FCB Fundamentals of Nucleic Acids
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what do DNA/RNA do?
store, transmit and express genetic information
DNA and RNA are....
...nucleic acids which are condensation polymers of nucleotides
nucleic acids
condensation polymers of nucleotides
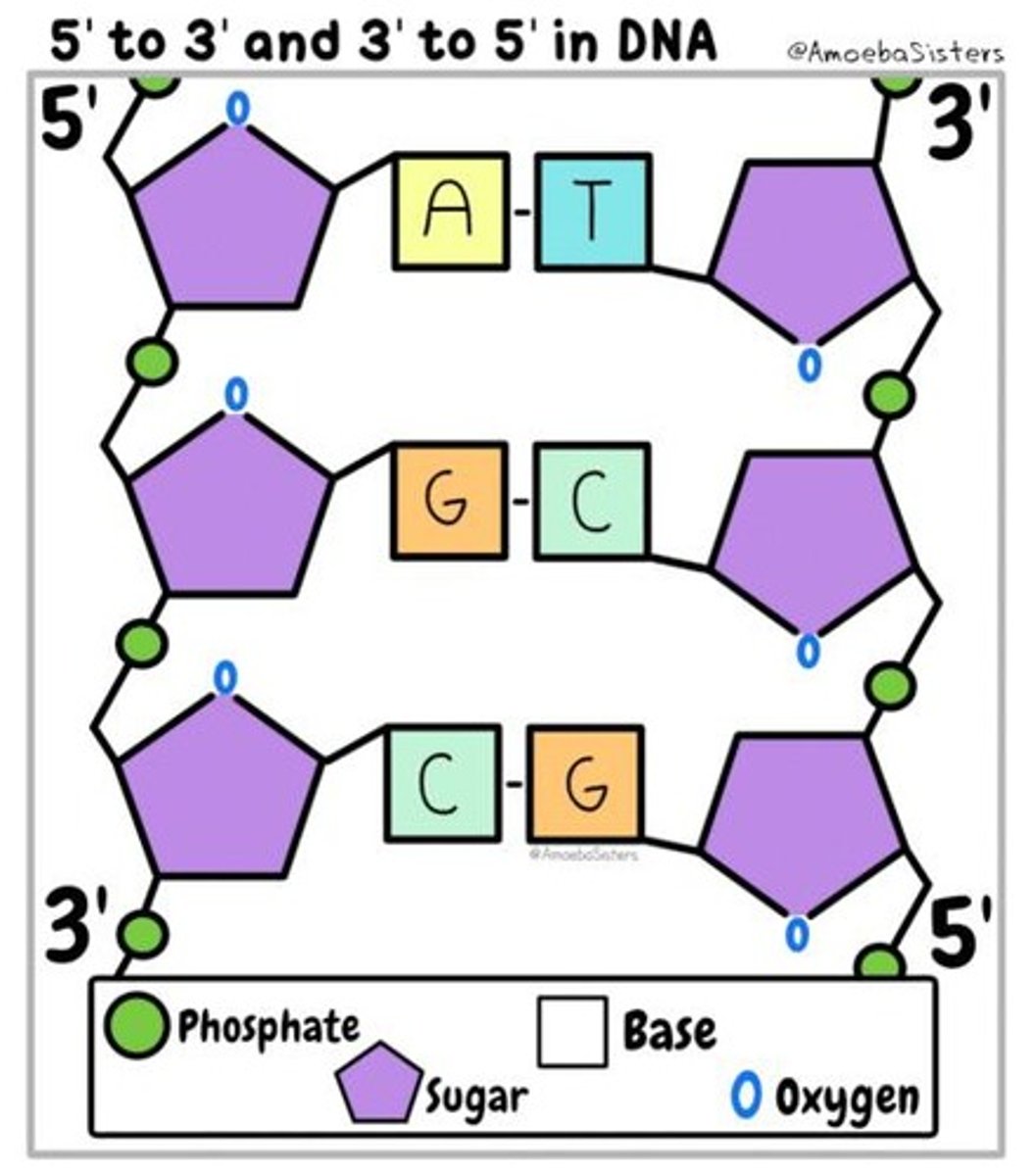
in what direction are DNA and RNA synthesised and why?
