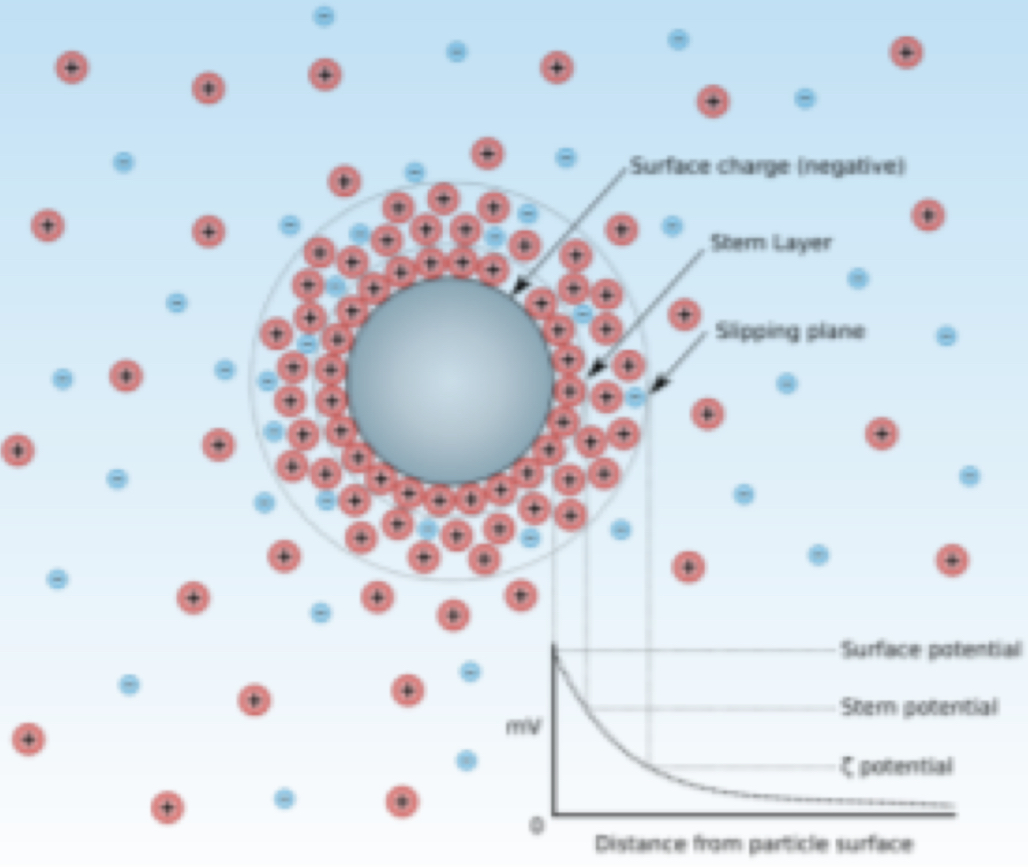
10. Electro kinetic potential
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Last updated 12:37 PM on 7/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Where in the cell is the potential-generating charge located?
Fixed on the surface of the cellular membrane
2
New cards
For which of the following cases the thickness of the double electric layer will increase?
A) when the ion concentration in the vicinity of the cell in increased
B) when the ion concentration in the vicinity of the cell is decreased
C) when there is an increase in the hydrogen bonding in the water solution around the cell
A) when the ion concentration in the vicinity of the cell in increased
B) when the ion concentration in the vicinity of the cell is decreased
C) when there is an increase in the hydrogen bonding in the water solution around the cell
B) When the ion concentration in the vicinity of the cell is decreased
3
New cards
Which of the following potential differences the electro kinetic potential of the cell:
A) the potential difference between intracellular and extracellular environments
B) the potential difference between the fixed surface charge of the membrane and the extra cellular fluids
C) the potential difference in the liquid medium of the cell, between the plane of the adsorption layer and the bulk o the medium
A) the potential difference between intracellular and extracellular environments
B) the potential difference between the fixed surface charge of the membrane and the extra cellular fluids
C) the potential difference in the liquid medium of the cell, between the plane of the adsorption layer and the bulk o the medium
C) the potential difference in the liquid medium of the cell, between the plane of the adsorption layer and the bulk of the medium
4
New cards
What is the sign of the electro kinetic potential (zeta) for living cells under normal physiological conditions?
