Cognitive Psychology Chpt. 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
observe
record
hypothesize
analyze
report
scientific method steps
cognitive psychology
the science of how the mind is organized to produce intelligent thought and how the mind is realized in the brain
intellegence
the ability to recall facts, solve problems, reason, learn and use language
intellectual curiosity
Implications for other fields
Practical applications
Motivations for studying cognitive psychology (3)
empiricism
position of philosophical thought that posits all knowledge comes from experience (Locke, Berkley)
nativism
position of philosophical thought that posits knowledge is innate (Descartes, Kant)
introspection
a methodology much practiced at the turn of the 20th century in Germany that attempted to analyze thought into components through self-analysis
behaviorism
theory that psychology should be concerned only with behavior and not refer to mental constructs underlying behavior
Gestalt Psychology
an approach to psychology that emphasizes principles of organization that result in holistic properties of the brain that go beyond the activity of their parts
cognitive revolution
broad movement in psychology beginning in the 1950s moving away from behaviorism and toward the scientific study of cognition
Research on human performance
computer (AI) development
linguistics - study of language structure
3 main influences of the cognitive revolution
information theory
abstract way of analyzing the processing of info
cognitive science
feild that attempts to integrate research efforts from psychology, philosophy, linguistics, neuroscience, and AI
information processing approach
an analysis of human cognition into a set of steps for processing an abstract entity called “information”
no reference to the brain
processing of information has a highly symbolic character
comparable to computer processing
measurement of time to make decision is critical, happens in discrete stages
4 features of classic information processing approach
replicability crisis
in psychology (and other fields), finding that experimental results with a p value below .05 are not replicated with the experiment is repeated
Sternberg paradigm
an experimental procedure in which participants are first presented with a memory set consisting of a few items and then must decide whether various probe items are in the memory set
encode (perceive)
compare to memory set
make decision
generate response
4 steps of the Sternberg paradigm
dualism
a philosophical position that posits the mind and body are separate kinds of entities
cognitive neuroscience
the study of the neural basis of cognition
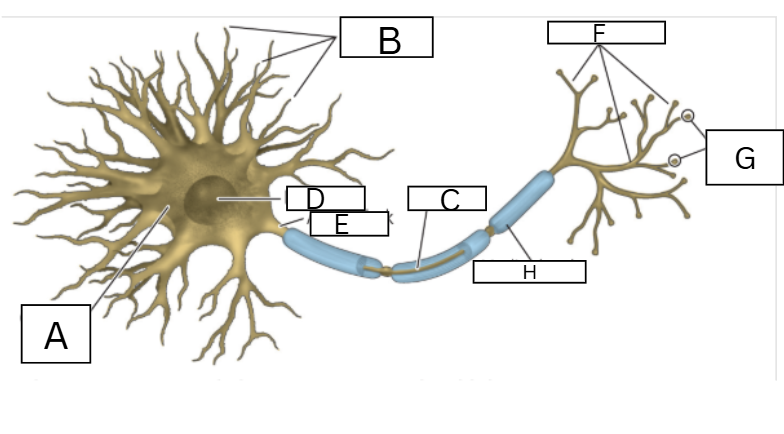
neuron
cell that receives and transmits signals through electrochemical activity
synapse
the gap between a terminal bouton of the axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron
neurotransmitter
chemical that crosses the synapse from the axon of one neuron and alters the electric potential
dendrites
short branches attached to the soma of a neuron that form synapses with the terminal boutons of axons of other neurons; they act as an input radar system
soma
cell body of a neuron made up of cell parts and fluid
axon
long tube extending from the soma of a neuron and branching into terminal boutons that form synapses with dendrites of other neurons, provides the fixed path by which neurons communicate with each other
releasing neurotransmitters
neurons communicate by….
