neuro 206 lecture 3; development and basic neuroanatomy
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
what is neurulation?
the process of formation of the hollow neural tube by folding of the epithelial neural plate
neurulation is induced by
cells in the primitive pit and notochord
how is the neural groove created?
the edges of the neural plate fold inward
What happens when the neural groove is closed?
formation of the neural tube
signals from midline structures do what?
generate motor structures ventrally and sensory interneurons dorsally
The early embryonic neural tube consists of
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon, spinal cord
Prosencephalon is another term for
forebrain
Mesencephalon is another term for
midbrain
Rhombencephalon is another term for
hindbrain
The lumen of the neural tube becomes
ventricular system
The prosencephalon develops into what structure(s)
telencephalon and diencephalon
The telencephalon’s lumen develops and contains what structure
lateral ventricle
The diencephalon develops and contains what structures
third ventricle and optic vesicle
The mesencephalon develops into what structure(s)
stays the same
The mesencephalon develops and contains what structure
future cerebral aqueduct
The rhombencephalon develops into what structure(s)
metencephalon and myelencephalon
the metencephalon develops and contains what structure
fourth ventricle
the spinal cord contains
the central canal
the more commonplace name for the telencephalon is…
cerebrum
what is the brainstem?
a collection of structures that connect the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. In charge of automatic functions of the body
what structures does the brainstem consist of?
midbrain, pons, medulla
what two structures are derived from the metecephalon?
pons and cerebellum
what structure is derived from the myelenocephalon
medulla
how many cerebral lobes are there?
4
the cerebral lobes consist of
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
cerebral lobes are mostly separated by
sulci and fissures
what is a sulcus?
a groove or furrow in the brain
what is a fissure?
a deep groove in the brain
what is a gyrus?
a ridge or fold in the brain
cingulate gyrus and cingulate sulcus are located in…
the frontal lobe
the frontal and parietal lobes are separated by
central sulcus
the parietal and occipital lobes are separated by
parieto-occipital sulcus
the right and left hemispheres of the brain are separated by
longitudinal fissure
the frontal and parietal lobes are separated from the temporal lobe by the…
lateral/Sylvian fissure
the region deep in the lateral sulcus is the…
insula
The diencephalon carries what two neighboring structures of the brain?
hypothalamus and thalamus
what is the hypothalamus’s main function?
regulates emotions and visceral nervous system
what is the visceral nervous system?
autonomic nervous system; controls non-voluntary bodily functions like heart rate and digestion to maintain homeostasis
What is the thalamus’s main function?
acts as the brain's central info relay station and "gatekeeper," processing and directing incoming sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex (EXCLUDING SMELL)
what is the tectum?
a key sensory processing area in the dorsal midbrain of vertebrates; dorsal to the hypothalamus
the tectum contains what two pairs of bumps?
superior colliculus
inferior colliculus
superior colliculus
Involved in directing behavioral responses to visual stimuli, controlling saccadic eye movements, and visual tracking.
inferior colliculus
Act as major auditory centers, helping to localize sounds and trigger auditory reflexes.
directional terms are
relative
what pair of directional terms relate to midline?
medial and lateral
medial
closer to midline
lateral
further from midline
what pair of directional terms relate anatomy to back and belly?
dorsal and ventral
dorsal
backside
ventral
bellyside
what pair of directional terms relate anatomy to front and back?
anterior/rostral
posterior/caudal
anterior/rostral
towards head
posterior/caudal
towards back
in the nervous system, the spinal nerves become
ventral and dorsal roots
what are the dorsal components of the spinal cord?
dorsal horn
dorsal roots
dorsal root ganglion
dorsal roots
A bundle of nerve fibers (axons) that enters the posterior side of the spinal cord. It carries sensory (afferent) impulses from the periphery towards the central nervous system.
dorsal root ganglion
A cluster of neuron cell bodies located on the dorsal root, just outside the spinal cord. These cells process sensory information such as pain, temperature, and touch.
dorsal horn
Region that receives sensory information from the body. It consists of interneurons and sensory nuclei.
what are the ventral components of the spinal cord?
ventral roots
ventral horn
ventral roots
the motor (efferent) roots of the spinal nerve, which carry motor signals away from the spinal cord to the periphery
ventral horn
contain motor neurons (alpha and gamma) that innervate skeletal muscles, with large horns in the cervical and lumbar regions for limb control.
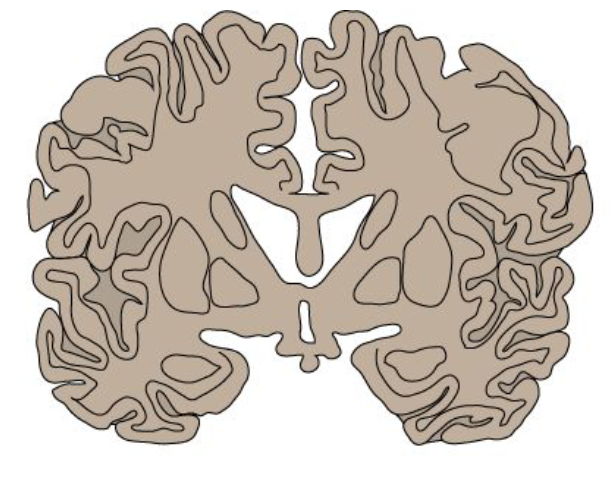
the dorsal and ventral horn are made up of
grey matter
the dorsal and ventral horns are surrounded by
white matter
grey matter has mostly
soma, dendrites
white matter has mostly
axons
how do anatomical terms differ between quadrupeds and bipeds?
