Beliefs in society
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Definitions of religion
Substantive:
Focuses on the belief in a supernatural power or God
Exclusive definition
Western bias
Functional:
Focuses on social or psychological functions for an individual or society
Inclusive
suggests a football chant is religion
Social Constructionist:
focusses on how members of society define religion
can not produce a universal definition
+ deeper meaning
Impossible to generalize
Features of religion
Beliefs- in the supernatural and/or incomprehensible powers eg God or sacred symbols
Theology- a set of teachings and beliefs
Practice- rituals of ceremonies to express beliefs
Institutions- some form of organisational worshippers eg: churches
Consequences- a set of moral or ethical values to guide everyday behaviour
Belief sytems

Ideology

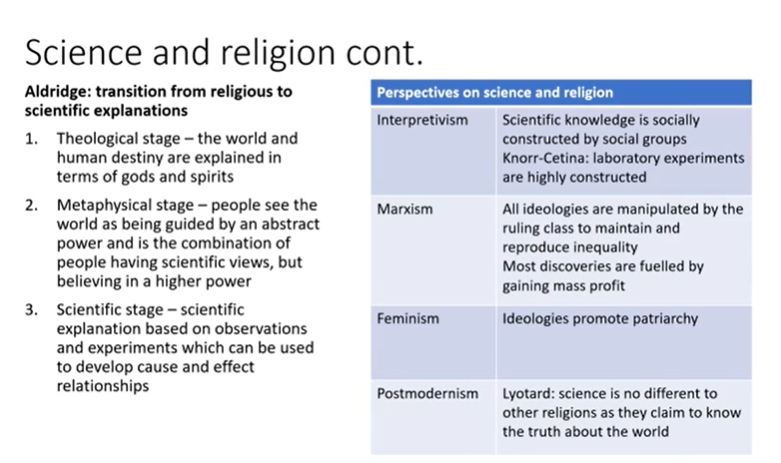
Science and Religion

cont Science and religion
Functionalist perspective

Marxist perspective

Neo-marxist perspective

Feminist

Postmodernist perspective
NAMs- new age movements

Religion as a conservative force

Religion as a force for social change

Is religion a force for social change, or a conservative force?

