Anatomy of Synovial Joints: Classification, Movements, and Structures
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is a monoaxial joint?
A joint with only one degree of movement, moving only in one plane.
What type of joint can move through two planes?
Biaxial joint.
What are joints that can move in more than two planes called?
Multiaxial joints.
What is abduction of the neck?
A movement that involves tilting the head away from the midline.
What structure attaches a muscle to bone and helps stabilize a synovial joint?
Tendon.
What does the classification of a joint as bony, fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial describe?
How the bone ends are held together within the joint.
What is circumduction?
Making a conical motion with a limb, as in drawing a circle.
What is the highest degree of movement in synovial joints called?
Ball-and-socket joint.
What is protraction of the scapulae?
Drawing the shoulders anteriorly or protruding the mandible outward.
What is retraction of the scapulae?
Pulling the shoulders back, as in sticking out your chest.
What is the movement that tips the soles laterally called?
Eversion.
What is the movement that tips the soles medially called?
Inversion.
What is supination?
Movement that turns the palms anteriorly or upward.
What is pronation?
Movement that turns the palms posteriorly or downward.
What type of joint is formed by the fusion of bones through ossification?
Synostoses.
What is a syndesmosis held together by?
Collagen fibers.
What are immovable joints called?
Synarthrosis.
What are slightly movable joints called?
Amphiarthrosis.
What is an example of a symphysis joint?
The joint between the bodies of two vertebrae.
What is an example of a synchondrosis joint?
The attachment of the clavicle to the sternum.
What is a fibrous joint between two skull bones called?
Suture.
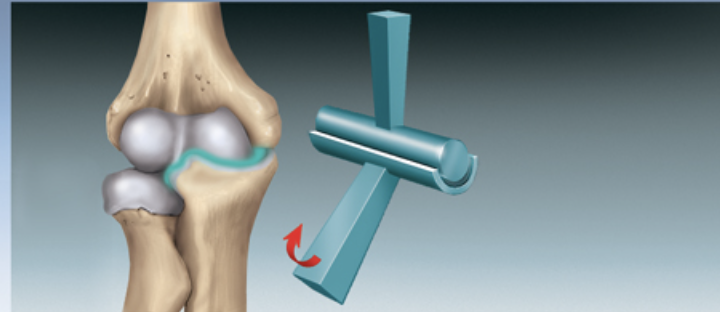
Hinge Joint
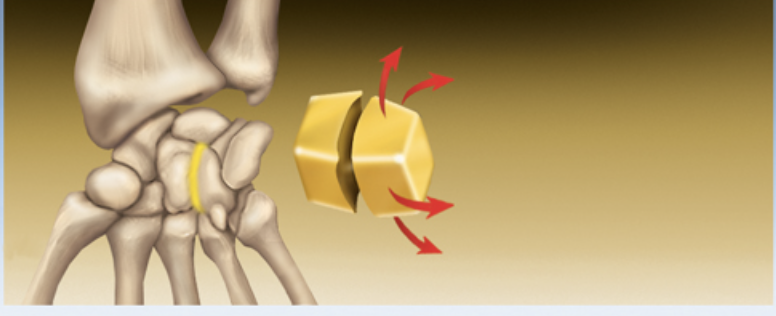
Plane joint
Condylar Joint
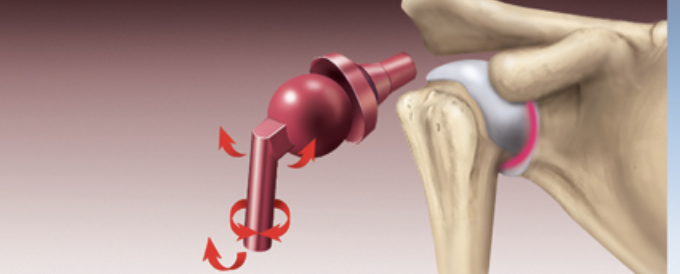