Bipeds use the terms superior/inferior instead of dorsal/ventral for top/bottom differentiation
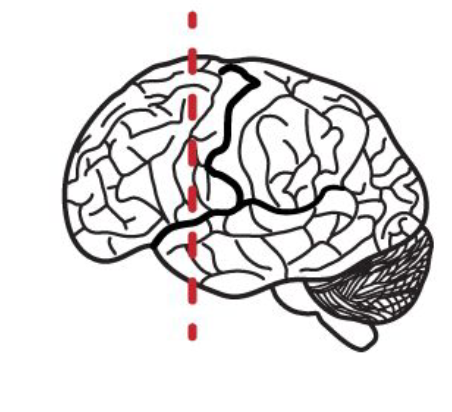
What anatomical plane is this?
frontal/coronal
What anatomical plane is this?
Sagittal
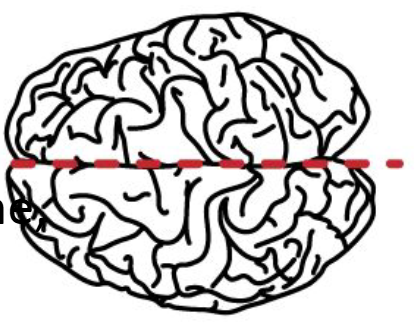
What anatomical plane is this?
horizontal
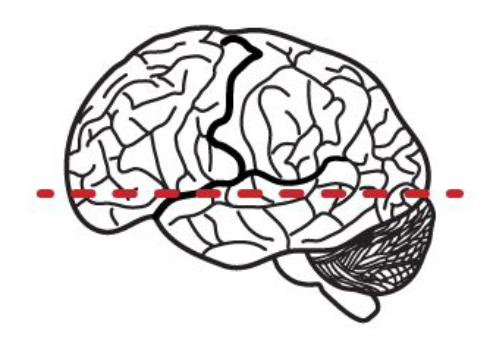
what type of section is this?
frontal/coronal
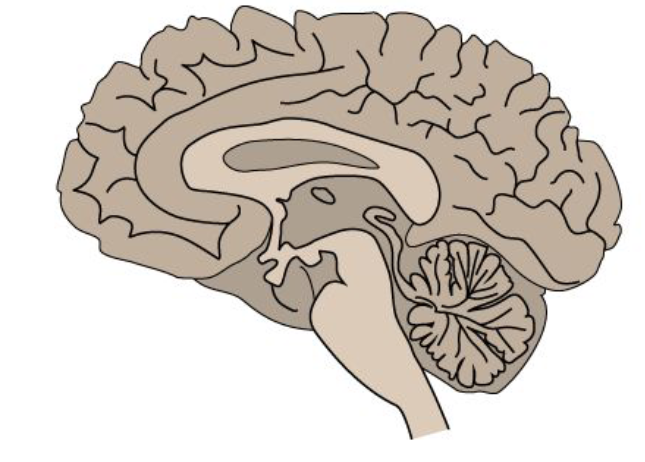
what type of section is this?
sagittal/parasagittal
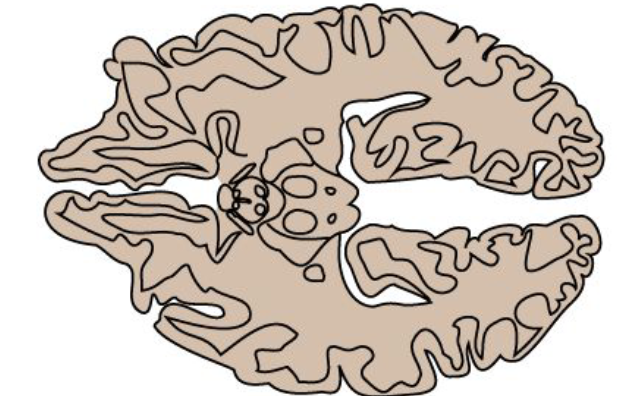
what type of section is this?
horizontal
the two cerebral hemispheres are
highly interconnected
the three major sites of hemispheric communication is at…
corpus callosum
anterior commissure
posterior commissure
corpus callosum
the primary pathway for interhemispheric communication, enabling the coordination of sensory, motor, and cognitive functions.
what is a commissure?
commissural axons; axons that cross the midline, connecting opposite regions of the brain or spinal cord
what is a corpus callosotomy?
severing of corpus callosum; used as a treatment for severe epilepsy to cut communication and confine seizures to one hemisphere of the brain