5' to 3' direction bc nucleotides can only be added to the 3' OH group
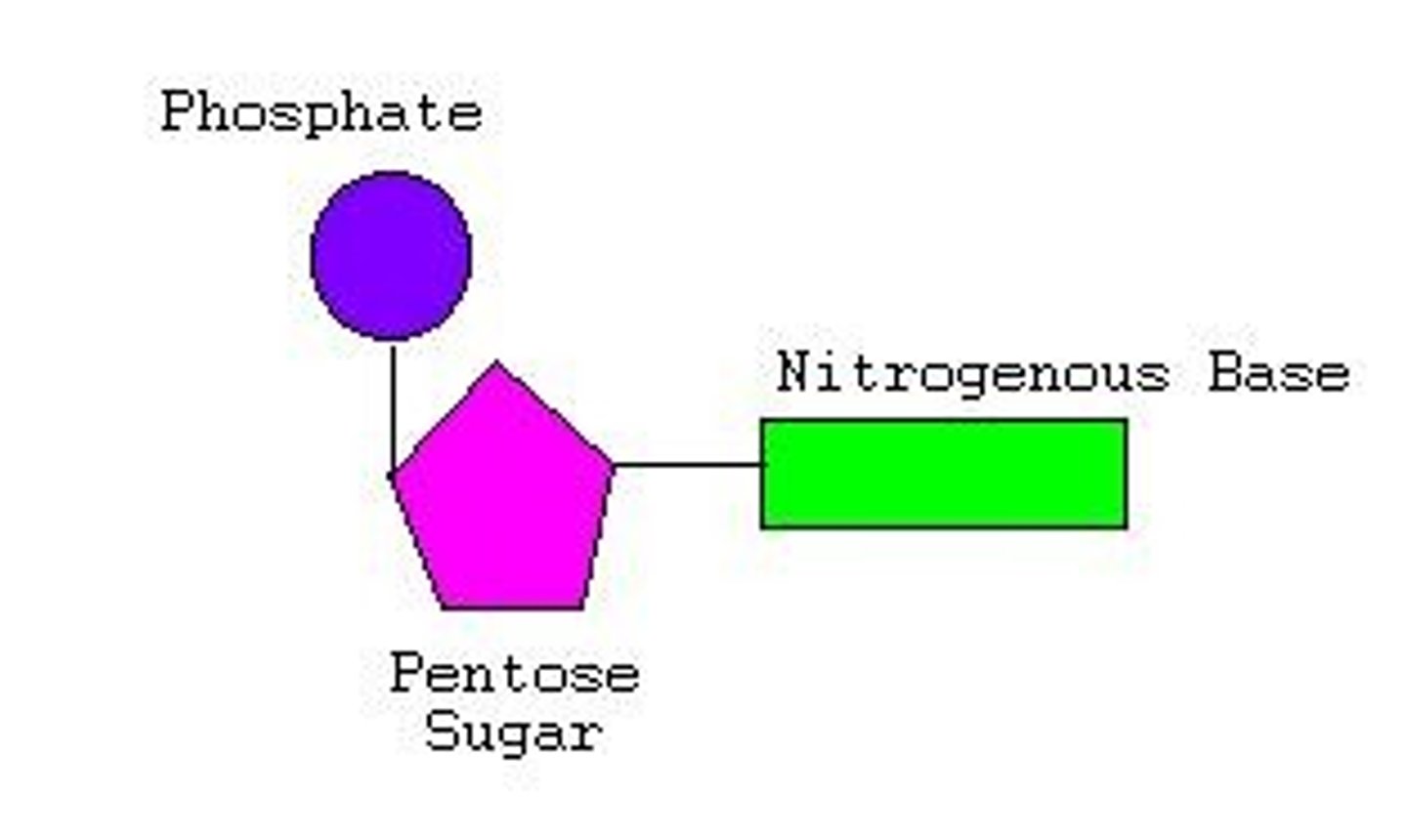
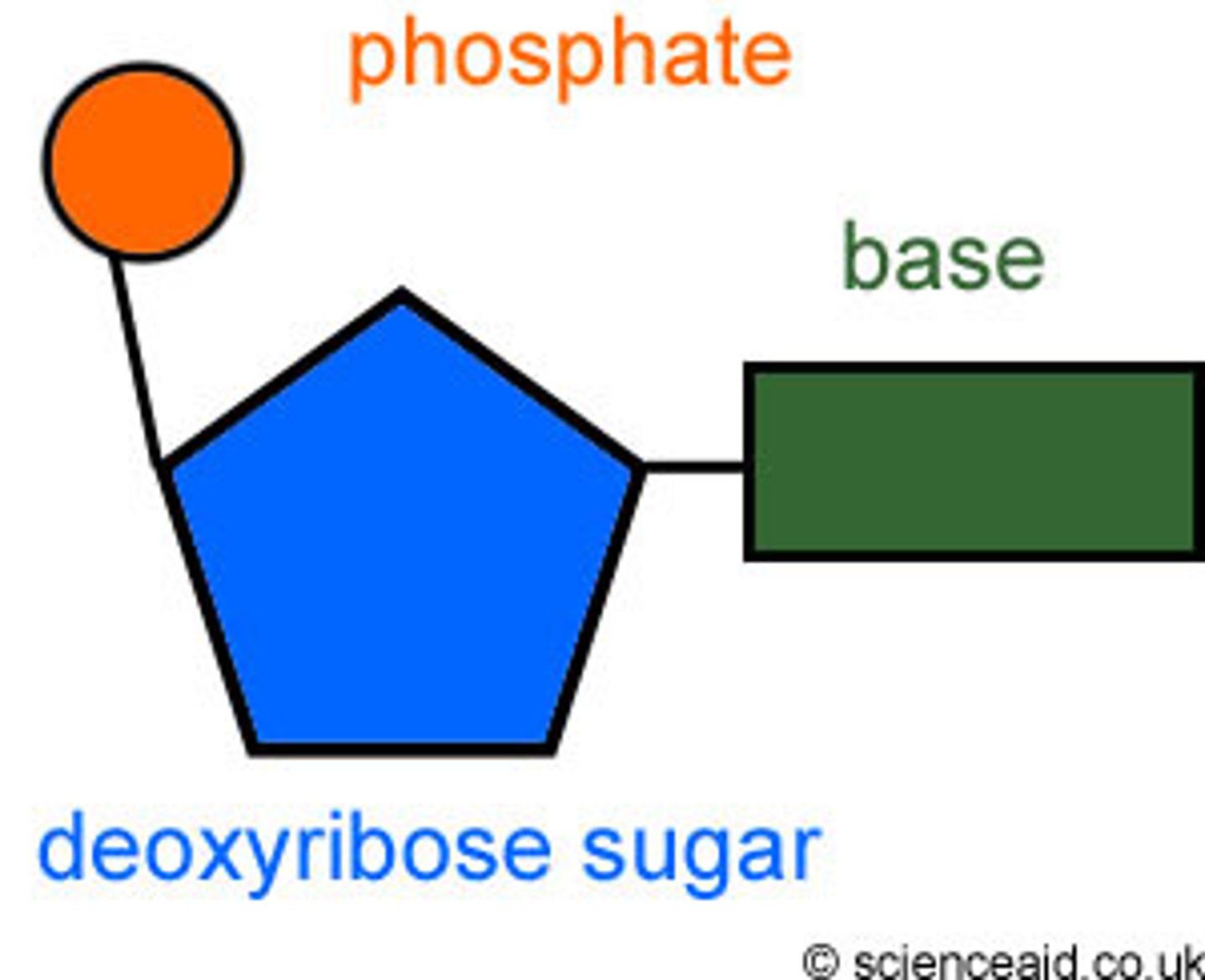
nucleotide structure
1. pentose (deoxyribose or ribose sugar)
2. phosphate on 5' C
3. nitrogenous base (C,G,A,T,U) on 1' C
DNA basic function
carries genetic information
where is DNA contained?
in chromosomes which are found in the nucleus of most cells but small amount are found in the mitochondria!
genetics
study of heredity and the variation of inherited traits
gene therapy
using genes to treat/prevent disease. might replace some drugs/surgeries in the future!
pharmacogenetics
application of genetic analysis to predict drug response, efficacy and toxicity. its used in prescribing to determine the best drug based on pt genotype for e.g.
congenital
present from birth
RNA basic function
important for gene expression & regulation and protein synthesis
where is RNA contained?
all throughout the cell e.g. nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosome etc.
DNA vs RNA nucleotide structure
DNA: H attached to 2' C
RNA: OH attached to 2' C
how are Cs numbered in nucleotides?
1' to 5' going from R->L where the top corner is acc an O
nucleic acid nitrogenous bases
Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, Thymine (DNA only) and/or Uracil (RNA only)
thymine vs uracil structure
same except thymine has a methyl group also attached!