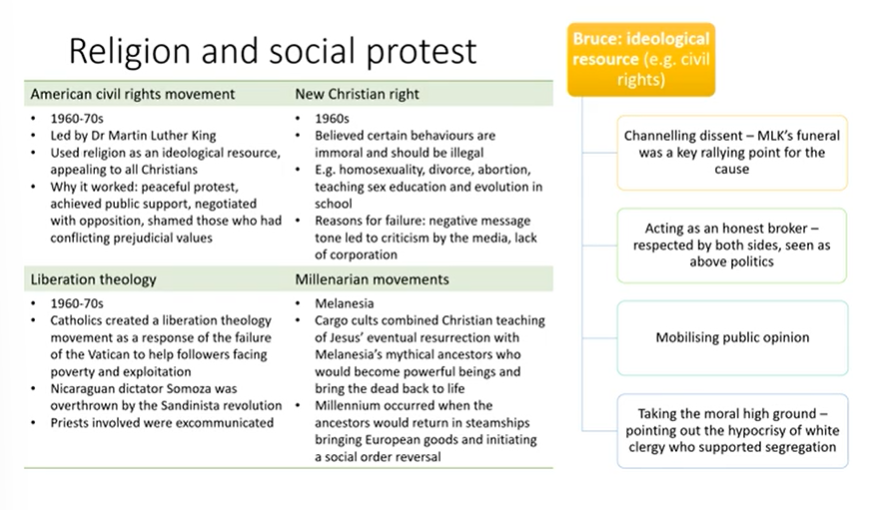
Religion and social protest
Religious organizations
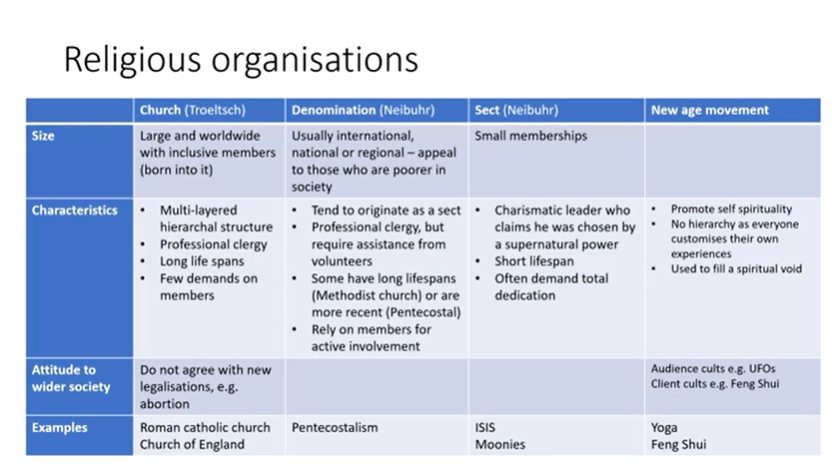
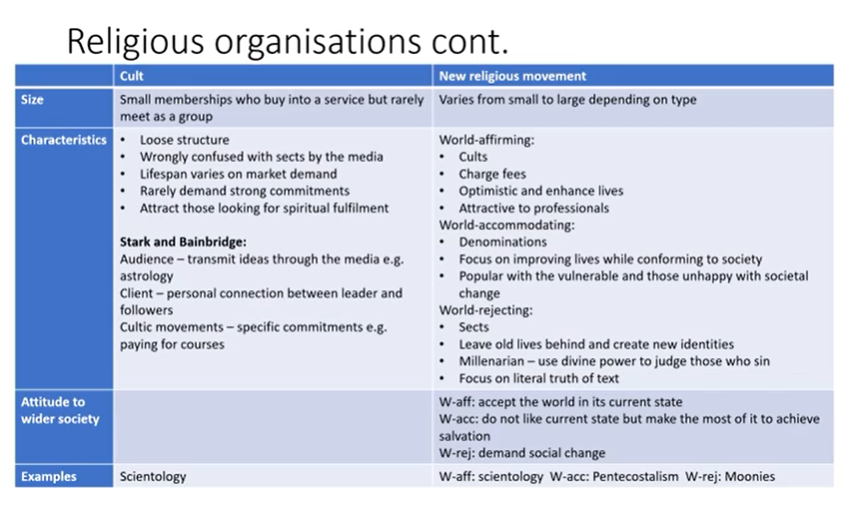
Religious organisations cont
Growth or religious new movements

Dynamics of sects

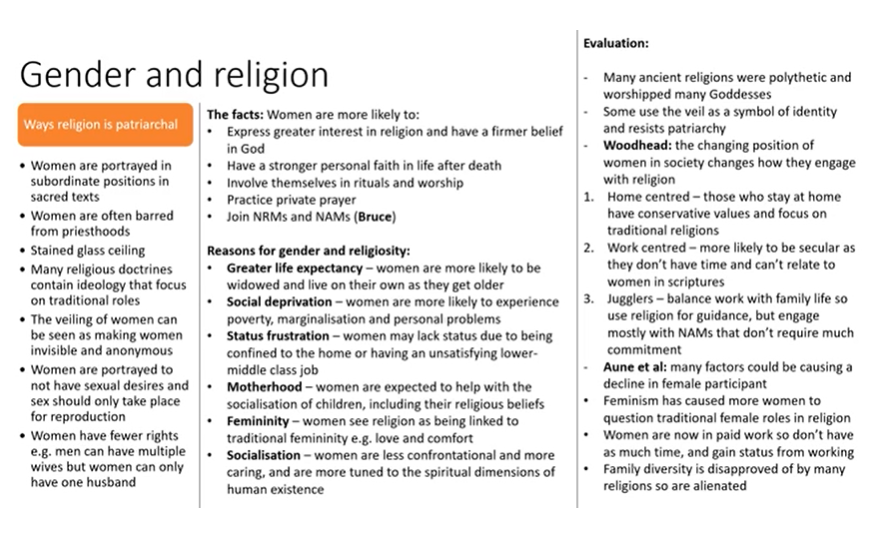
Gender and religion
Ethnicity and religion

