nitrogen metabolism
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
what are amino acids used in (4 things)
protein synthesis
synthesis of important nitrogenous compounds
use of carbon skeletons for fuel in TCA cycle
use of carbon skeletons to make glucose and ketone bodies
use of carbon skeleton requires
excretion of amino nitrogen
(cuz you want the carbon group not the nitrogen group)
the more important fate of amino acids (by mass)
generation of carbon skeletons and N-containing compounds
this is more important than protein synthesis
essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by humans
MTW HF LIV (R)K
M - methionine
T - threonine
W - tryptophan
H- histidine
F - phenylalanine
L - lysine
I - isoleucine
V - valine
R - arginine
K - lysine
is arginine essential
to develop embryo and fetus but we can synthesize it as adults
so only for embryo and fetus
nonessential amino acids that we can make from glucose
serine
glycine
cysteine
alanine
aspartate
asparagine
glutamate
glutamine
proline
arginine
basically all the others except tyrosine
nonessential amino acid that we make from an essential amino acid
what amino acid makes it
tyrosine
comes from phenylalanine
carbons of cysteine come from ___ but the sulfur comes from ____
glucose
methionine
some plant proteins are deficient in
how to remedy this
amino acids
complement one source of plant protein with another
legumes lack
methionine
grains lack
lysine
beans and rice together (legumes and grains) provide
all the essential amino acids
soybeans are equivalent to _____ in terms of digestible protein value
but they have low ____ content