Ball And Socket
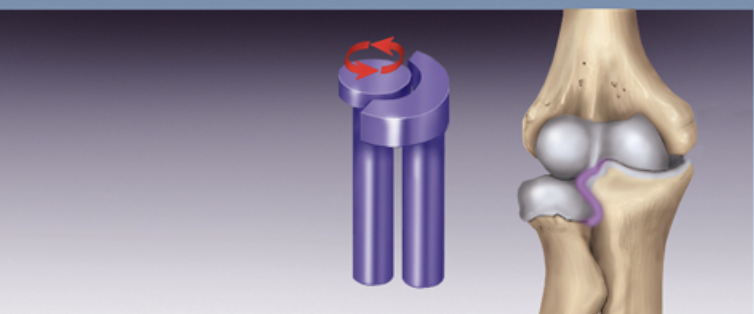
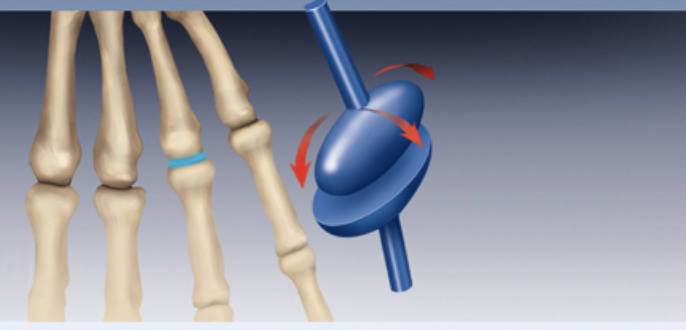
Pivot Joint
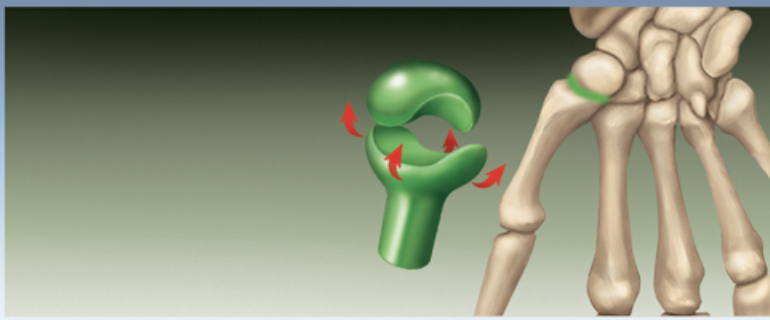
Saddle Joint
Acromion
Glenoid cavity of scapula
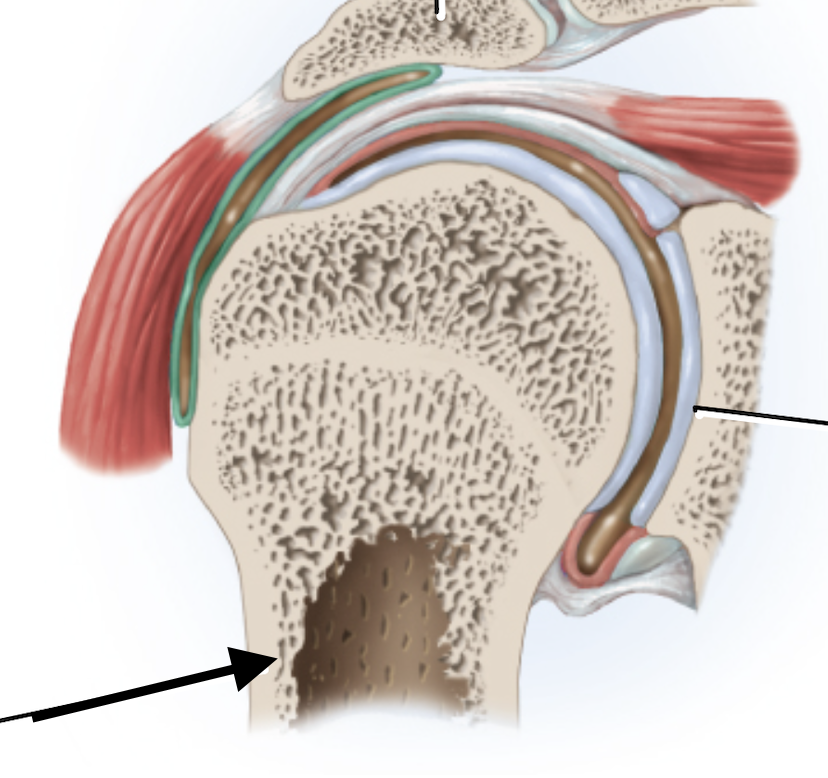
Humerus
Supraspinatus tendon
Subscapularis tendon
Biceps brachii(Long h)
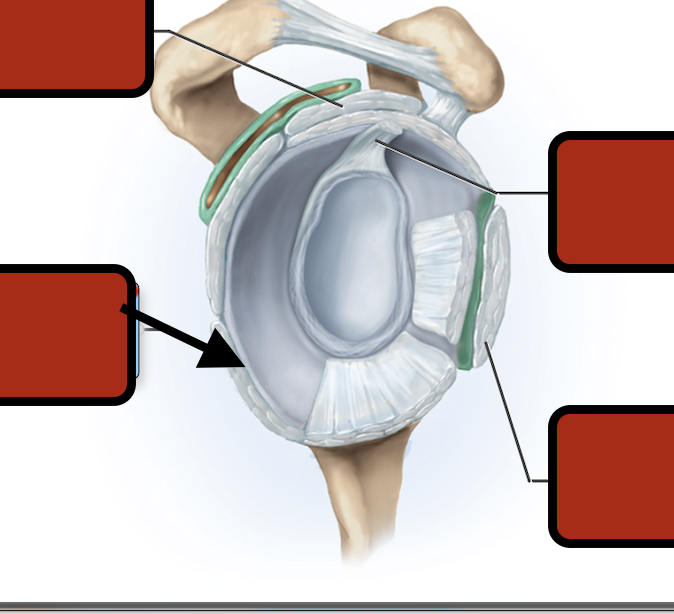
Teres minor tendon
Lateral condyle
Fibula
Tibia
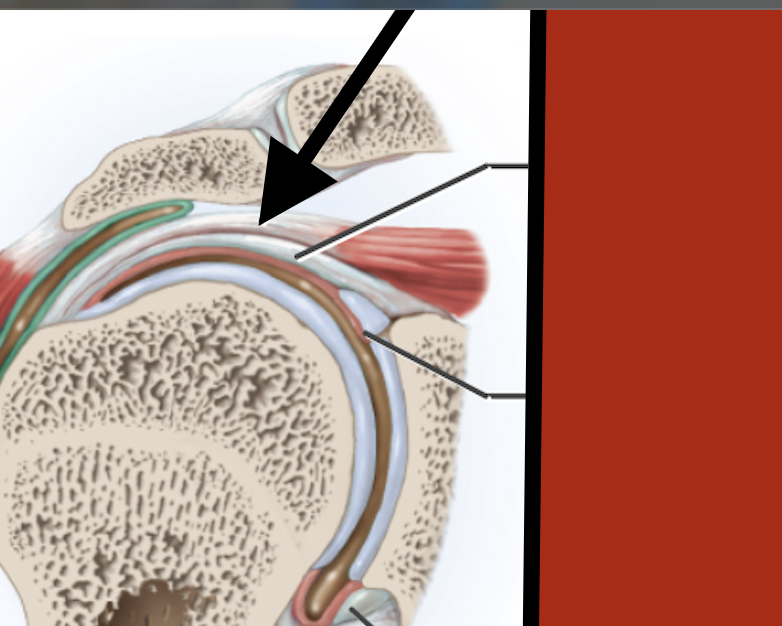
Supraspinous tendon
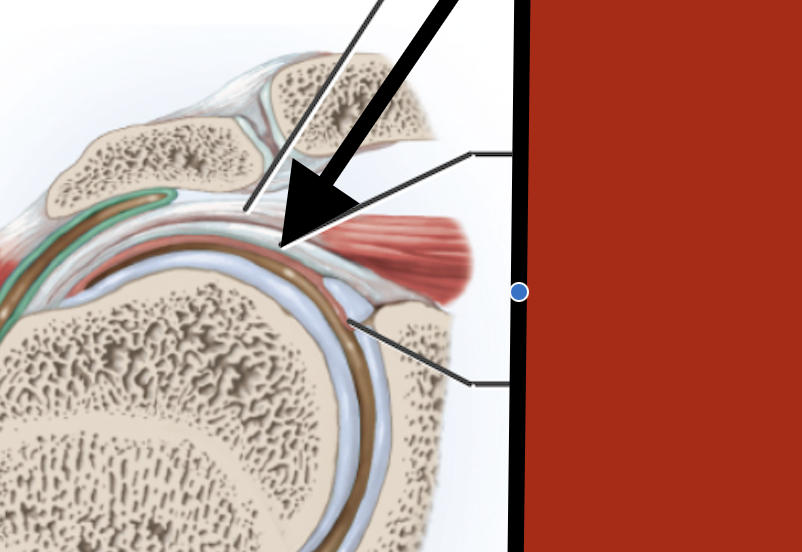