Negative
5
New cards
What is the isoelectric point of the zeta potential?
The pH of the dispersion medium fro which the electro kinetic potential is zero
6
New cards
In which of the following cases there is an electro kinetic potential?
A) when cells are placed in electrolyte solution
B) when the liquid surrounding the cells moves
C) when cells do not move in an external electric field
A) when cells are placed in electrolyte solution
B) when the liquid surrounding the cells moves
C) when cells do not move in an external electric field
When cells are placed in electrolyte solution
7
New cards
Which of the following is not an electrokinetic phenomenon?
A) electro tonic potential
B) sedimentation potential
C) streaming potential
A) electro tonic potential
B) sedimentation potential
C) streaming potential
A) electro tonic potential
8
New cards
Potential-generating layer is:
The accumulated, non compensated charge of the surface of the dispersed phase (particle)
9
New cards
The ions of the adsorption and defuse layers are called counter ions because:
They have the opposite charge to that of the potential generating ions
10
New cards
The adsorption layer is:
Counter ions attracted to the surface of the bio-object
11
New cards
The double electric layer is defined as:
The volume surrounding the bio-object, where the potential-generating charges and the counter ions have an asymmetrical distribution, which is electro-neutral as a whole
12
New cards
What happens to the zeta potential when the ionic strength of the dispersion medium is increased?
It decreases
13
New cards
The electro kinetic potential is measures/ calculated by:
The speed of the dispersed phase in external electric field
14
New cards
The surface electric charge of the bio-objects is generated by:
Dissociation of ionogenic groups from the surface of the bio-objects
15
New cards
Electrokinetic (zeta) potential is:
The potential difference between the adsorption layer and the medium beyond the diffuse layer
16
New cards
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
A) Debye length of screening is qual to the length of the diffuse layer
B)Debye length of screening is equal to the distance from the surface where he potential decreases by 10 times
C) Debye length of screening is equal to the distance from the surface where the potential decreases e- times ( where e= 2.71)
A) Debye length of screening is qual to the length of the diffuse layer
B)Debye length of screening is equal to the distance from the surface where he potential decreases by 10 times
C) Debye length of screening is equal to the distance from the surface where the potential decreases e- times ( where e= 2.71)
B) Debye length of screening is equal to the distance from the surface where the potential decreases by 10 times
17
New cards
How far does the diffuse layer spread around a bio-object?
From the adsorption layer to the point where the potential decreases e-times (where e=2.71)
18
New cards
What is the relation between zeta potential and the pH of the dispersion medium?
Zeta potential dependence on the pH follows a sigmoid function
19
New cards
The quantity μ = v/E is defined as:
Electrophoretic mobility
20
New cards
The zeta potential of a cell do not depend on:
Shape of the cell
21
New cards
If concentration of diva lent and multitalented ions in a dispersion medium in increased
Zeta potential will decrease
22
New cards
How does the pH of the medium affect the surface charge of the cell?
The pH affects the dissociation activity of basic and acidic surface groups
23
New cards
What is the ratio of positive/negative potential-generating charges at the isoelectric point of the cell? How does it affect the interaction between cells?
The ratio of positive/negative charge is unity (one) and there is agglutination of the cells
24
New cards
Why zeta potential decreases when the ionic strength of the medium in increased?
Because the diffusion layer around the particle decreases
25
New cards
What value of zeta potential indicate instability of the dispersion and higher probability for aggregation of the particles (Cells)?