eggs
low methionine content
every amino acid except lysine (K) and leucine (L) are
which means what
glucogenic
their carbon skeletons contribute to making glucose with gluconeogenesis --> they can be metabolized to pyruvate or TCA cycle intermediate
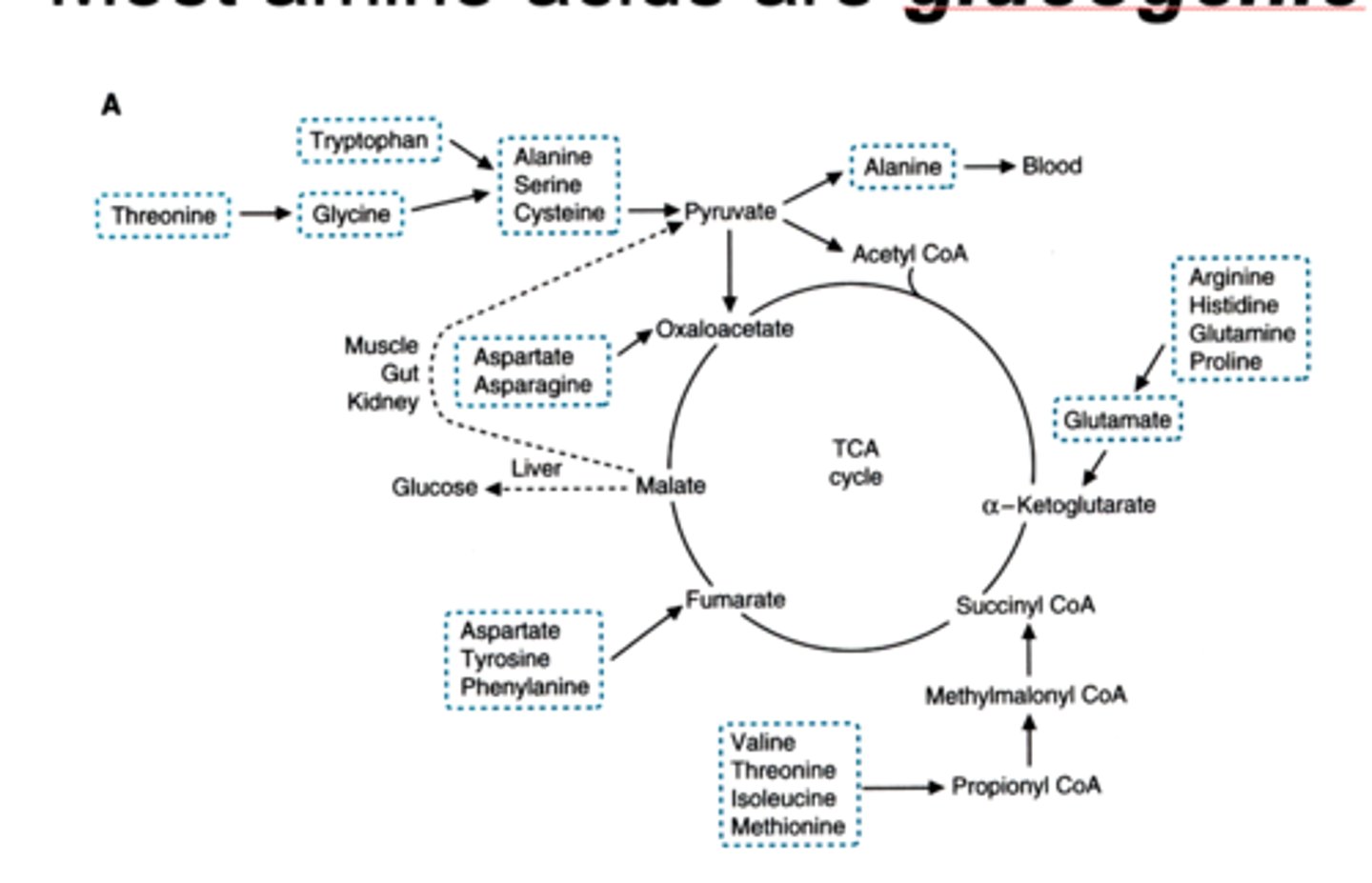
strictly ketogenic amino acids
lysine and leucine
which amino acids can do both
form ketone bodies and glucogenic
tryptophan
isoleucine
threonine
tyrosine
phenylalanine
WITY F
(wity fugger)
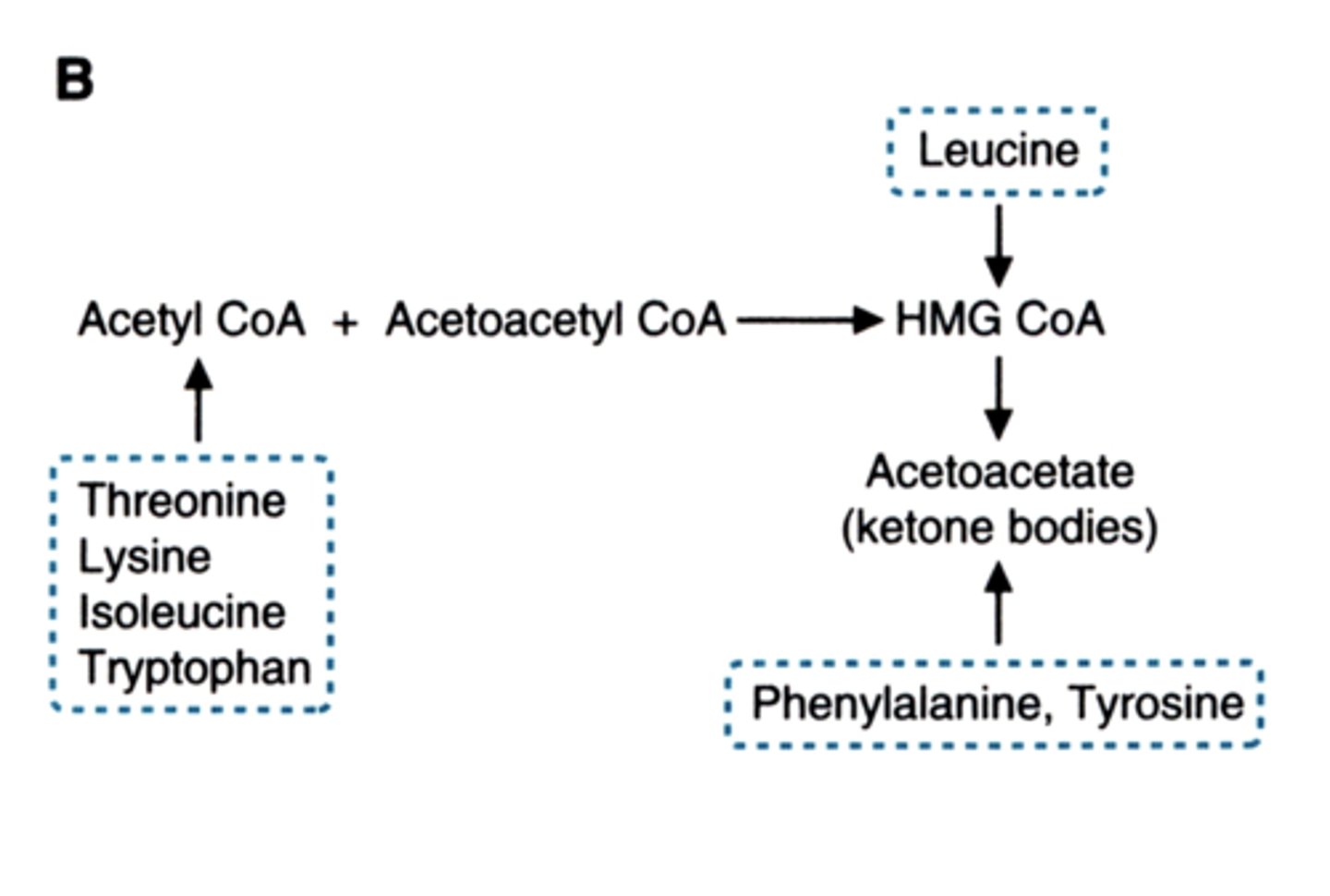
main precursors of gluconeogenesis (4)
this makes up ____ percent
lactate
alanine // glutamine in kidney
glycerol (converts to DHAP through F6P)
90%
"LAG"
main precursor for gluconeogenesis in kidney
glutamine (not alanine)
the other 10% of precursors for gluconeogenesis
other amino acids get metabolized to TCA cycle intermediates
which eventually become oxaloacetate
How does oxaloacetate get to location needed for gluconeogenesis
malate transports it to the cytosol
to generate PEP
what do lysine and leucine get metabolized to
acetyl coA
(not pyruvate or TCA intermediates)
2 long term storage forms of energy in the body
protein and fat
fatty acids only produce ___ they cannot make ___
acetyl coA
glucose (glycerol can)
amino acids make blood glucose during ___
fasting state (12+ hours)
skeletal muscle starts getting degraded to make glucose
the excess ammonium produced when amino acids make glucose during fast gets converted to
urea
when blood glucose is low
acetyl coA in the liver is used to form
(so this is what leucine and lysine and some others make)
acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate
these are ketone bodies
carbons from acetyl CoA get released as ____ in the TCA cycle
co2
can animals form new glucose from co2 (that is released from TCA)
no
only plants and some prokaryotes can
acid in the stomach
HCl
endoprotease vs exoprotease
cut protein inside the peptide chain
cut from the ends of the chain (N or C terminus)
pepsin
key role
location
cleaves after
endoprotease
FIRST protease
in stomach
Phe, Tyr, Glu, Asp
(F, Y, E, D)
zyomgen of pepsin
how it gets activated
pepsinogen
by acid (H+), by pepsin
trypsin
key role
location
cleaves after
endoprotease
ACTIVATES OTHER ZYMOGENS
intestine
Lys, Arg
(its a basic bish)
zyomgen of trypsin
how it gets activated
trypsinogen
enterokinase
(enteropeptidase)
proteases are born as
zymogens (proenzymes)
3 zymogens trypsin activates
chymotrypsinogen --> chymotrypsin
proelastase --> elastase
procarboxypeptidase --> carboxypeptidases
amino acid transport in the intestinal lumen brush border, gut, and kidney
what proteins do it
specificity is ___
5 specificity groups are
sodium linked carriers
broad specificity
1) system A
2) N
3) X-AG
4) ASC
5) y+L
4 nitrogenous urinary excretory products
(disposed nitrogen to use carbon skeleton)
urea
NH4+
creatinine
uric acid
aminotransferase reactions (transamination) are when
give example
the amino group is transferred
AA1 <--> aKetoacid1
aKetoacid2 <--> AA2
example:
aspartate <-> oxaloacetate
a-ketoglutarate <-> glutamate
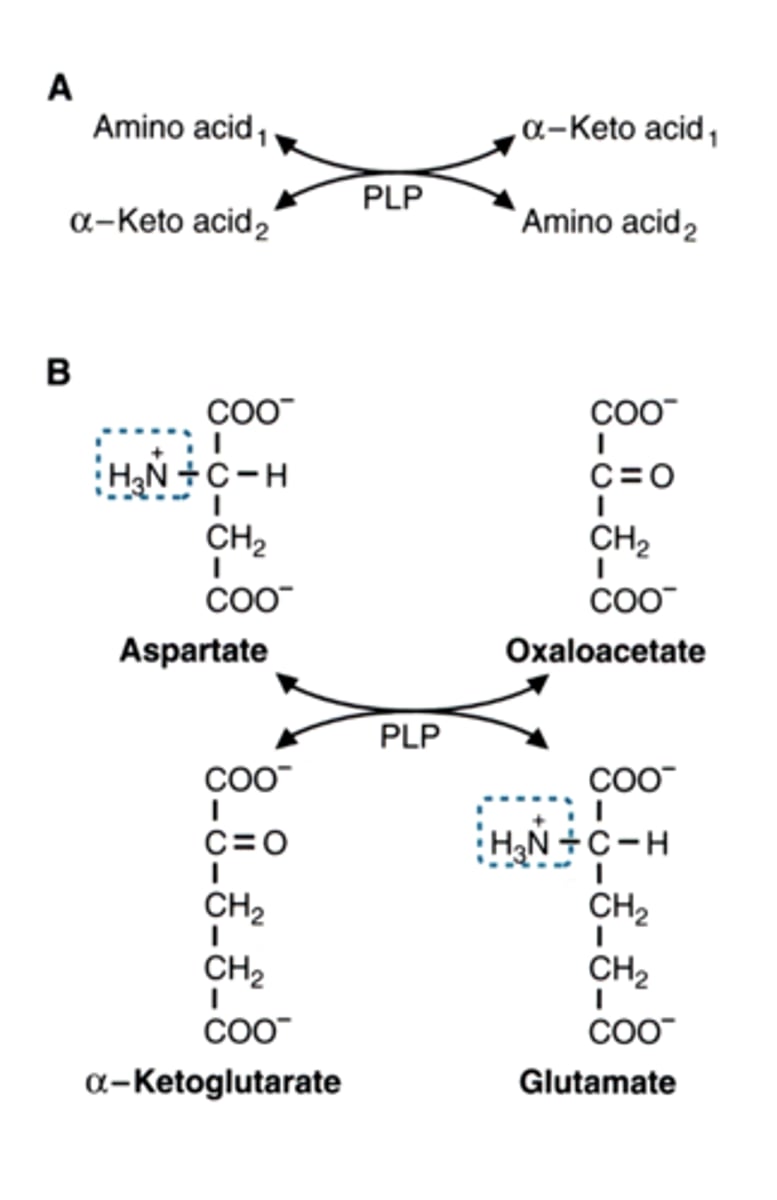
what is the cofactor used in aminotransferase reactions