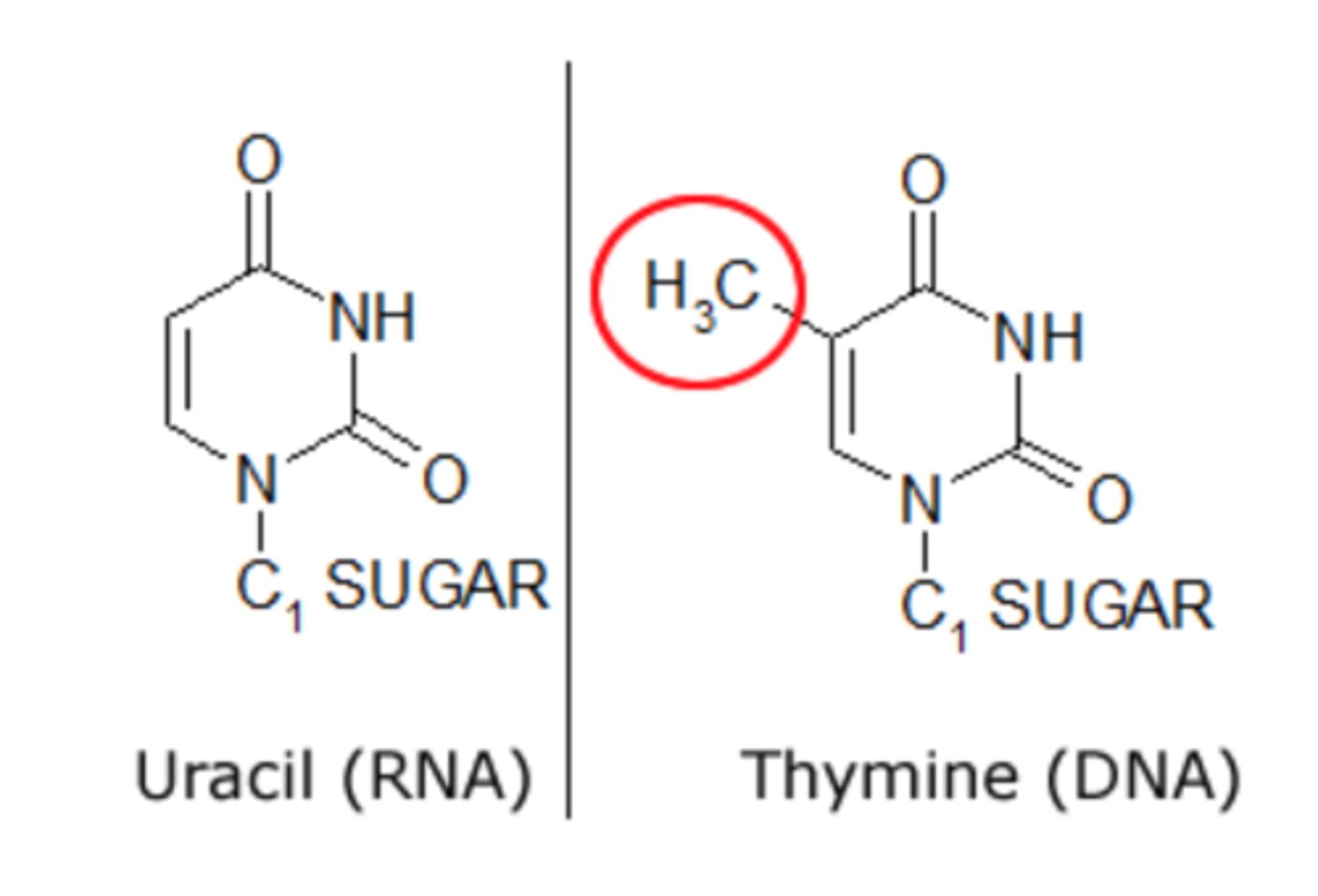
how to tell if its DNA or RNA based on nucleic acid structure?
1. check 2' C. if H attached = DNA, if OH attached = RNA
2. check if it has thymine or uracil NOTE: look for a hexagon w 2 carbonyl groups. if it has a methyl group also attached = DNA if no methyl group = RNA
adenine and guanine are...
...double ring purine bases
cytosine, thymine and uracil are...
