Evidence Based Medicine- Follen
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Define evidence-based medicine (EBM)
objective
“the integration of best research evidence w/ clinical expertise and patient values”
incorporates evidence along w/ clinical experience and patient preferences into the decision-making process
Define evidence:
findings from clinical research, especially from patient-centered research, that are relevant to patient care
Clinical expertise definition:
using clinical skills and previous experience to evaluate evidence and the patient’s health status and experiences
Patient values and preferences definition:
collection of goals, expectations, predispositions, and beliefs that individuals have for certain decisions and their potential outcomes
__________________________________ refers to the setting as primary, secondary, or tertiary care in which care is provided
clinical circumstances
Identify steps involved in EBM
objective
asking an appropriate/ answerable question
finding evidence
appraising evidence
applying evidence to practice
What method is used to ask an answerable question??? (aka step 1 of EBM)
PICO method
P- patient, population, program, or problem
I- intervention
C- comparison
O- outcome

In the second step of EBM, you are finding evidence. Which of the following would you NOT use to find evidence:
a. PubMed
b. Cochrane
c. Google
d. SCOPUS
c
The third step of EBM is appraising (aka assessing) evidence. What are the main points in appraising information?
assessing internal validity
assessing freedom from bias, reliability, usefulness bias the hierarchy of evidence
Basically: checking the info so that it’s reliable
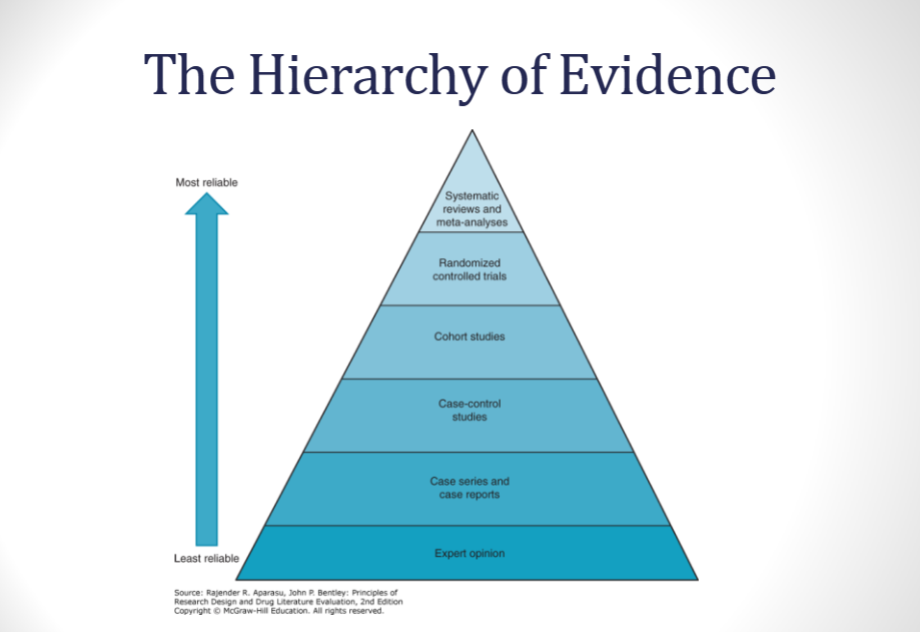
Identify the hierarchy of evidence
objective
a pyramid that categorizes evidence from least- most reliable
used in step 3 of EBM, when you are appraising evidence
use the photo attached for the hierarchy
The 4th step of EBM is applying evidence. What must you pay critical attention to when apply evidence?
external validity
clinical significance
patient’s goals
shared decision-making
Discuss strengths (advantages) of EBM
objective
attempts to find and incorporate interventions that work
provides guidance on how to keep up with new literature
improves critical thinking skills
can create communication btwn professional
Discuss disadvantages of EBM
objective
focuses on WHETHER an intervention works, not HOW it might work
requires knowledge, skills, and support mechanisms to practice it efficiently
aka students might struggle/ lack clinical role models to practice EBM
some have dismissed EBM as “cookbook medicine” and a threat to autonomy
bad if you think this way- EBM is necessary
many important questions do not yet have answers
What is the purpose of the MAARIE framework?
objective
kinda an FYI
The basis for a step-by-step approach to reading the clinical research literature.
Another tool practitioners can use for EBM
What does the MAARIE framework stand for?
objective
MAARIE stands for:
M- methods
A- assignment
A- assessment
R- results
I- interpretation
E- extrapolation
What makes up the “M” or “Methods” of the MAARIE framework?
PURPOSE
hypotheses
POPULATION
who’s being studied
STUDY SAMPLE
sample size/statistical power
Ex: how many ppl in study and control group
What makes up the “A” or “Assignment” of the MAARIE framework?
Allocation(assignment) of participants to study and control groups
basically, placing the participants in their groups
includes how they were assigned, why, etc.
What makes up the “A” or “Assessment” of the MAARIE framework?
measurement of outcomes or end points in the study and control groups
primary, secondary, and safety endpoints
statistical analysis methods
do NOT include study results here
What makes up the “R” or “Results” of the MAARIE framework?
comparison of outcomes in the study and control groups
did we achieve our endpoints?
What makes up the “I” or “Interpretation” of the MAARIE framework?
meaning of the results for THOSE INCLUDED IN THE INVESTIGATION
authors conclusions
limitations, strengths, bias, etc.
What makes up the “E” or “Extrapolation” of the MAARIE framework?
meaning of the results for THOSE NOT INCLUDED IN THE INVESTIGATION
Identify the components within the MAARIE framework
objective
basically a summary of all the cards above^
“MAARIE”
M- methods: the purpose, population, and study sample for investigation
A- assignment: allocation of participants to study and control groups
A- assessment: measurement of outcomes or end points in the study and control groups
R- results: comparison of outcomes in the study and control groups)
I- interpretation: meaning of the results for those included in the investigation)
E- extrapolation: meaning of the results for those not included in the investigation)
PRACTICE:
Which of the following does the “I” stand for in the MAARIE Framework?
a. Investigational
b. Intentional
c. Interpretation
d. Interpersonal
c
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of EBM?
a. it does not provide guidance on how to best keep up w/ new literature
b. focuses on whether an intervention works, no how it might work
c. requires skills, knowledge, and support to practice
d. some have dismissed EBM as “cookbook medicine” and a threat to autonomy
a
PRACTICE:
In what component of the MAARIE framework do we measure the primary, secondary, and safety endpoints?
a. Results
b. Assessment
c. Assignment
d. Interpretation
b
PRACTICE:
Which of the following correctly places the steps in practicing EBM in the correct order?
a. applying evidence, appraising evidence, finding evidence, asking an appropriate question
b. asking an appropriate question, appraising evidence, finding evidence, applying evidence
c. finding evidence, appraising evidence, asking an appropriate question, applying evidence
d. asking an appropriate question, finding evidence, appraising evidence, applying evidence
d
PRACTICE:
Which method is used to ask an answerable question?
a. PICO
b. MAARIE
c. RICO
d. EBM
a
PRACTICE:
T/F Extrapolation is the meaning of the results for those included in the investigation.
F- Extrapolation is for those NOT INCLUDED
PRACTICE:
Based on the hierarchy of evidence, which of the following is the most reliable? Which is the least reliable?
a. case studies
b. expert opinion
c. cohort studies
d. systematic reviews
most reliable- d. systematic review
least reliable- b. expert opinion