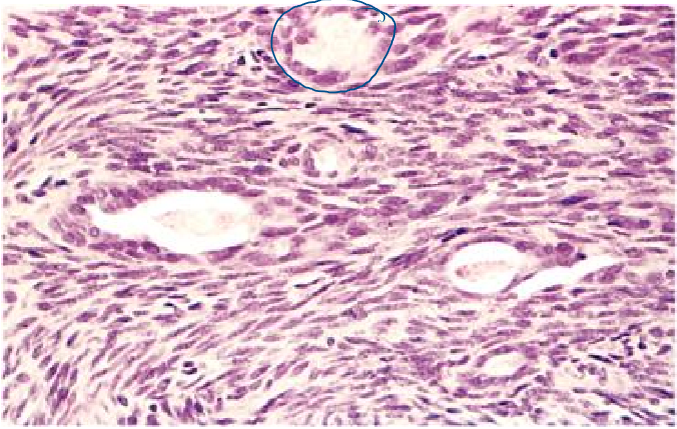
soft tissue tumors
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
diseases of skeletal muscle
neurogenic disease, myasthenic syndromes, & dystrophies
may all cause muscular weakness & fatigability
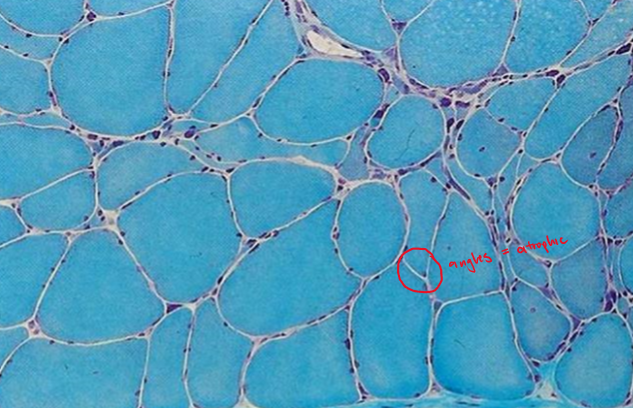
denervation atrophy
a peripheral neuropathy in which there is axial degeneration that leads to secondary muscle atrophy
atrophic muscles consists of small angulated fiber
muscle fiber is usually reinnervated by collateral sprouting from an adjacent nerve fiber
muscle fiber type determined by innervation → regenerated fibers will be the same as adjacent fibers
type grouping & group atrophy
ATPase stains differentiate type I & II fibers
clinical presentations
weakness & fasciculations → lower motor neuron deficit
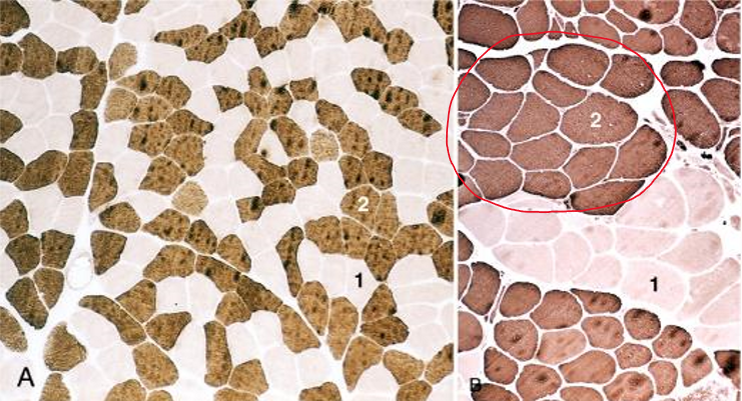
type grouping
repeated denervation & reinnervation by collateral sprouts produces clusters of fibers of a single type
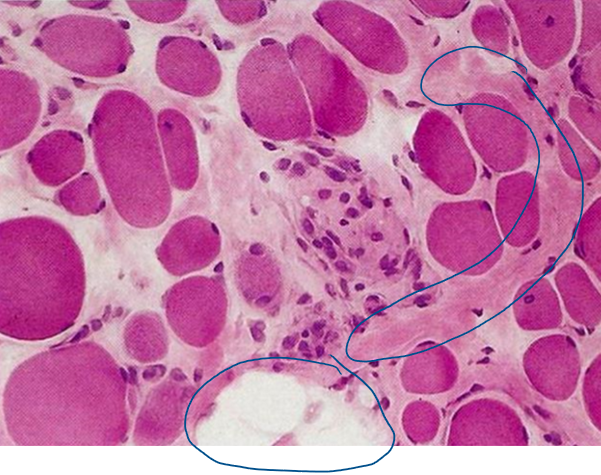
group atrophy
with damage of the innervating axon, the muscle fibers that undergo atrophy will be in groups
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
most commonly occurring dystrophy with an X-linked defect causing deficiency in dystrophin
morphology
ongoing damage in the form of segmental myofiber degeneration & regeneration associated with an admixture of atrophic myofibers
muscle tissue is replaced by collagen & fat cells (“fatty replacement” or “fatty infiltration“) leading to pseudohypertrophy of the calves
clinical presentations
first indications of muscle weakness are clumsiness & inability to keep with with peers around age 5
