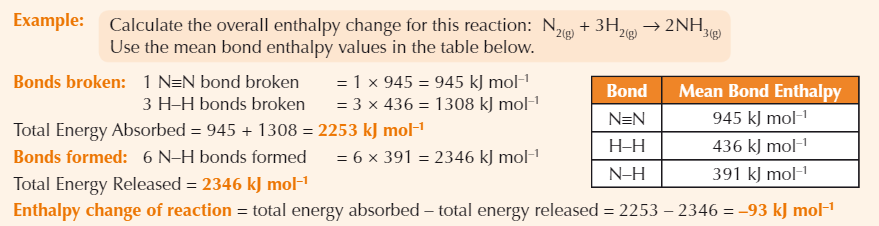3.1.4 - ENERGETICS
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Enthalpy change
The heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant pressure
Symbol: ΔH
Units: kJ mol⁻¹
Standard conditions
Pressure: 100kPa
Temperature: stated in method
What does ΔH⦵ mean?
Substances in standard states and measurement made under standard conditions
Exothermic reaction
Give out energy
Negative ΔH
Temp increases
Endothermic reaction
Absorb energy
Positive ΔH
Temp decreases
Standard enthalpy of combustion
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen under standard conditions
Standard enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
How do you find the enthalpy of combustion of a liquid?
To find enthalpy of combustion of flammable liquid, burn it in calorimeter
As fuel burns, it heats water → can calculate heat energy absorbed by water using mass of water, temp change and specific heat capacity
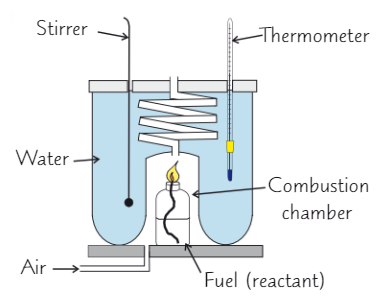
Why are enthalpy of combustion values often inaccurate?
Heat lost to surroundings
Some incomplete combustion
Some fuel lost to evaporation (flammable liquids often volatile)
How do you measure enthalpy changes in solution?
Calorimetry can be used to find enthalpy change for reactions in solutions, such as neutralisation, dissolution (dissolving), displacement
To find enthalpy change of neutralisation reaction, add a known volume of acid to insulated container (e.g. polystyrene cup) and measure temp
Add known volume of alkali and record temp at regular intervals (stir solution to distribute heat)
Find temp change for experiment
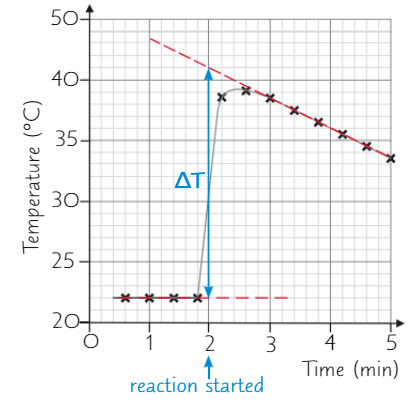
How do you use a graph to find temperature change?
During experiment, record temp at regular intervals, starting 3 mins before reaction begins
Plot graph of results - draw two lines of best fit: one through points before reaction started, and one through points after it started
Extend both lines so they both pass the time the reaction started
Distance between two lines at time when reaction started = accurate temp change
Formula for enthalpy change
q = mcΔT
What does each symbol in enthalpy equation stand for?
q = heat lost/gained (J)
m = mass of water/other solution (g)
c = specific heat capacity of water (4.18 J g-1 K-1)
ΔT = temp change (K)
Hess’s Law
Total enthalpy change of reaction is independent of the route taken
Hess’s Law example

Calculating enthalpy change using enthalpy of formation
Need to know ΔfH⦵ of all reactants + products that are compounds
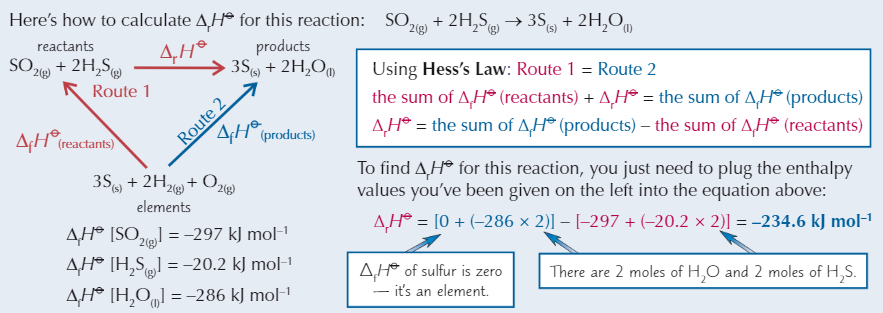
Hess’s Law equation
ΔrH⦵ = sum of ΔfH⦵ products - sum of ΔfH⦵ reactants
Calculating enthalpy change using enthalpy of combustion
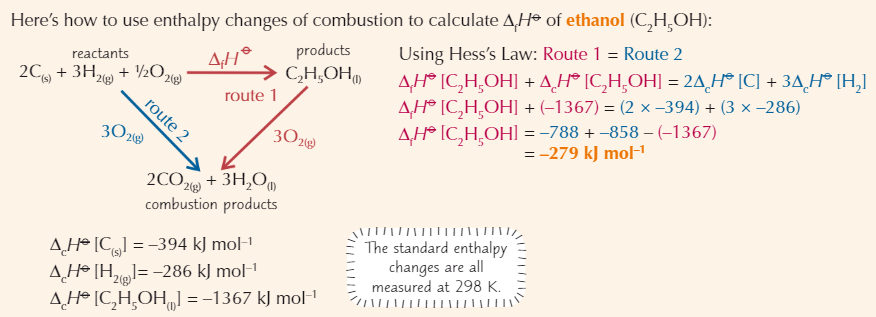
Hess’s Law diagram with backwards arrow example

Bond breaking
Endothermic - requires energy to break bonds
ΔH positive
Stronger bonds take more energy to break
Bond making
Exothermic - releases energy by breaking bonds
ΔH negative
Stronger bonds release more energy when they form
Bond enthalpy
The energy required to break bonds
Mean bond enthalpy
Average energy needed to break a certain type of bond, over a range of compounds
Always positive - breaking bonds = endothermic

Bond enthalpy variation
Energy needed to break a bond depends on its environment → same type of bond may require different amounts of energy to break
Enthalpy change of reaction formula
Enthalpy change of reaction = total energy absorbed - total energy released
Example bond enthalpy calculation