Maryland Life Chapter 3
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Attained age
the insured's age at the time the policy is renewed or replaced
Deferred
withheld or postponed until a specified time or event in the future
Face amount
the amount of benefit stated in the life insurance policy
Fixed life insurance products
contracts that offer guaranteed minimum or fixed benefits
Lapse
policy termination due to nonpayment of premium
Level premium
the premium that does not change throughout the life of a policy
Nonforfeiture values
benefits in a life insurance policy that the policyowner cannot lose even if the policy is surrendered or lapses
Policy maturity
in life policies, the time when the face value is paid out
Securities
financial instruments that may trade for value (for example, stocks, bonds, options)
Variable life insurance products
contracts in which the cash values accumulate based upon a specific portfolio of stocks without guarantees of performance
Term insurance
temporary protection because it only provides coverage for a specific period of time
greatest amount of coverage for the lowest premium as compared to any other form of protection
pure death protection
If the insured dies during this term, the policy pays the death benefit to the beneficiary;
If the policy is canceled or expires prior to the insured's death, nothing is payable at the end of the term; and
There is no cash value or other living benefits.
Know This
Term insurance provides the greatest amount of coverage for the lowest premium. Term insurance has no cash value.
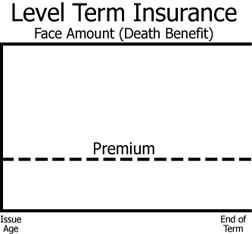
Level term insurance
most common type of temporary protection purchased
refers to the death benefit that does not change throughout the life of the policy.
Level premium term
provides a level death benefit and a level premium during the policy term
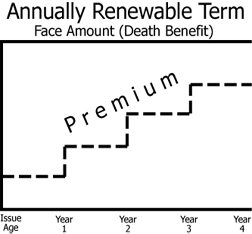
Annually renewable term
death benefit remains level (in that sense, it’s a level term policy), and the policy may be guaranteed to be renewable each year without proof of insurability, but the premium increases annually according to the attained age, as the probability of death increases
Convertible Term
provides the policyowner with the right to convert the policy to a permanent insurance policy without evidence of insurability. The premium will be based on the insured's attained age at the time of conversion
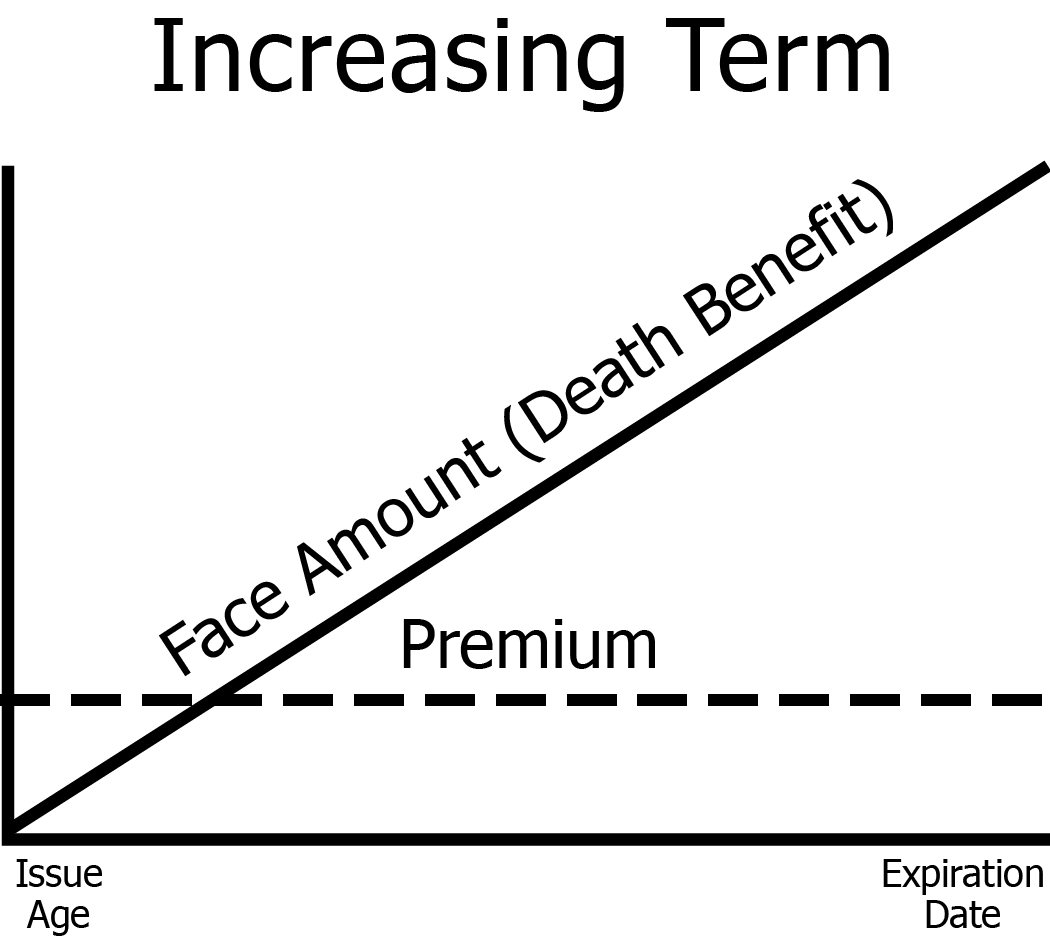
Increasing term
level premiums and a death benefit that increases each year over the duration of the policy term
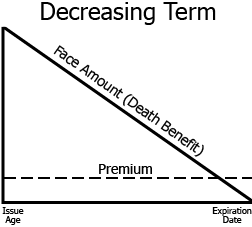