weakness begins in the pelvic girdle muscles & then extends to the shoulder girdle (proximal muscles)
mean age of wheelchair dependence is around 9.5 years
mean age of death is 25 - 30 years of age (from respiratory insufficiency, pulmonary infection, or heart failure)
Becker muscular dystrophy
X-linked defect causing insufficiency in dystrophin
milder type of Duchenne dystrophy
later onset of disease
inflammatory myopathies
non-infectious, immunologically mediated injury & inflammation of skeletal muscles
examples
dermatomyositis
polymyositis
inclusion body myositis
acanthosis nigricans
Bower’s disease
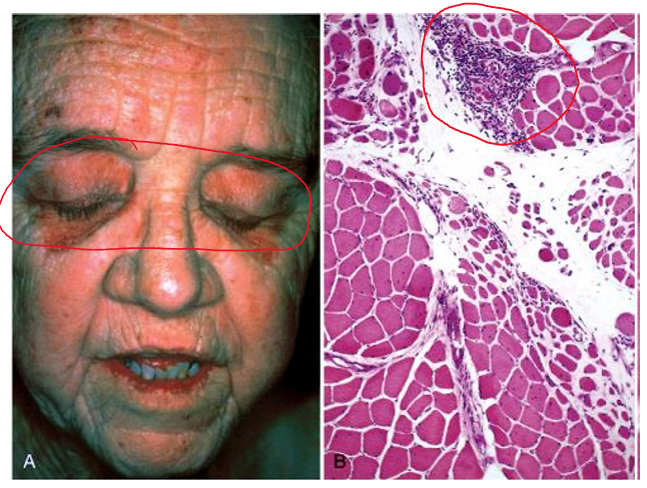
dermatomyositis
inflammatory myopathy associated with damage to small blood vessels
clinical presentations
heliotrope skin rash & proximal muscle disease
infiltrates of mononuclear inflammatory cells in the perimysial connective tissue & around blood vessels
risk of developing visceral cancers
polymyositis
inflammatory myopathy associated with proximal muscle weakness
CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are prominent part of the inflammatory infiltrate in affected muscle
inclusion body myositis
inflammatory myopathy associated with distal muscle weakness in the elderly
patchy often endomysial mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrates rich in CD8+ T cells
abnormal cytoplasmic inclusions described as “rimmed vacuoles“
myasthenia gravis
an autoimmune disease with antibody production to the acetylcholine receptor (AchR) of the neuromuscular junction
type II hypersensitivity
antibodies to the AchR present in the serum of 85 - 90% of patients
clinical presentations
female-to-male ratio 2:1 in the young adults but male predominance in older adults
