unit 2: pollution and energy - honors earth & environmental science FINAL
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
municipal solid waste
non-liquid waste generated by homes and businesses
industrial solid waste
waste generated by the production of consumer goods in factories, mining, agriculture, etc.
hazardous waste
solid or liquid waste that is corrosive, toxic, flammable, or highly reactive.
waste water
water that is used from sinks, showers, washing machines, etc.
biodegradable
material that can be broken down by naturally occurring decomposers in the environment
non-biodegradable
synthetic material that is unable to be broken down.
surface water
freshwater above ground in lakes, rivers, etc.
groundwater
freshwater that soaks into soil and is stored in tiny spaces underground
aquifers
underground rock layers where groundwater is stored
water stress
occurs when the demand for water exceeds the supply
freshwater pollution
the introduction of chemical, physical, or biological agents into water that degrades the water and affects the organisms dependent on it.
point pollution
pollution that is discharged from a single source, which makes it easy to trace and, therefore, control.
non-point pollution
pollution that comes from many different sources, which results in it being difficult to trace and control.
biological magnification
an effect of water pollution: pollutant concentration increased in the bodies of living organism along each step of the food chain.
artificial eutrophication
an effect of water pollution: the overabundance of nutrients in a body of water. rapidly accelerates the growth of plants like algae (called an algal bloom)
oxygen depletion
an effect of water pollution: the reduction in the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water. an algal bloom can cause this, which suffocates other organisms.
thermal pollution
excessive amounts of heat are added to a body of water.
oil pollution
an excessive amount of oil is added to a body of water, like a river or ocean. river flows can add oil to an ocean, as well. caused by human activity, is harmful to aquatic organisms
air pollution
occurs when harmful substances end up in the air at unhealthy levels
primary pollutants
pollutants that are put directly into the air by humans
secondary pollutants
formed when a primary pollutant comes in contact with another primary pollutant or a naturally occurring substance.
macroplastics
plastics larger that 0.5 cm
microplastics
plastics smaller than 0.5 cm. result from the breakdown of waste.
renewable sources
can be replenished at the rate they’re used
non-renewable sources
cannot be replenished at the rate they’re used. take millions of years to form, and are harmful to the environment.
what does the waste stream include?
municipal solid waste, industrial solid waste, hazardous waste, and waste water.
how is waste managed?
open dumps: waste is left out in the open to contaminate the environment
sanitary landfills: waste is buried or piled in places engineered to keep the waste from contaminating the environment
incineration: waste is burned in large furnaces
how is waste reduced?
recycling: the reprocessing of discarded materials into new products.
composting: a proces by which organic matter is biologically decomposed, under controlled conditions, into soil conditioner
biological degradation: the process by which microorganisms break down organic material under anaerobic conditions
waste reduction: the avoidance of producing waste
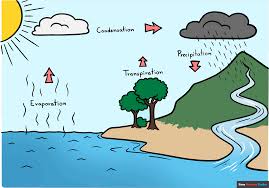
what is the water cycle?
the process by which water is circulated, which makes it a renewable resource
evaporation: water goes from liquid to gas form (water vapor)
condensation: water vapor condenses back into liquid
precipitation: water falls to the ground from the atmosphere. ex.: rain, hail, snow
transpiration: the loss of water vapor through plant stomata, which cools them down in hot weather (plant sweating)
what are the kinds of freshwater pollutants?
pathogens: disease causing organisms
organic matter: biodegradable remains of animals and plants
organic chemicals: pesticides, fertilizers, plastics, detergents, gasoline, and oil
inorganic chemicals: acids, salts, and toxic metals
toxic chemicals: chemicals that are poisonous to living things. ex.: heavy metals, household chemicals
physical agents: heat and suspended oil
radioactive waste: from power plants and nuclear processing.
what are the kinds of ocean pollution?
oil pollution
plastic polluton
what are the effects of water pollution?
biological magnification
artificial eutrophication
oxygen depletion
thermal pollution
what are the kinds of primary air pollutants?
carbon monoxide (CO)
nitrogen oxides (NOx)
sulfur dioxide (SO2)
volatile organic compounds: organic compounds that evaporate easily at room temperature
particulate matter
lead (Pb)
mercury (Hg)
what are the kinds of secondary pollutants?
ground-level ozone (O3)
smog: air pollution that hands over urban areas and reduces visibility
acid precipitation: forms when water in the atmosphere comes in contact with SO2 and NOx
how is plastic pollution harmful?
plastics have the potential to move around the world, far from where they were discarded, and quickly, by currents at sea
animals can be harmed by plastics
animals can accidentally eat plastics after mistaking them for real food
animals can be physically restricted by plastics
animals can by harmed by chemicals plastics leech into the water
plastics can degrade and damage animal habitats
what is the law of conservation of energy?
the law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
what are common non-renewable energy sources?
oil
natural gas
coal
nuclear energy
what are common renewable energy sources?
solar power
hydroelectric/tidal power
wind power
biomass
geothermal energy