Age and religion

Social class and religion

Secularisation in UK vs US
2006 church census not valid as it was carried out by church rather than through a national census

Evidence for secularisation UK vs US cont

Arguments for and against secularisation

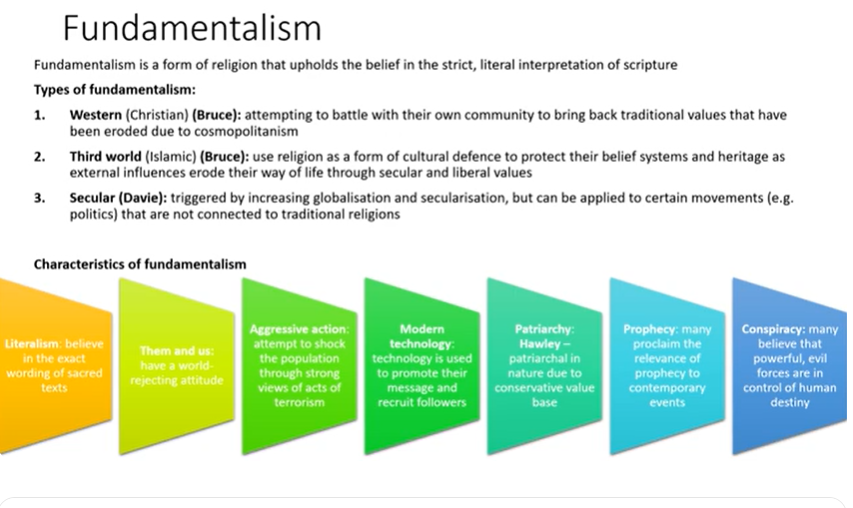
Fundamentalism
ISIS- videos of beheading (Aggressive reaction)
Fundamentalism Cont
Clash of civilisations (Huntington 1996)
Huntington argues that religion has become more important in ‘civilizational identity’ as other sources of identity are undermined. As a result, globalisation, which brings cultures in closer contact, makes religion more important as a source of identity and conflict.
Karen Armstrong argues that the perception that Western Imperialism is undermining religion has led to the increase of religious Fundamentalism.

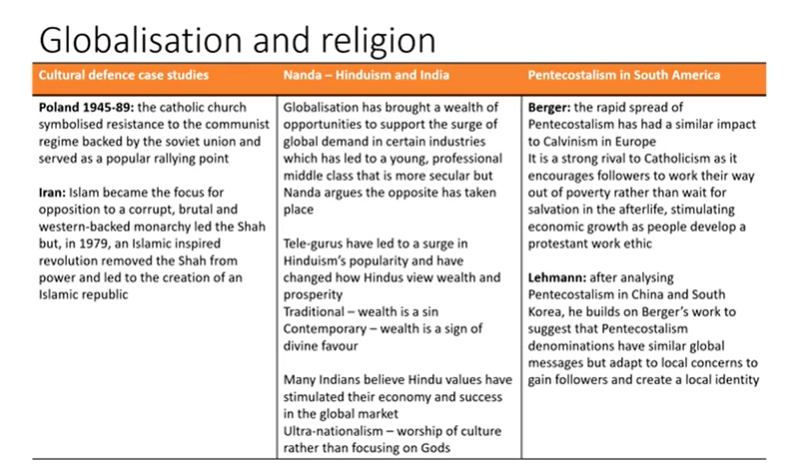
Globalisation and religion
Monopoly of truth religions might be in decline, but more postmodern religions may be taking their place – such as New Age religions.
Globalisation may have increased the prevalence of the scientific worldview globally, but science is not necessarily incompatible with religion