fluctuating weakness that worsens with exertion & often over the course of the day
ocular muscle weakness common
later involves muscles producing dysphagia & dysarthria
trunk & limb muscles affected in late stages
10% of the patients have a thymoma & 30% have thymic hyperplasia
treatments
< 5% mortality rate now
thymectomy usually beneficial in patients with thymoma
response to anticholinesterase drugs seen in some patients
plasmapheresis & immunosuppressive drugs
soft tissue tumors
tumors of non-epithelial tissue excluding the skeleton, joints, CNS, hematopoietic & lymphoid tissues
benign — outnumber malignant sarcoma by 100x
arise in the extremities, especially the thigh
vimentin positive
superficial tumors are usually benign
deep (& retroperitoneal) tumors are usually malignant
majority of sarcomas are sporadic & have no known predisposing cause
origins unknown
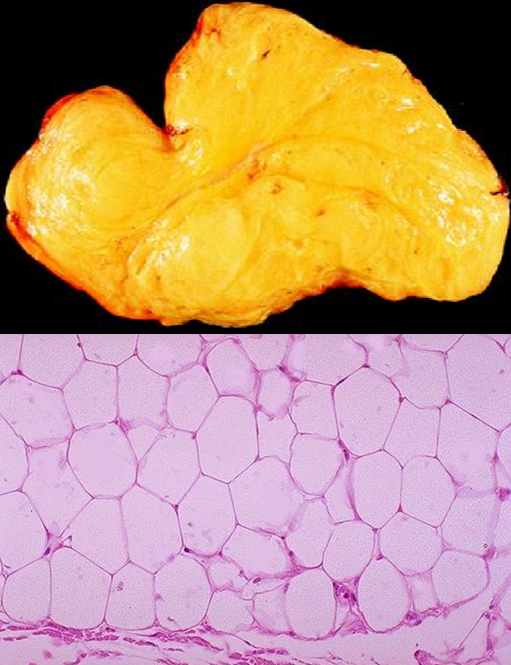
lipoma
most frequent soft tissue tumor, usually arising in the subcutis of the proximal extremities & trunk
clinical presentation
during middle adulthood
superficial lesion which is well-circumscribed & partially encapsulated
soft & doughy to touch; rubbery & moves easily when touched
histologically looks likes normal adipose tissue
liposarcoma
one of the most common adult sarcomas that are derived from primitive mesenchymal cells & arise deep in the proximal extremities or retroperitoneum of people in their 50s & 60s
well-differentiated & pleomorphic types
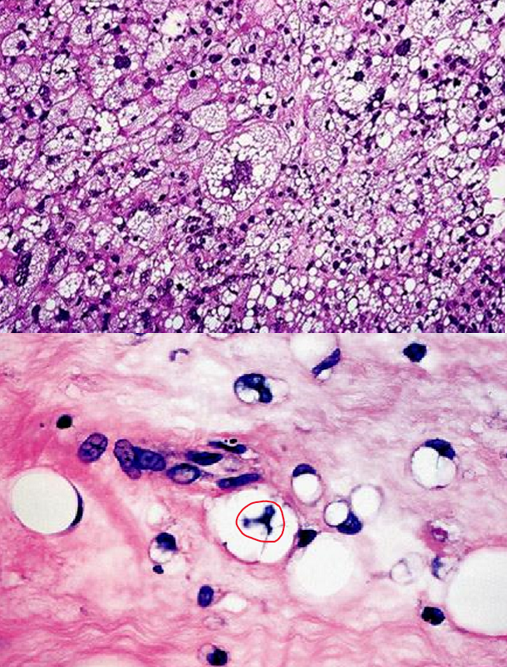
well-differentiated liposarcoma
liposarcoma that has adipocytes & atypical spindle cells & indolent course
pleomorphic liposarcoma
