Biology 8 - Cells and Transport
5.0(1)Studied by 40 people
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:00 AM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
At what level of organization does life begin?
Cell
2
New cards
What surrounds all cells?
Cell Membrane
3
New cards
What is semipermeable?
allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others.
4
New cards
What 2 things make up the cell membrane?
phospholipids and embedded proteins
5
New cards
The cell membrane is also called the ----- membrane
Plasma
6
New cards
Centrioles are found inside of what type of cells?
Animal
7
New cards
What additional layer is found around the outside of plant cells and bacteria?
Cell wall
8
New cards
Centrioles are found at the center of the...
Centrosome
9
New cards
How do centrosomes help the cells?
Cell division
10
New cards
Where is DNA found inside a cell?
Nucleus
11
New cards
What cell process is controlled by the nucleus?
protein synthesis
12
New cards
DNA coils tightly during division and assembles into visible...
Chromosome
13
New cards
Where are organelles located?
Cytoplasm
14
New cards
Where are proteins made in a cell?
Ribosomes
15
New cards
Do all cells need ribosomes? Why?
yes because all organisms need to make proteins.
16
New cards
The process of making proteins is called...
protein synthesis
17
New cards
How does rough ER differ from smooth ER?
rough er has ribosomes on the surface while smooth er does not.
18
New cards
Rough ER is connected to the ---membrane and to ---ER.
nuclear and smooth
19
New cards
Proteins made by rough ER travel to the Golgi in sacks called ---. Golgi --- and ---proteins for export out of the cell.
cistern, modify, packages
20
New cards
What are Smooth ER jobs?
Make proteins, controls calcium level, detoxifies poisons.
21
New cards
What process takes place inside chloroplasts?
photosynthesis
22
New cards
What is the energy for photosynthesis?
Sun
23
New cards
What pigment traps the energy?
chlorophyll
24
New cards
Chloroplasts are found in what type of cell(s)?
plant cells
25
New cards
Both chloroplasts and mitochondria are alike in that they both have ---membrane and their own--
double and DNA
26
New cards
Food, water, and wastes are stored inside
Vacuoles
27
New cards
Digestion takes place inside---containing---
lysosomes and digestive enzymes
28
New cards
The largest organelle in plants is the...
