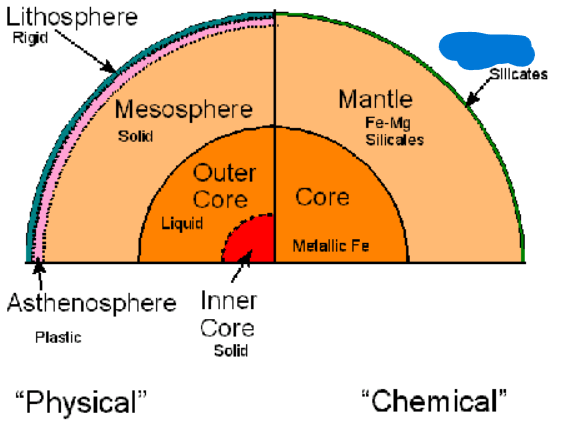
What is the first layer of the Earth’s Compositional layers? It is 3-70 km thick. It is a thick, rocky shell on the outer shell of the Earth.
Crust
This part of the crust is thicker at 40 km and less dense at 2.7 g/cm³. It is comprised of Felsic materials.
Continental Crust
This part of the crust is thinner at 5 km and more dense at 3 g/cm³. It is comprised of Mafic materials.
Oceanic Crust
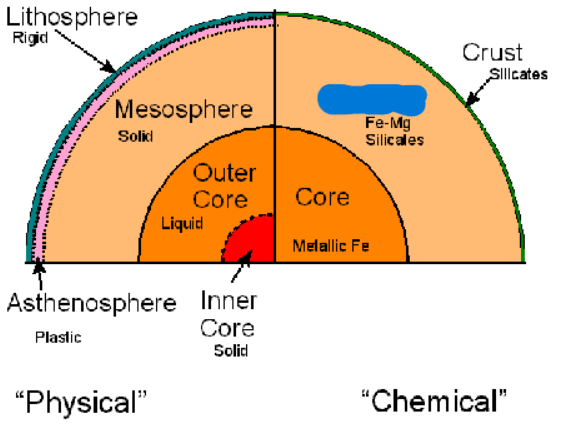
What is the second layer of the Earth’s Compositional layers? It is 2900 km thick and 3.2 - 5 g/cm³ dense. It is the largest layer in the Earth. It is made of silicate rocks with magnesium and iron. It is made of Ultramafic materials
Mantle
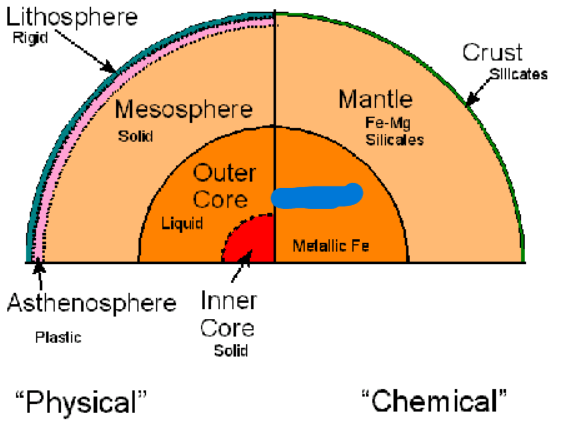
What is the third layer of the Earth’s Compositional layers? It has a 3500 km radius and a density of 10.8 g/cm³. It is made of iron-nickel alloy (90-95% iron/ 5-10% nickel).
Core
How do scientists know what’s in the core of the Earth?
Sampling the crust and mantle, studying meteorite composition and seismic waves.
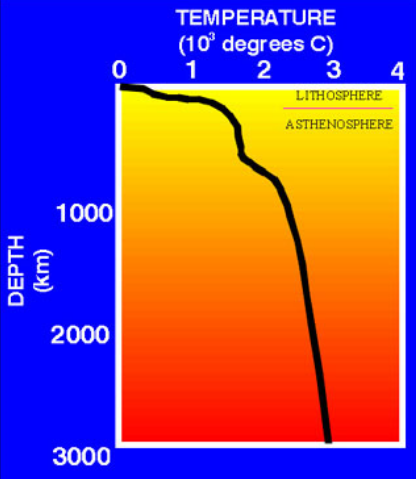
At what rate does Earth’s temperature increase with depth?
25o C per km
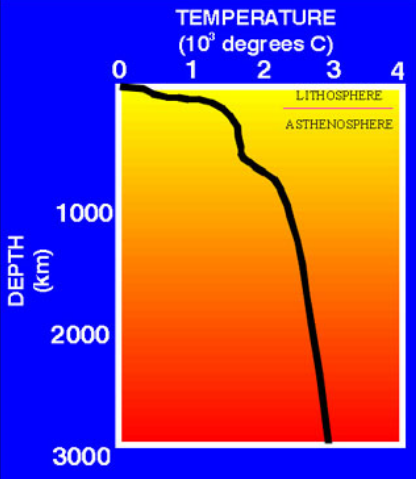
What is the Geothermal gradient?
The rate the Earth’s temperature increases with depth.
