Amino Acids
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
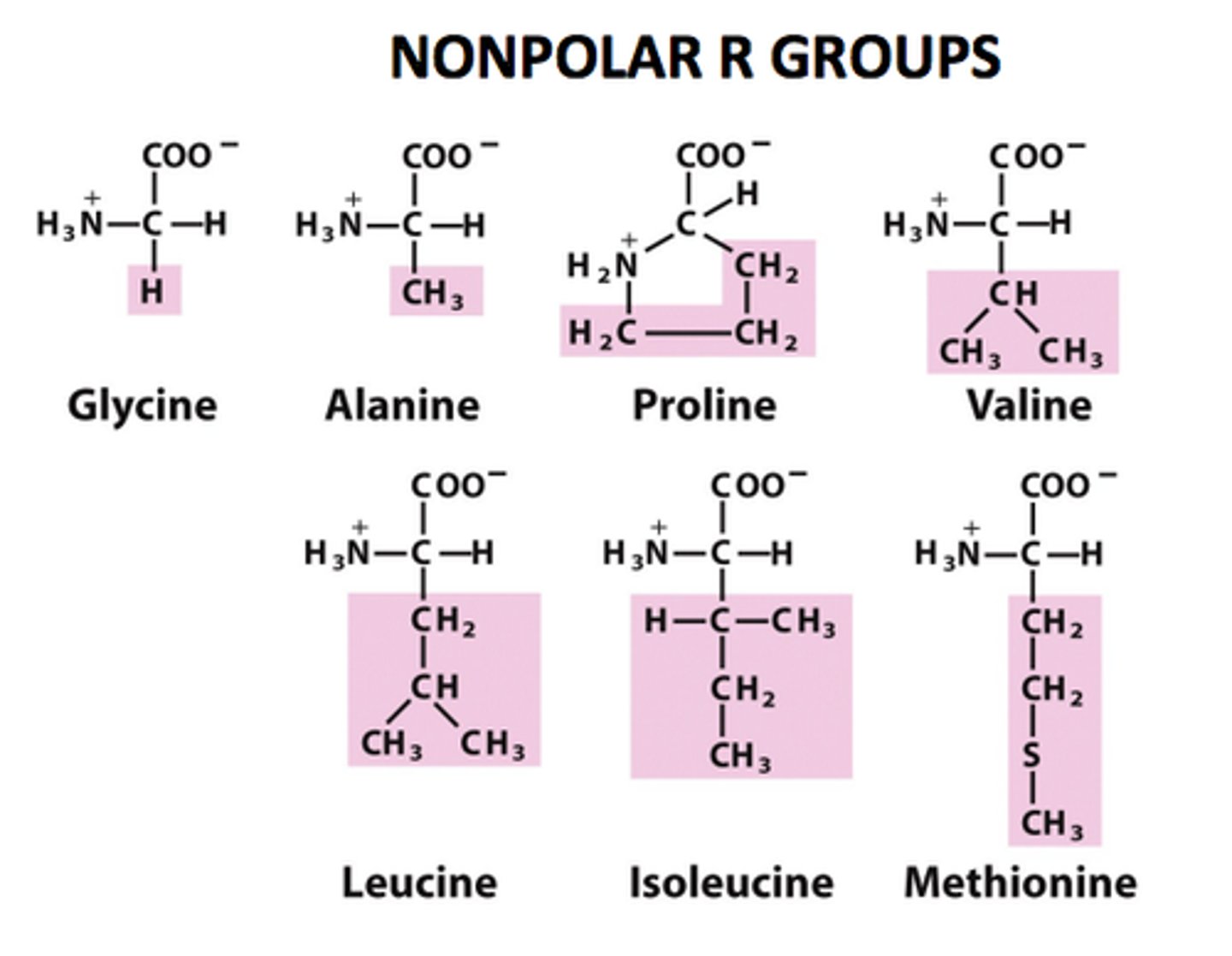
7 - Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline
Nonpolar Uncharged
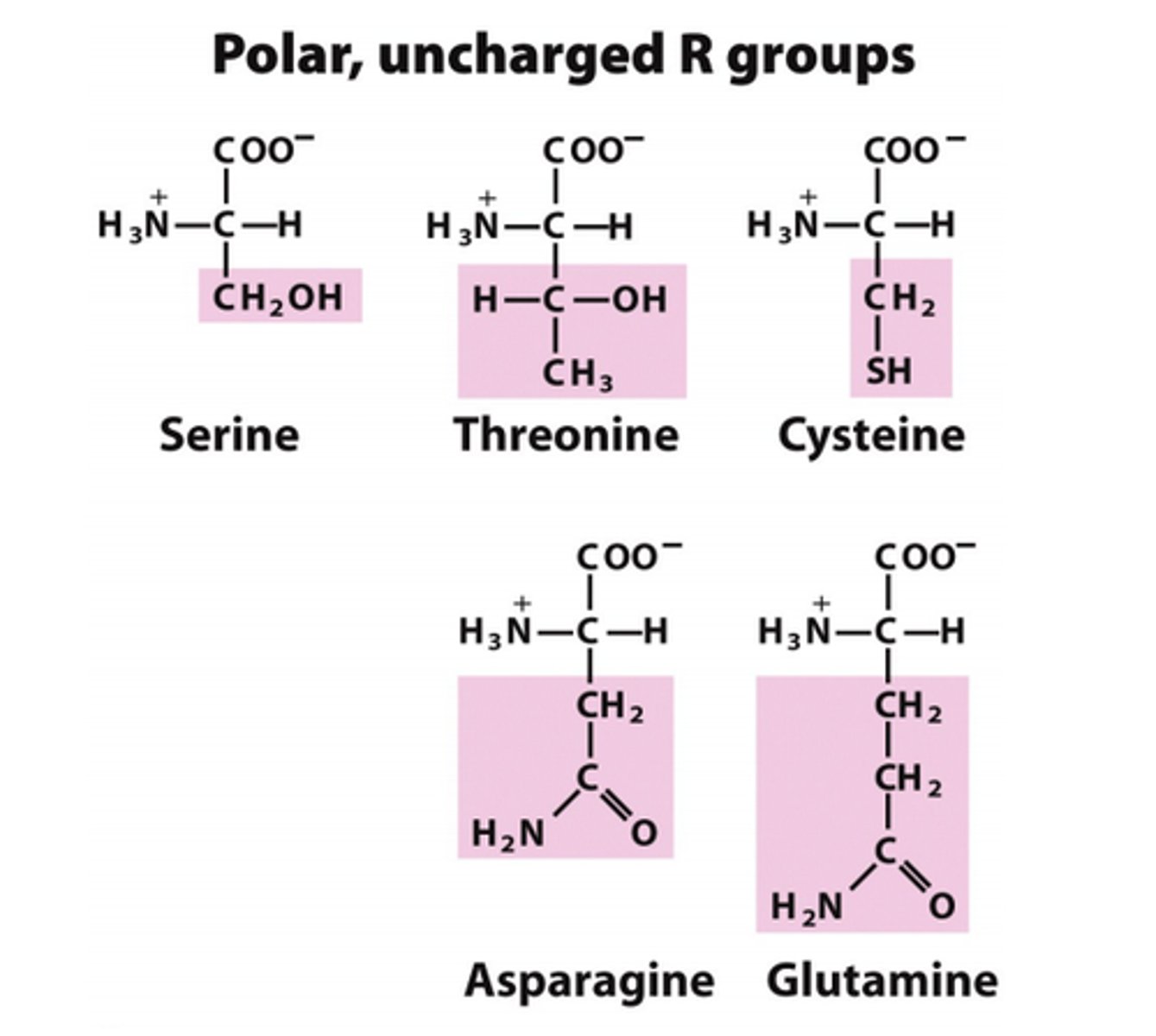
5 - serine, cystine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine
polar uncharged