central vacuole
29
New cards
What organelle breaks down and recyles worn out cells?
lysosomes
30
New cards
Cell membrane: Plant/animal/both
Both
31
New cards
Cell membrane - Function
Provides a boundary between the cell and its environment. Controls what enters/exits cell. Provides protection/support for cell.
32
New cards
cell wall - Function
Surrounds the cell membrane and its contents- give the plant its shape
33
New cards
cytoplasm - Plant/animal/both
both
34
New cards
cytoplasm - Function
Watery cell fluid that contains the cell organelles-many life processes take place here
35
New cards
vacuole - Plant/animal/both
both
36
New cards
vacuole - Function
Store water, wastes, and food. Much bigger in plant than animal cells.
37
New cards
ribosome - Plant/animal/both
both
38
New cards
ribosome - Function
Make proteins
39
New cards
Golgi bodies- Plant/animal/both
both
40
New cards
Golgi bodies - Function
Synthesize, package, and secrete cell products
41
New cards
rough ER - Plant/animal/both
both
42
New cards
smooth ER - Plant/animal/both
both
43
New cards
smooth ER - Function
Makes proteins and lipids that will be exported by the cell, controls calcium level and detoxifies poisons & drugs
44
New cards
central vacuole - Plant/animal/both
plant
45
New cards
central vacuole - Function
Takes up most of the space in plant cells. Store water, wastes, and food
46
New cards
chloroplast - Plant/animal/both
plant
47
New cards
chloroplast - Function
Involved in manufacturing of food (photosynthesis)
48
New cards
mitochondria -Plant/animal/both
both
49
New cards
mitochondria - Function
Convert energy stored in glucose into ATP
50
New cards
nucleus -Plant/animal/both
both
51
New cards
nucleus - Function
Control cell activities
52
New cards
nucleolus -Plant/animal/both
both
53
New cards
nucleolus - Function
Makes ribosomes
54
New cards
nuclear membrane -Plant/animal/both
both
55
New cards
nuclear membrane - Function
Materials move from the nucleus to the cytoplasm through nuclear pores in the nuclear membrane
56
New cards
centrosome - Plant/animal/both
animal
57
New cards
centrosome - Function
Makes microtubules, important for cell division
58
New cards
lysosomes - Plant/animal/both
animal
59
New cards
lysosomes -function
Contain digestive enzymes, breaks down & recycle worn out cells
60
New cards
microtubules - Plant/animal/both
animal
61
New cards
microtubules -function