Capsular ligamen
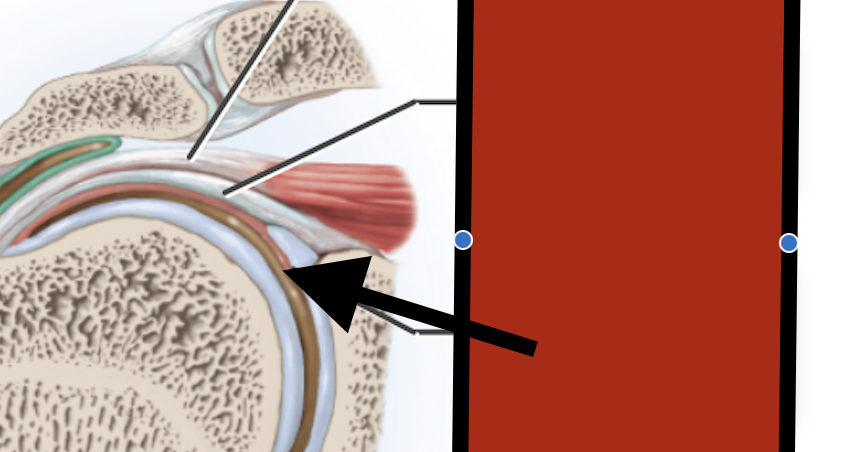
Synovial membrane
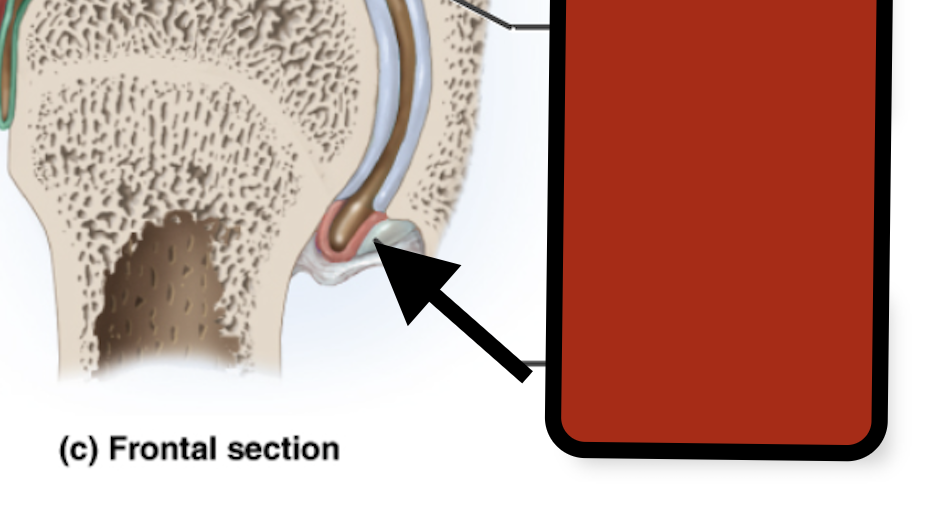
Glenoid labrum
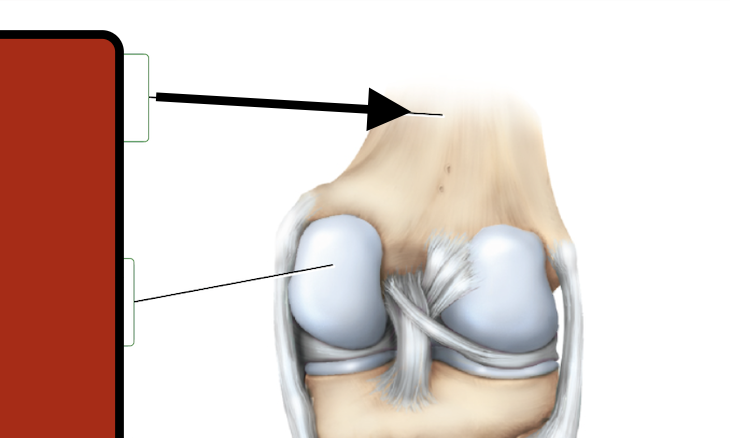
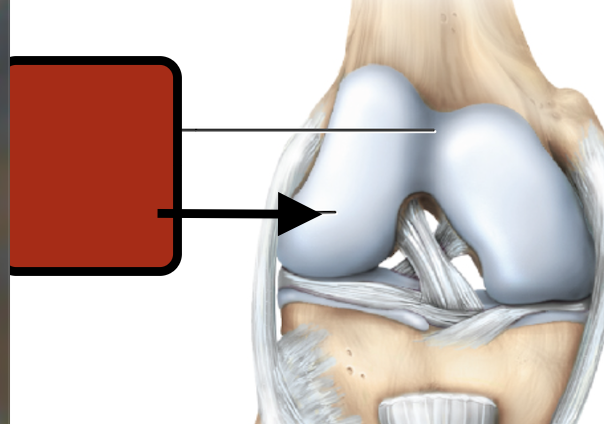
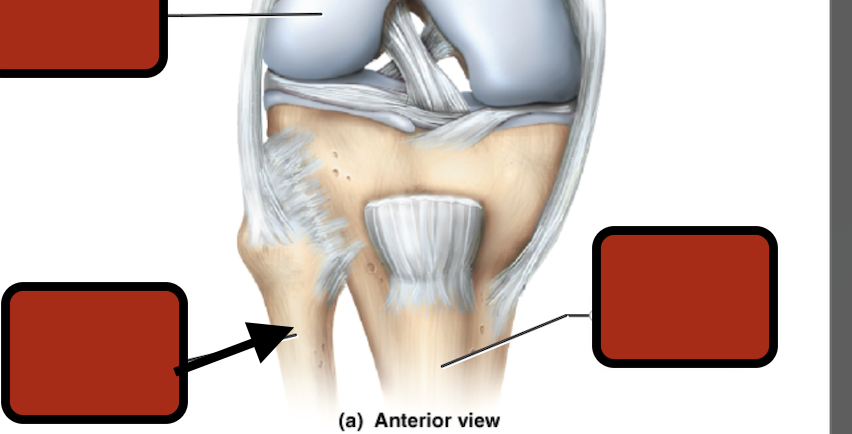
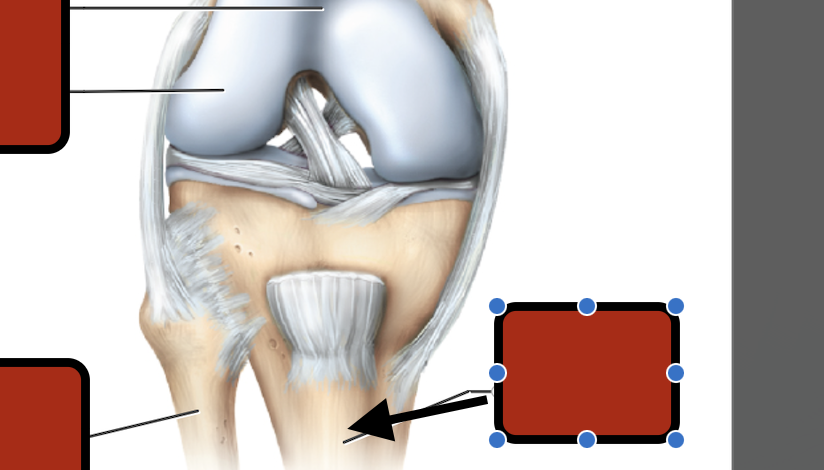
Femur
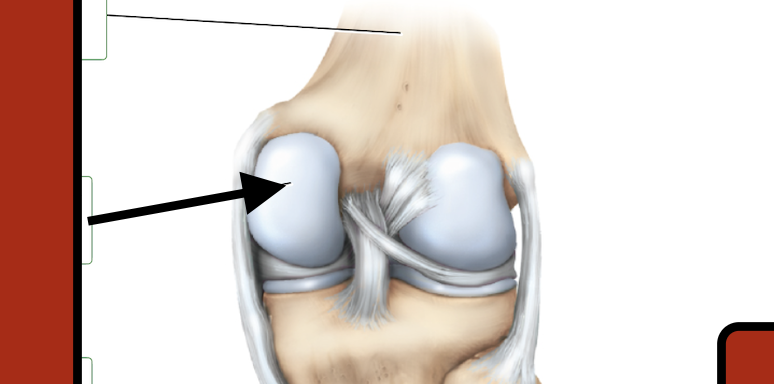
medial condyle
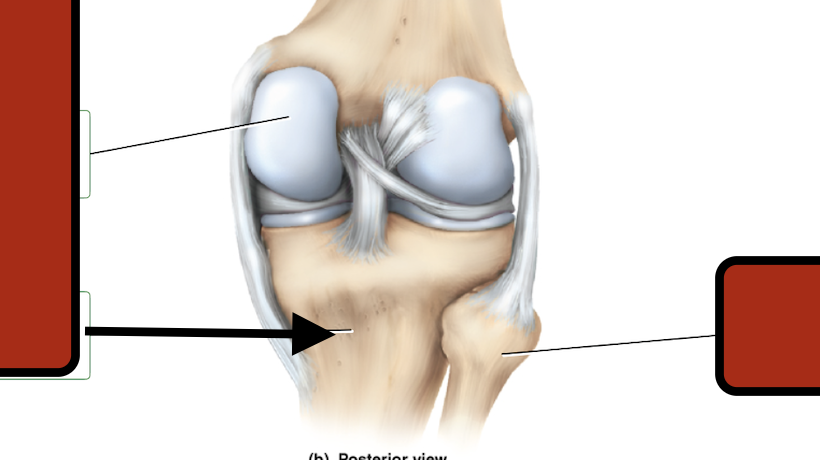
Tibia
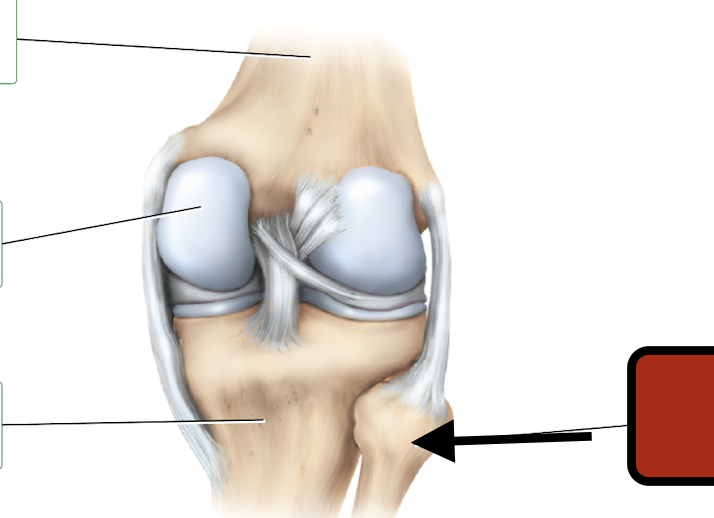
Fibula
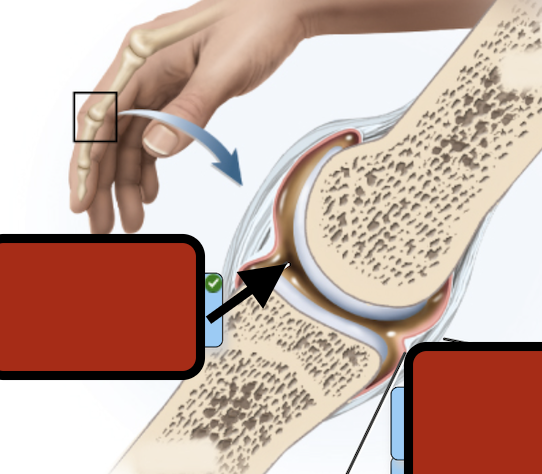