PLP = pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6)
what is the universal receiver of amine groups
a-keto acids
(a-ketoglutarate)
characteristics of aminotransferases (3)
freely reversible (the amino can go both ways)
AT for all amino acids
most use glutamate/alpha-ketoglutarate as one pair (glu is the gathering point)
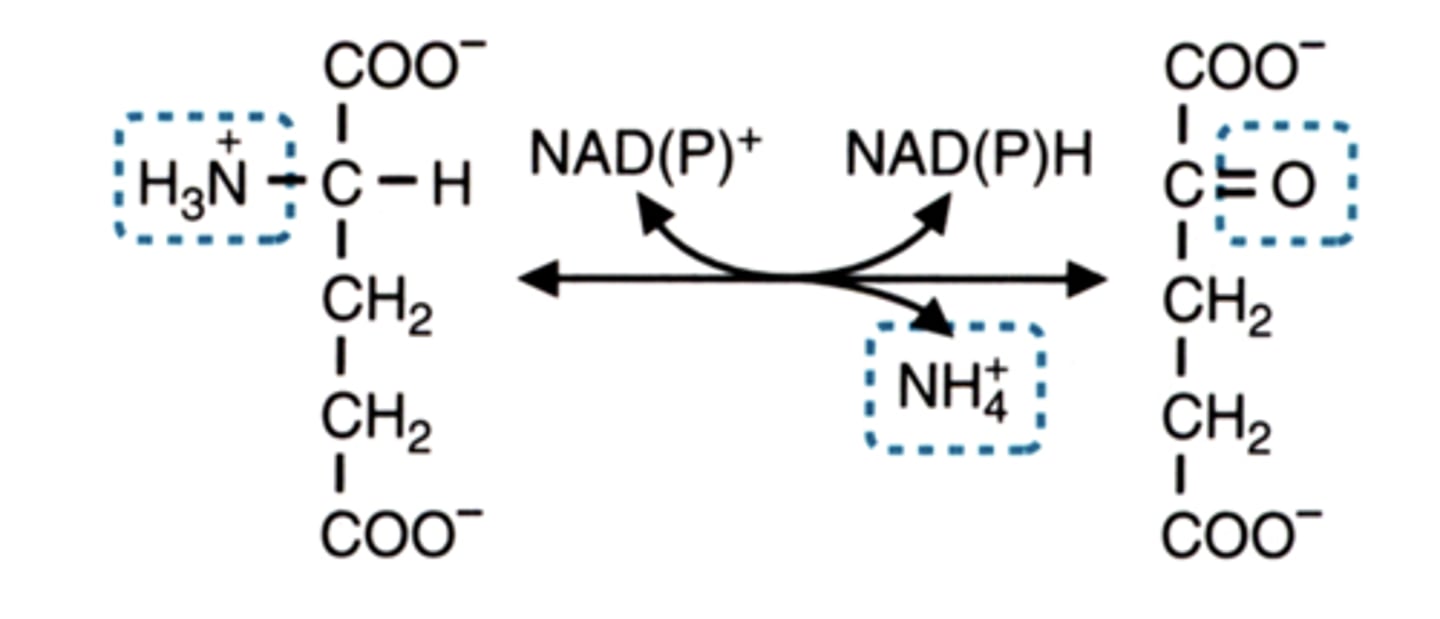
glutamate dehydrogenase reaction
what becomes what
what is used
what is released
Glutamate <-->
α-Ketoglutarate
uses NADP+
releases NADPH and ammonium
Ammonium is ________
how to prevent its accumulation
toxic
UREA CYCLE (makes it less toxic)
key precursors of urea cycle
amino acids (glutamate, aspartate)
a-ketoglutarate from transamination rxns
ammonium (NH4+)
other reactions
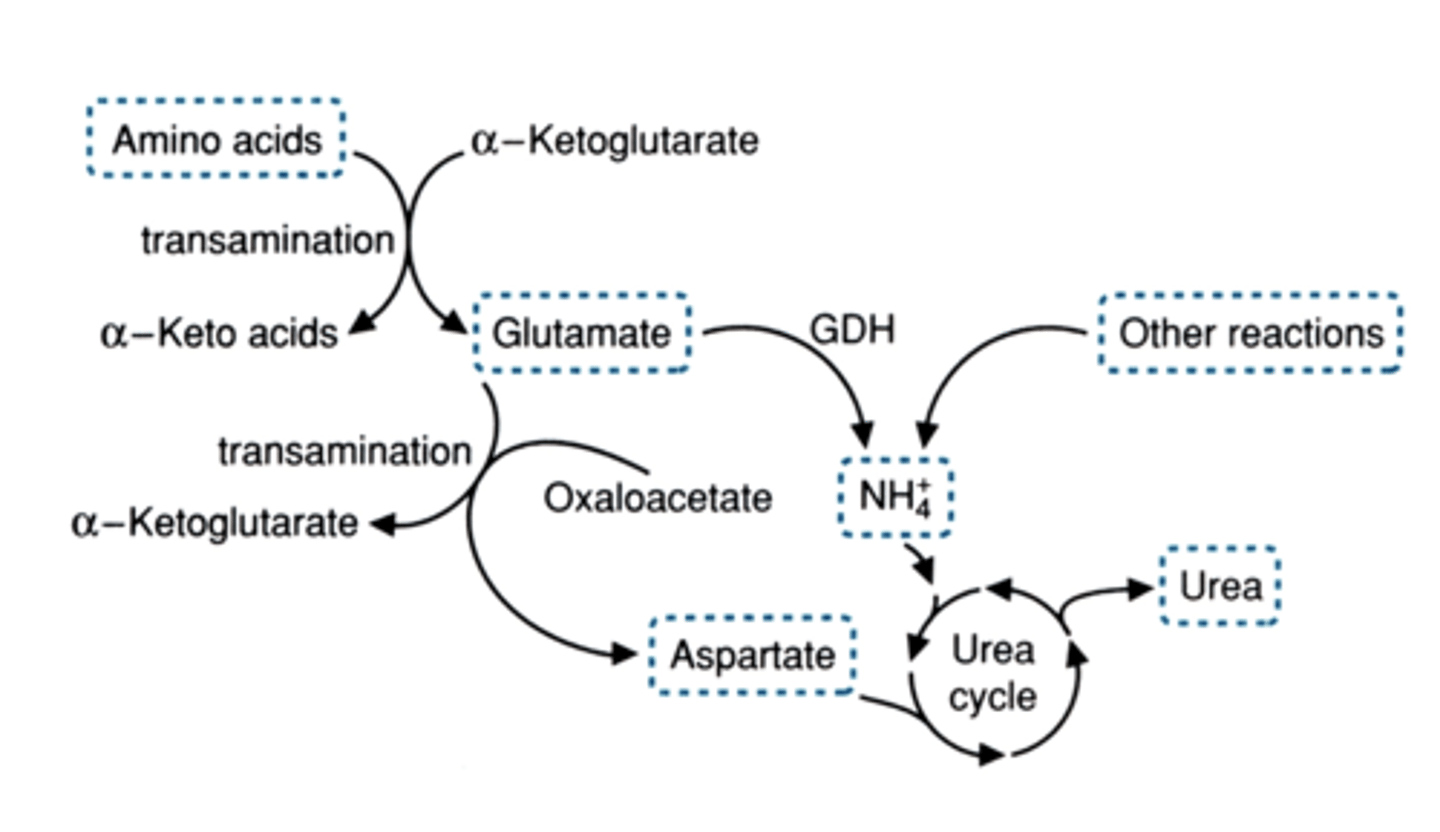
3 places ammonium comes from to enter the urea cycle
1. alanine conversion to pyruvate (gluconeogenesis generates NH4)
2. glutamate dehydrogenase (this one makes free ammonium)
3. aspartate formed by amination of oxaloacetate
AGA
amination of oxaloacetate makes
aspartate
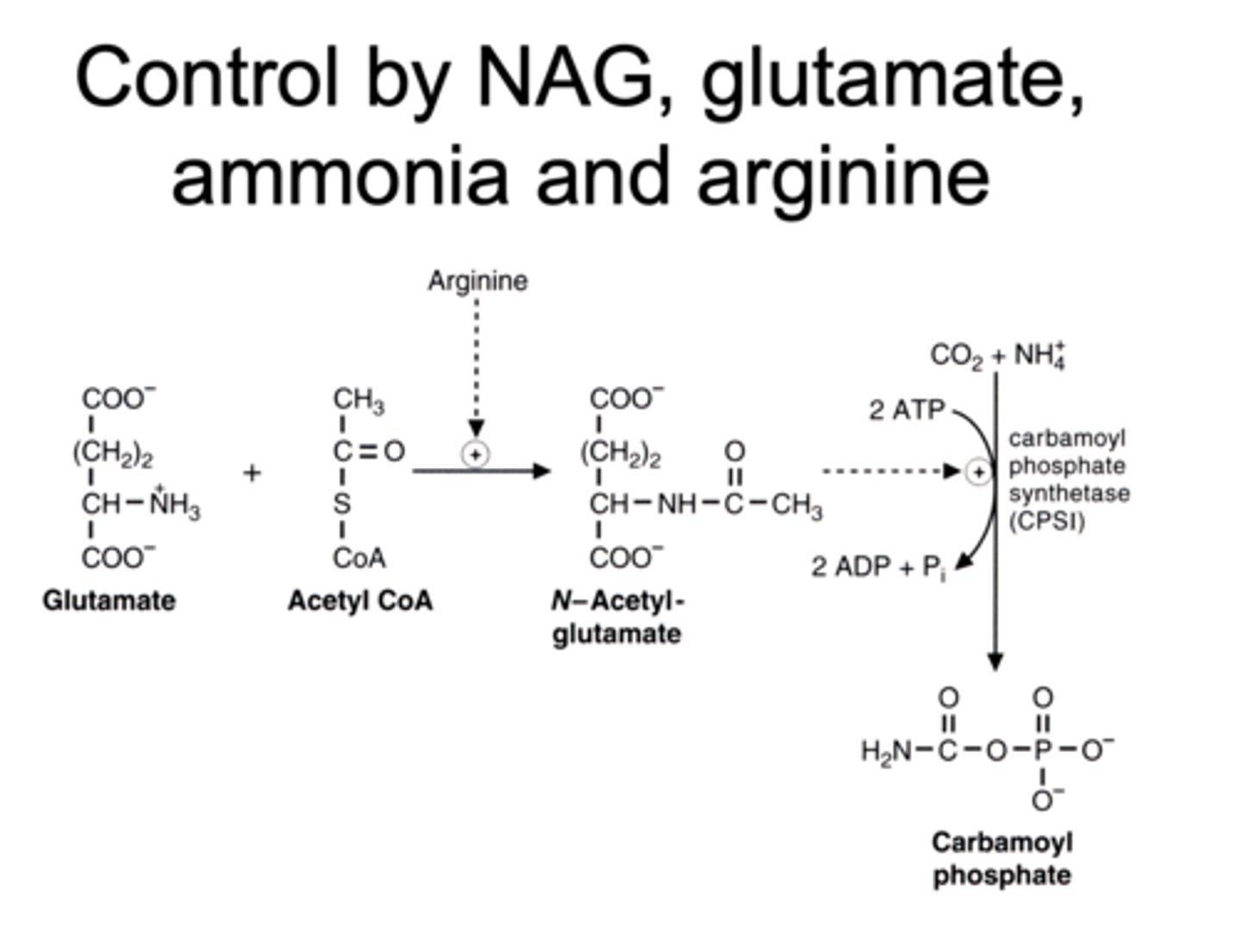
N-acetyl glutamate
made up of what 2 things
activated by what
activates what
significance of it
glutamate + acetyl coA
activated by Arginine
it activates CPS-1 which drives the urea cycle
so it is the key enzyme and regulator of the urea cycle
why does arginine activate NAG synthesis
arginine excess means excess of ammonia
so turns on NAG to start urea cycle
what does carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPSI) catalyze
turns co2 + ammonium
into
carbamoyl phosphate
these 2 enzymes collaborate to send nitrogen into urea cycle