What is the source of Earth’s internal heat?
Residual heat from asteroids from Earth’s early history
Radioactive decay from isotopes
Iron Catastrophe (friction)
Compression of rock material due to gravity
Internal Heat drives…
volcanoes, mountain building, plate tectonics, the magnetic field, and mantle convection
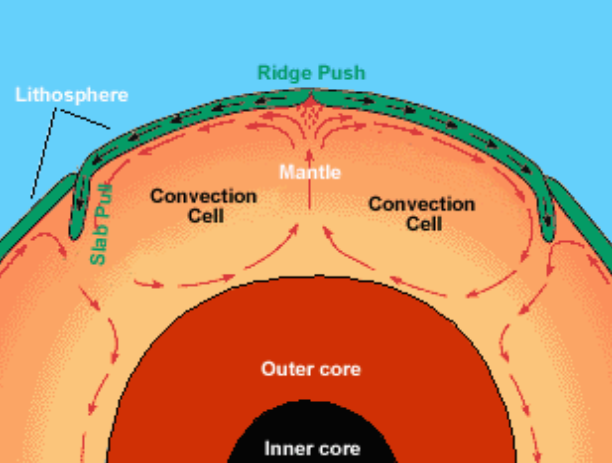
In mantle convection, hot, less dense material….
rises from the mantle
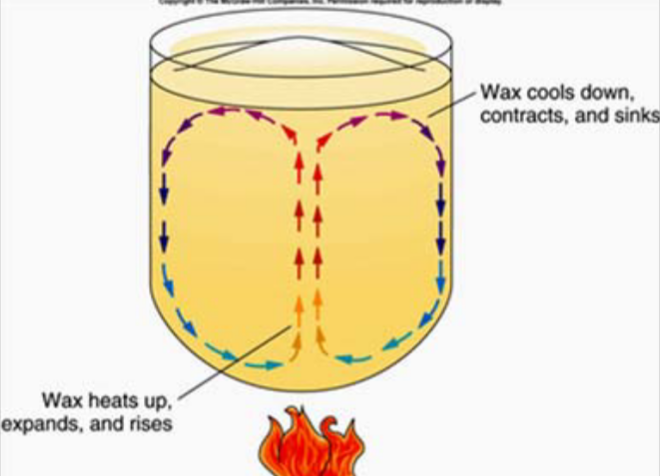
In mantle convection, cool, more dense material….
Sinks from the crust
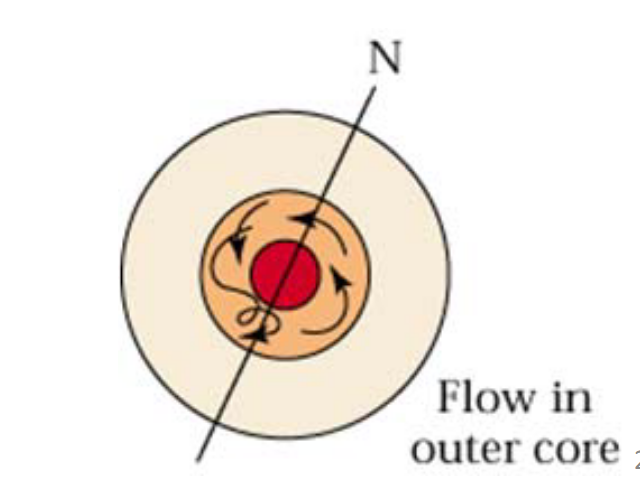
How does internal heat create Earth’s magnetic field?
The liquid iron nickle outer core convects around the solid inner core.
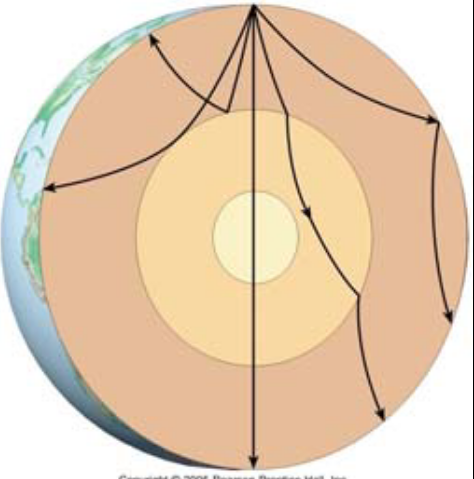
Seismic waves are not straight as they traverse the Earth because…
The waves refract through different properties
Which seismic wave compresses and expands & can travel through liquids and solids. These waves are faster than their counterpart.
P-waves or compressional waves
Which seismic wave moves up and down & can travel through only solids. These waves are slower than their counterpart.
S-waves or shear waves
How old is the Earth?
4.6 billion years old
What was Earth’s early composition like?
It was similar to meteorites
The meteorites that are compositionally similar to Earth contain 35% iron, while Earth’s surface only contains 6%. What happened to this extra iron?
Due to iron’s density and gravity, the liquefied iron sunk to the center of the Earth.

Are you geeked or locked in?
you better lock in