When the absolute value of zeta decreases the propensity for aggregation increases
26
New cards
Describe the process of dissociation of protein molecules which leads to the formation of surface electric charge on bio-objects in basic and acidic mediums:
Interphase potential: The strongly expressed heterogeneity of biological structures is the cause for the occurrence of electric potential differences of a specific type.
\
The interphase potential difference can arise between the surface of the solid phase (e.g cellular surface) and the liquid phase in which ions are present.
One of the basic processes that lead to that is the dissociation of the ionogenous groups of protein molecules on the surface of the solid phase.
\
Regions of non-compensated charges arise and in proximity to the surface of the solid phase several layers are differentiated a structure referred to as double electrical layer \[DEL\].
\
The interphase potential difference can arise between the surface of the solid phase (e.g cellular surface) and the liquid phase in which ions are present.
One of the basic processes that lead to that is the dissociation of the ionogenous groups of protein molecules on the surface of the solid phase.
\
Regions of non-compensated charges arise and in proximity to the surface of the solid phase several layers are differentiated a structure referred to as double electrical layer \[DEL\].
27
New cards
Sketch on a the dependence of the zeta potential on the ionic strength of the medium
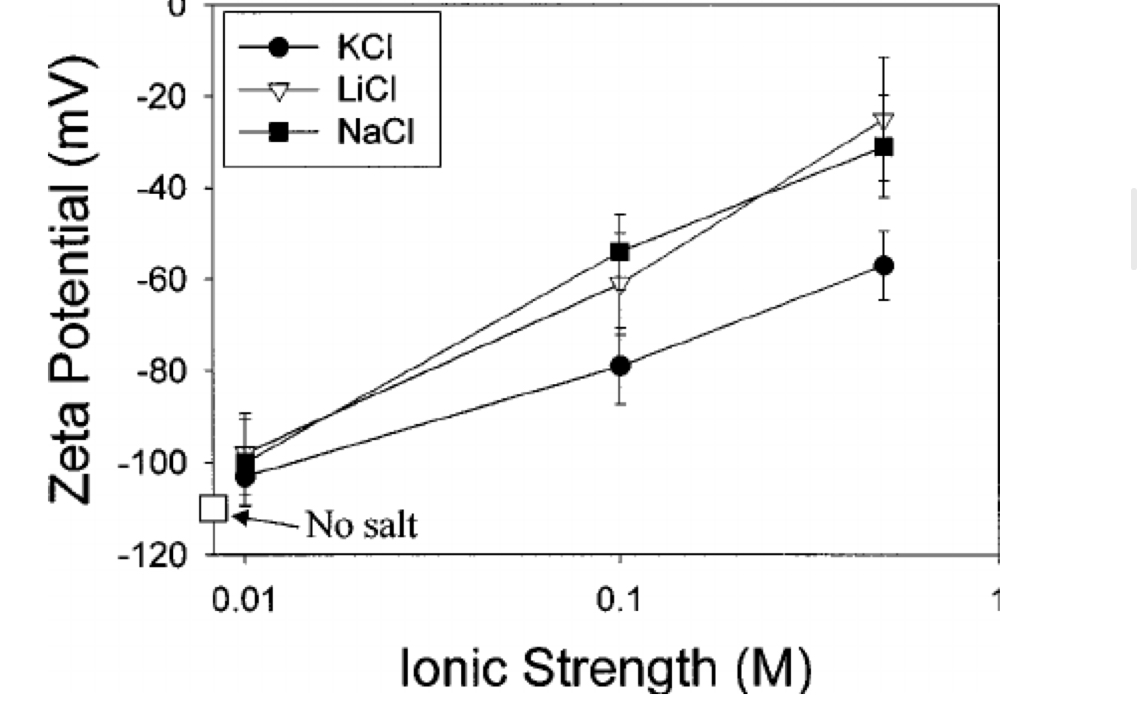
28
New cards
List all of the electrokinetic phenomena that you know of:
● Electrophoresis - movement of charged particles (dispersed phase) in a dispersion medium by the force of external electric field.