aminotransferases
glutamate dehydrogenase
urea production increases during
fasting
muscle starts using protein and makes free alanine which becomes pyruvate to make glucose and ammonium in the liver
so that ammonium goes into urea cycle
humans can synthesize carbon skeletons of many amino acids from __
glucose
(the glucogenic ones)
(this leads to free toxic ammonium)
what are the things you need to make NONESSENTIAL amino acids
(3 main things and one enzyme)
glucose
methionine (for sulfur in cysteine)
phenylalanine (for tyrosine)
transaminases
serine synthesized from
3-phosphoglycerate
(3 PG)
2 enzymes that turns
3-phosphoglycerate into serine
serine inhibits this (feedback inhibition)
3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase
(3PG DH)
phosphoserine phosphatase
glycine synthesized from (2 things)
mostly from
serine or threonine
mostly serine
proline is synthesized from
glutamate semialdehyde
glutamate gets reduced to it
ornithine synthesized from
glutamate semialdehyde
glutamate semialdehyde is a direct precursor for (2 things)
proline
ornithine
arginine is synthesized from ___
in the ____ cycle
ornithine
becomes Arg in the urea cycle
Cori Cycle analog uses
branched chain amino acids
shuffles them from muscle to liver
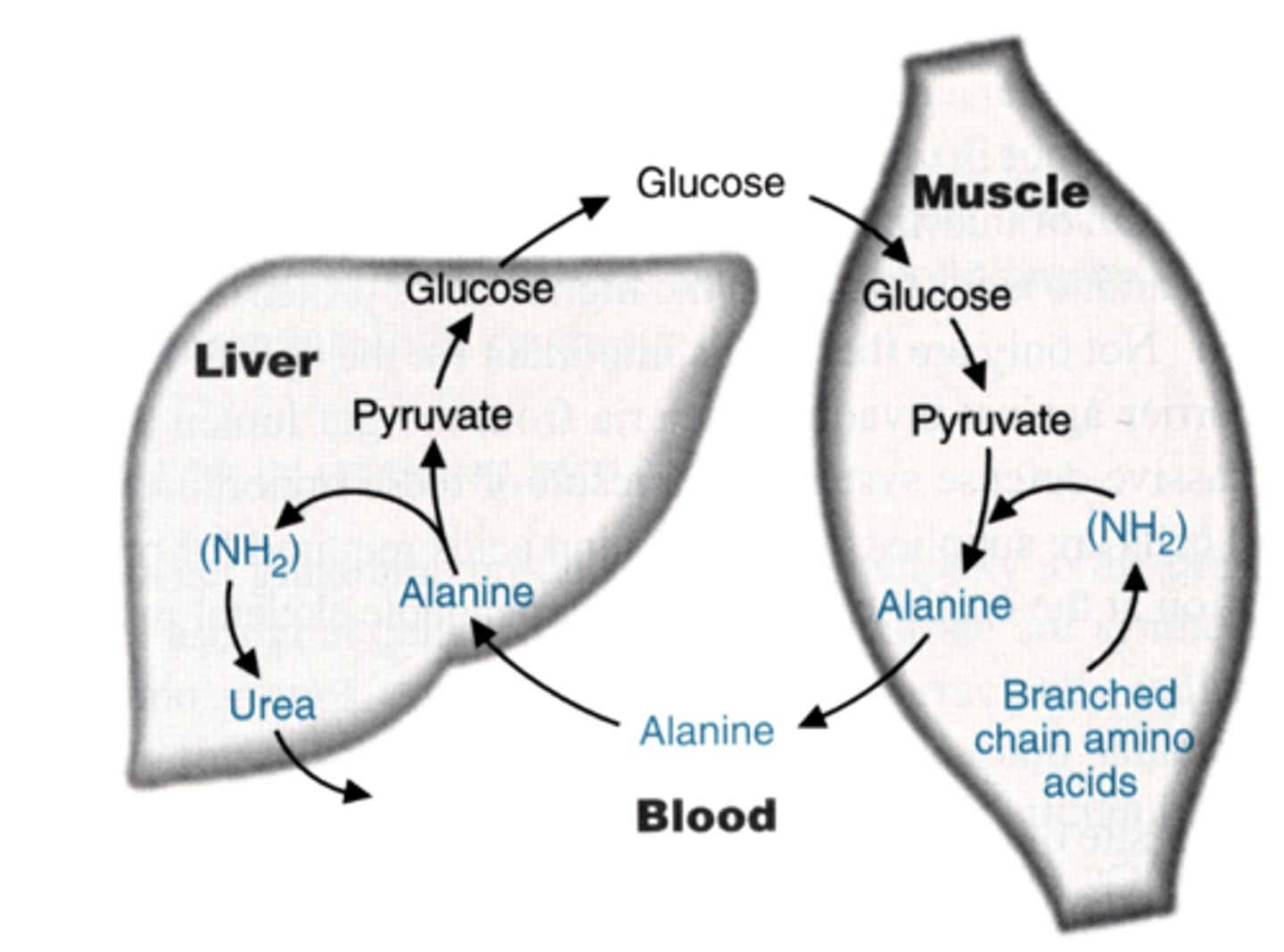
branched chain amino acids get ____
where does this happen
where does it not happen
deaminated and metabolized
(for carbon skeleton)
in the muscle and brain
they do NOT get oxidized in the liver
3 branched amino acis
valine
isoleucine
leucine
first 2 steps of metabolism of branched amino acids