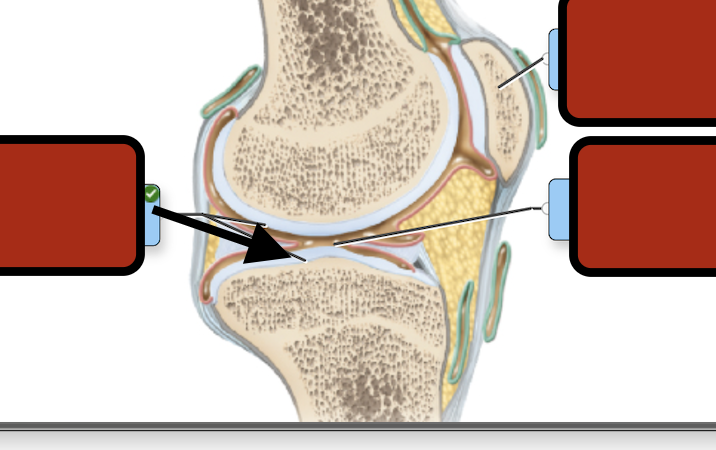
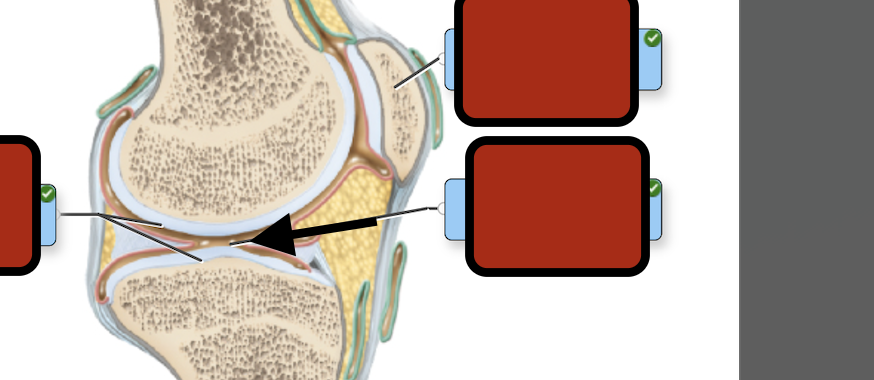
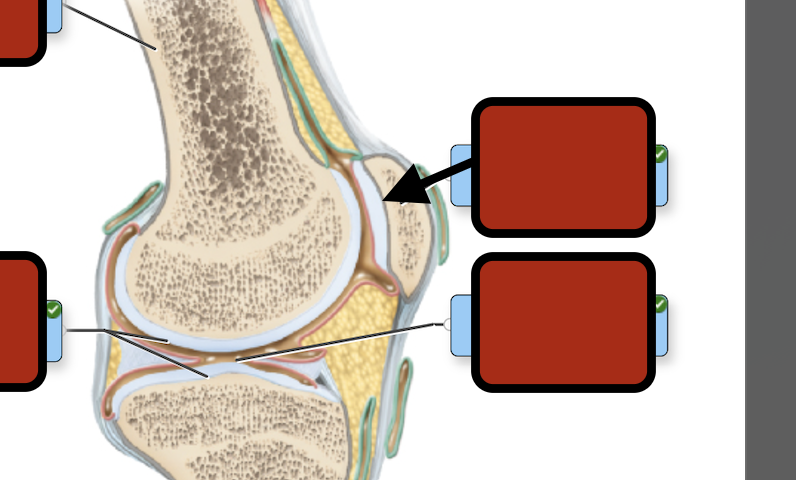
Joint cav synovial fluid
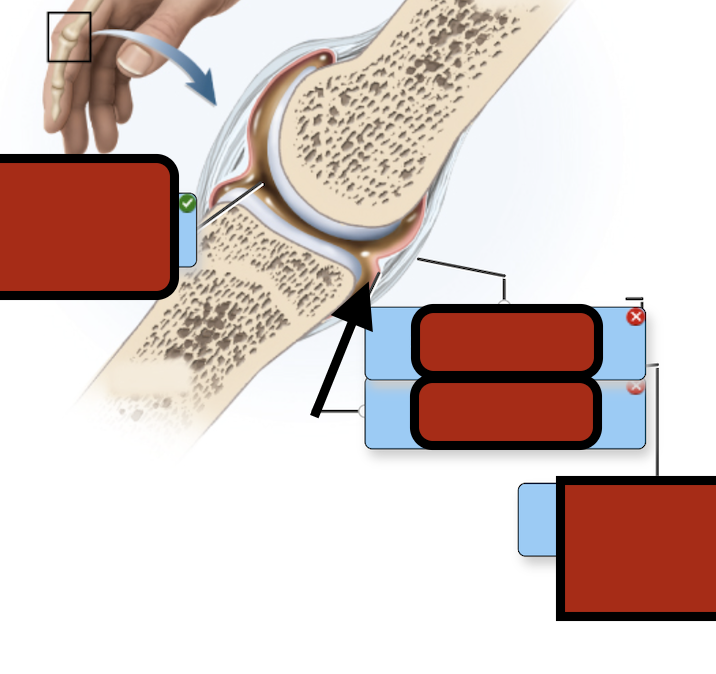
Synovial membrane
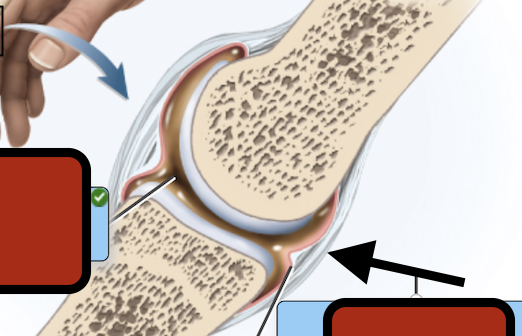
Fibrous capsule
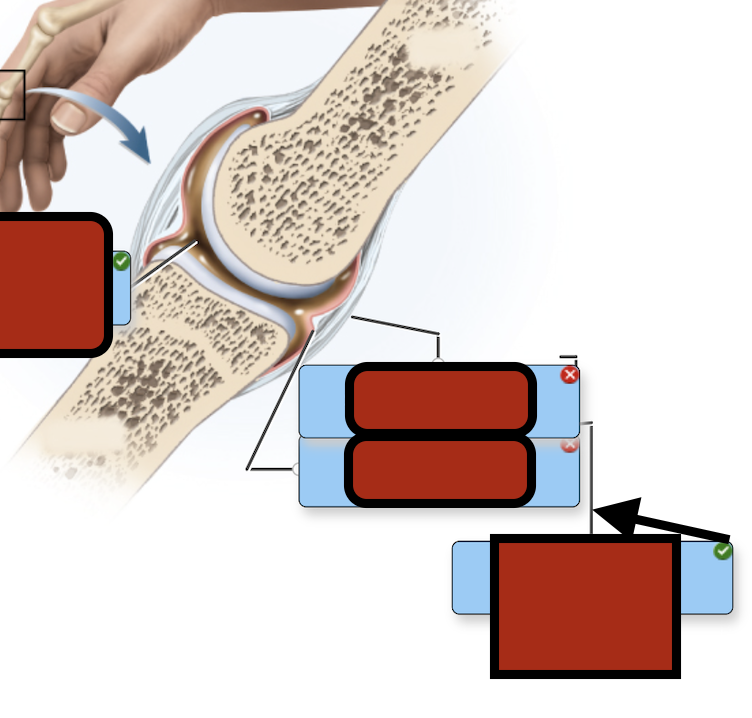
Joint capsule
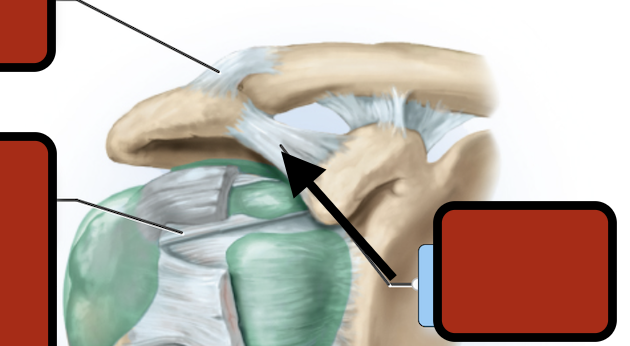
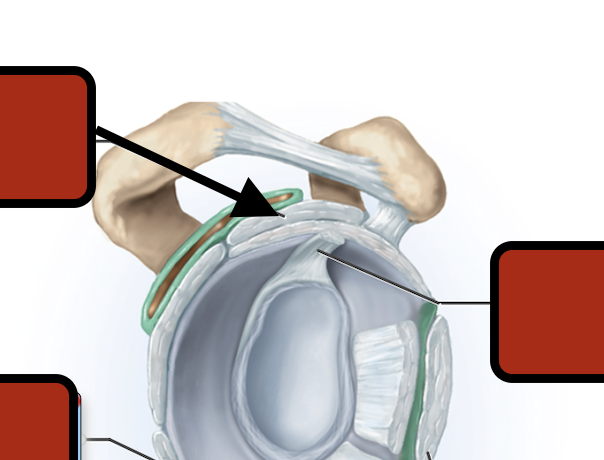
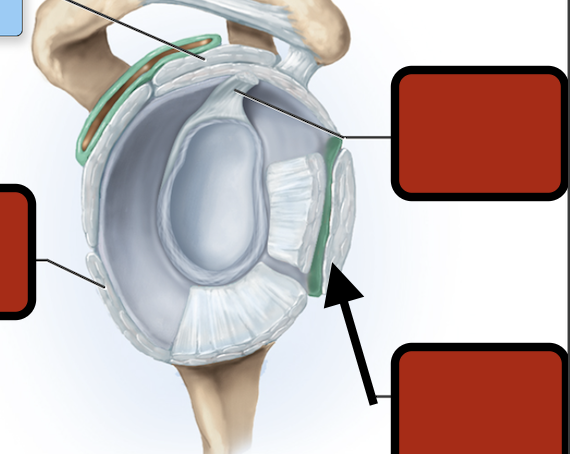
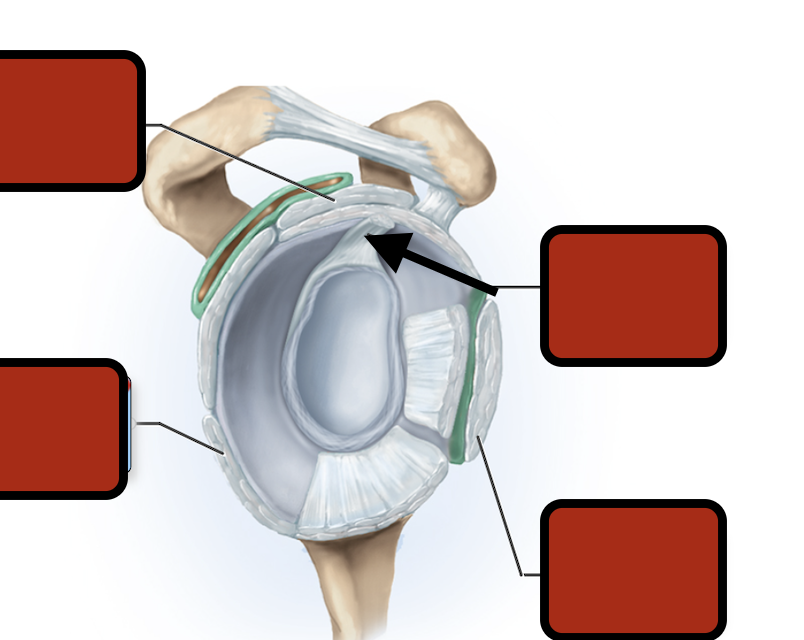