excitatory synapses
synapse in which the neurotransmitter released by the terminal bouton of the axon decrease the potential difference across the membrane of the dendrite of the receiving neuron
inhibitory synapses
synapse in which the neurotransmitter released by the terminal bouton of the axon increase the potential difference across the membrane of the dendrite of the receiving neuron
action potential
a sudden change in electrical potential that travels down the axon of a neuron
a. soma
b. dendrites
c. axon
d. nucleus
e.axon hillcock
f. arborizations
g. terminal boutons
h. myelin sheath
Name the parts of the neuron
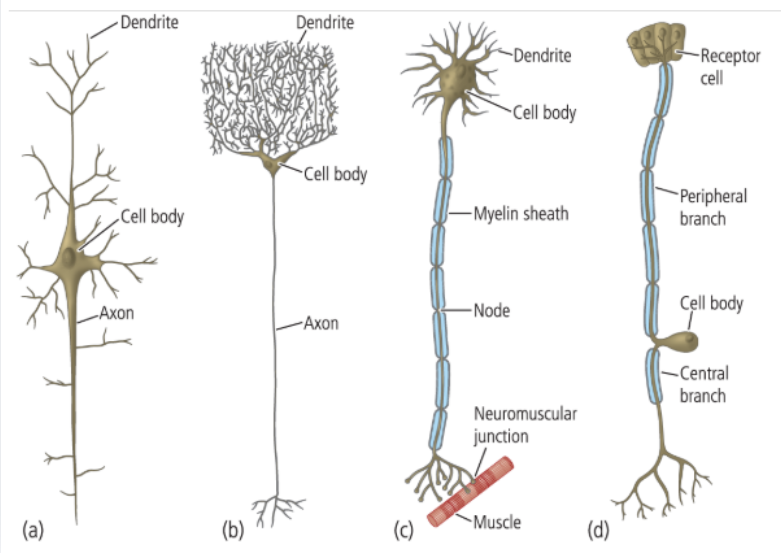
a. pyramidal cell
b. cerebellar Purkinje cell
c. motor neuron
d. sensory neuron
Name the types of neurons
membrane potential can be more or less negative
rate of firing - the number of action potentials an axon transmits per second
2 quantities of neural representation of information
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
spinal cord
part of the central nervous system that carries motor messages from the brain to the muscles and sensory messages from the body to the brain
neocortex
part of the cerebral cortex and the most recently evolved portion of the brain, associated with our panda mind or Kahneman’s system 2
cerebral cortex
outer layers of the brain consisting mainly of neocortex but also other more primative structures
gyrus
outward bulge of the cerebral cortex
sulcus
an inward crease between gyri
primative
lower brain parts closer to the brain are more _______
medulla
lower brain part that maintains homeostasis
cerebellum
lower brain part that coordinates smooth movement (walking, talking, etc.)
pons
lower brain part that connects the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
midbrain
brain part that uncounsiously detects motion, orients visual and audiotory perceptions, and is associated with instincts
higher species
high brain parts only develop in …
hypothalamus
higher brain part responsible for mamilllian instincts like sex, hunger, and puberty
pituitary
higher brain part responsible for releasing hormones and thermoregulation
optic nerve
higher brain part responsible for taking in visual stimuli
cognition
all processes by which the sensory input is transformed, reduced, elaborated, stored, recovered, and used (Neisser)
Mid 1960s
cognitive psychology is born/formalized in ____
doctrine that states that the brain is made up of individual units, the ____
neuron doctrine
frequency modulation (fm) not amplitude modulation (am)
electrical energy in our neurons changes in _________ not _________
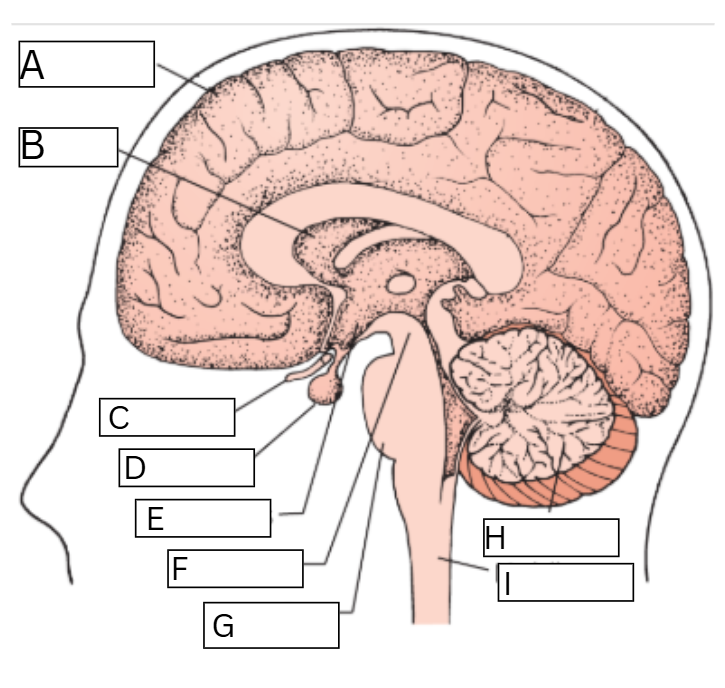
a. neocortex
b. thalamus
c. optic nerve
d. pituitary
e. hypothalamus
f. midbrain
g. pons
h. cerebellum
i. medulla
Name the brain parts
Occipital
Parietal
Temporal
Frontal
4 cortical regions of the brain
left hemisphere
hemisphere responsible for linguistic and analytic processing
right hemisphere
hemisphere responsible for perceptual and spatial processing
corpus callosum
broad band of fibers connecting the right and left hemispheres
broc’s area
area of the brain critical for speech. Damage to this area often results in errors with grammar
wernick’s area
area of the brain critical for speech. Damage to this area often results in semantic or vocabulary errors
topographic organization
principle of neural organization in which adjacent areas of the cortex process information from adjacent parts of the sensory feild
Electrocephalography (EEG)
a direct measurement of electrical activity of the brain using electrodes on the scalp. Can be used to measure various states of consciousness (ie: sleep)
Event related potentials (ERPs)
changes in electrical activity at the scalp in response to an external event as measured by EEG
Magnetencephalography (MEG)
a direct measurement of magnetic fields produced by electrical activity in the brain
Positron emission tomography (PET)