● •Streaming Potential - generation of electric field, when liquid medium moves past a stationary charged surface (such as capillary).
● Electro-osmosis - movement of liquid through porous charged surface (such as capillary) when external electric field is applied. In a sense it is the reverse of the streaming potential.
● Sedimentation Potential – electric potential due to charged particle sedimentation
● Electroacoustics
● Diffusiophoresis
● Zeta potential
● •Streaming Potential - generation of electric field, when liquid medium moves past a stationary charged surface (such as capillary).
● Electro-osmosis - movement of liquid through porous charged surface (such as capillary) when external electric field is applied. In a sense it is the reverse of the streaming potential.
● Sedimentation Potential – electric potential due to charged particle sedimentation
● Electroacoustics
● Diffusiophoresis
● Zeta potential
29
New cards
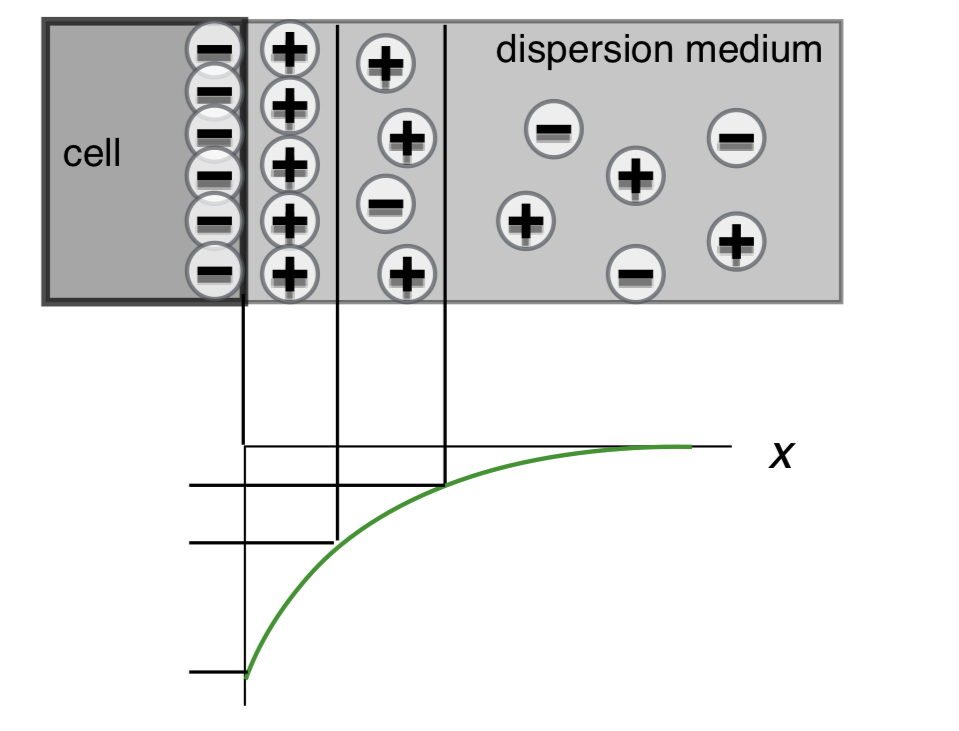
The surface charge of dispersed particles leads to formation electric potential difference (voltage) with respect to the bulk of the medium. The absolute value of the potential is maximum at the surface and it decreases away from the surface. The potential at different points is numbered from 1 to 4. Please Abel the 4 points on the graph.