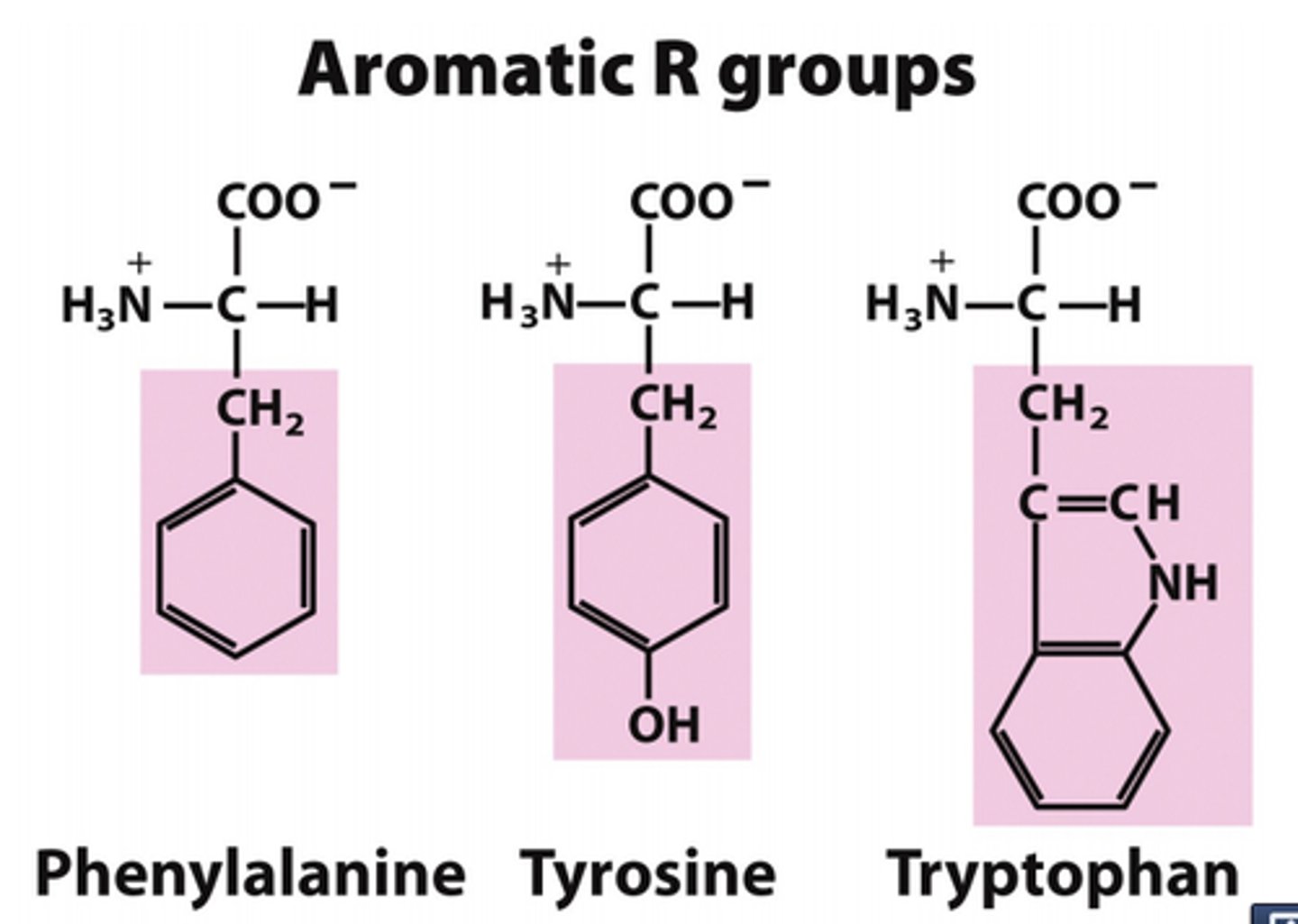
3 - phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
aromatic
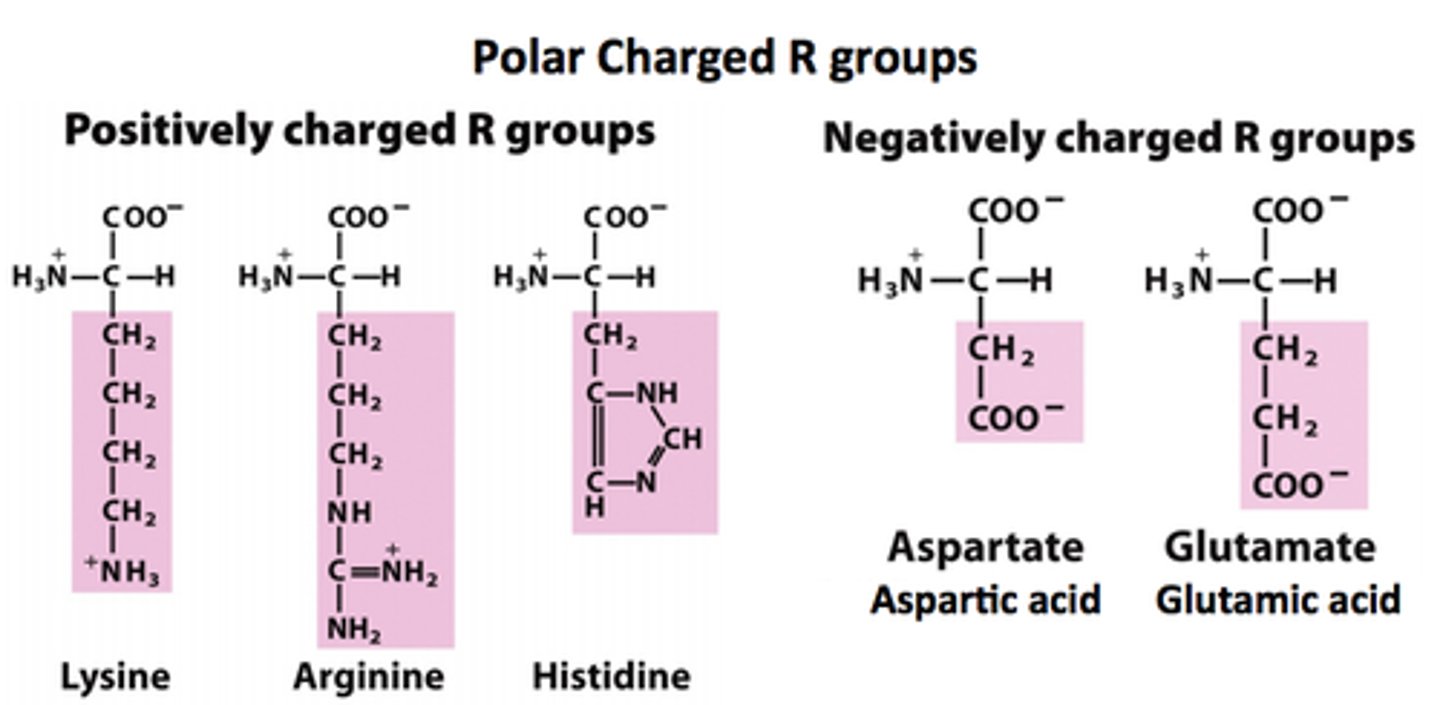
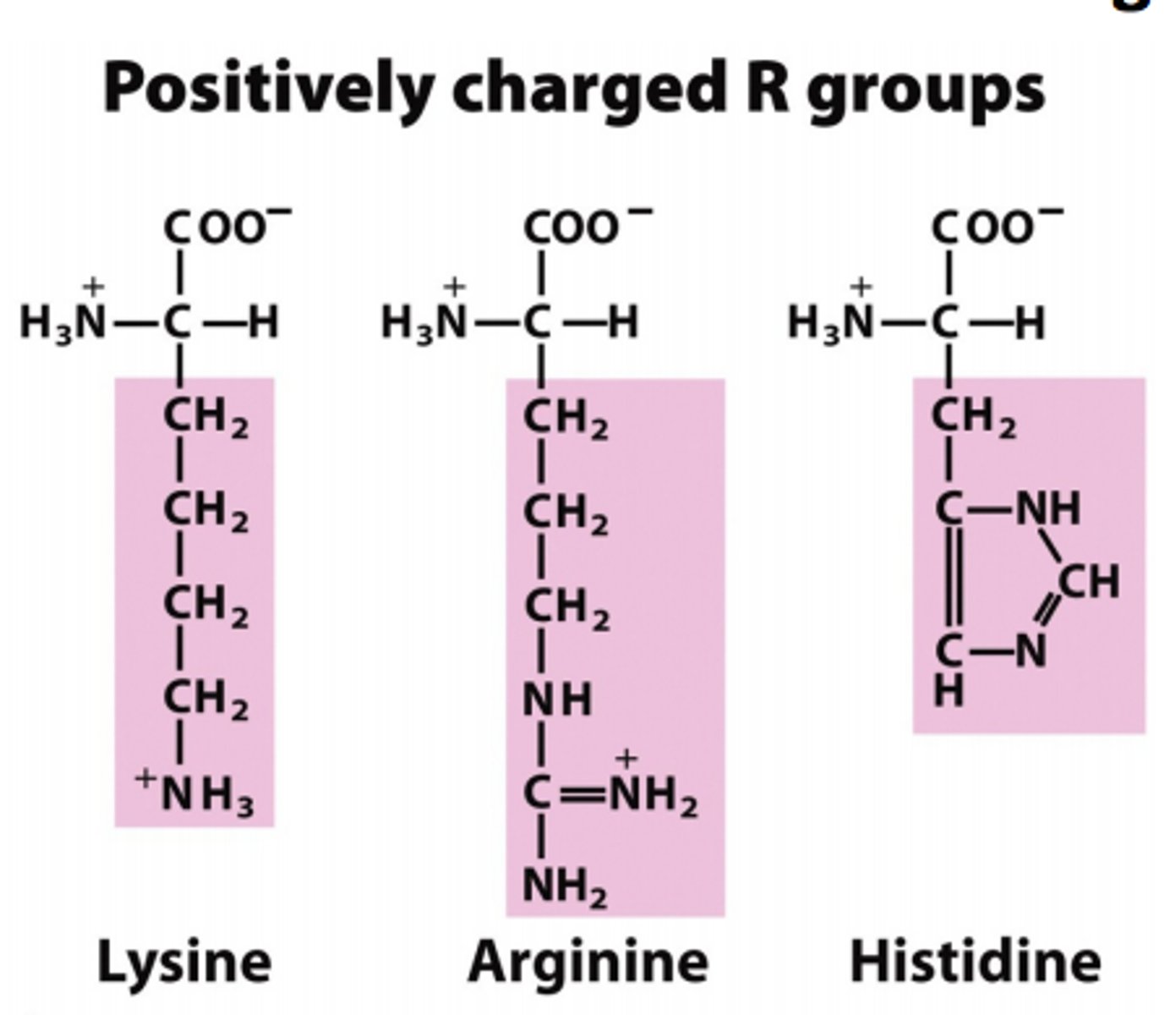
5 - (+) lysine, arginine, histidine
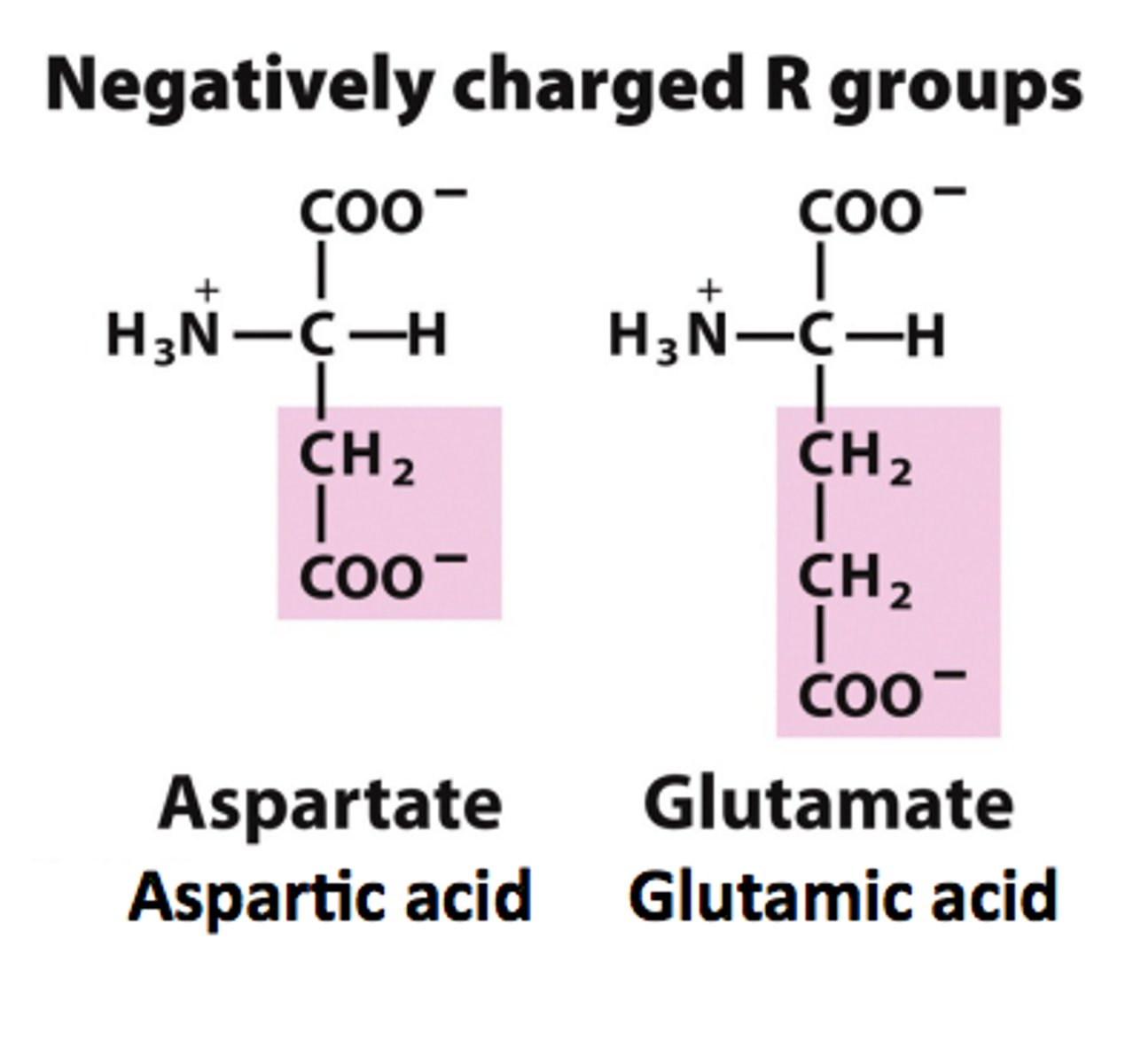
(-) aspartate, glutamate
Charged
3 - (+) lysine, arginine, histidine