consists of sheets of anaplastic cells, bizarre nuclei & variable amounts of immature adipocytes (lipoblasts)
nodular (pseudosarcomatous) fasciitis
subcutaneous growth involving the extremities & has rapid growth
richly cellular & contains plump, immature-appearing fibroblasts & myofibroblasts arranged randomly or in short fascicles reminiscent of tissue culture fibroblasts
often mistaken for sarcoma
spontaneously regresses & rarely recurs if excised
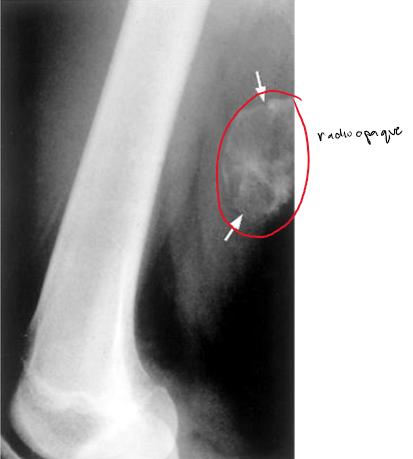
myositis ossificans
ossification of injured muscles usually caused by trauma
may be mistaken for malignancy
feels hard/firm
fibromatoses
benign superficial proliferations of fibrous tissue
make be palmar, plantar, or penile
palmer = Dupuytren's contracture (digit 4 & 5)
penile = Peyronie’s disease (may constrict urethra & cause painful erections)
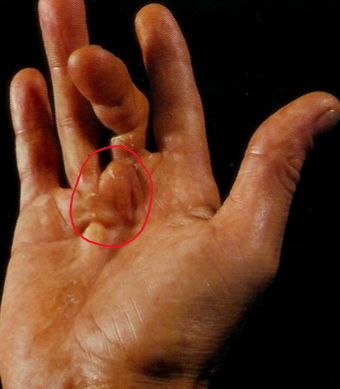
desmoid tumor
aggressive fibromatoses commonly found in the abdominal wall of women
associated with pregnancy & has estrogen receptors
mutations in APC or β-catenin genes
intraabdominal lesions seen with Gardner syndrome
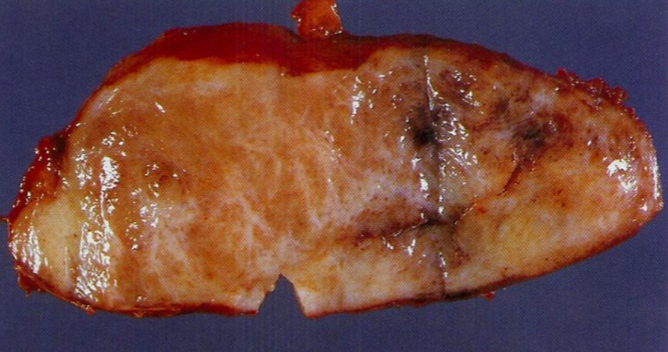
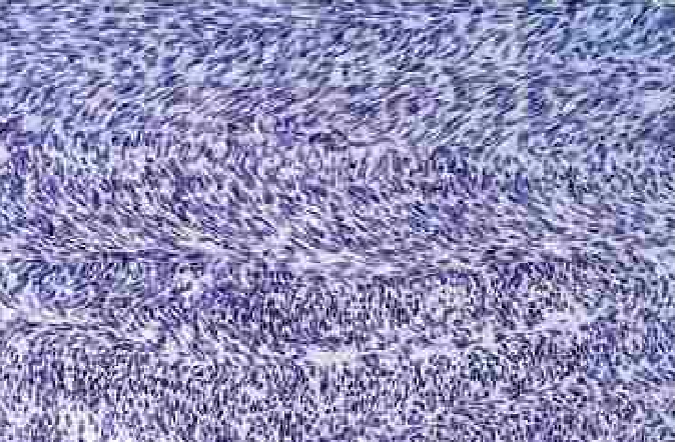
fibrosarcoma
rare soft tissue tumor that occurs mostly in the retroperitoneum, thigh, knee, & distal extremities
encapsulated, infiltrative, soft, fish flesh masses with areas of hemorrhage & necrosis
highly cellular neoplasm of spindle cells growing in a herringbone (or basket-weave) fashion which nuclear pleomorphism & frequent mitosis

benign fibrous histiocytoma
a tumor consisting of fibroblasts and histiocyte-like cells, typically found in the skin of the lower extremities (95%)
