Histology exam 2
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What are the functions of the integument? Include the components that compose each function.
Barrier
temperature
water
pathogen protection
Thermoregulation
vasodilation→ blood vessels dilate→cool
vasoconstriction→ blood vessels constrict→ warm
innervation of dermis (not epidermis)
Secretion and Excretion
glandular elements
sweat glands secrete ammonia
sebaceous glands secrete oil
mammory glands secrete milk
Species and sex recognition
males brighter (bold patterns in birds)
Sensory organ
tactile sensation and pressure sensation
heat, pain, cold
Identify the 5 layers of epidermis, moving from outermost to innermost layer.
Stratum corneum
hardened, compressed
stratified squamous
“bags” of keratin
adaption to abrasion
Stratum lucidum
clear band of dead cells with keratin
Stratum granulosum
granules of keratin
release of lipids (via keratinocytes) which remain in epidermis, lipids called lamellar bodies→ water barrier
Stratum spinosum
desmosomes attach neighbor cells
allow “stretchiness” quality of skin
melanin degrades
Stratum basale
adjacent to dermis
melanocytes→ secrete melanin into environment→ pigment
keratinocytes→ phagocytose melanin (stain darker)
Which layer of the epidermis varies in thickness with physical labor? Describe how it can vary.
Stratum corneum can vary in thickness. It is adapted to abrasion and is the tissue that forms calluses out of keratin.
What structures are found in the dermis?
CT layers
blood supply via dermal papillae
innervation
hair follicles
glands
What tissue is the primary component of the hypodermis?
adipose CT
In which of the three layers of skin is nervous input found?
Dermis
In what layer of the epidermis are melanocytes found? What is the function of melanocytes?
Stratum basale
They secrete melanin into environment to pigment.
What is the function of desmosomes in the stratum spinosum?
They attach neighboring cells. Allow for the “stretchiness” quality of skin.
How do desmosomes appear microscopically?
white spine-ish boundaries between keratinocytes
Which layer of the epidermis provides a water barrier?
Stratum granulosum
Keratinocytes release lipids called lamellar bodies that act as water barrier.
Identify the functions of hair.
insulation
camouflage
display
How does the microscopic appearance of the medulla of a hair differ from the cortex of a hair?
The medulla is the innermost component and not always visible. Cortex is pigmented medulla is light pink.
What is the function of the cuticle of a hair?
protection of hair
What is the function of the dermal papilla of a hair follicle?
It is the entrance and exit of blood vessels.
Distinguish between sebaceous and sweat glands by their function and structure/appearance.
Sebaceous
empty onto hair
produces “sebum” for scent and waterproofing
foamy appearance
Sweat gland
empties onto skin
cooling, excretion, scent
two types- apocrine and eccrine
Distinguish between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands by their secreted products, structure, and anatomic location.
eccrine- excretion, cooling; more uniform and cuboidal
apocrine- odorless fluid secreted onto hair→ encounters microbes that digest sweat to create scent
Describe each of the 3 characteristics of nervous tissue.
excitable- detects changes in local environment
conductive- transmit responses to other cells
secretory- neurotransmitter secreted
Describe tissues that compose the central nervous system compared to the peripheral nervous system.
CNS- brain and spinal
PNS- all other nerves and ganglia
INCOMPLETE
Describe the organization of the peripheral nervous system.
Somatic
voluntary
Autonomic
sympathetic
fight or flight (heart rate, pupil)
parasympathetic
rest and digest (homeostasis)
Diagram and label a neuron. Indicate the function of each “part.”
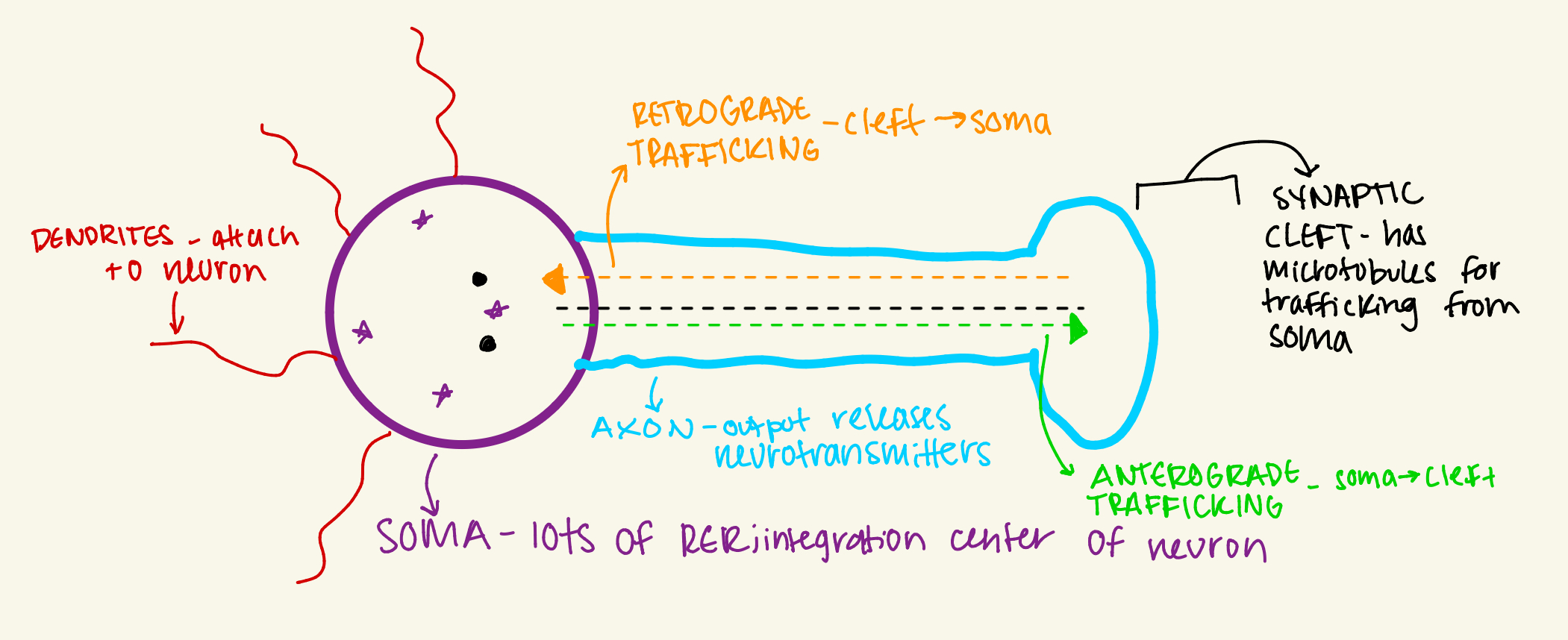
Distinguish/ diagram the 3 classifications of neurons. Which type is found in ganglia?