positively charged
2 - (-) aspartate, glutamate
negatively charged
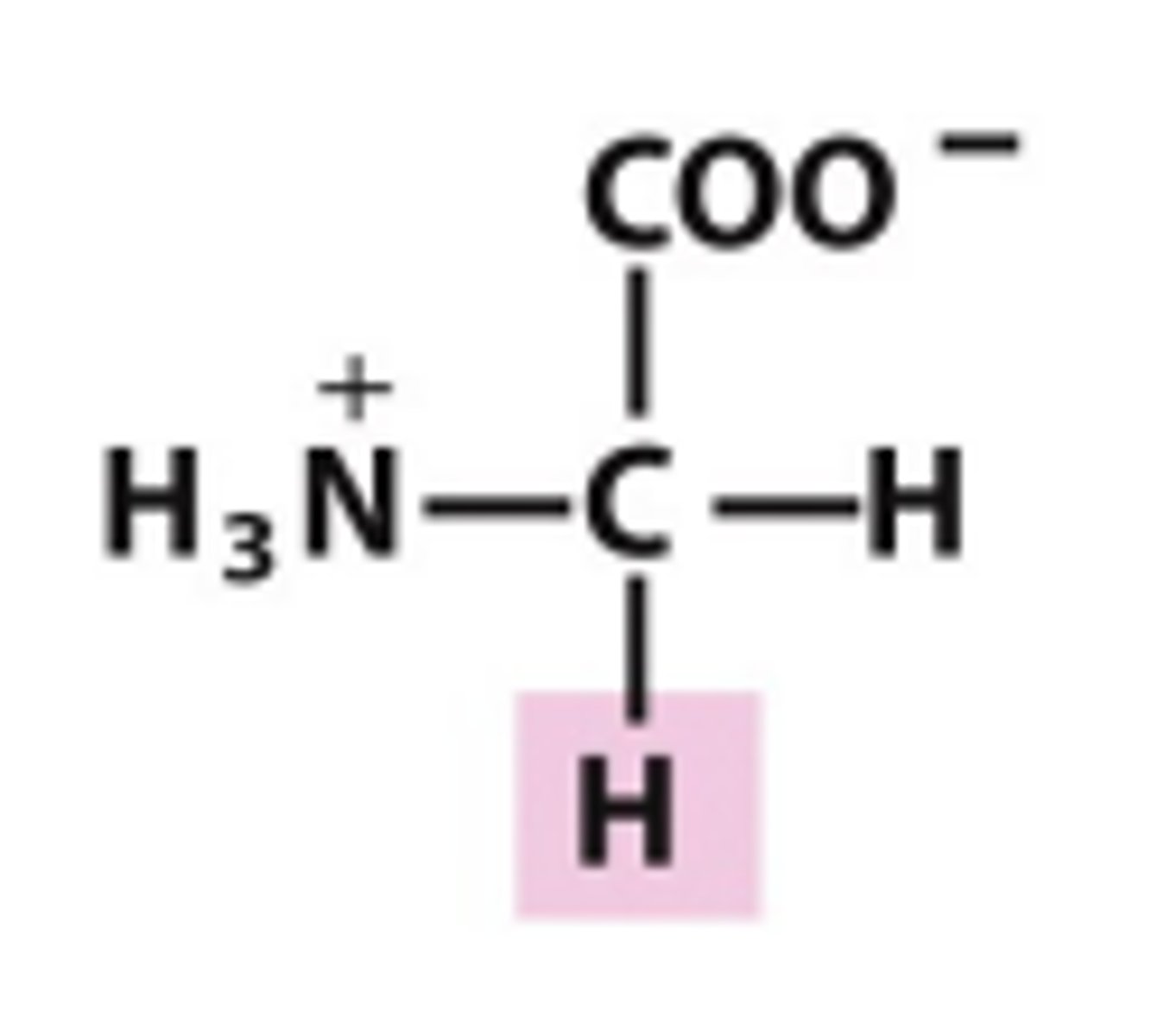
Glycine
Which amino acid is this?
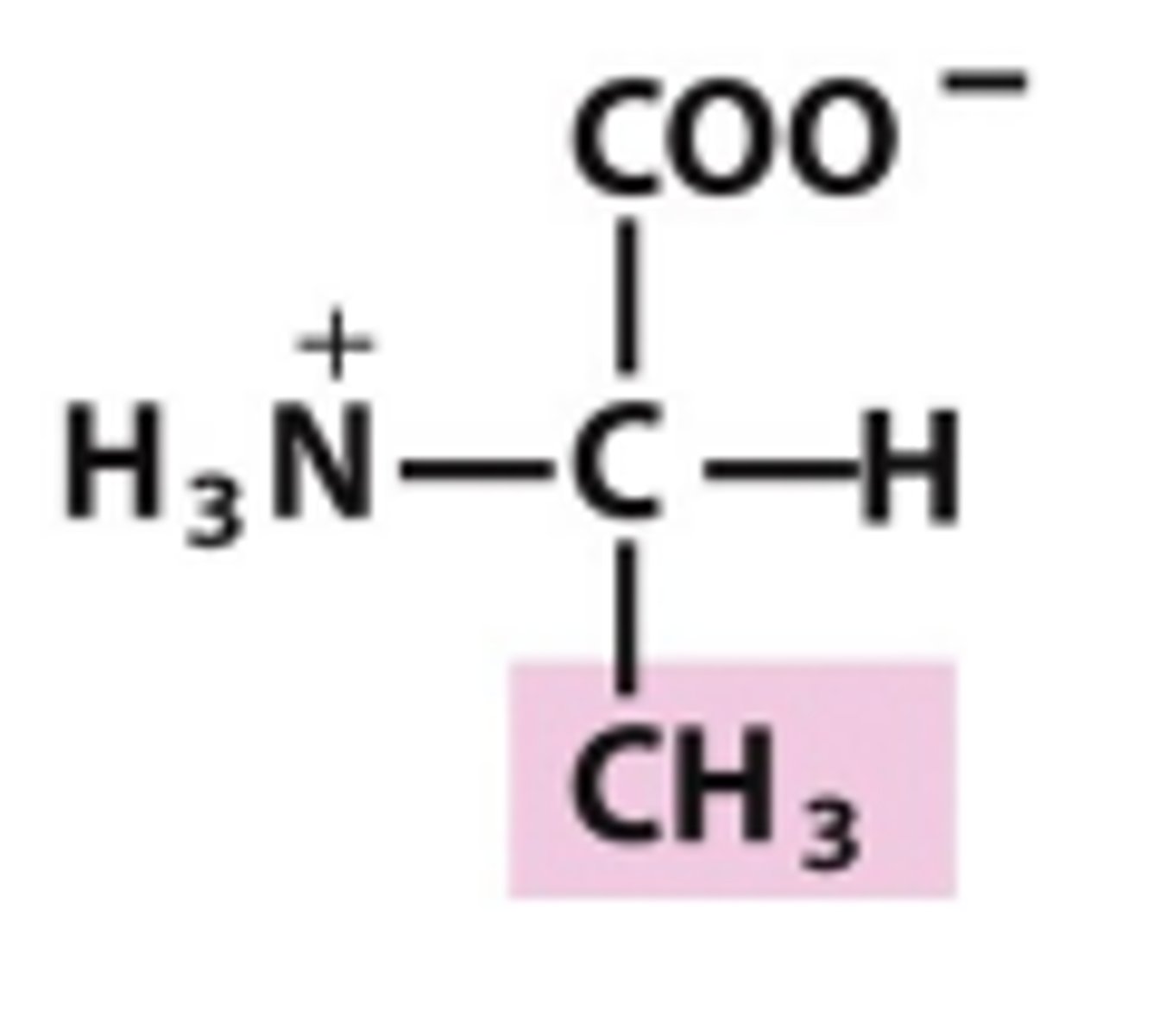
Alanine
Which amino acid is this?
Valine
Which amino acid is this?
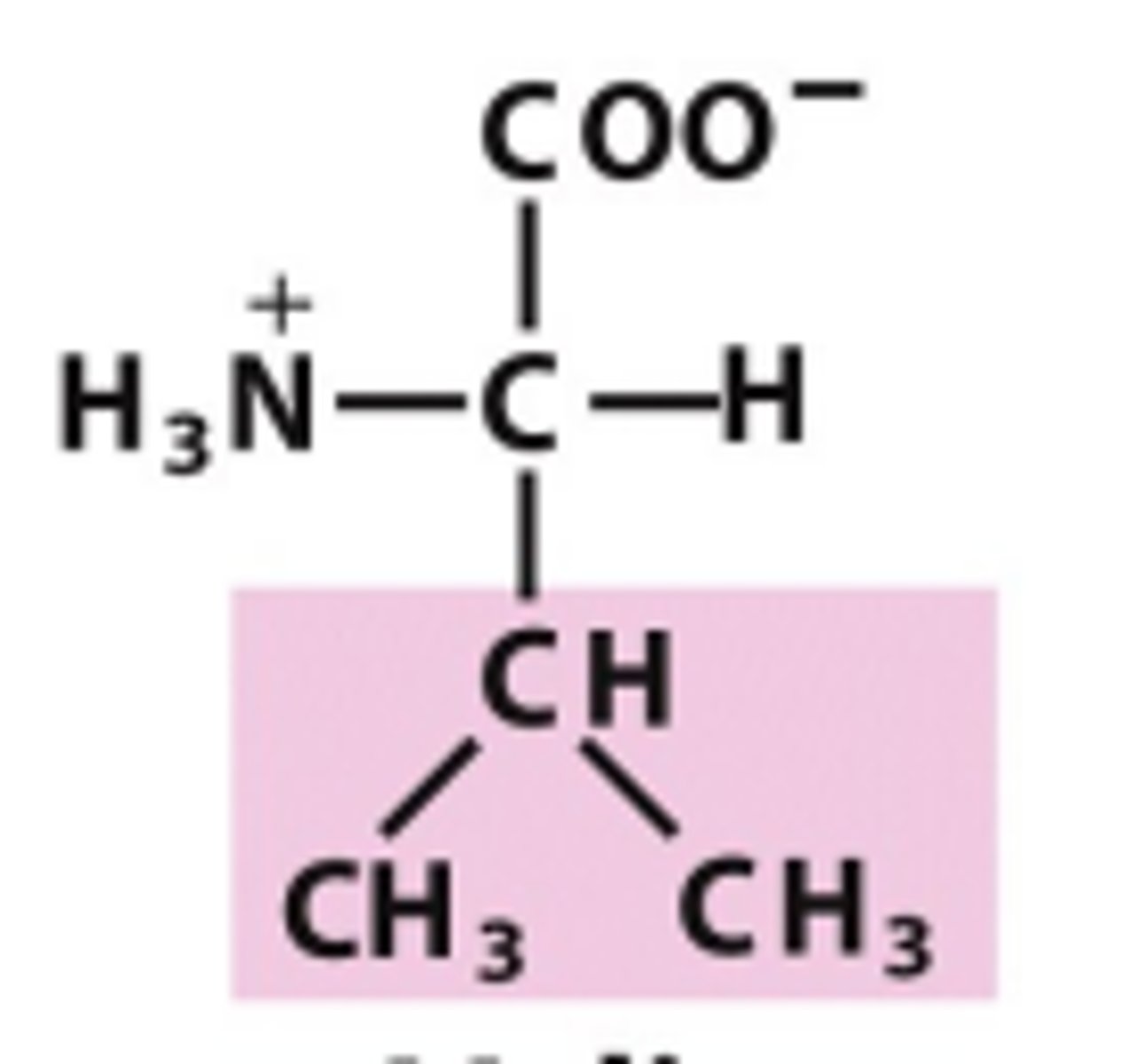
Leucine
Which amino acid is this?