Give the nucleus and cell its shape
62
New cards
nuclear pores -Plant/animal/both
both
63
New cards
nuclear pores -function
Allows materials to move through nucleus and cytoplasm
64
New cards
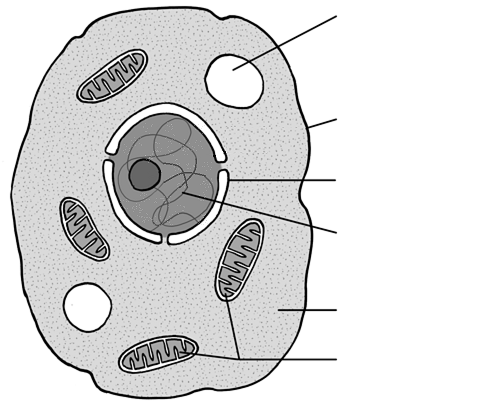
Identify the organelle for 92
Vacuole
65
New cards
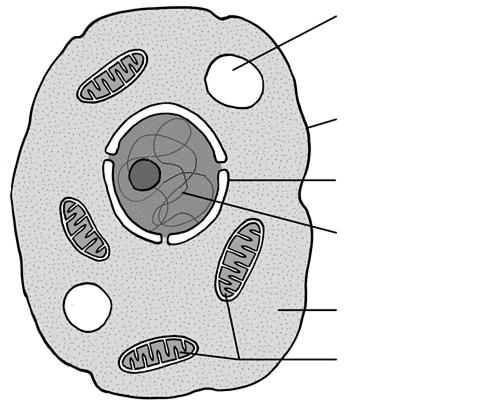
Identify the organelle for 93
Cell Membrane
66
New cards

Identify the organelle for 94
Nucleus
67
New cards
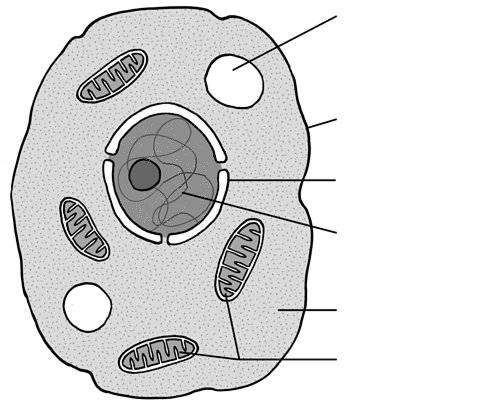
Identify the organelle for 95
DNA
68
New cards
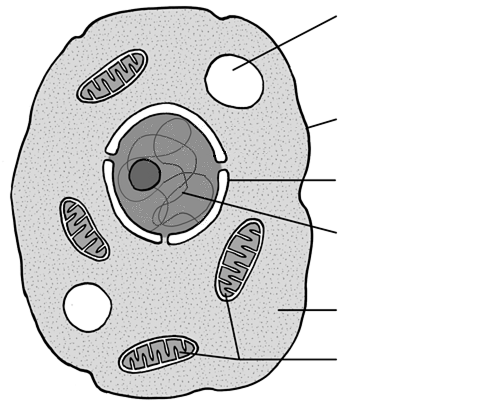
Identify the organelle for 96
Cytoplasm
69
New cards
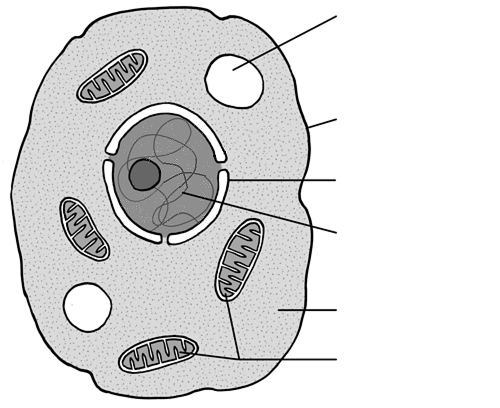
Identify the organelle for 97
Mitochondria
70
New cards
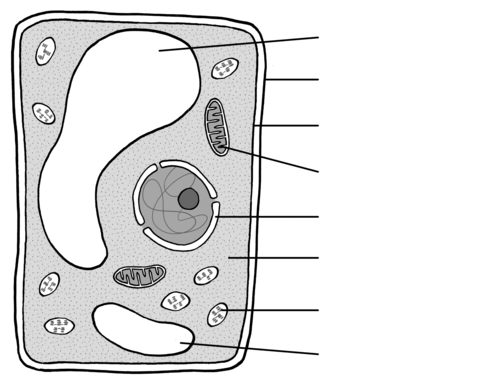
Identify the organelle for 98
Vacuole
71
New cards
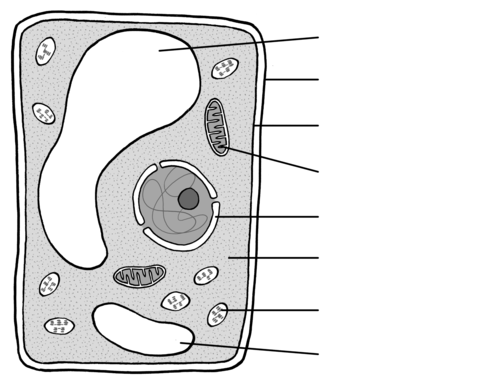
Identify the organelle for 99
Cell Wall
72
New cards
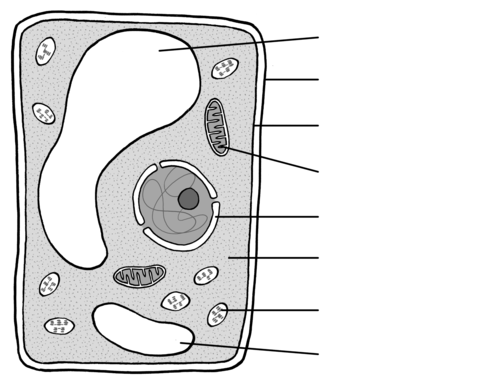
Identify the organelle for 100
Cell Membrane
73
New cards
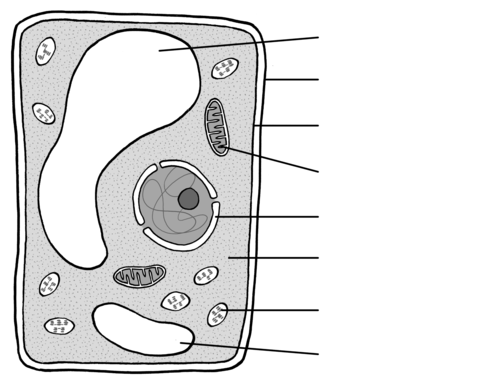
Identify the organelle for 101
Mitochondria
74
New cards
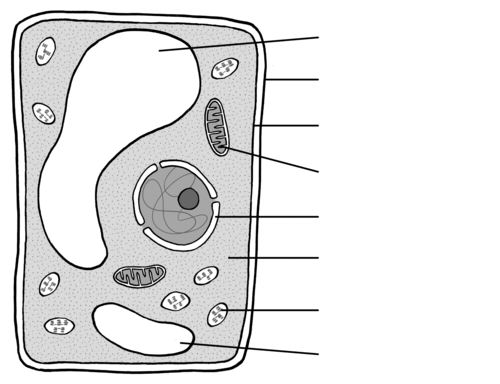
Identify the organelle for 102
Nucleus
75
New cards
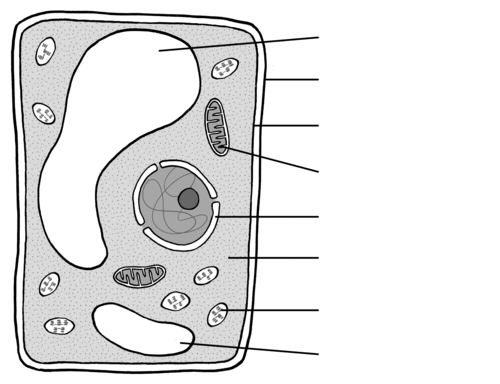
Identify the organelle for 103
Cytoplasm
76
New cards
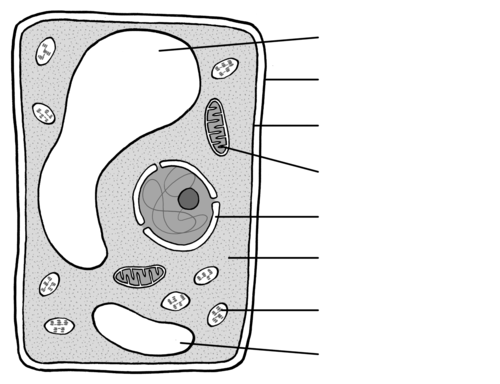
Identify the organelle for 104
Chloroplast
77
New cards
Passive transport
The cell does not use energy. High to low concentration. types - 1.Diffusion , 2.Facilitated diffusion, 3. Exocytosis
78
New cards
Active transport
The cell uses energy. Low to high concentration. types - 1. Protein pumps, 2. Endocytosis, 3. Exocytosis
79
New cards
Osmosis
diffusion
of water through a
selectively permeable
membrane
of water through a
selectively permeable
membrane
80
New cards
•Phagocytosis-
cytoplasm of cell
surrounds and engulfs large
surrounds and engulfs large
81
New cards
•Pinocytosis-
plasma membrane
"pinches in" to permit entry of
molecules too large to diffuse
through
"pinches in" to permit entry of
molecules too large to diffuse
through
82
New cards
Semi-permeable membrane (selectively
permeable)
permeable)
-allows some molecules to pass
but not others
but not others
83
New cards
Isotonic:
The concentration of solutes in the solution
is equal to the concentration of solutes inside the cell.
is equal to the concentration of solutes inside the cell.