Decreasing term
policies feature a level premium and a death benefit that decreases each year over the duration of the policy term
Return of premium (ROP) life insurance
increasing term insurance policy that pays an additional death benefit to the beneficiary equal to the amount of the premiums paid
Permanent life insurance
refer to various forms of life insurance policies that build cash value and remain in effect for the entire life of the insured (or until age 100) as long as the premium is paid
Whole life insurance
provides lifetime protection, and includes a savings element (or cash value)
Level premium
the premium for whole life policies is based on the issue age; therefore, it remains the same throughout the life of the policy
Death benefit
the death benefit is guaranteed and also remains level for life
Cash value
created by the accumulation of premium, is scheduled to equal the face amount of the policy when the insured reaches age 100 (the policy maturity date), and is paid out to the policyowner
Living benefits
the policyowner can borrow against the cash value while the policy is in effect, or can receive the cash value when the policy is surrendered
Know This
Whole life insurance provides lifetime (permanent) protection and accumulates cash value.
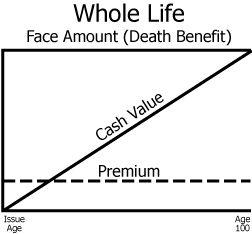
Continuous Premium (Straight Life)
the basic whole life policy (illustrated above). The policyowner pays the premium from the time the policy is issued until the insured’s death or age 100 (whichever occurs first)
will have the lowest annual premium
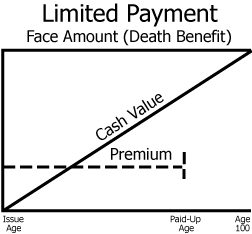
Limited Payment whole life
designed so that the premiums for coverage will be completely paid-up well before age 100
Single premium whole life (SPWL)
designed to provide a level death benefit to the insured's age 100 for a one-time, lump-sum payment. The policy is completely paid-up after one premium and generates immediate cash
TERM LIFE
Type of protection | Temporary |
Premium | Level |
Death benefit |
|
Living benefits | Not available |
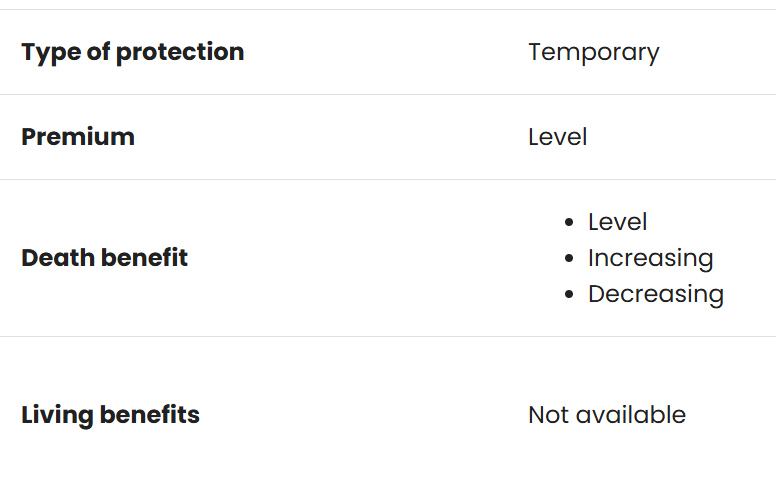
WHOLE LIFE
Type of protection | Permanent until age 100 |
Premium | Level |
Death benefit | Level |
Living benefits |
|
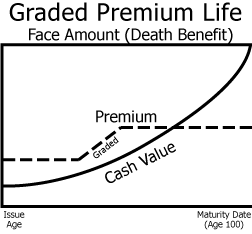
Graded-premium whole life
similar to modified life in that premiums start out relatively low and then level off at a point in the future
typically starts with a premium that is approximately 50% or lower than the premium of a straight life policy. The premium then gradually increases each year for a period of usually 5 or 10 years, and then remains level thereafter.