1. aminotransferase
2. decarboxylating dehydrogenase
3. stuff happens and then final fates
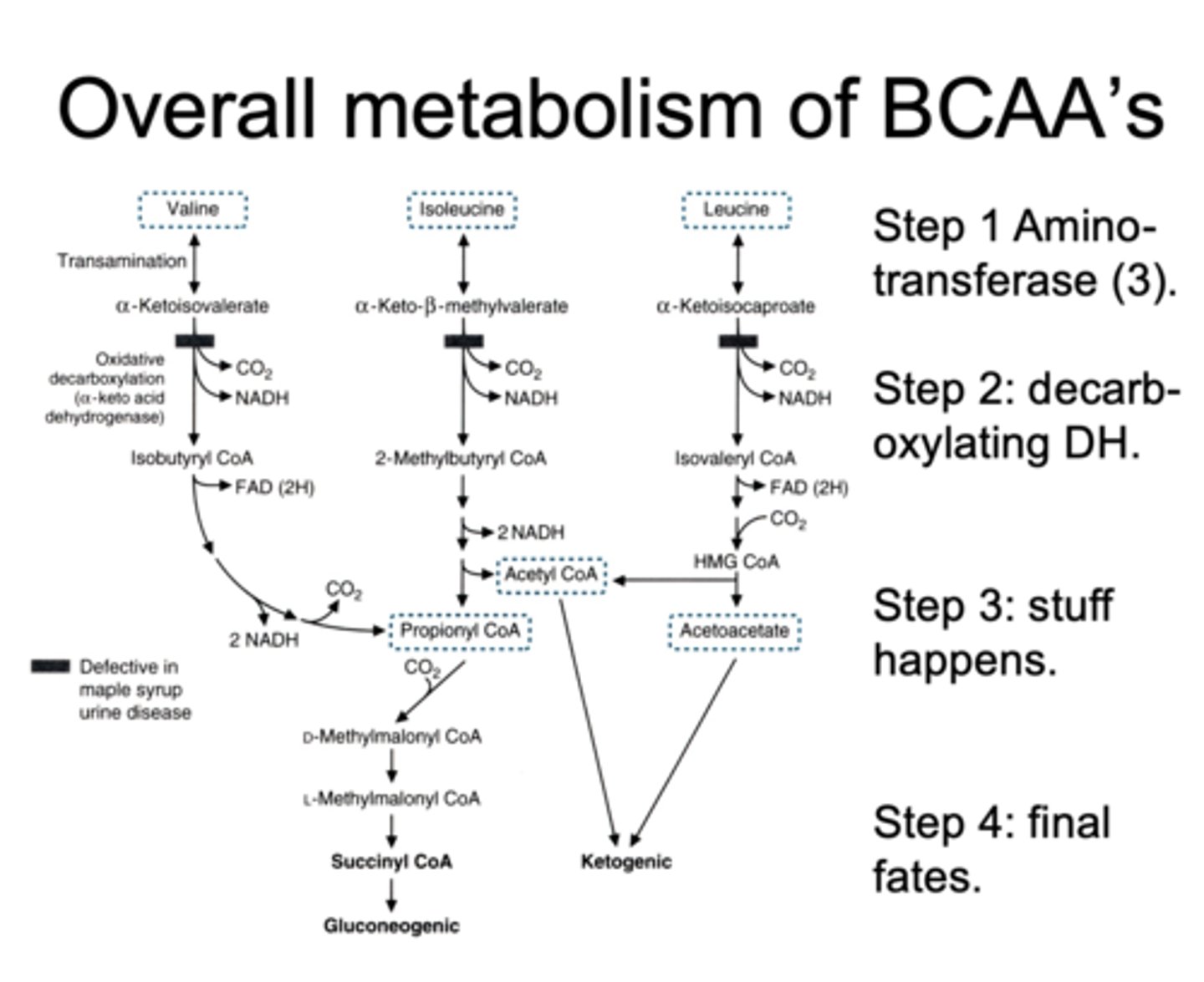
maple syrup urine disease
defective in
presents after
causes accumulation of
a-keto acid dehydrogenase
after first protein meal - it's a amino acid metabolism disorder
branched chain alpha keto-acids
symptoms of maple syrup urine disease
failure to thrive
feeding difficulties
developmental delay
convulsions
why is it called maple syrup urine disease
sweet odor of branched chain alpha keto acids + byproducts
(sweet urine)
single carbon pool aka __
synthesizes __ and __
folate cycle
synthesis of neurotransmitters and nucleotides depends on this
sources of one carbon units in the folate cycle
serine
glycine
histidine
formaldehyde
formate
tryptophan?
H G S, F F
the one carbon pool in folate cycle includes (3)
THIS IS HOW THE ONE CARBONS CAN EXIST
carried by a ___
formyl <->
methylene <->
methyl
carried by FH4 (tetrahydrofolate)
products of folate cycle/single carbon pool (4)
dTMP
serine
purines
B12 - methyl
what happens in the absence of folate in blood
megaloblastic anemia
because failure of blood cell precursors to make final division
key role of folate
which is needed to
nucleotide synthesis
replicate DNA
low folate in first weeks of pregnancy cause
neural tube defects
--> spina bifida
sources of folate (3)
leafy green veggies (foliage)
orange juice
its required in flour now
nutritional folate gets reduced to ___ inside of us
what enzyme does this
FH4 = tetrahydrofolate
(this is the one that can carry a carbon in the pool)
dihydrofolate reductase (does it twice and releases 2 NAP+)