E) surface potential φ0
F) potential of adsorption layer φa
G) Zeta potential ζ
H) diffuse potential φd
E) surface potential φ0
F) potential of adsorption layer φa
G) Zeta potential ζ
H) diffuse potential φd
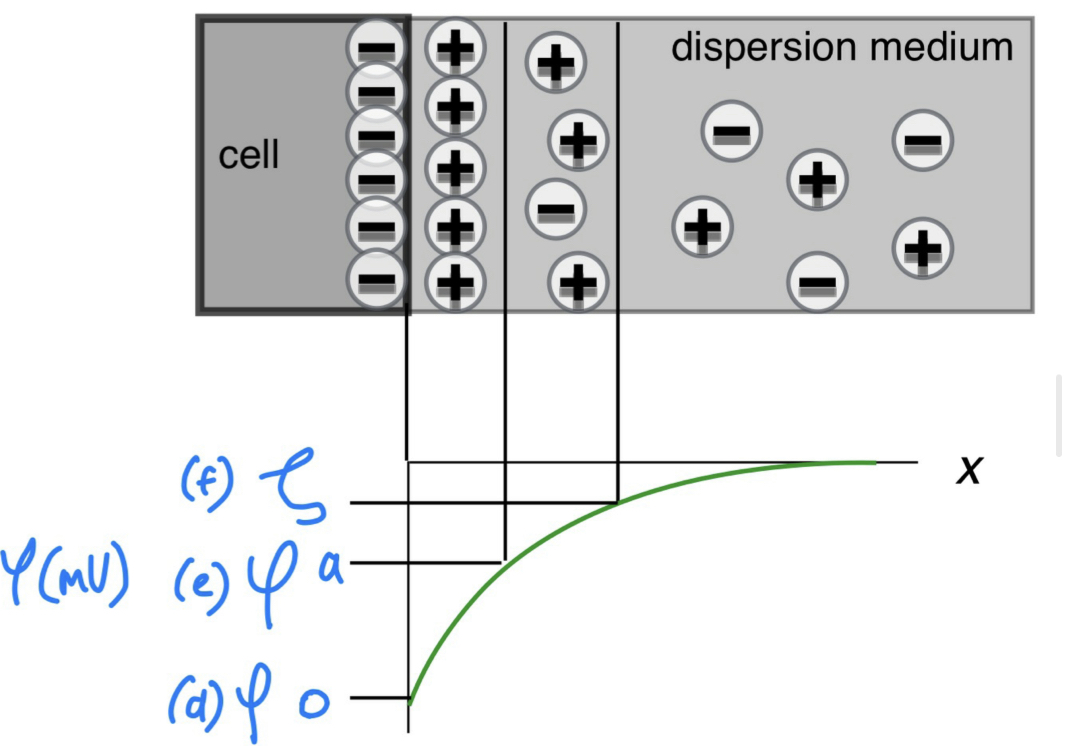
30