Interest-sensitive whole life
whole life policy that provides a guaranteed death benefit to age 100. The insurer sets the initial premium based on current assumptions about risk, interest and expense. If the actual values change, the company will lower or raise the premium at designated intervals
provides the same benefits as other traditional whole life policies with the added benefit of current interest rates, which may allow for either greater cash value accumulation or a shorter premium-paying period
indexed whole life
the cash value is dependent upon the performance of the equity index, such as S&P 500 although there is a guaranteed minimum interest rate
Adjustable Life
developed in an effort to provide the policyowner with the best of both worlds (term and permanent coverage)
can assume the form of either term insurance or permanent insurance. The insured typically determines how much coverage is needed and the affordable amount of premium. The insurer will then determine the appropriate type of insurance to meet the insured’s needs. As the insured’s needs change, the policyowner can make adjustments in the policy
Universal life insurance (flexible premium adjustable life)
implies that the policyowner has the flexibility to increase the amount of premium paid into the policy and to later decrease it again
minimum premium
amount needed to keep the policy in force for the current year
target premium
recommended amount that should be paid on a policy in order to cover the cost of insurance protection and to keep the policy in force throughout its lifetime
Know This
If an insured skips a premium payment on a universal life policy, the missing premium may be deducted from the policy’s cash value. The policy will NOT lapse.
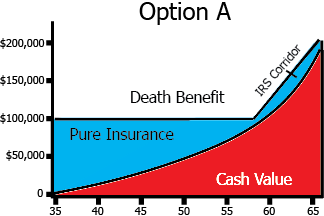
Option A (Level Death Benefit option)
death benefit remains level while the cash value gradually increases, thereby lowering the pure insurance with the insurer in the later years
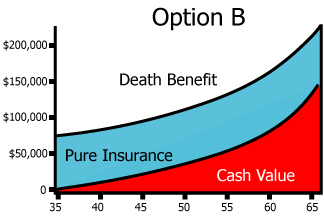
Option B (Increasing Death Benefit option)
death benefit includes the annual increase in cash value so that the death benefit gradually increases each year by the amount that the cash value increases
Variable life insurance
level, fixed premium, investment-based product
The cash value of the policy, however, is not guaranteed and fluctuates with the performance of the portfolio in which the premiums have been invested by the insurer. The policyowner bears the investment risk
Know This
In variable contracts, the policyowner bears the investment risk (assets in a separate account).
Variable universal life insurance
type of insurance that combines many features of the whole life with the flexible premium of universal life and the investment component of variable life, making it a securities version of the universal life insurance
A flexible premium that can be increased, decreased or skipped as long as there is enough value in the policy to fund the death benefit;
Increasing and decreasing the amount of insurance; and
Cash withdrawals or policy loans.
Unlike universal life, most of the investment vehicles in ______ policies do not guarantee return.
Agents selling variable life insurance products must:
Be registered with FINRA;
Be licensed by the state to sell life insurance; and
Have received a securities license.