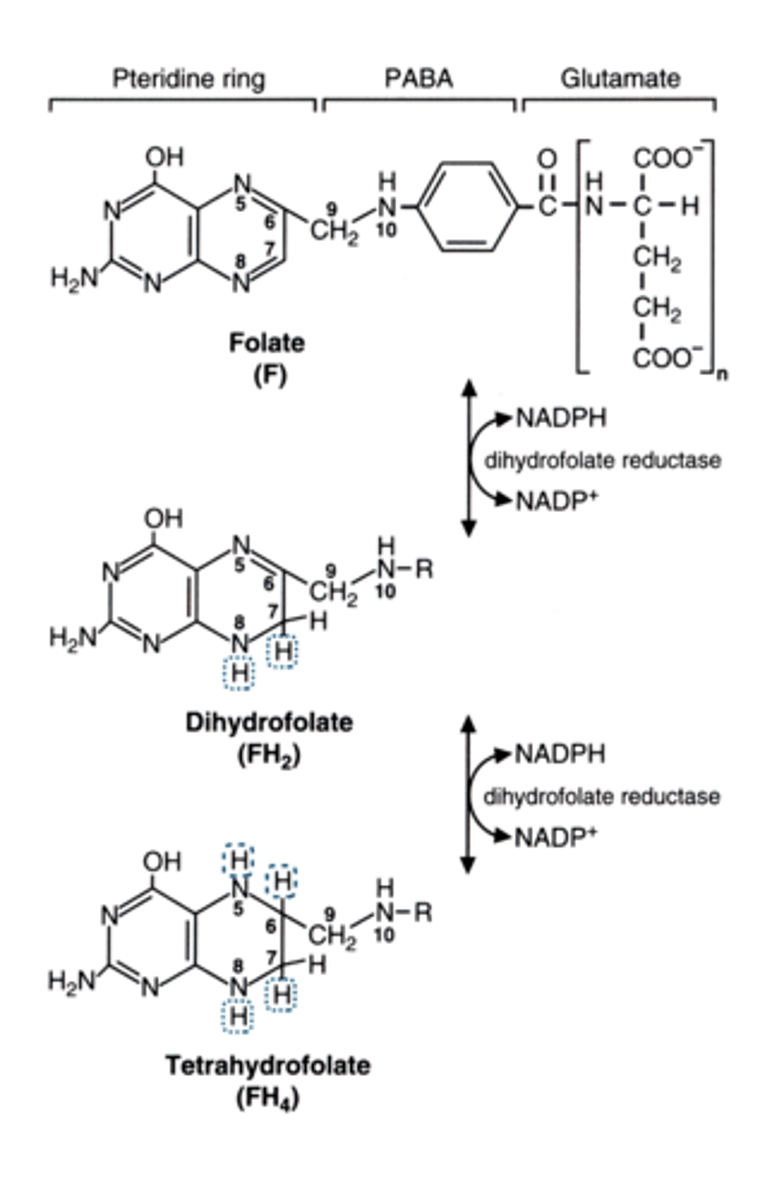
FH4 carries single carbons in a variety of
list the path
oxidation states
FH4 becomes:
N10-formyl-FH4
N5,N10-methenyl FH4
N5,N10-methylene-FH4
N5-Methyl-FH4
THE LAST STEP GOING FROM METHYLENE FH4 TO METHYL IS NOT REVERSIBLE
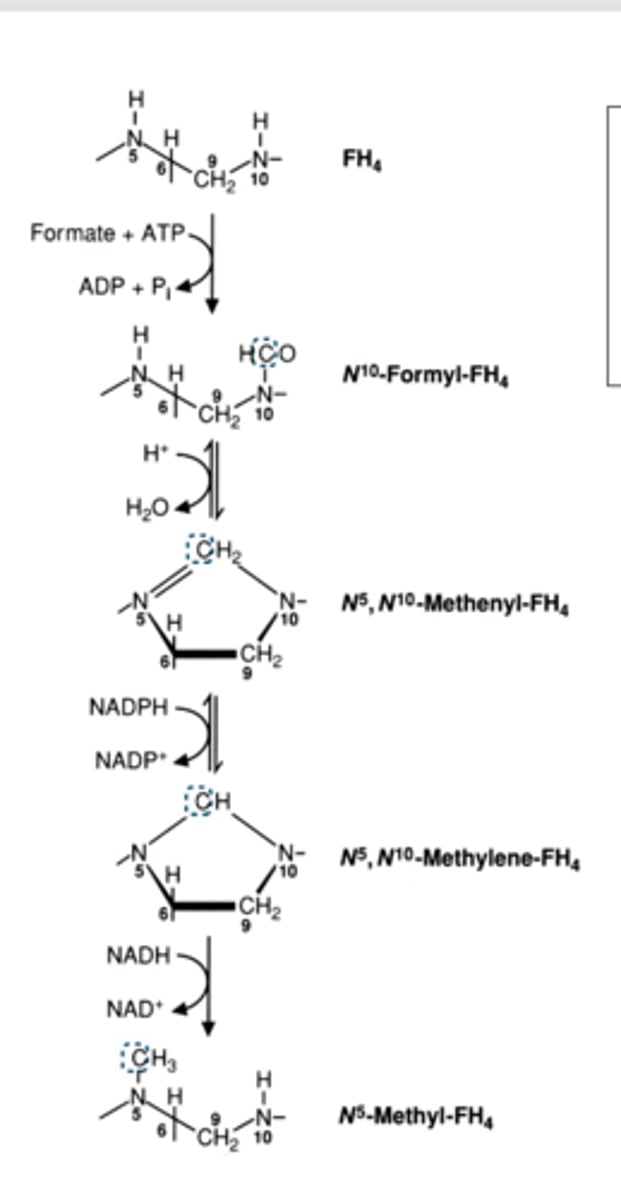
primary donor of single carbons
what do they feed into
more abundant than
serine and glycine
feed into N5 N10 METHYLENE FH4
they are more abundant than histidine and tryptophan
(histidine feeds into n5n10 methenyl
tryptophan feeds into n10 formyl)
what is the major acceptor of methyl groups from folate
how does this happen
what does this generate
vitamine B12
methylene gets reduced to methyl which goes to B12
methionine from homocysteine methylase
without vitamin B12 folate will get trapped in this form
methylated form
not enough folate leads to _____
not enough vitamin B12 leads to _____
anemia
ALSO anemia (folate gets TRAPPED SO THERE IS LACK OF FOLATE)
vitamin B12 is required by (2 enzymes of 2 reactions)
methylmalonyl coA mutase
homocysteine methylase
B12 deficiency causes a buildup of _______ (2 reactions its in)
what do these cause
buildup of homocysteine (methionine)
causes heart disease
buildup of methylmalonate (MMCoA)
causes demyelination
what is needed to absorb B12
INTRINSIC FACTOR in stomach
pernicious anemia
treatment
cells that secrete intrinsic factor get destroyed in autoantibodies
B12 injections or sublingual B12 (bloodstream)
other enzymes/factors needed in methionine metabolism to become glucose
folate
B12
SAM
PLP (B6)