method for determining the location of neural activity by measuring metabolic activity in different regions of the brain with the use of a radioactive tracer
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
method for determining location of neural activity by measuring magnetic field produced by the iron in oxygenated blood in the brain (indirect measurement)
hemodynamic response
the flow of oxygenated blood to a region of the brain that has greater activity
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
a method for determining the function of a brain region: a magnetic field is applied to the surface of the head to disrupt the neural processing in that region
BOLD response (blood oxygen level dependent)
a measure of the amount of oxygen in the blood in fMRI studies
Brainstem/Midbrain - physiological brain
Limbic System - emotional brain
Cortex - rational, human brain
Brain Anatomy in Three Parts
a simple neural tube
The central nervous system of all chordates begins with…
Blastula
hollow, 3 layer ball of cells present at the beginning of human development which goes onto form the neural tube
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
The functions of the neural tube are organized similarly to which model?
Forebrain
region of the brain made up of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary that supports the 4 Fs (fight, flight, feed, fornication) and mammalian parenting
Thalamus
region of the brain with more advanced sensory processing than the midbrain telling us what and where something is
Limbic System
area of the brain referred to as our emotional brain or “monkey mind” that allows for short cuts and intuitive responses
Cortex
area of the brain referred to as our rational, human brain or “panda mind” that supports high level perception and cognitive processing
Occipital Lobe
cortical region of the brain responsible for visual perception (color, motion, texture)
Parietal Lobe
cortical region of the brain responsible for touch (pressure and pain) and spatial orientation
Temporal lobe
cortical region of the brain responsible for hearing (speech/language) and memory
Frontal lobe
cortical region in which the frontal area is responsible for executive functioning (problem solving, planning) and the back area is responsible for movement
ENIGMA
The German WWII cipher coding device was called the ______ machine
1850s
When did Donders complete his reaction-time experiment?
Alan Turning
What was the name of the British Mathematician who broke the German U-Boat code?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A neural imaging technique that involves measuring the brain tissue’s water content by measuring hydrogen density using magnetism, which depicts brain structures well
Advantages and disadvantages of MRI/fMRI
Advantages: best for spatial resolution and studying complex multi-step takss
Disadvantages: slow so poor temporal resolution
Advantages and Disadvantages of EEG
Advantage: better at time/ temporal resolution than MRI, best for studying brief cognitive tasks
Disadvantage: not good at spatial resolution as MRI
Advantages and Disadvantages of MEG
Advantage: Equally as good at time/temporal resolution as EEG, better at spatial resolution
Disadvantage: Not as good at spatial resolution as MRI, more expensive than EEG
fMRI is less intrusive, measures over longer periods of time, and has finer temporal and spatial resolution
Why is fMRI preferred over PET?
Noematachograph
machine created by Donders to measure reaction time of cognitive tasks
Hippocrates
prominent figure from ancient Greece who found a clear correlation between structure and function
nucleus
part of the neuron that houses the DNA
axon hillock
part of the neuron where the action potential is initiated
myelin sheath
part of the neuron that provides insulation for the axon allowing action potentials to travel faster
arborizations
part of the neuron that allows for multiple inputs
terminal boutons
part of the neuron that holds neurotransmitters