Adjustable Life
Key Features: Can be Term or Whole Life; can convert from one to the other
Premium: Can be increased or decreased by policyowners
Face Amount: Flexible; set by policyowner with proof of insurability
Cash Value: Fixed rate of return; general account
Policy Loans: Can borrow cash value
Universal Life
Key Features: Permanent insurance with renewable term protection component
Premium: Flexible; minimum or target
Face Amount: Flexible; set by policyowner with proof of insurability
Cash Value: Guaranteed at a minimum level; general account
Policy Loans: Can borrow cash value
Variable Life
Key Features: Permanent insurance
Premium: Fixed (if Whole Life); flexible (if Universal Life)
Face Amount: Can increase or decrease to a stated minimum
Cash Value: Not guaranteed; separate account
Policy Loans: Can borrow cash value
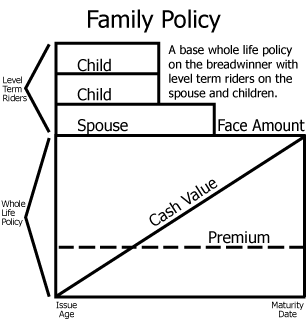
family protection or family policy
combines whole life with term insurance to cover family members in a single policy, providing coverage on every member of a family
Joint Life (First-to-die)
single policy that is designed to insure two or more lives
would be less than for the same type and amount of coverage on the same individuals
The premium is based on a joint average age that is between the ages of the insureds; and
The death benefit is paid upon the first death only.
Know This
Premium rates on a joint life policy are determined by averaging the ages of both insureds
Survivorship Life (Second-to-die)
insures two or more lives for a premium that is based on a joint age
pays on the last death rather than upon the first death
joint life expectancy in a sense is extended, resulting in a lower premium than that which is typically charged for joint life, which pays upon the first death. This type of policy is often used to offset the liability of the estate tax upon the death of the last insured.
Know This
Joint life = first to die; survivorship life = second to die (last survivor)
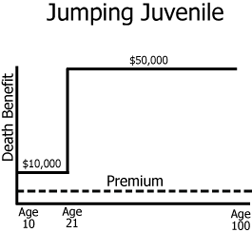
Juvenile life insurance
any life insurance written on the life of a minor
group life insurance
issued to the sponsoring organization, and covers the lives of more than one individual member of that group
written for employee-employer groups, but other types of groups are also eligible for coverage. It is usually written as annually renewable term insurance
Evidence of insurability is usually not required (unless an applicant is enrolling for coverage outside the normal enrollment period); and
Participants (insureds) under the plan do not receive a policy because they do not own or control the policy.
certificate of insurance
evidencing that they have coverage
master policy/contract
issued to the sponsor of the group, which is often an employer. The group sponsor is the policyholder and is the one that exercises control over the policy.
Know This
Group insurance is written as annually renewable term insurance. In group insurance, the master contract is for the employer, and certificates of insurance are for individual insureds
Purpose or nature of the group
The group must be created for a purpose other than to obtain group insurance
Size of the group
The larger the number of people in the group, the more accurate the projections of future loss experience will be. This is based on the Law of Large Numbers of similar risks.
Turnover of the group
From the underwriting perspective, a group should have a steady turnover: younger, lower-risk employees enter the group, and older, higher-risk employees leave
Financial strength of the group
Because group insurance is costly to administer, the underwriter should consider whether or not the group has the financial resources to pay the policy premiums, and whether or not it will be able to renew the coverage
Employer-Employee Groups
When a policy is issued to an employer, the employer or trustee will be the policyholder to insure employees of the employer for the benefit of persons other than the employer. A policy on which no part of the premium is paid by insured employees must insure all eligible employees, except those who reject such coverage in writing.
Debtor Groups
policy issued to a creditor or its parent holding company or to a trustee, trustees or agent designated by two or more creditors, which are deemed to be the policyholder, is subject to the following requirements:
The debtors eligible for insurance under the policy must all be the debtors of the creditor;
The premium for the policy must be paid either from the creditors funds, or from charges collected from the insured debtors, or from both;
An insurer may exclude any debtors as to whom evidence of individual insurability is not satisfactory to the insurer; and
The amount of insurance on the life of any debtor may at no time exceed the greater of the scheduled or actual amount of unpaid indebtedness to the creditor.
Labor Union Groups
insure members of the organization for the benefit of persons other than the union or organization are subject to the following requirements:
The members eligible for insurance under the policy must be all the members of the union or organization, or all of any class or classes thereof.
The premiums for the policy must be paid either from funds of the union, or from funds contributed by the insured members specifically for their insurance, or from both. A policy on which no part of the premiums is to be derived from funds contributed by the insured members specifically for their insurance must insure all eligible members, except those who reject such coverage in writing.
An insurer may exclude or limit the coverage on any person as to whom evidence of individual insurability is not satisfactory to the insurer.
Multiple-Employer Trust (MET)
made up of two or more employers in similar or related businesses who do not qualify for group insurance on their own because they have a small number of employees.
Credit Union or Credit Union Trusts
group life policy may be issued to a credit union or to a trustee, or trustees or agent designated by two or more credit unions to insure the lives of members of the credit unions for the benefit of persons other than the policyholder, subject to the following requirements:
All of the members of the credit union must be eligible for coverage;
The premium for the policy will be paid by the policyholder from the credit union's funds and must insure all eligible members; and
An insurer may exclude or limit coverage on any member as to whom evidence of individual insurability is not satisfactory to the insurer.
association group
can buy group insurance for its members. The group must have at least 100 members, be organized for a reason other than buying insurance, have been active for at least two years, have a constitution, by-laws, and must hold at least annual meetings. These groups include, but are not limited to, trade associations, professional associations, college alumni associations, veteran associations, customers of large retail chains, and saving account depositors, to name a few. ______ plans may be either contributory or noncontributory.
Dependent coverage
usually applies to the insured's spouse and children, but may also include dependent parents or anyone else on which dependency can be proven
noncontributory plan
When an employer pays all of the premiums, the plan is referred to as a __________
contributory plan
When the premiums for group insurance are shared between the employer and employees, the plan is referred to as a _________
characteristic of group insurance
Conversion to Individual Policy
employee has the right to convert to an individual policy without proving insurability at a standard rate, based on the individual's attained age
Know This
When converting from group life to individual life insurance, evidence of insurability is not required
Credit Life Insurance
special type of coverage written to insure the life of the debtor and pay off the balance of a loan in the event of the death of the debtor
usually written as decreasing term insurance, and it may be written as an individual policy or as a group plan
Know This
Credit life insurance cannot pay out more than the balance of the debt
General Characteristics: TERM LIFE
Pure protection
Lasts for specific term
No cash value
Level Premium Term
Level death benefit and level premium
Annually Renewable Term
Renews each year without proof of insurability
Premiums increase due to attained age
Decreasing Term
Coverage decreases at predetermined times gradually; best used when the need for protection declines from year to year
General Characteristics: WHOLE LIFE
Permanent protection
Guaranteed elements (face amount, premium, and cash value) until death or age 100
Level premium
Cash value and other living benefits
Straight Life (Continuous Premium)
Basic policy
Level death benefit
Insured pays premiums for life or until age 100
Limited Payment
Premiums are paid until a certain age or time; coverage in effect to age 100
Single Payment
Premiums paid in one lump sum and coverage continues to age 100
General Characteristics: FLEXIBLE PREMIUM
Types of whole life insurance
Flexible premium
Adjustable Life
Policyowner may adjust the premium and premium-paying period, the face amount, and the period of protection.
Can be converted from term to whole life and vice versa
Cash value only develops if the premiums paid are more than the cost of the policy
Universal Life
Has an insurance component in the form of annually renewable term
2 death benefit options: Option A - level death benefit, and Option B - increasing death benefit
Can make partial surrender/cash withdrawal
Flexibility through unbundling (separating)
Variable Life
Fixed premium, minimum death benefit
Cash value and the actual amount of death benefit are not guaranteed
Assets in separate accounts
Agents must be dually licensed in insurance and in securities
Group Life
Master Contract goes to the sponsor, usually employer
Certificate of Insurance goes to member
Underwritten as a group
If coverage after open enrollment-proof of insurability is required
Conversion to individual policy in 31 days - same face amount but higher premiums due to attained age