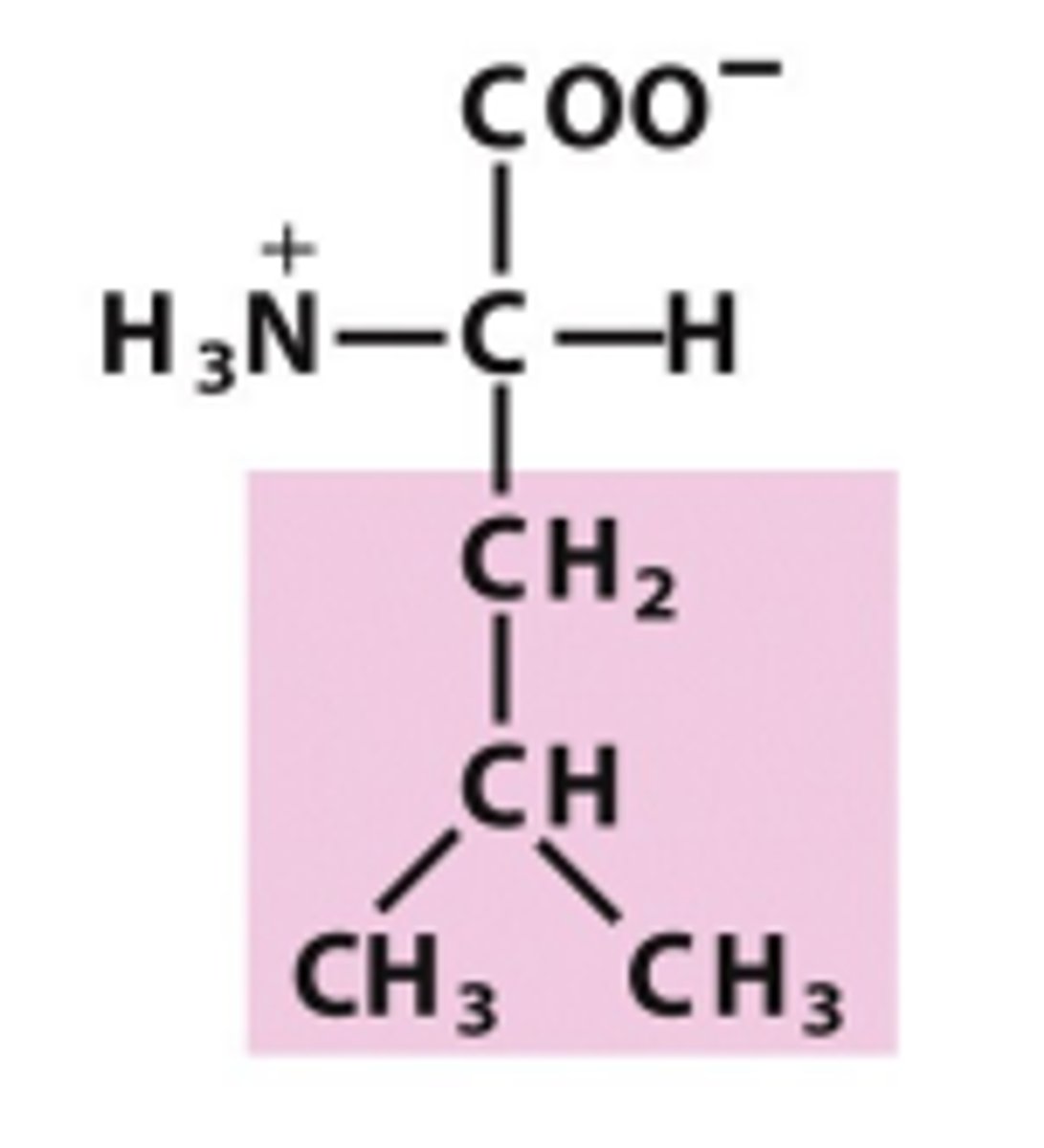
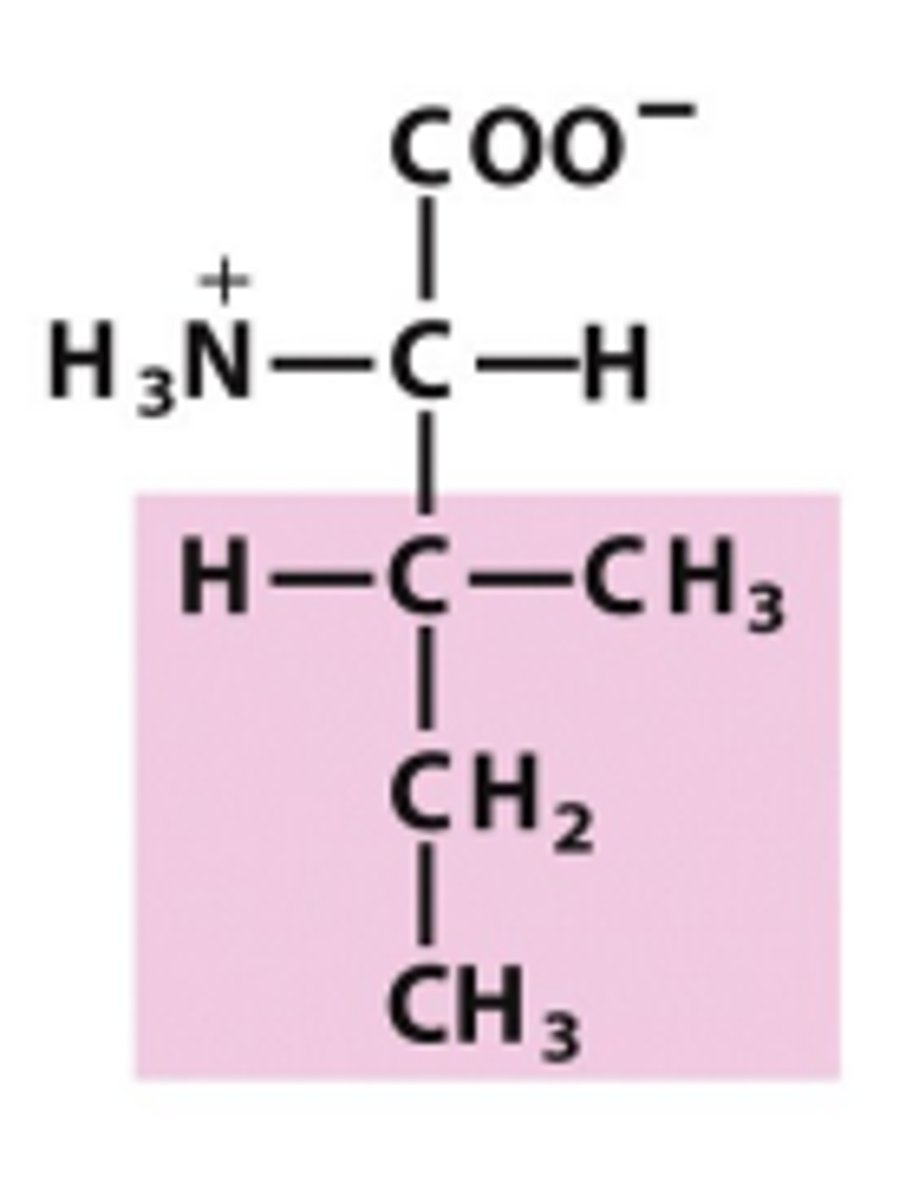
Isoleucine
Which amino acid is this?
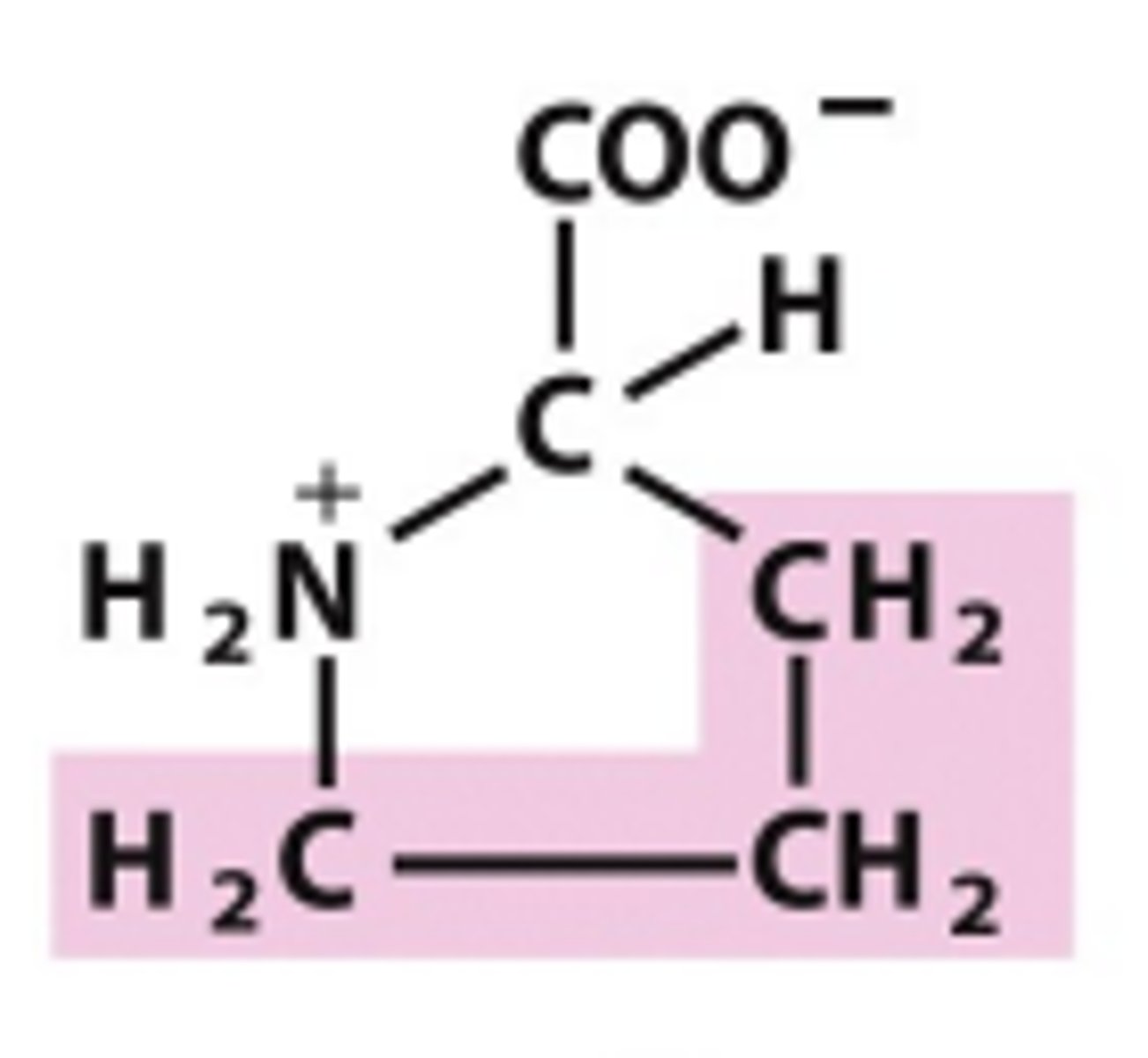
Proline
Which amino acid is this?
Methionine
Which amino acid is this?

serine
Which amino acid is this?