multipolar- 1 axon and many dendrites
bipolar- 1 dendrite and 1 axon
psuedounipolar- found in ganglia
integrates and relays sensory and motor
Distinguish between astrocytes and pericytes.
astrocyte
foot processes
removes excess neurotransmitters from synapse
more throughout CNS
phagocytosis of dead/ dying cells
pericyte
around capillary
INCOMPLETE
How are oligodendrocytes different from Schwann cells? How are they the same?
oligodendrocyte-
schwann-
Describe the location, structure, and function of ependymal cells.
Location
ventricles of the brain and through spinal cord
bloo
Structure
ciliated epitheliated cells
columnar and cuboidal
Function
circulate CSF through ventricles
works with choroid plexus to synthesize CSF
wash debris from CNS
discharged into blood
Why does lipofuscin accumulate in nervous tissue?
INCOMPLETE
Diagram and label how nerves are organized.
Describe the composition and function of the molecular layer of the cerebellum.
Composition
primarily dendrites of purkinje cells
basket cells
medulla
cortex
Function
synapse to inhibit purkinje cells ability to integrate information from two layers
Describe the composition and function of the granular layer of the cerebellum.
Composition
axons
granule cells
Function
granule cells synapse on dendrites of purkinje cells to excite allowing response to signals from cerebellum and spinal cord
How does the structure of Purkinje cells contribute to their integrative function of the other layers?
INCOMPLETE
Where are large motor neurons found? Be specific!
INCOMPLETE
How does the location of grey commissure contribute to it’s function?
integrates both dorsal and ventral horns; found around central canal
Where is the choroid plexus located? What is its function?
inbetween the cerebellum and cerebrum
looks like free space
synthesizes CSF
What are some mechanisms of the innate immune system that protect the body?
inflammation
phagocytose and present antigen to acquired to digest the pathogen
physical and chemical barriers
complement protein
What cells compose the acquired immune system?
B cells and T cells
How does the timing of the immune response differ between the acquired and innate immune system?
innate is immediate response and acquired is slow/ delayed response
Where do T cells mature?
in thymus
Name 2 types of T cells and the functions of each
helper T- coordinate acquired and innate overlap, secrete exokine proteins, recruit cells, inflammation, suppress response
cytotoxic T- precisely binds and kills infected cell; binds cells, creates a hole, kills
What is the function of a B cell?
mature in spleen and lymphnode
activated by helper T
produces antibodies that bind antigen preventing pathogen from infecting other cells
What is the function of lymphatic fluid?
INCOMPLETE
Distinguish between the afferent and efferent lymphatic vessels.
INCOMPLETE
Diagram and label the broad structure of a lymph node.
INCOMPLETE
Describe and label the structure of the cortex of the lymph node.
INCOMPLETE
What is the distinguishing feature of the juxtamedullary cortex of the lymph node? What is the function of this structure?
contains HEV; T cells and naive lymphocytes leaves HEV for mantle (T) and germinal center (lymph)
naive lymphocytes and T cells exit blood into lymph node
lymphocytes can enter directly from blood
What is the function of the medulla of the lymph node?
Lymphocytes enter sinuses, empty into efferent vessel at hilus (combined efferent vessel and vein)
IMCOMPLETE
Diagram and label the organization of the spleen.
INCOMPLETE
Describe how diffuse white pulp differs from follicular white pulp.
Diffuse
T cells in peri-arteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS)
Follicular
beside PALS
germinal center
mantle
marginal zone
Diagram flow of blood through spleen, including where it encounters white pulp. Label where there is open circulation and closed circulation.
INCOMPLETE
Describe the function of the cortex and medulla differ in the thymus.
cortex- CD4+/CD8+ → CD4+ OR CD8+
medulla- macrophages cull autoreactive T cells; macrophages remove T cell that recognize self antigen / distinguish self from nonself
hassel’s corpuscles
What is the function of hassell’s corpuscles? How does their appearance differ from the surrounding thymus?
function
release interleukin proteins which assist with T cell maturation/ education
appearance
cluster of epithelial cells
What does the acronym MALT stand for?
Mucosa- Associated Lymphatic Tissue (underlies epithelial)
Where is MALT found?
Tonsils and small intestine.