25.3 the chemistry of phenol
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
phenol as a week acid
phenol is less soluble in water than alcohols due to the presence of the non-polar benzene ring
when dissolved in water, phenol partially dissociates forming the phenoxide ion and a proton
because of this ability to partially dissociate to produce protons, phenol is classed as a week acid
it is more acidic than alcohols but less acidic than C.A so can only react with strong bases eg. sodium hydroxide
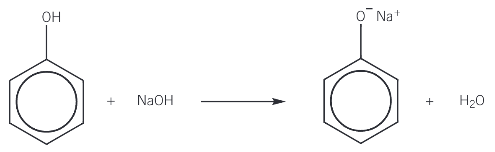
reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide
phenol reactions with sodium hydroxide to form the salt, sodium phenoxide and water in a neutralisation reaction
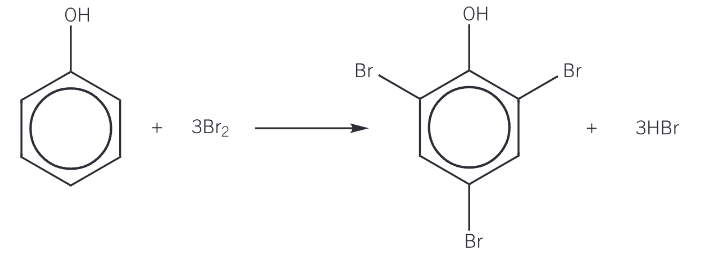
bromination of phenol
phenol reacts with bromine water to form a white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromophenol
the reaction colourises the bromine water
with phenol, a halogen carrier catalyst is not required and the reaction is carried out a room temperature
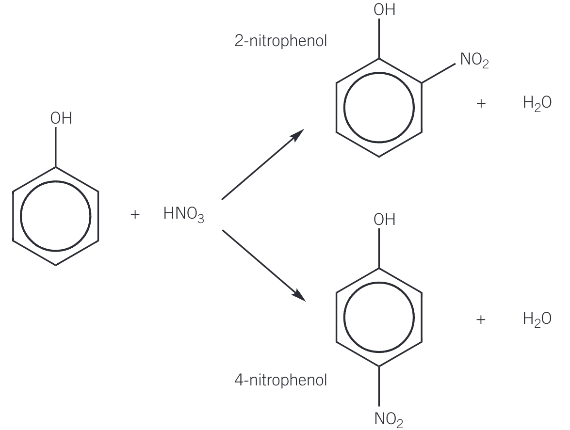
nitration of phenol
phenol reacts readily with dilute nitric acid at room temperature
a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol is formed
comparing the reactivity of phenol with benzene
bromine and nitric acid react more readily with phenol than they do with benzene
the increased reactivity is caused by a lone pair of electrons from the oxygen p-orbital of the -OH group being donated into the Pi system of phenol
the electron density of the benzene ring in phenol is increased. This increased electron density attracts electrophiles more strongly than with benzene
the aromatic ring in phenol is therefore more susceptible to attack from electrophiles than in benzene. For bromine, the electron density in the phenol ring structure is sufficient to polarise bromine molecules and so no halogen carrier is needed