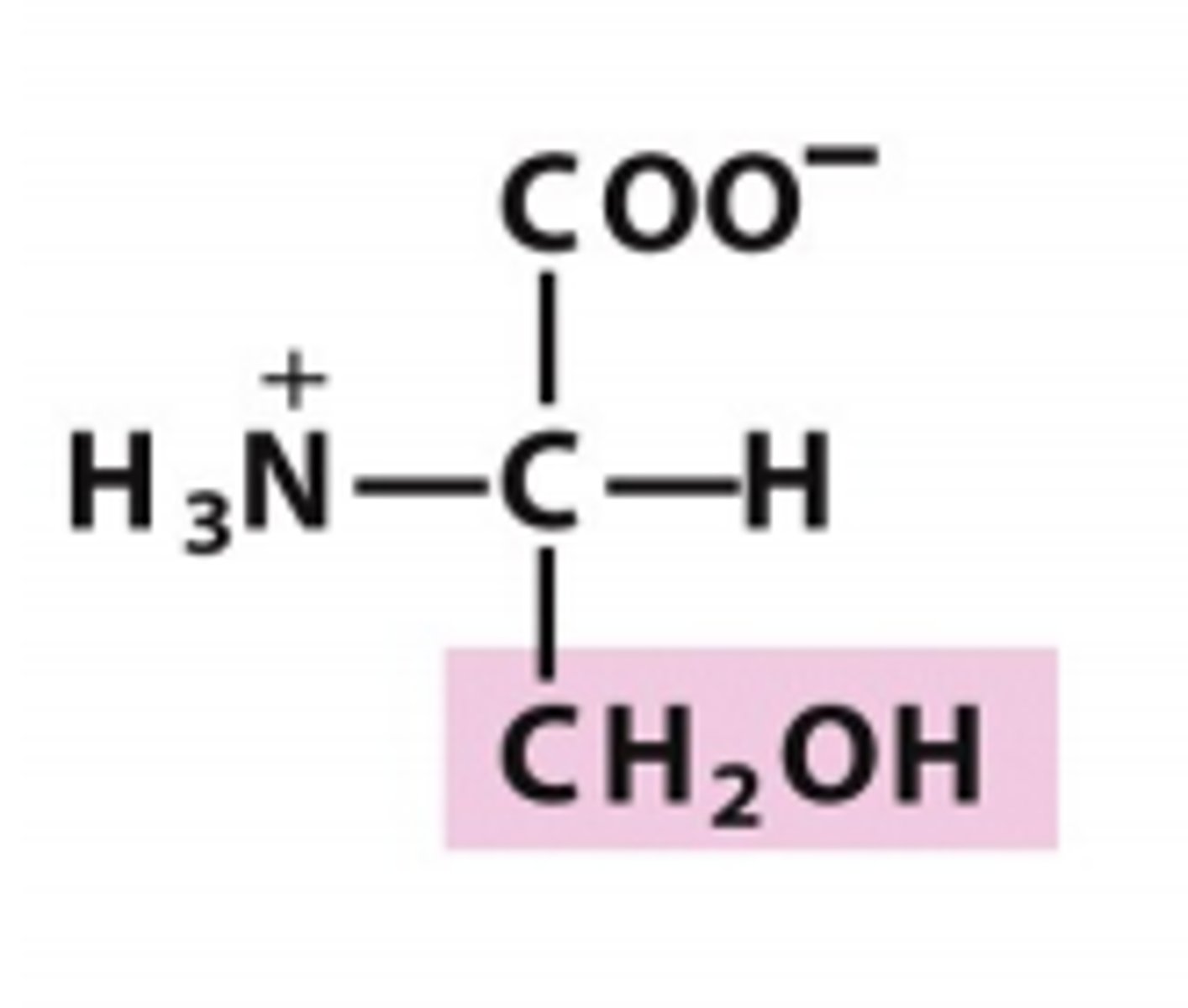
cystine
Which amino acid is this?
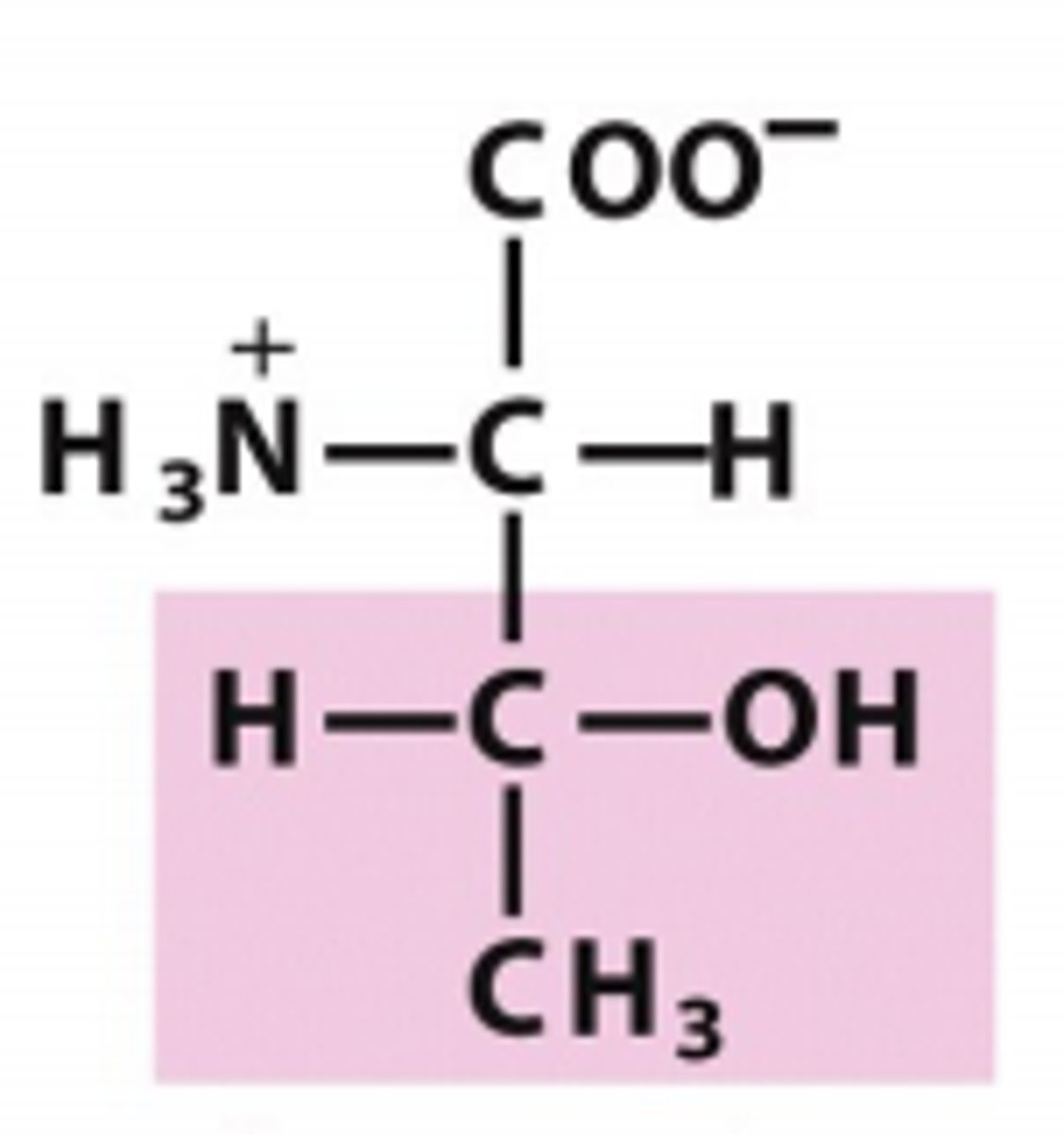
threonine
Which amino acid is this?
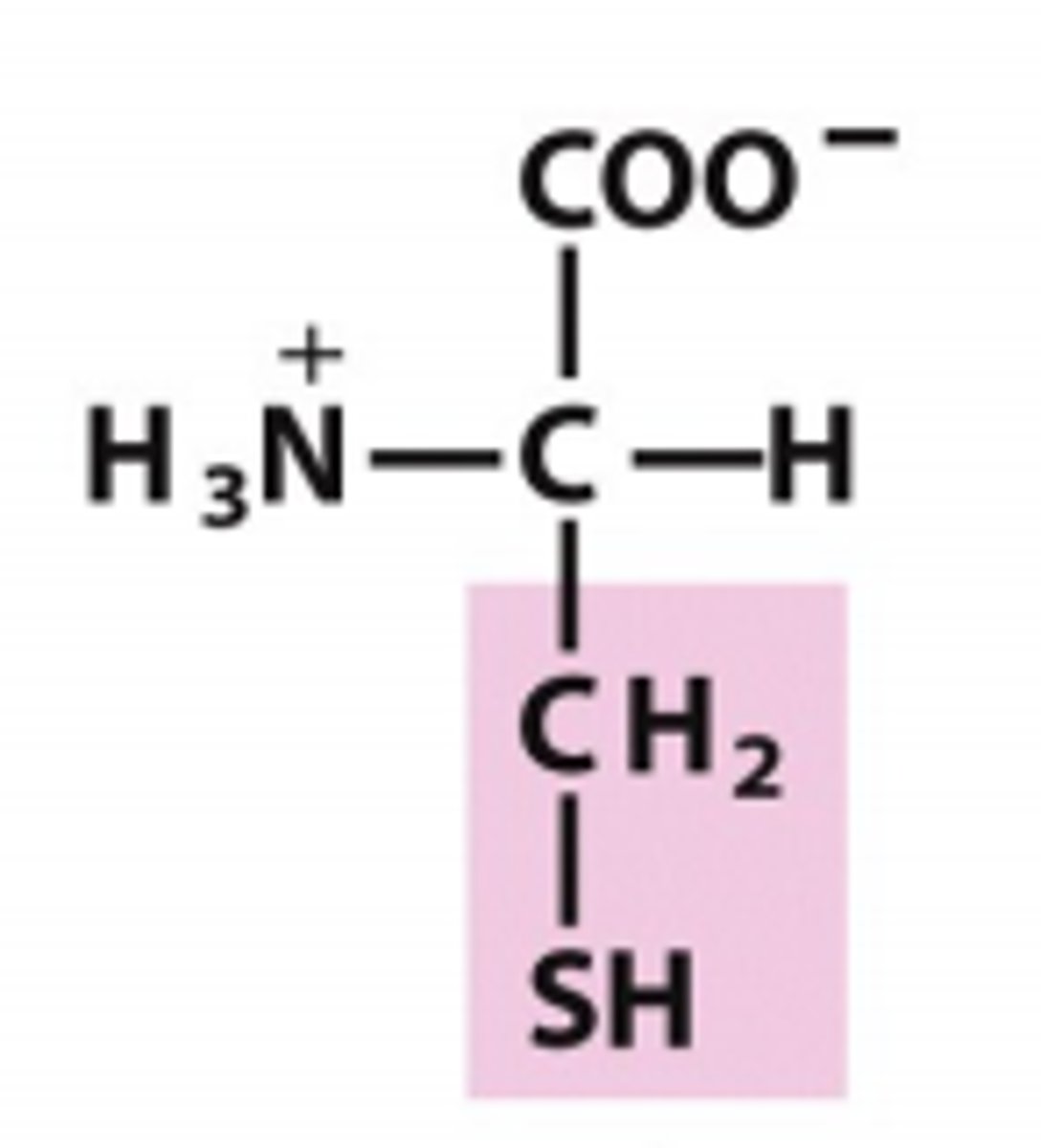
asparagine
Which amino acid is this?
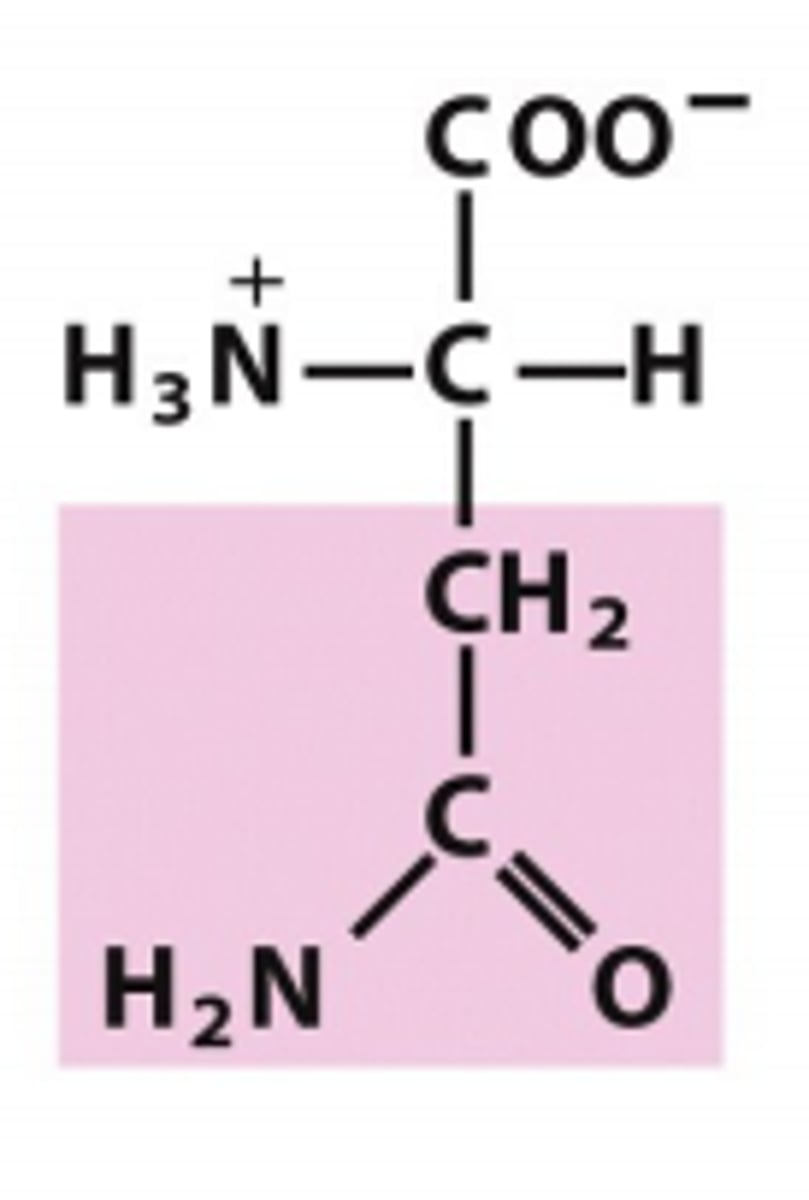
glutamine
Which amino acid is this?
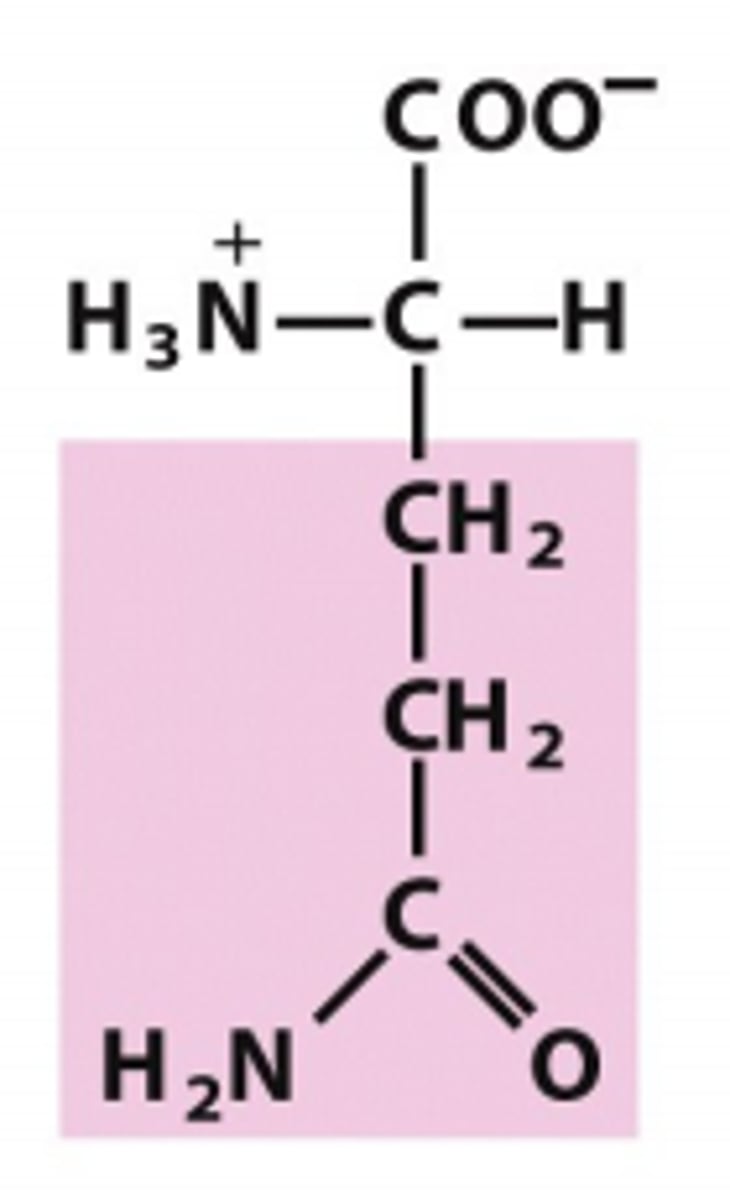
phenylalanine
Which amino acid is this?
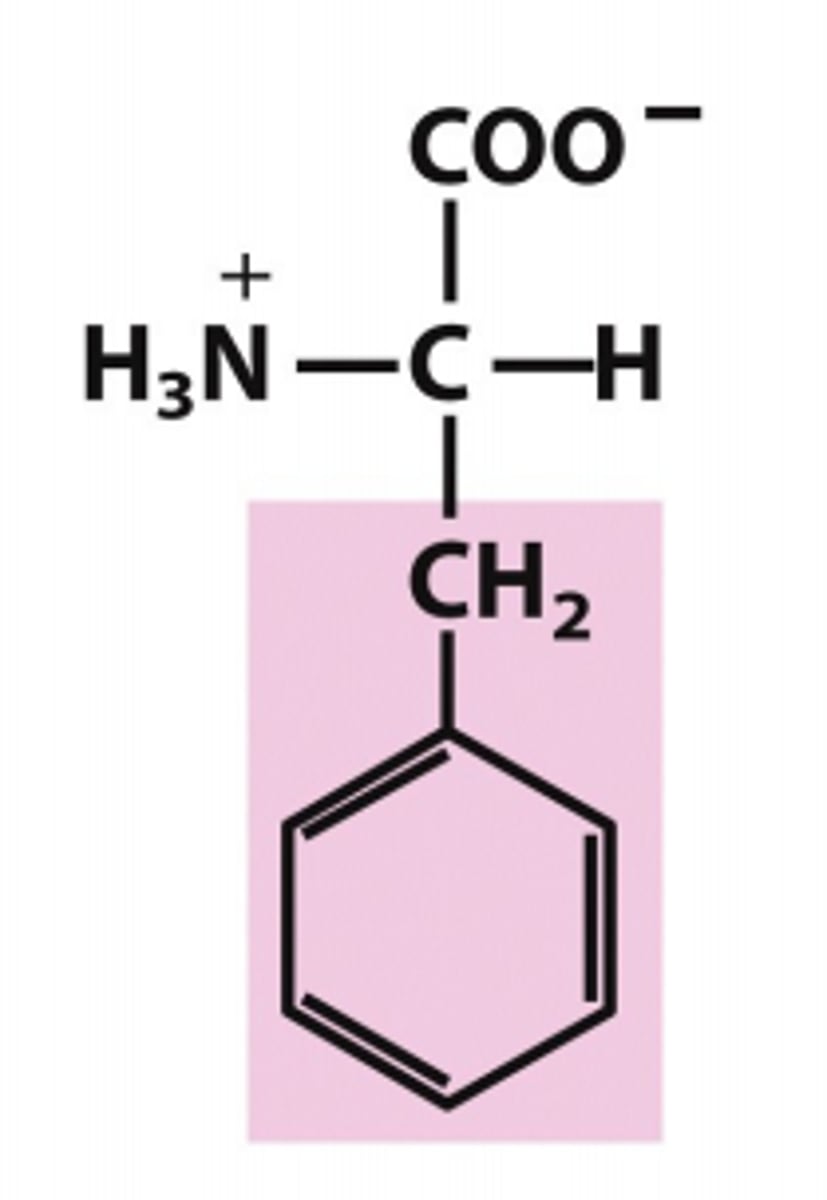
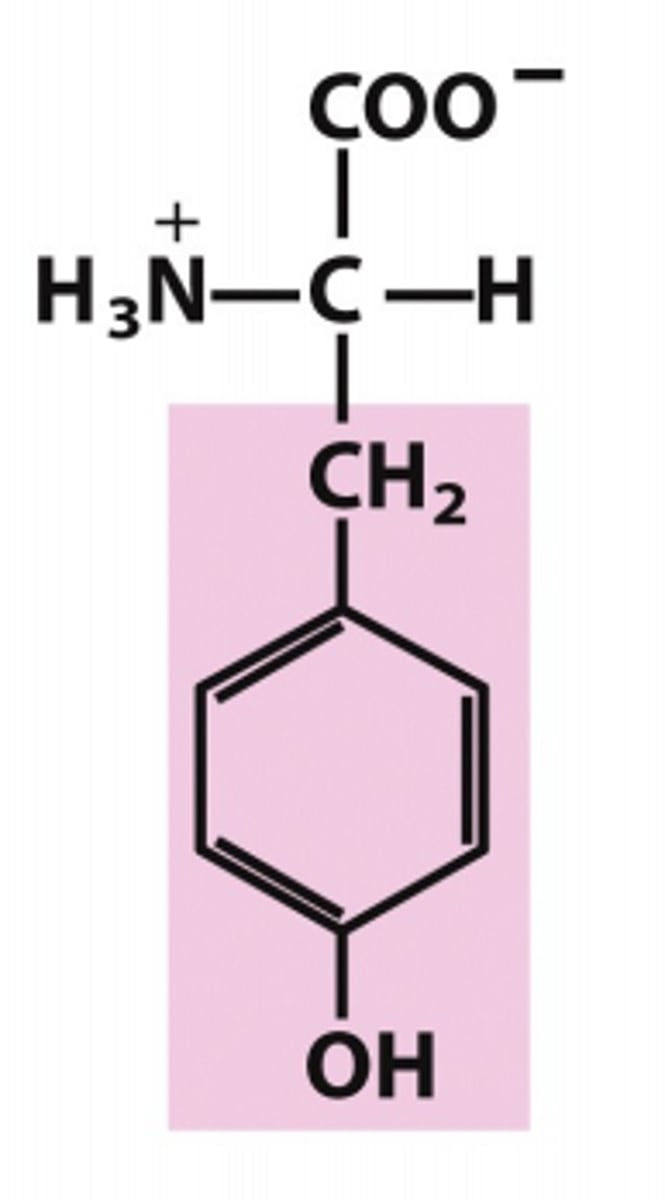
tyrosine
Which amino acid is this?
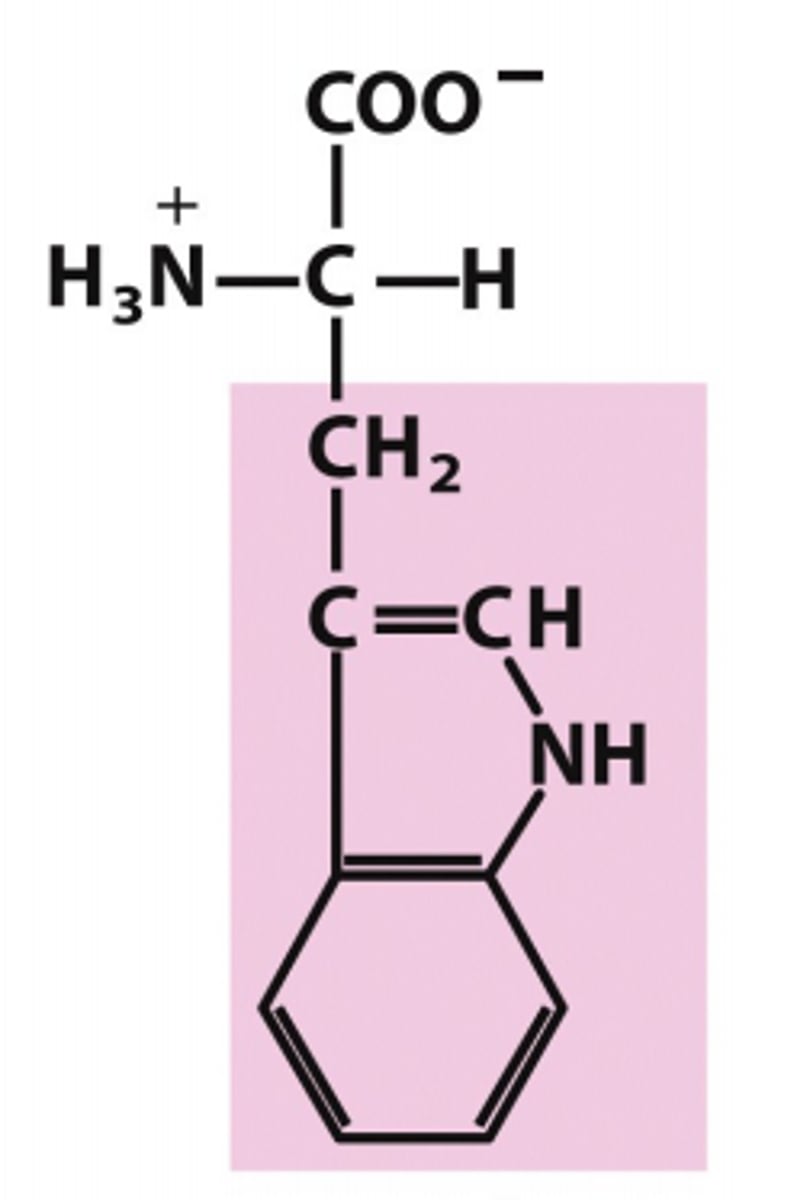
tryptophan
Which amino acid is this?
lysine
Which amino acid is this?
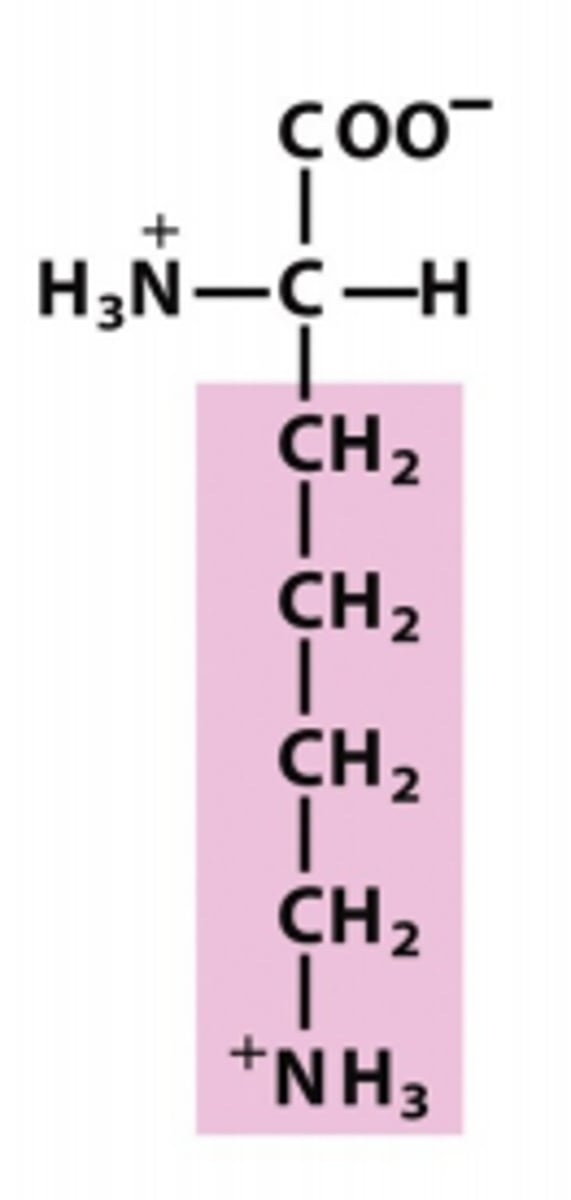
arginine
Which amino acid is this?
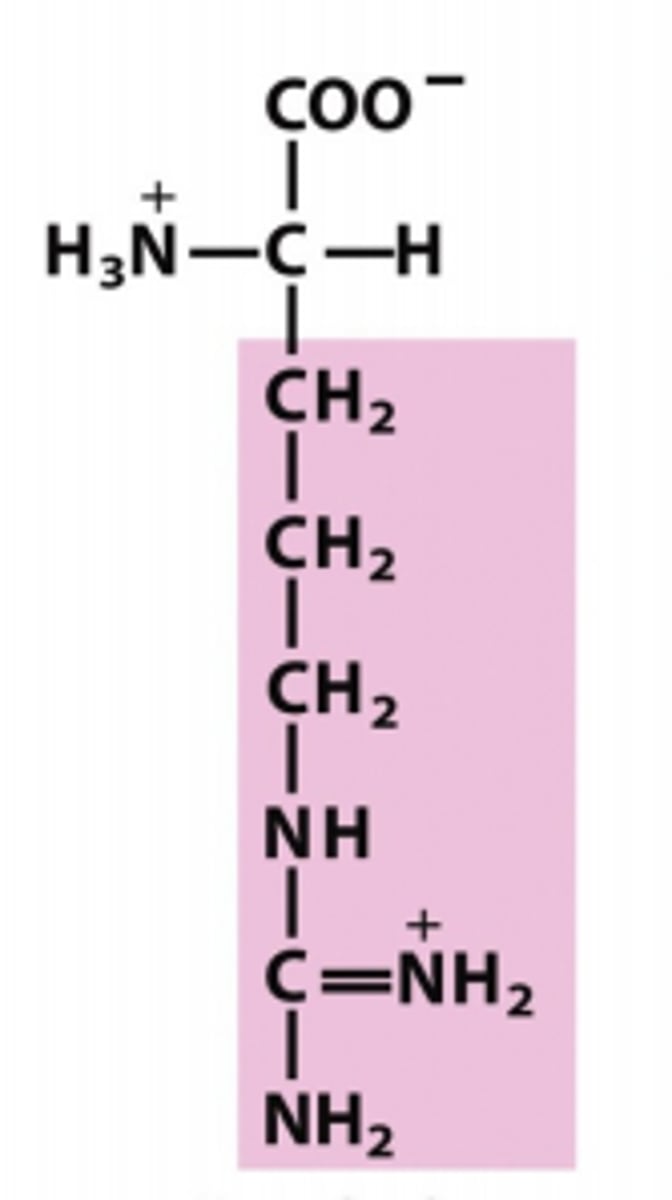
histidine
Which amino acid is this?
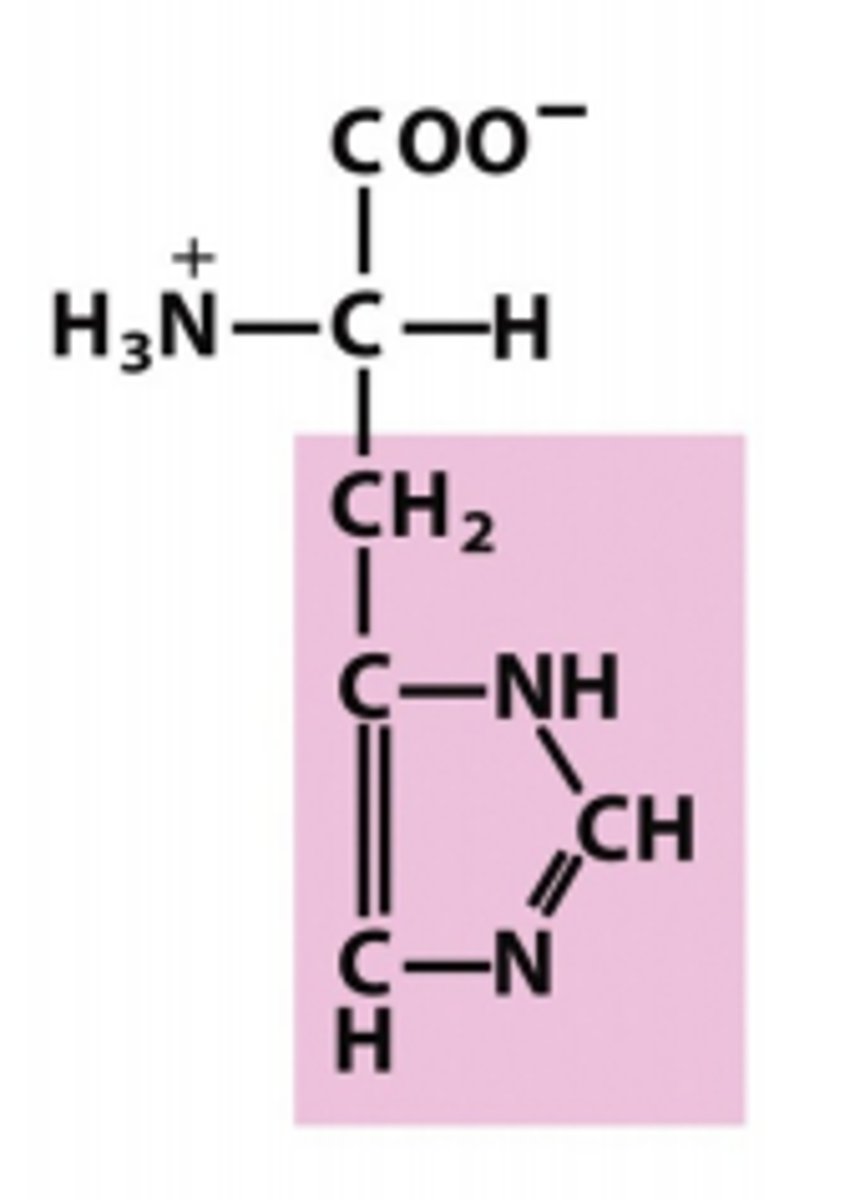
aspartate
Which amino acid is this?
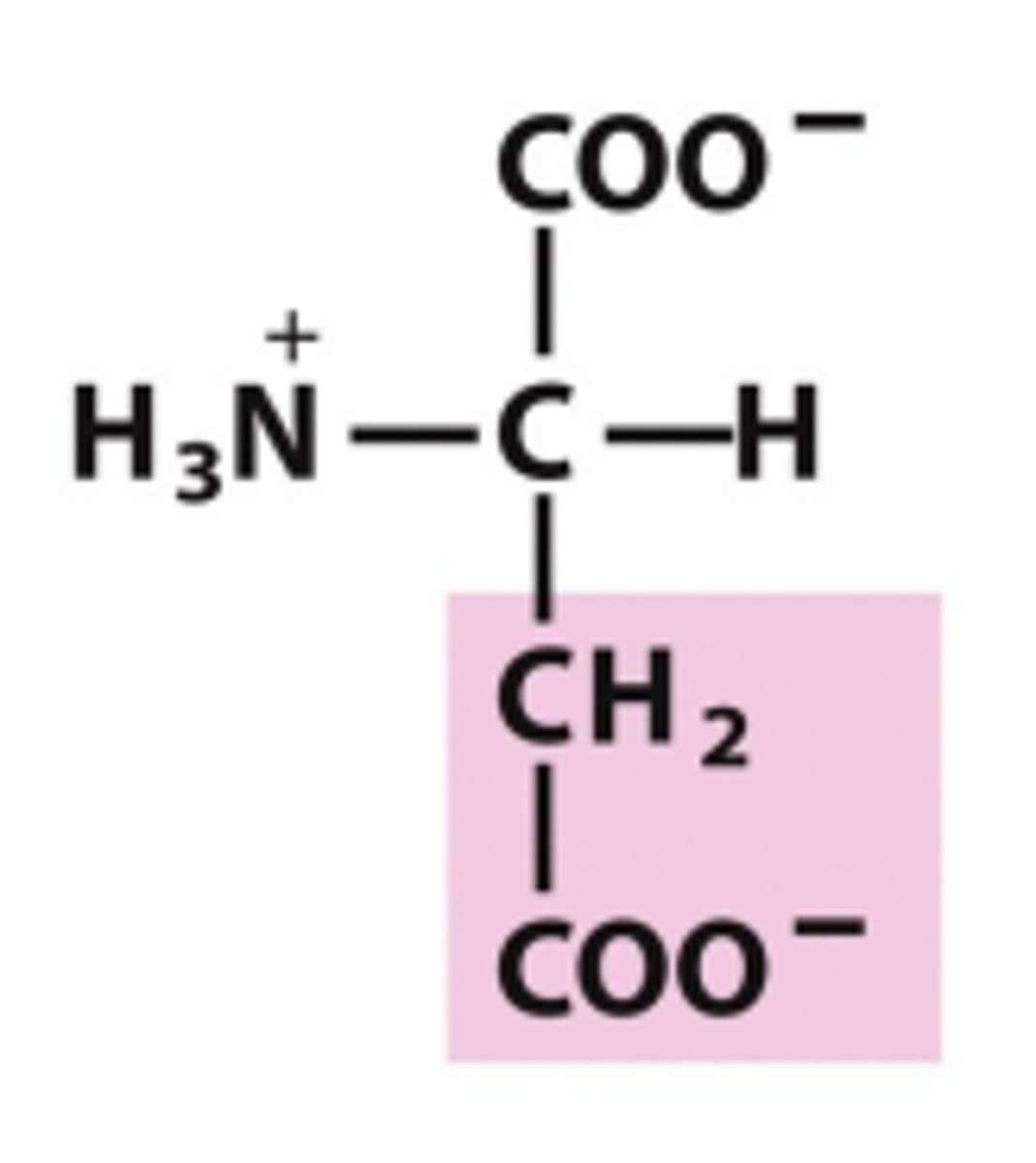
glutamate
Which amino acid is this?
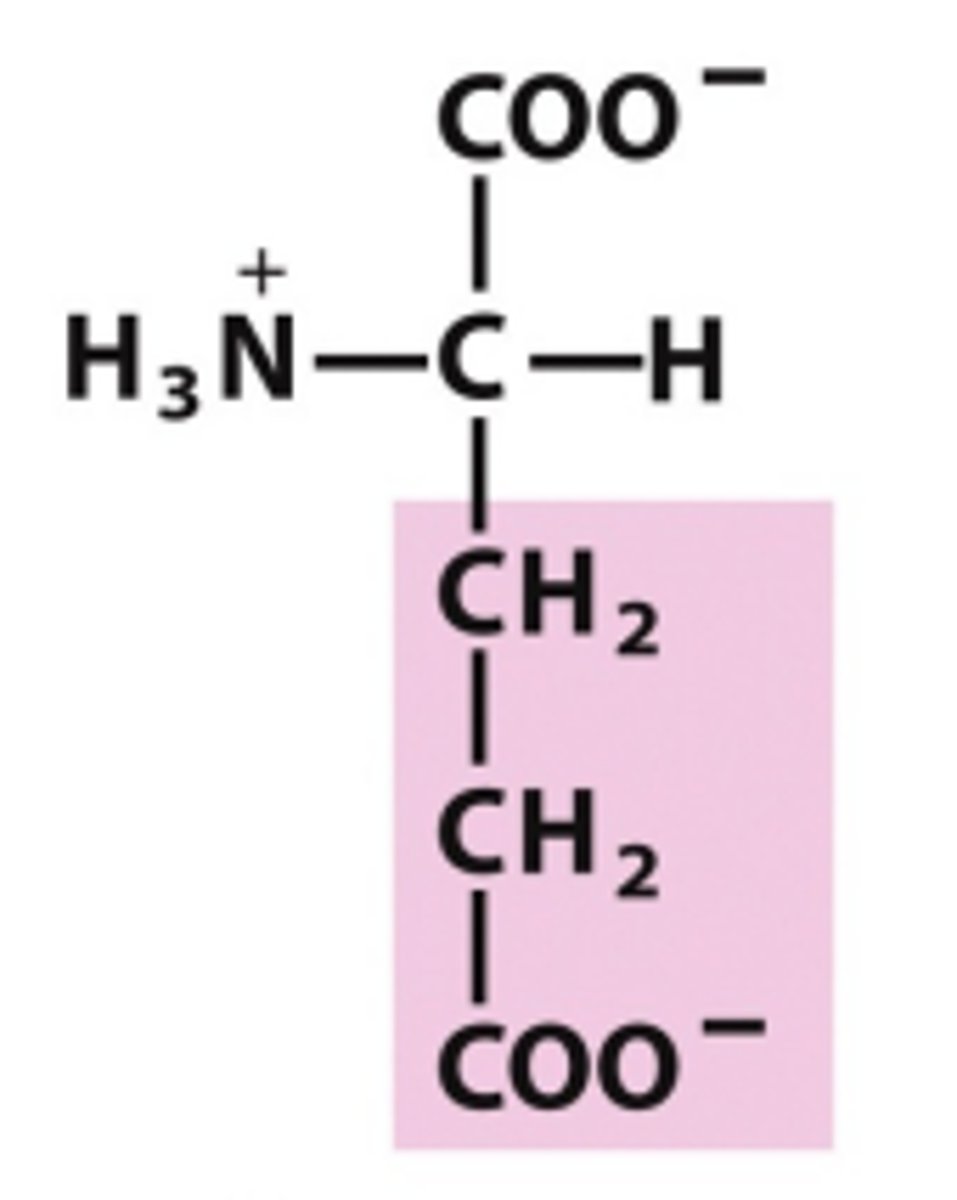
glycine
simplest AA, achiral because 2 H substituents, least steric hindrance, nonpolar/uncharged
alanine
second simplest AA, R group is simply a methyl group, nonpolar/uncharged
valine
R group is a like a V of methyls (isopropyl), nonpolar/uncharged
Leucine
R group is a like Valine w/ a V of methyls but has an additinal carbon before the V splits, nonpolar/uncharged
isoleucine
structural isomer of leucine - the first carbon in the R group branches to have one methyl attached, and one ethyl attached, and one H attached, nonpolar/uncharged
proline
R group has three carbons that form a ring and bond w/ the nitrogen group of AA, nonpolar/uncharged, cyclic w/ no aromaticity
methionine
R group has 2 carbons sulfur carbon (ends w/ thioether), considered "nonpolar"/uncharged
serine
R group has two carbons and ends w/ an alcohol, polar/uncharged
[similar to cystine but w/ oxygen instead of sulfur]
cystine
R group has two carbons and ends w/ an thiol, polar/uncharged, form disulfide bonds
[similar to serine but w/ sulfur instead of oxygen]
threonine
R group has on additional carbon w/ two branches, a methyl and an alcohol, polar/uncharged
asparagine
R has one carbon and then a carbamate, polar/uncharged
glutamine
R group has two carbons and then a carbamate, polar uncharged
phenylalanine
R group has one carbon and than a phenyl ring, aromatic nonpolar/uncharged
[similar to tyrosine except w/out an OH on ring]
tyrosine
R group has one carbon and than a benzene ring, aromatic polar/uncharged
[similar to phenylalanine except w/ an OH on ring]
tryptophan
unusual R group, has two conjoined rings. First ring has a CC double bond then bonded to a nitrogen that connects to another carbon in a 5 membered ring. A 6 membered phenyl ring is a attached to this ring. nonpolar/uncharged aromatic
lysine
R group w/ a chain of four carbons ending w/ a positively charged ammonium subsituent
arginine
R group w/ a chain of 3 carbons - nitrogen - carbon w/ two nitrogen attached, one nitrogen is positively charged (ammonium ion) substituent
histidine
R group has a carbon and then a 5 membered ring w/ two nitrogens. (carbon-nitrogen-carbon-nitrogen-carbon.)
aspartate
R group has one carbon and a negatively carboxylate anion
glutamate
R group has two carbons and a negatively carboxylate anion
aspartate has one carbon and then carboxylate anion, and glutamate has two carbons and then carboxylate anion
names and differences between 2 AAs with carboxylate anion
tyrosine has an alcohol substituent on the aromatic ring and phenylalanine does not
two aromatic amino acids w/ one substituent difference
asparagine and glutamine both have R groups w/ terminal carbamates but glutamine has one more carbon in chain first (1 carbon prior to carbamate vs 2 carbons prior to carbamate)
two AAs w/ carbamates, how are the different
after first carbon, serine has an alcohol and cystine has a thiol
two amino acids who differ only w/ alcohol vs thiol substituent in R group
Isoleucine (Ile), Asparagine (Asn), Glutamine (Gln), Tryptophan (Trp)
What AAs unusual three letter codes
Phenylalanine (F), Tyrosine (Y), Tryptophan (W), Asparagine (N), Glutamine (Q), Lysine (K), Arginine (R), Aspartate (D), Glutamate (E)
unusual one letter codes
Isoleucine
Ile
Asparagine
Asn
Glutamine
Gln
Tryptophan
Trp
Phenylalanine
F
Tyrosine
Y
Tryptophan
W
Asparagine
N
Glutamine
Q
Lysine
K
Arginine
R
Aspartate
D
Glutamate
E
F
Phenylalanine (one letter)
Y
Tyrosine (one letter)
W
Tryptophan (one letter)
N
Asparagine
Q
Glutamine
K
Lysine
R
Arginine
D
Aspartate
E
Glutamate