...single ring pyrimidine bases
nucleic acid joining structure
phosphate joins 3' C of 1 pentose to 5' C of next pentose to get that repeating pattern
where are nitrogenous bases attached on nucleic acids?
1' C always
order of nitrogenous bases on nucleic acid...
...is important as it determines the genetic information of a molecule
DNA structure
double helix
RNA structure
single stranded
how are nitrogenous bases joined to each other in DNA?
hydrogen bonds
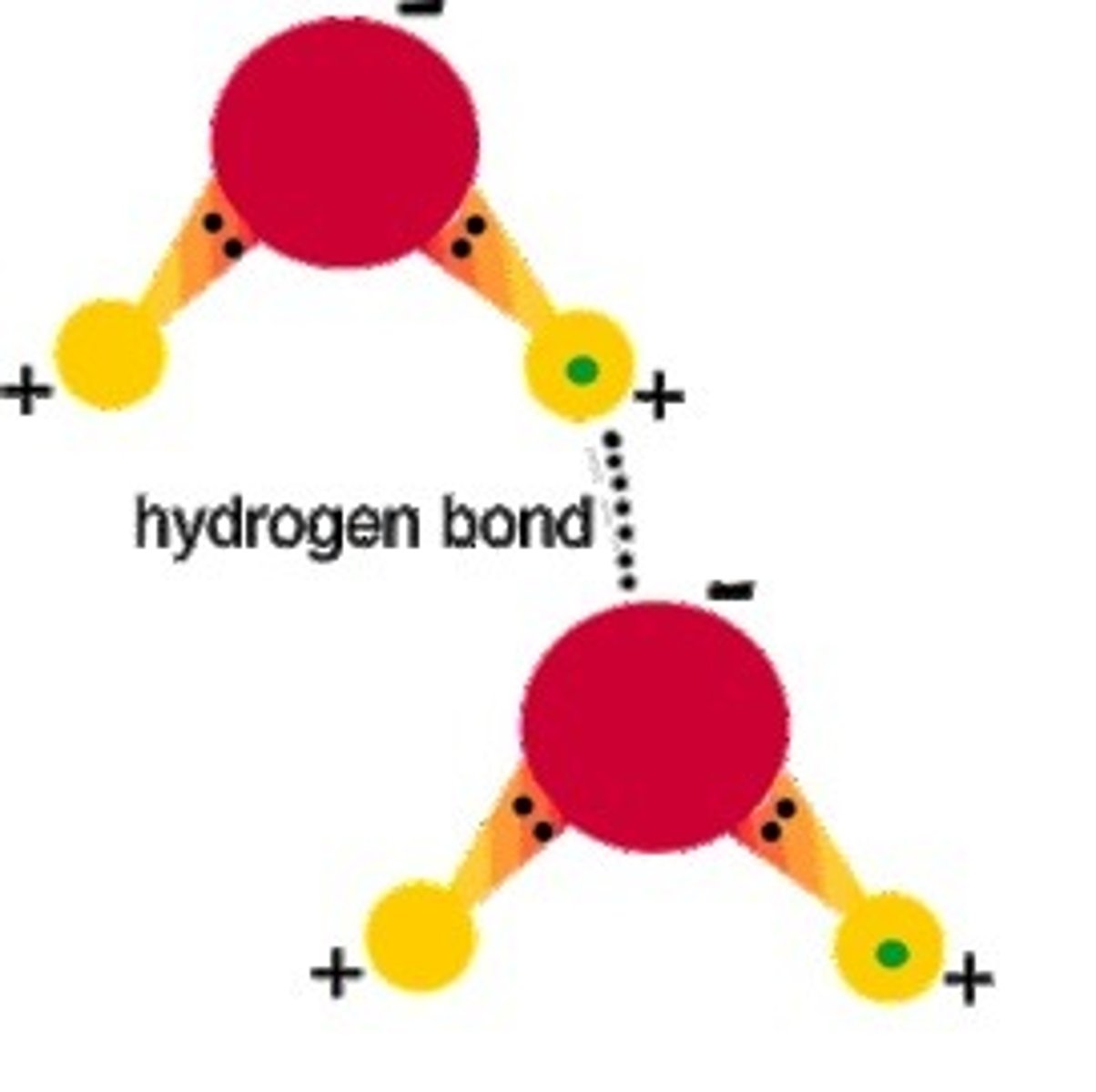
DNA double helix strand structure
they're antiparallel sister strands (complementary NOT identical!)
nucleic acid complementary base pairs
C+G
A+T/U
i.e. purine + pyrimidine
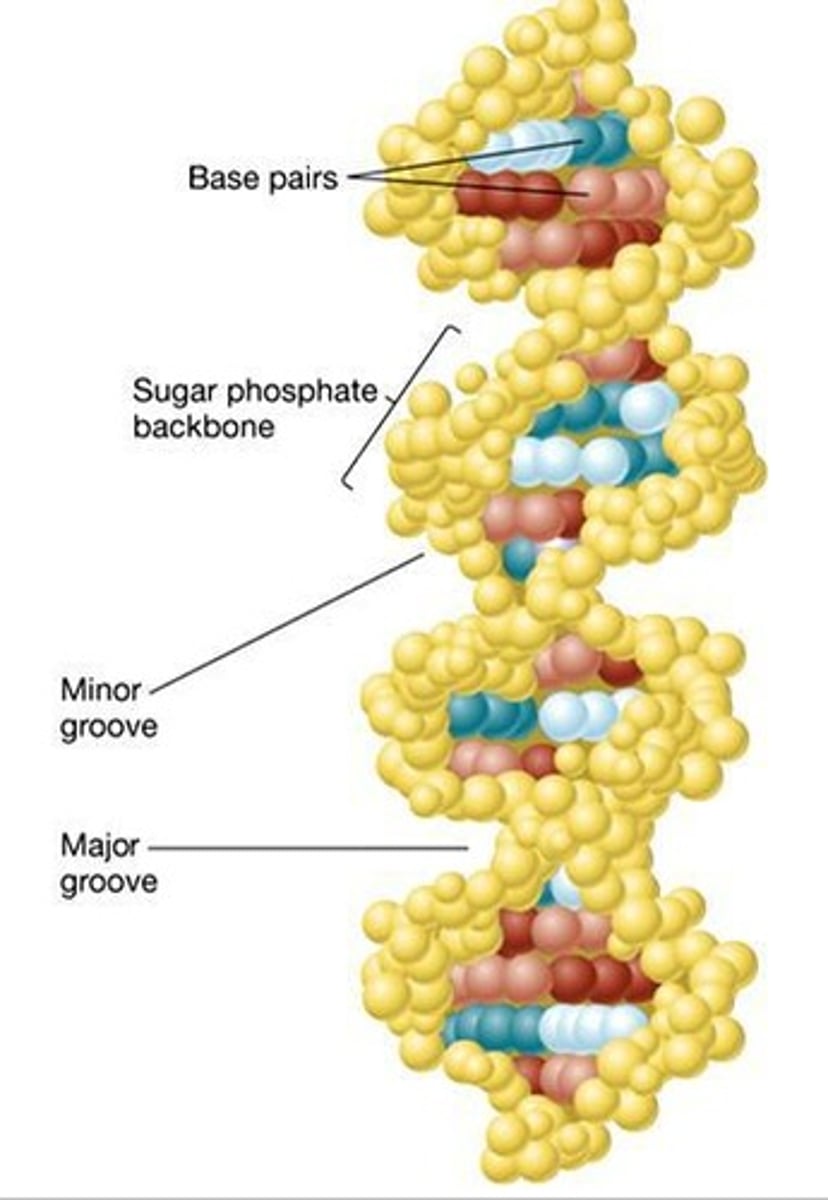
DNA grooves
minor groove: when strands are close together
major groove: when strands are far apart
NOTE: many anti-cancer drugs are groove binders!
DNA amount...
...is constant proving that they're the molecule of heredity
3 types of RNA
1. mRNA
2. tRNA
3. rRNA
what do the 3 RNA types do?
translate genetic code into proteins
how is mRNA generated?
during transcription, it's transcribed from DNA in the nucleus
what does mRNA do?
carries genetic code (codons) from nucleus to cytoplasm
what does tRNA do?
helps to decode mRNA sequence into a protein by carrying AAs to ribosome
where does tRNA carry AAs?
at 3' end
what is rRNA?
the structural and functional part of the ribosome
what do ribosomes consist of?
rRNA and proteins
ribosomes are the site of...
...protein synthesis and are a major antibiotic target e.g. tetracyclines
miRNA and siRNA
RNAs that degrade mRNA or block translation to regulate gene expression