DNA mutations and DNA repair mechanisms
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What is a mutation?
a change in a genetic sequence of an organism
Where do mutations typically appear?
not in every cell - most multicellular organisms are mosaics
What is a point mutation?
the change of a singular nucleotide for another
What are point mutations also often called?
single nucleotide variant (SNV)
State the 2 purines
guanine and adenine
State the 3 pyrimidines
thymine, cytosine, uracil
Transitions
purine → purine
pyrimidine → pyrimidine
Transversions
purine → pyrimidine
pyrimidine → purine
Insertion mutation
extra basepair(s) inserted
Deletion mutation
basepair(s) removed
What is the umbrella term for insertion and deletion mutations?
indel
List 3 diseases caused by point mutations
sickle-cell disease: GAG is mutated to GTG and glutamic acid becomes valine
many cancers
color blindness
List 1 disease caused by insertion mutations
huntington’s Disease - abnormal region of CAG repeats
List 1 disease caused by deletion mutations
duchenne muscular dystrophy
List 1 disease caused by frameshift mutations
crohn’s disease
What is a chromosomal mutation?
where a portion of a chromosome is changed
List the 5 types of chromosomal mutation
deletion
duplication
inversion
insertion
translocation
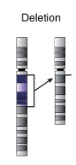
Chromosomal deletion
portion of chromosome is deleted
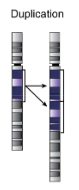
Chromosomal duplication
portion of chromosome is duplicated and attached
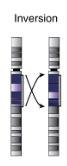
Chromosomal inversion
portion of chromosome is removed, flipped around, and reinserted
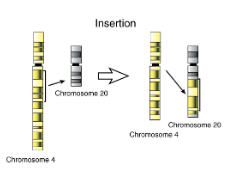
Chromosomal insertion
addition of a portion of one chromosome to the end of another
Chromosomal translocation
two portions of two chromosomes are removed and swapped
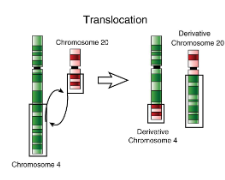
What is Robertsonian translocation?
a form of translocation that results in one extra long and one extra short chromosome
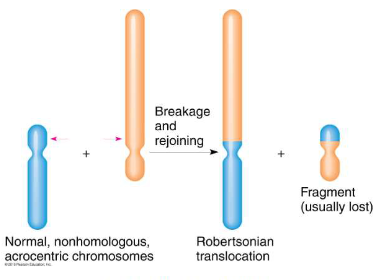
Where does Robersonian translocation occur?
within acrocentric chromosomes
What are acrocentric chromosomes?
Chromosomes who’s centromeres are located further to one end as opposed to in the middle
List 2 syndromes that can arise as a result of Roebrtsonian translocation
down’s syndrome
patau’s syndrome
Polyploidy
a general term for when a cell has more than one set of chromosomes (humans are diploidy)
Polysomy
a case of aneuploidy: having the wrong number of chromosomes
What is triploidy?
where cells have 3 copies of a genome
List 3 trisomy syndromes
down’s syndrome
edwards’s syndrome
patau’s syndrome
What are whole genome duplication caused by?
non-disjunction during meiosis
How has whole genome duplication served as an important mechanism of evolution?
allows duplicated genes to acquire new functions
What organisms are whole genome duplication common in?
plants
Give an example of whole genome duplication in plants
einkorn wheat has 14 chromosomes
after hybridisation with a grass tetraploid (four copies per chromosome) -> Durum wheat
another hybridisation event makes it hexaploid → Bread wheat
How does whole genome duplication cause larger fruits?
more chromosomes need larger nuclei and cells → larger fruit
How many copies of its genome do strawberries have?
8 - octoploid
What is colchine?
a chemical that causes meiosis failure and can induce genome duplication
What can colchine be used for?
commercial farming
Lethal mutations
mutations that can / will result in death
Conditional mutations
a mutation that only expresses itself under certain environmental conditions
Null mutation
results in the absence of coded protein
Dominant negative mutations
genetic mutations that create proteins that interfere with the normal function of wild-type proteins
Suppressor mutations
a second mutation that counteracts the effects of a previous mutation
Silent mutation
mutations, or changes, to a gene's DNA sequence that have no effect on the amino acid sequence coded for by that gene
Why do silent mutations occur?
as a result of the degenerative nature of genetic code
Nonsense mutation
a DNA sequence change that results in a premature stop codon, or nonsense codon, in the transcribed mRNA
What is depurination?
removal of a purine base from a nucleotide
How frequent is depurination in mammalian cells?