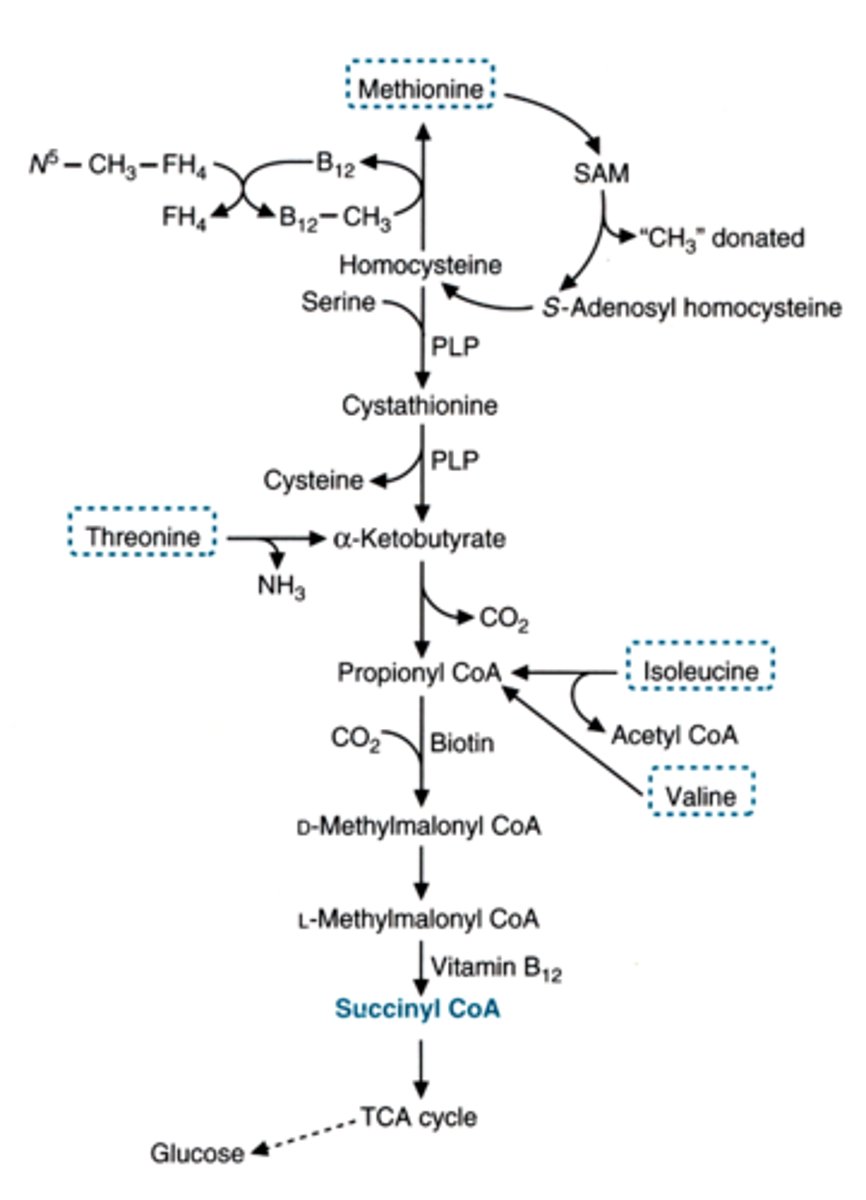
SAM 's relationship to methionine
required metabolite of methionine
a methyl group donor
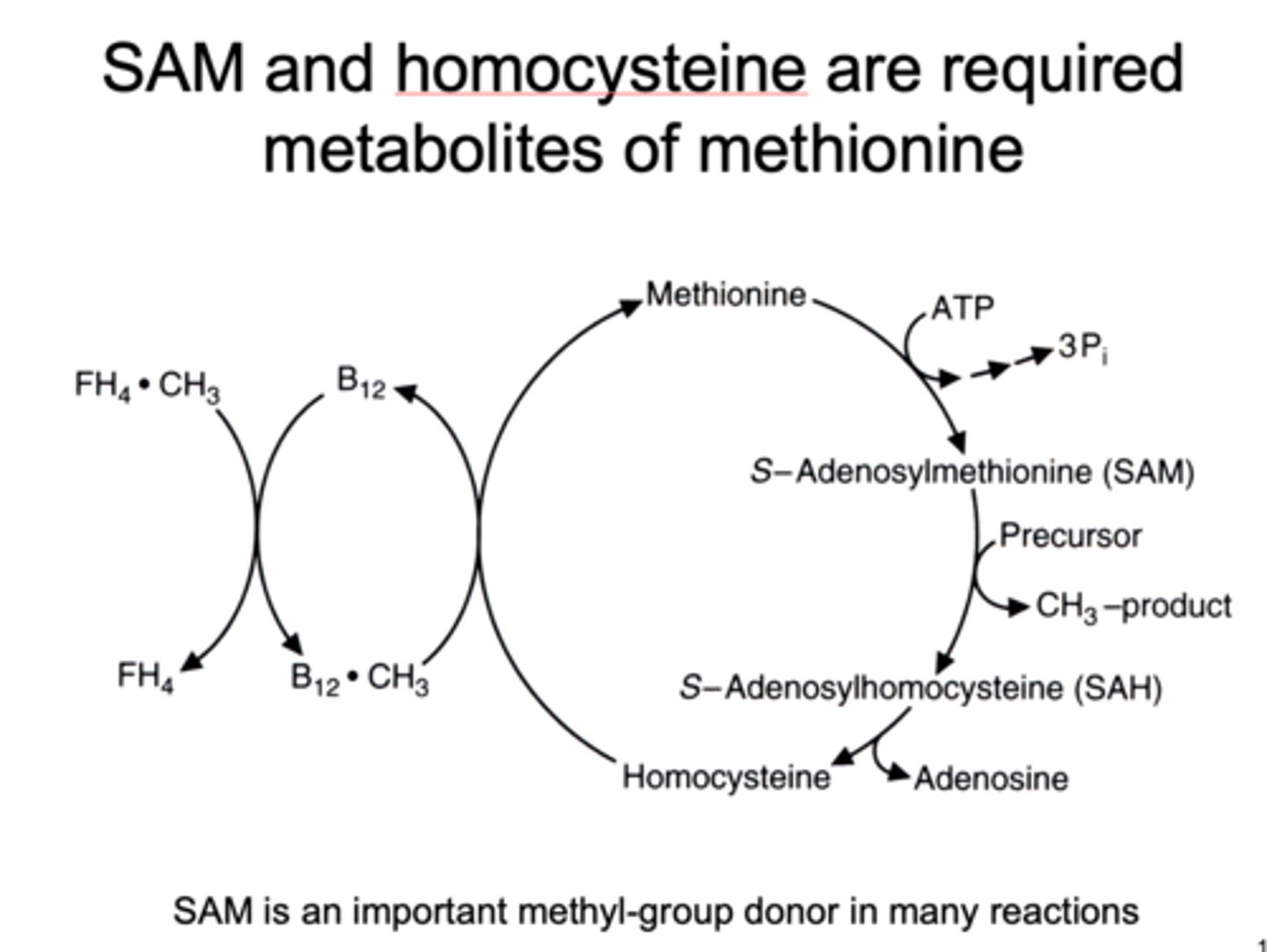
enzyme used in NON-B12 DEPENDENT METABOLISM OF HOMOCYSTEINE
deficiency in this can cause
symptoms
treatment
beta-synthase (CBS)
causes accumulation of homocysteine in blood/urine and increased risk of cardiovascular disease
lens dislocation, pectus excavatum, heart attack
treat with multivitamin (B6) or B12 to increase other path to metabolize it
uses of SAM
norepi --> epi
guanidinoacetate --> creatine
nucleotides --> methylated nucleotides
phosphatidylethanolamine --> phosphatidylcholine
acetylserotonin --> melatonin
IT CREATES METHYLATED PRODUCTS
serotonin and melatonin come from
tryptophan
synthesize of serotonin and melatonin
Trp hydroxylase
BH4 (tetrahydrobiopterin)
5HT becomes serotonin OR metabolized by MAO-A
serotonin gets acetylated
then gets methylated by SAM to make melatonin
SSRI's
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
enhance serotonin lifetime in depression, ocd, anxiety
prozac, etc.
catecholamines include _____ which come from
dopa, dopamine, NE, epi
come from phenylalinine/tyrosine
synthesis of catecholamines uses these enzymes (4)
phe hydroxylase
tyr hydroxylase
BH4 -- tetrahydrobiopterin
SAM
where does BH4 (tetrahydrobiopterin) come from
GTP
melanin (pigment) comes from
tyrosine
histamine comes from
histidine
histamine mostly made and released in
sometimes made in (2 places)
what does it do in each place
mast cells - inflammation
stomach - regulates H+
brain - regulates sleep/wake in hypothalamus