New cards
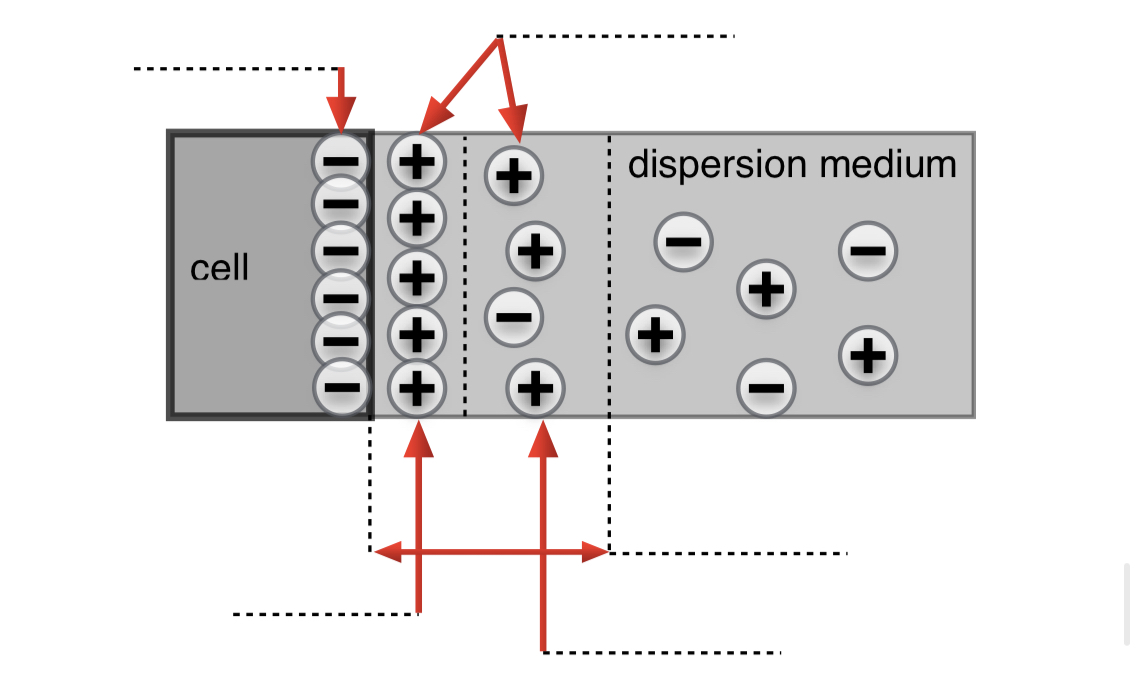
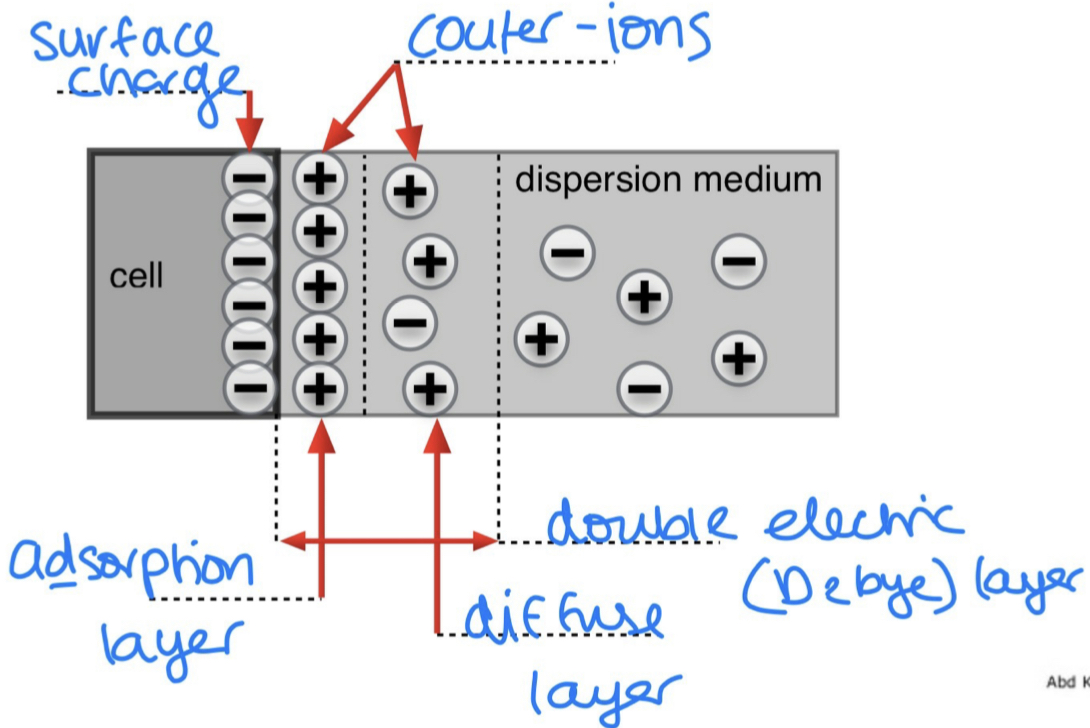
Label the sketch with the appropriate parameters
31
New cards
Sketch he distribution of counter-ions of he double electric layer around spherical biological object: