1/4 notes
1/264
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Network fundamentals - OSI models - ports and protocol
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
265 Terms
Network
Encompass a diverse range of connection extending to both wireless networks to wired networks
Clients
Devices users are going to access the network with
Servers
provide recourses to the network
hubs
old network devices that connect other devices like clients and servers over a local area network ( limits such as increased network errors due to broadcasting nature)
Switches
smarter hubs. Provide more security and more efficient bandwidth
Wireless access points (wap or ap)
allow wireless devices to connect to a wired network
routers
used to connect different networks together
firewalls
security barrier between internal network and external world (internet)
load balencers
devices or software that distribute network or app traffic across multiple servers
Proxy
acts as intermediary between a users device and the internet
Intrusion detection system (IDS)
Detect unauthorized access or anomalies and alert administrators
Intrusion prevention system (IPS)
Not only detect threats, but can also take action to prevent intrusion
controllers
In software defined networking (SDN). These are central units used to manage flow and control to networking devices
Network attached storage (NAS)
Dedicated file storage system that provides data access to a heterogeneous group of clients
Storage area networks (SAN)
high speed network that provides access to consolidated block level data storage
media
in networking, it refers to physical materials used to transmit data (cables and wireless signals)
Wide area network (WAN)
used to connect network over large geographical areas
client/server model
utilizes a dedicated server to provide access to network resources (files, scanners, printers) (backing up is easier) (centralized admin) (easier management) (better scaling) (opposite of peer to peer)
Peer to peer model
peers or other machines (laptops and desktops) can share resources together directly (low cost) (no specialized OS) (no dedicated resources) (No management) (poor scalability) (opposite of client/server )
Personal area network ( PAN )
Smallest type of wired or wireless network which covers a distance of 10 feet or less (bluetooth & USB hard-drive)
Local area network ( lan )
connects components in a limited distance (up to 100 meters ) (home)
Ethernet uses
IEE 802.3 standard
Wifi uses
IEE 802.11 standard
Campus area network ( CAN )
A building centric lan that is spread across numerous buildings in a certain area (college campus / business parks / military bases)
metropolitan area network ( MAN)
Connects locations that are scattered across the entire city
Wide area network ( WAN )
Connects geographically disparate internal networks (largest) (not always public) (connects 2 different businesses in different states)
Network topology
Refers to the arrangements of a different elements like links, nodes, clients, and servers that make up a computer network
physical topology
used to show how the network devices and components are physically cabled and connected together
logical topology
Talks about how the traffic is actually going to flow through our network
6 topologies
poiont to point - ring - bus - star - hub and spoke - mesh
point to point topology
simplest form of network topology - involves a direct connection between 2 devices
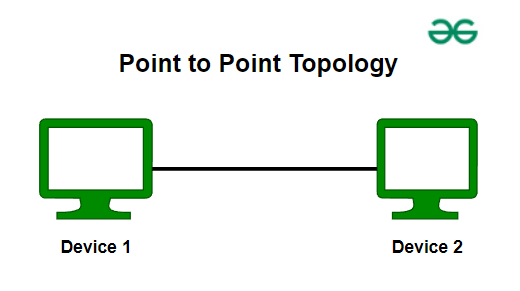
Ring topology
network configuration where each device is connected to 2 devices forming a circular path
Fiber distributed data interface (FDDI)
used to conduct data transmissions on fiber optic lines in a local area network (used with ring topology)
bus topology
all of the network devices are connected to a single central cable
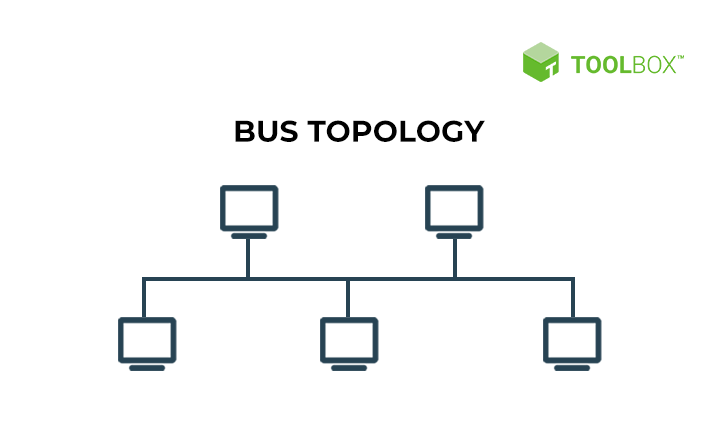
star topology
one of the most common network layout that is used today ( all devices are connected to one centralized network. if that fails they all fail. if one of the connected fail, the network is still up unaffected )
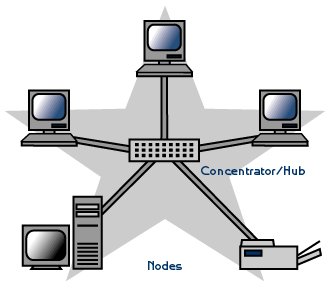
hub and spoke topology
a variation of the star topology where the central node (hub) is connected to multiple nodes (spokes). Its like layovers. Data goes to stop somewhere (spoke) to eventually go to the final destination (node)
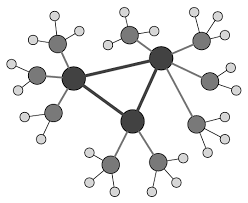
mesh topology
features point to point connection between every single device on the network to create a robust and redundant network
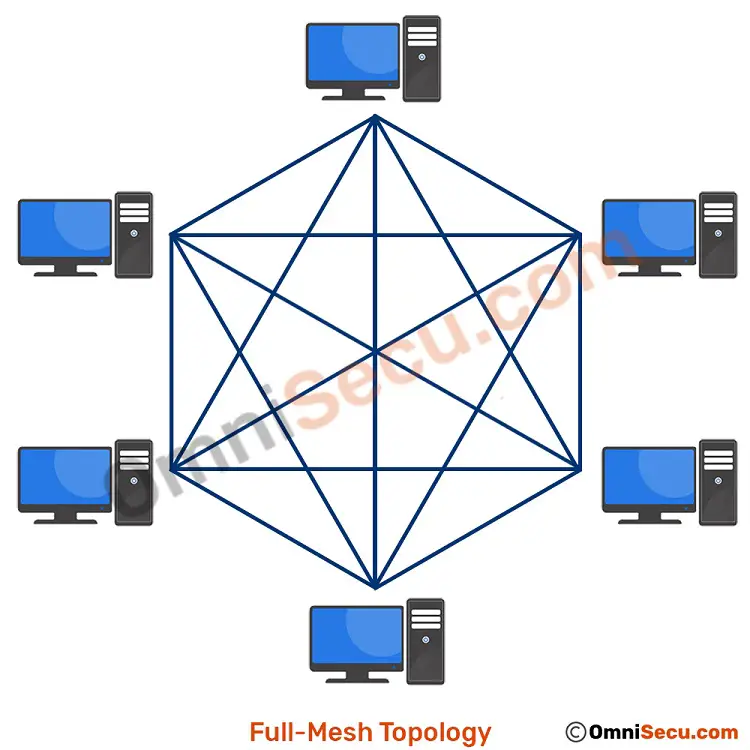
full mesh topology and calculation
every node is connected to every other node in the network ( ( n * ( n - 1 ) ) / 2 n is number of devices )
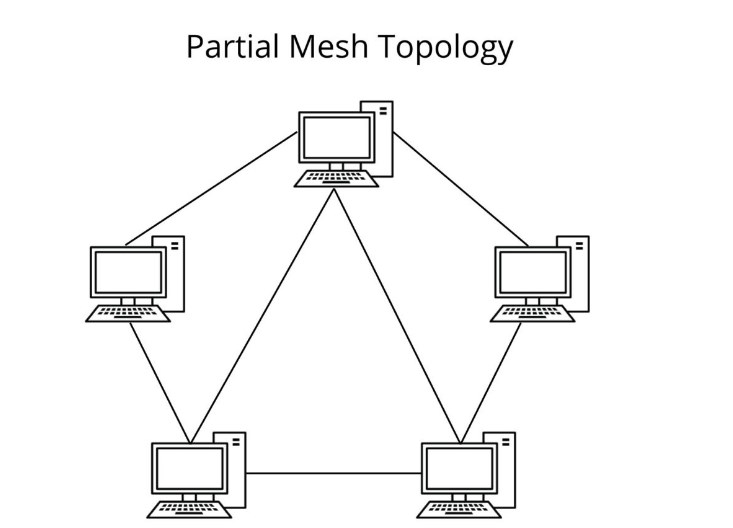
partial mesh topology
some nodes are organized in a full mesh scheme while others are only connected to one or two devices in the network
all topologies similarities and failures
point to point - simplest
bus - single points of failure
ring - single points of failure
star - central point failure
hub and spoke - central point failure
mesh - complex
infrastructure mode
the most common type of wireless network that uses a wireless access point as a centralized point
ad hoc mode
decentralized wireless network which creates peer to peer connection and does not require a router or access point
wireless mesh topology
an interconnection of different types of nodes and devices and radios ( combining bluetooth, cellular , wifi , satellite, microwave)
data center
any facility that businesses and other organizations use to organize, process, store, and disseminate large amounts of data
three tiered hierarchy
core , distribution/aggregation , access / edge (good for performance, management, scalability, redundancy ) ( 3 tier high way system )
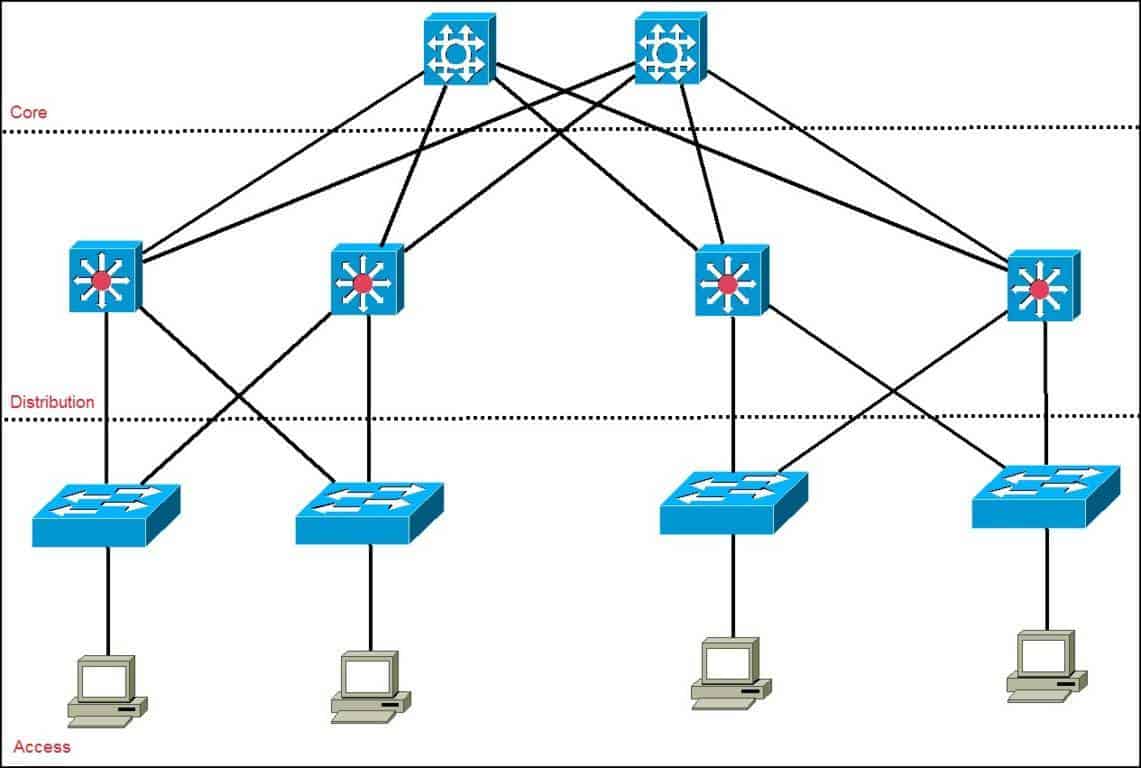
collapsed core
network architecture where the core and the distribution layers are being merged into a single layer
spine and leaf architecture
an alternative type of network architecture that focuses on the communication within the datacenter itself ( can give faster speeds and lower latency ) ( 2 tier highway system )
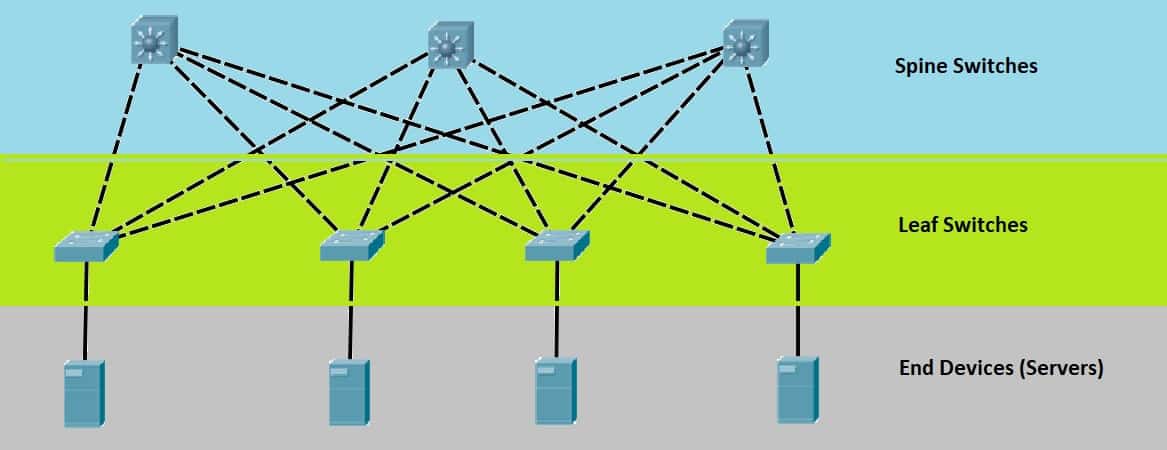
spine and leaf - (spine)
connects switches in a full mesh topology
spine and leaf - (leaf)
consist of all the access switches
spine and leaf architecture can be used in a combination with the 3 tier hierarchy
true
traffic flows
north south / east west
north - south
traffic that enters or leaves the data center from the system physically residing outside the datacenter (Northbound traffic LEAVES datacenter) (SouthBound Enters datacenter)
east - west
refers to the dataflow within a datacenter
OSI model (open system interconnection model )
is a reference model
Physical (use term bits)
Data Link (use term frames)
Network (use term Packets)
Transport (use term Segments)
Session (use term data)
Presentation (use term data)
Application (use term data)
Physical Layer
OSI Layer 1 - Where transmission of bits across the network occurs and includes physical and electrical network characteristics
transition modulation (physical layer)
if it changes during the clock cycle, then 1 is represented. 0 otherwise (on or off)
2 cable standards inside our network (physical layer)
crossover cables - uses different cablings from both ethernet ports
straight through cables - uses equal cables from both ethernet ports
(TIA/EIA - 568A) - (TIA/EIA - 568B)
Asynchronous (physical layer)
Asynchronous - Uses a start and stop bits to indicate when the transmissions occur from the sender to the receiver ( like a voice mail )
Synchronous (physical layer)
Synchronous - uses a reference clock to coordinate the transmissions by both sender and receiver
broadband (physcial)
divide bandwidth into seperate channels ( tv channels)
Baseband (physical)
uses all available frequencies on a medium (cable) to transmit data (telephone) (uses reference clock)
Multiplexing (physical)
enables simultaneous usage of a baseband connection by multiple users ( at same time)
examples in physical layer
Layer 1 devices are essentially repeaters, passing along whatever is received
Dumb devices
fiber optic cable
ethernet cable
coaxial cable
bluetooth
wifi
NFC
hubs
access points
media converters
DataLink layer
OSI Layer 2 Packages data into frames and transmits those frames on the network
Switches
bridges
mac addresses
MAC Address (data link)
physical addressing system of a device which operates on a logical topology (unique 48-bit physical address assigned to every NIC produced) ( D2:51:F1:3A:34:65 ) (first 6 letters is the manufacturor) (last 6 is unique value)
LLC (data link)
provides connection services and allows acknowledgment of receipt of messages. Basic form of flow control
Isochronous (data link)
network devices use a common reference clock source and create time slots for transmission . Opposite of synchronous
Synchronous (data link)
Network devices agree on clocking method to indicate beginning and end of frames and can use control characters . Opposite of Isochronous
Asynchronous : (data link)
network devices reference internal clocks and use start and stop bits for synchronization
Layer 3 : Network
Uses IP and key word is Packets
Devices:
Routers and multi Layer switches (normal switches are layer 2 datalink)
IPV4 and IPV6 (most common on exam)
ICMP
Packet switching (Network)
Data is divided into packet and then forwarded
Circuit switching (Network)
Dedicated communication link is established between 2 devices
Message switching (Network)
Data is divided into messages which may be stored then forwarded
Route discovery and selection (Network)
manually configured as a static route or dynamically through a routing protocol (routers telling each other how to deliver info)
ICMP (network)
Sends error messages and operational information to an IP destination
Uses ping and traceroute and can be very vulnerable
meant for speed not data integrity. SO ITS ONLY FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES
Layer 4: Transport layer
Dividing line between upper layers and the lower layers of OSI
TCP and UDP
Windowing and buffering
firewall and load balancers
Key word : Segments
TCP (Transport)
Connection oriented protocol that is a reliable way to transport segments across the network
Is more serious and for more serious tools
it does that by breaking data into small packets
Another keyword: Segments , Connection Oriented, Flow control windowing, sequencing (1,2,3,4,5)
Threeway handshake TCP (Transport)
Making sure both sides are ready to communicate and communicate to say packets recieved
SYN
SYN-ACK
ACK
UDP (Transport)
Connectionless protocol that is an unreliable way to transport segments across the network
Good for audio and media streaming & increase performance
SMALLER THAN TCP PACKETS
Relies on ports
Another keyword: DataGram, Connectionless, No windowing , no retransmission, No sequencing (2 ,3 1, 5, 6) , Low LATENCY (means no delay and quick)
Windowing ( Transport)
Allows the clients to adjust the amount of data in each segment (speeding up and slowing down effeciently)
Buffer ( Transport)
Occurs when devices allocate memory to store segments if bandwidth is not available
Layer 5 Session layer
Key word DATA, NETBOIS, H.323 (ends calls)
Keeps conversations separate to prevent intermingling of data
Set up Session (Session)
Checking of user credentials and assigning numbers to sessions to help identify them
Maintain Session (Session)
Giving data to each other back and forth
Tear Down Session ( session)
Ending Session
RTP (H.323) (session)
Streaming audio / video
Netbios ( session)
Share files over a network
Layer 6 - Presentation Layer
Formats the data to be exchanged and secures that data with proper encryption
Scripting language (HTML Java), standard text, Pics
Key words : DATA, Data formatting (GIfs, ASCII, PIcs) and encryption
ASCII (data formatting) (presentation)
Text based language to use
Encryption ( Presentation )
Used to scramble the data in transit to keep it secure from others and provide confidentiality
Layer 7 Application
provides application level services where users communicate the computer
POP3, IMAP , SMTP, Service advertisement
Keywords: File transfer , network transfer, DATA
Application services ( Application)
Unites communicating components from more than one network application
Service advertisement (application)
Sending out of announcements to other devices on the network to state the services they offer
Encapsulation (Moving down in OSI layer from 7 to 1)
The process of putting headers around some data ( like closing a letter in an envelope)
Decapsulation (Moving up in OSI 1 to 7)
opening the headers around data
PDU
single unit of information transmitted in a computer network
SYN
Used to synchronize connection in 3 way handshake
ACK
used during 3 way handshake to acknowledge data recieved
FIN
used to tear down connections in 3 way handshake
RST
used when a client or server receives a packet that it was not expecting during the current connection