also known as dermatofibroma
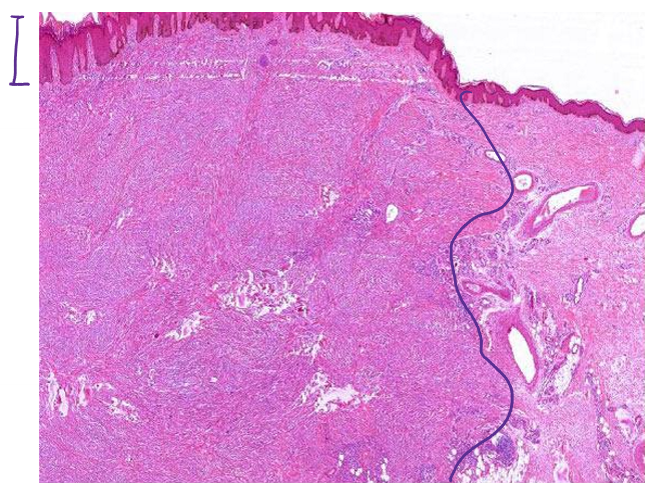
malignant fibrous histiocytoma
undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS); most common adult sarcoma that may invade bone & is osteolytic
storiform-pleomorphic type is the most common - sheets of large anaplastic spindled to polygonal cells with hyperchromatic irregular, sometimes bizarre nuclei
treated with surgery & adjuvant chemotherapy, and/or radiation
most are aneuploid & prognosis is generally poor
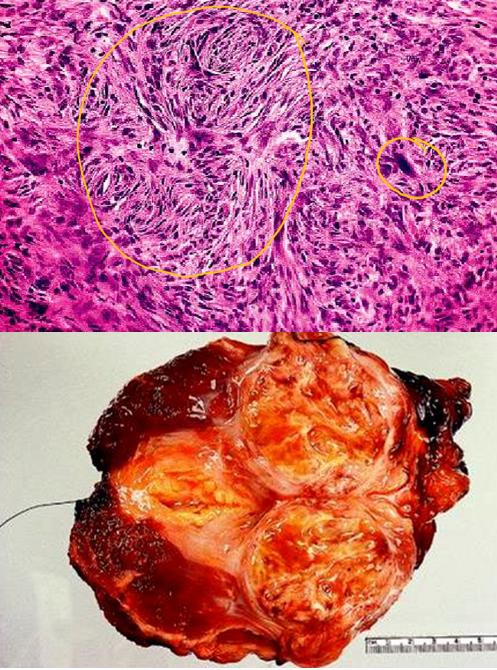
rhabdomyosarcoma
most common soft tissue sarcoma in children & adolescents (alveolar & embryonal) that often arise in the sinuses, head, neck, & genitourinary tract
only 20 - 25% arise in skeletal muscles
desmin & myoglobin usually present in all types
actin ,myosin, & glycogen also seen
overall average survival ~ 3 - 5 years
~ 20% already have metastases @ diagnosis
pleomorphic type = worse prognosis
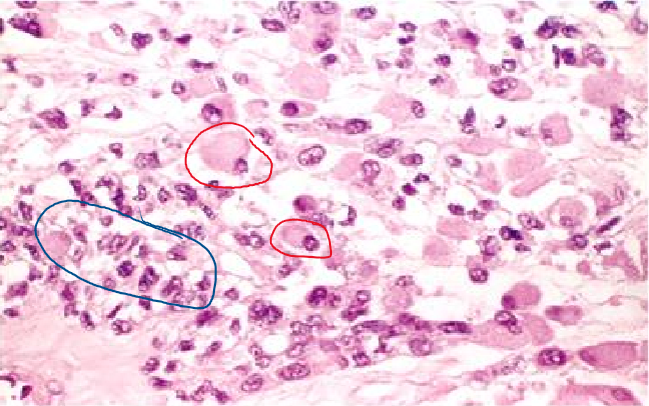
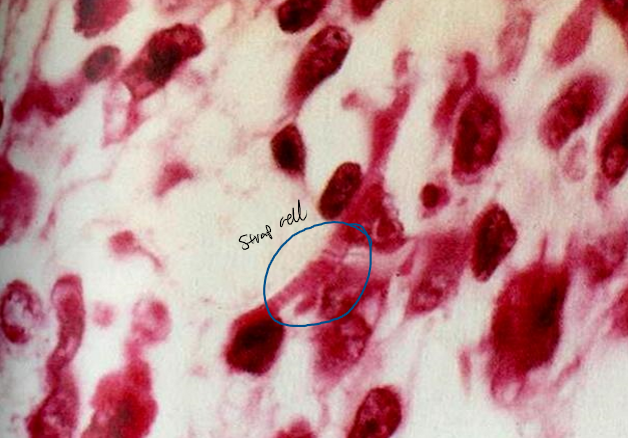
embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
rhabdomyosarcoma that include cambium layer with primitive around cells, oval cells, strap cells, & racquet-shaped cells
sarcoma botryoides - variant which presents as grape-like mass
synovial sarcoma
rare soft tissue tumor that occurs near joints but not usually in joints
associated with gene fusions SS18-SSX1, -SSX2, or -SSX4 (chimeric transcription factors)
probably arises from multipotential mesenchyme
clinical presentations
can present in locations that lack synovium (chest wall, head, neck)
most occur in people in their 20s - 40s
microscopically has a biphasic pattern of spindle cells & glands