18,000x in 24 hours
What is deamination?
removal of an amino acid from a nucleic base
What can a deaminated cytosine turn into?
uracil
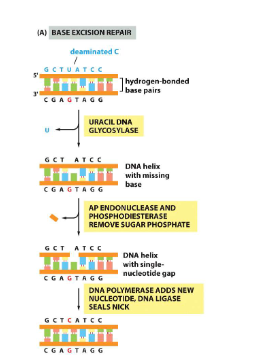
Base excision repair (4 steps)
DNA glycosylases remove the damaged base
AP endonuclease then excises the empty sugar phosphate backbone
DNA nuclease adds new nucleotide with correct base
DNA ligase seals nick
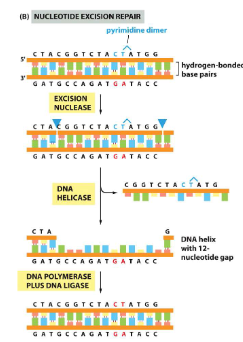
When is nucleotide excision repair needed
For larger mutations such as dimers caused by UV exposure
Nucleotide excision repair (4 steps)
multi-enzyme complex scans DNA and cuts phosphate backbone on either side
DNA helicase removes piece of DNA between single strand cuts
DNA polymerase fills in
DNA ligase seals nick
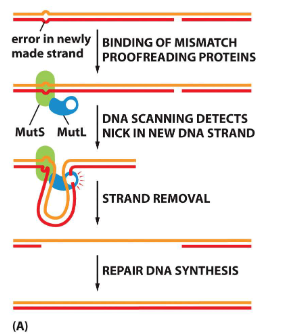
How does mismatch repair work? (3 points)
new strand contains nicks
repair complex scans DNA for nicks and removes new strand starting at nick and including wrong base
DNA polymerase and ligase fill and seal gap.
List 2 methods of repairing double strand breaks
non homologous end joining
homologous recombination
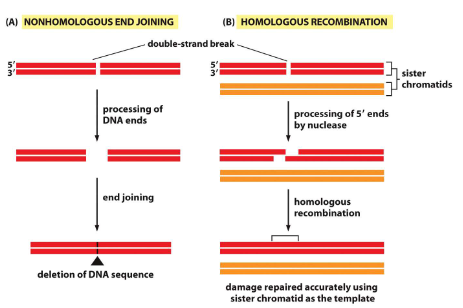
List 2 issues with non-homologous end joining
introduces mutations
often involve loss of DNA
List 2 mutations that may arise as a result of non-homologous end joining
indel
chromosomes with two/no centromeres
Why is it okay that non-homologous end joining is predominant in humans? (3 points)
98% of genome is non-coding
works within cell cycle
crucial for VDJ joining (important in lymphocytes)
NHEJ scars count
by age 70 the average somatic cell genome has 2,000 NHEJ scars
What does homologous recombination require?
sister chromatids to use as templates
When does homologous end joining occur?
just after DNA replication
Why is homologous recombination more accurate?
collision of two complimentary strands result in annealing of bases - rapid zippering
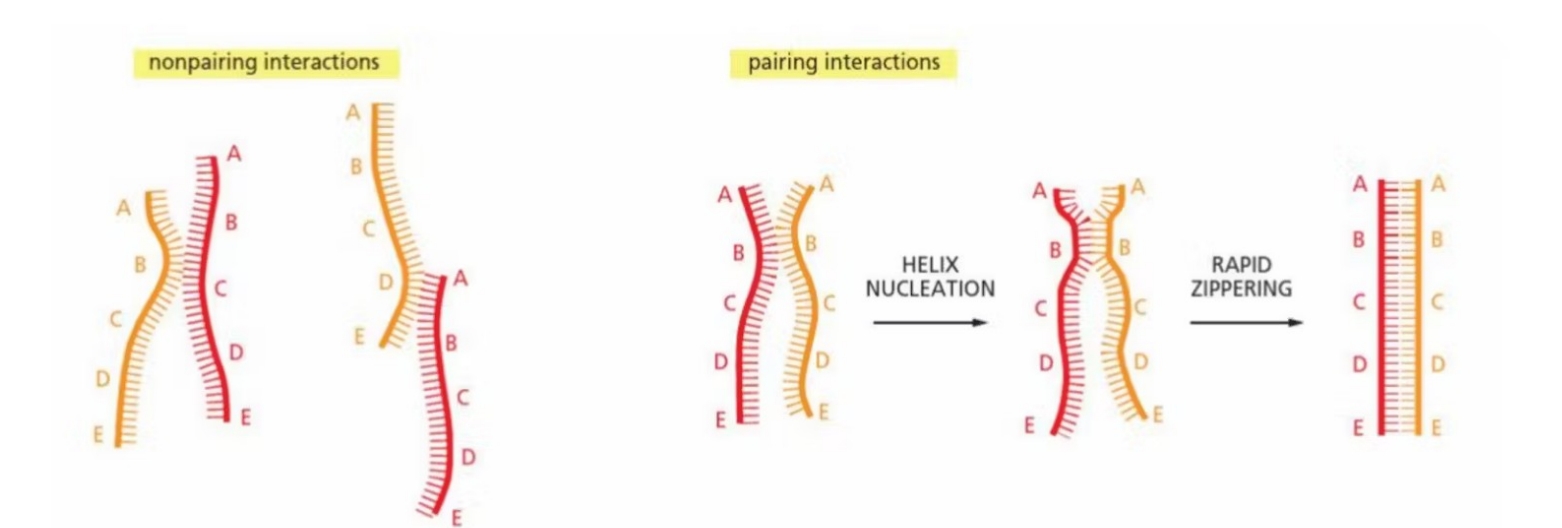
What can homologous recombination result in?
a heteroduplex
What is a heteroduplex
a piece of DNA double strand from two different DNA molecules
Homologous recombination: step 1
nuclease resect 5’ strands to create overhangs
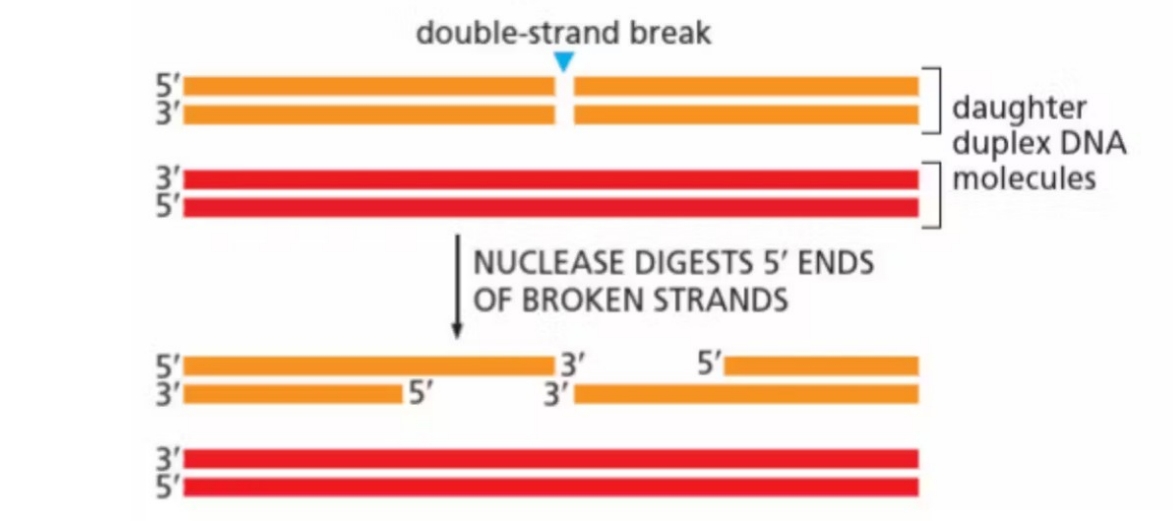
Homologous recombination: step 2
overhang invades sister chromatid through base pairing
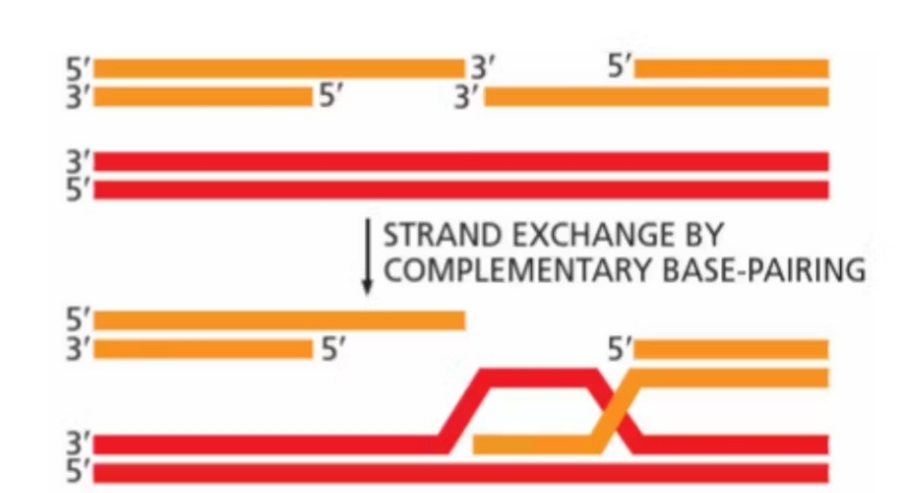
Homologous recombination: step 3
DNA polymerase extends broken strand using undamaged sister chromatid DNA as template
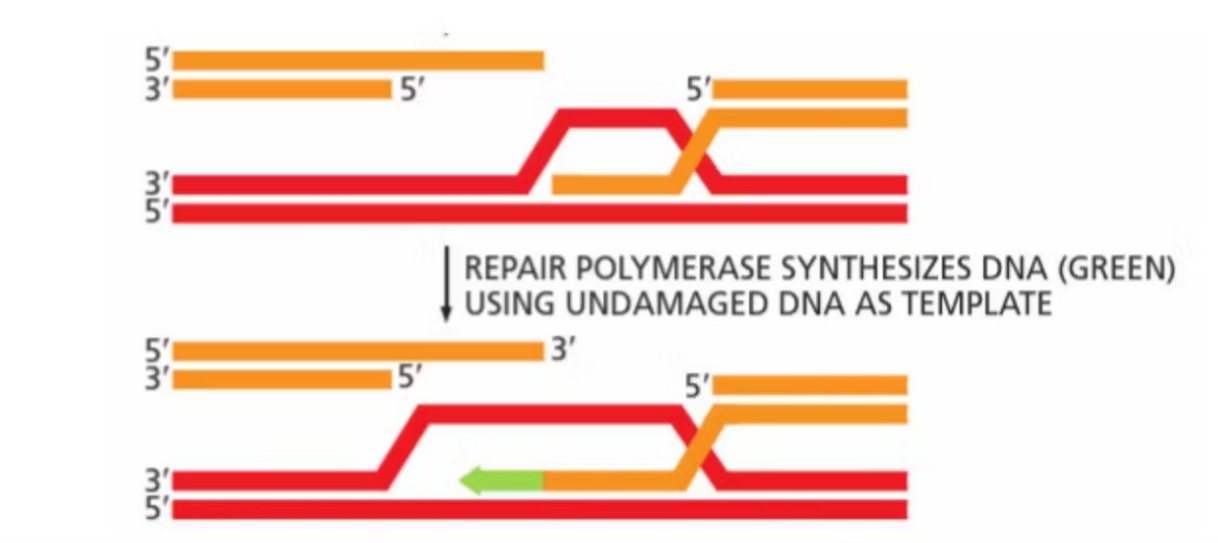
Homologous recombination: step 4
extended single strand pairs up again with original complimentary strand
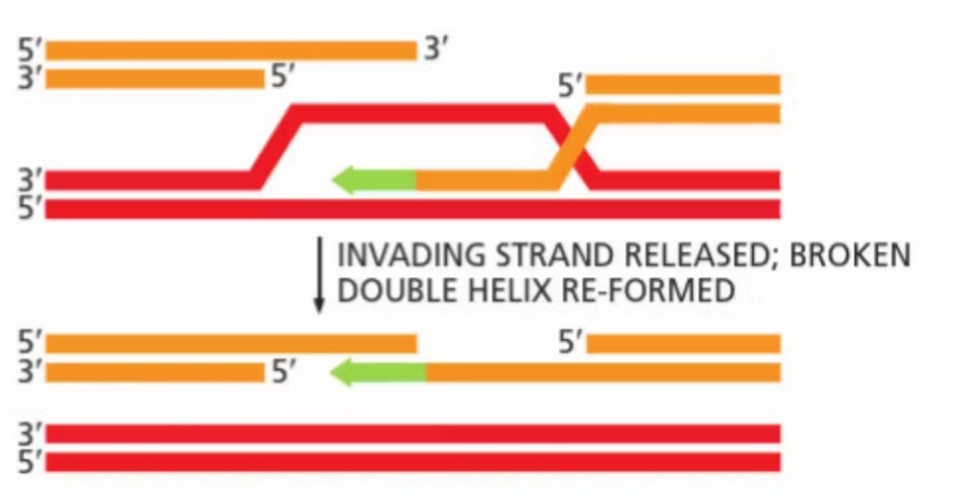
Homologous recombination: step 5
gaps are filled
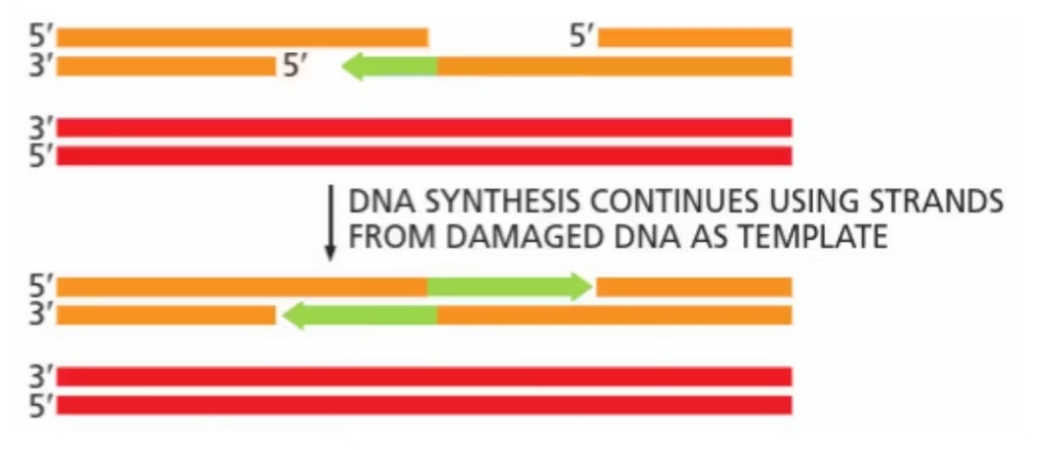
Homologous recombination: step 6
DNA ligase seals nicks
What is CRISPR?
an adaptive immune response to phage attacks in bacteria
How can CRISPR be used for genome editing? (2 points)
needs synthetic guide RNA to target a specific genome region
Cas9 protein cuts target DNA
List 2 methods of genome editing using CRISPR
DNA repairs through NHEJ
homologous recombination
State an issue with using NHEJ for genome editing
creates indel mutations
State two advantages to using HDR for genome editing
allows targeted insertion of DNA
allows insertion of tags
List 2 diseases that affect DNA repair machinery
Werner syndrome
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency
List 4 symptoms of Werner syndrome
premature ageing
osteoporosis
type 2 diabetes
hair thinning
State the affected gene in Werner syndrome
WRN RecQ like Helicase
What is the role of the affected gene in Werner syndrome?
double strand break repair (homologous recombination)
State two symptoms of SCI
increased susceptibility to infection
B and T cell deficiency
State the affected gene in SCI
ARTEMIS
What is the role of the affected gene in SCI?
double strand break repair in somatic VDJ recombination