Coracoacromial ligament
corachohumeral ligament
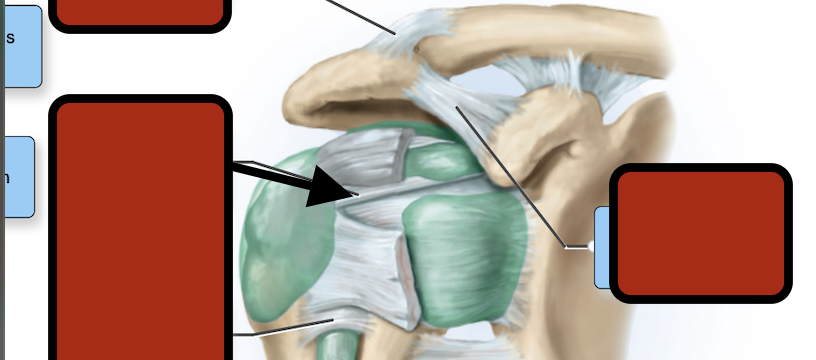
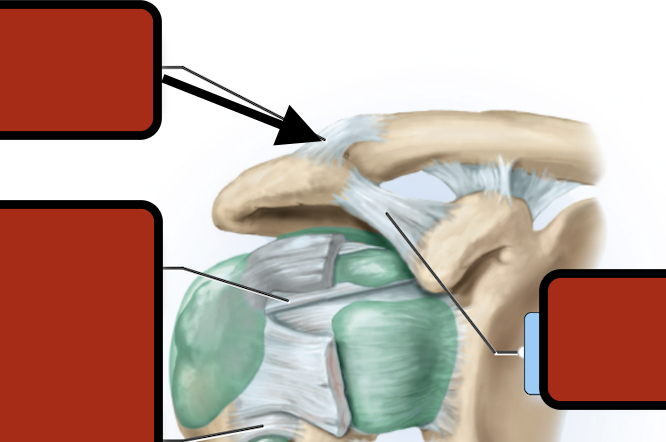
Acromioclavicular ligament
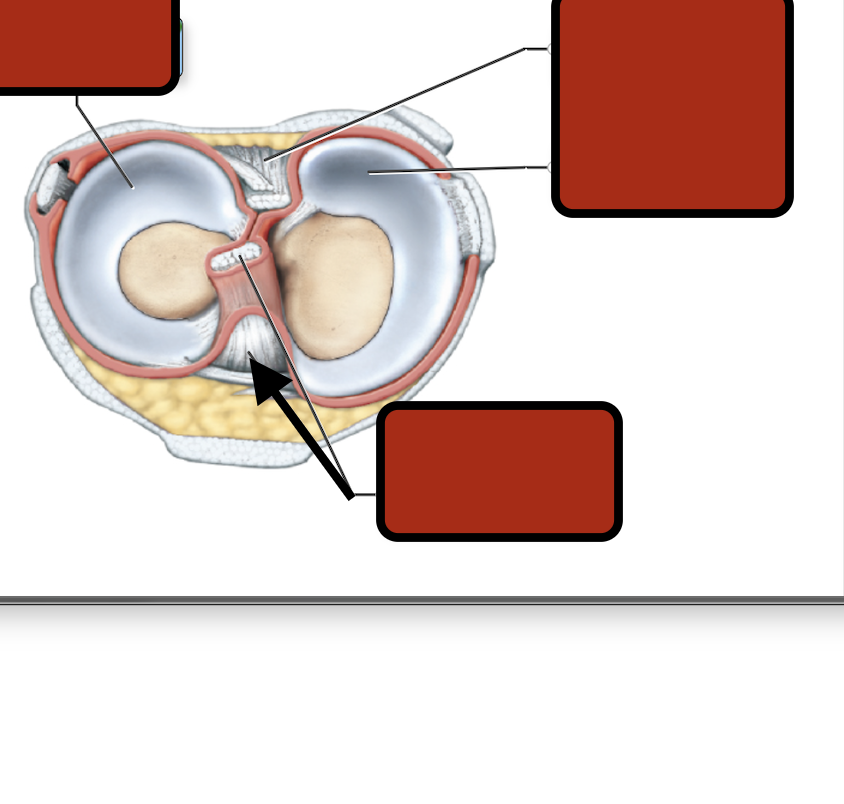
Ant. cruciate ligament
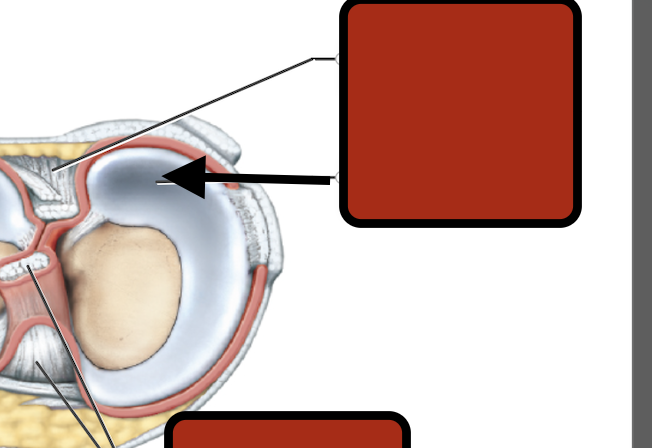
medial meniscus
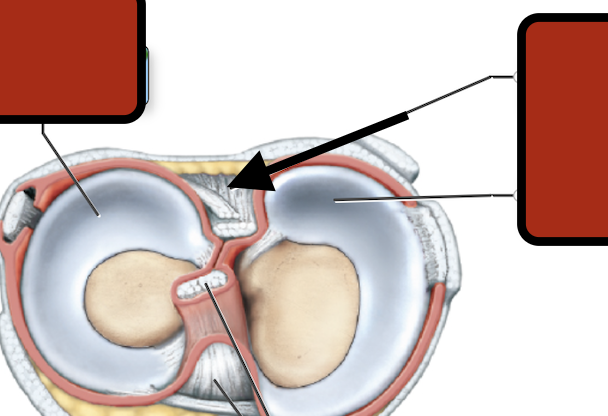
Posterior cruciate ligament
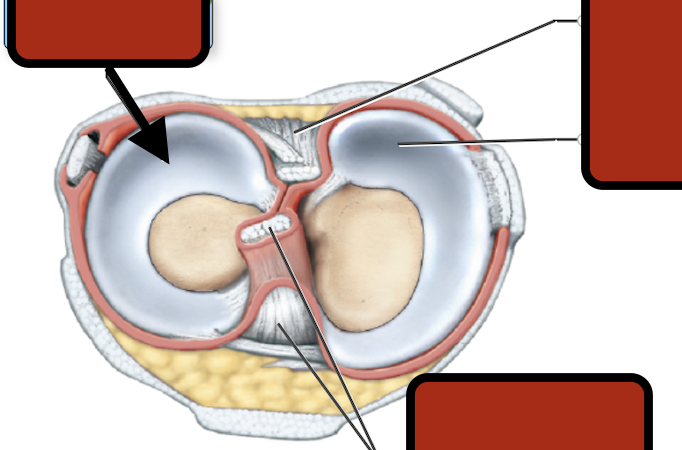
Lateral meniscus
Femur
Articular cartilage
Joint cavity
Petalla
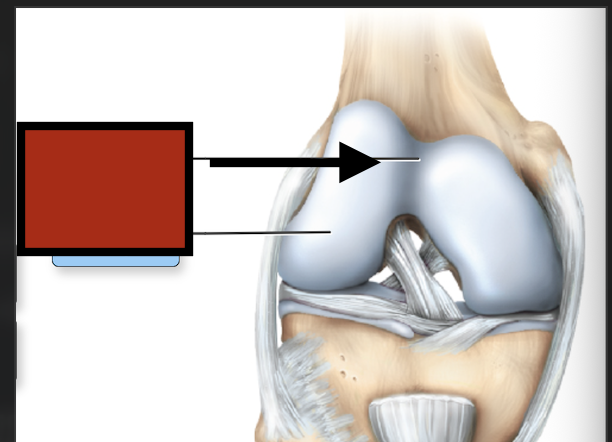
Patellar surface
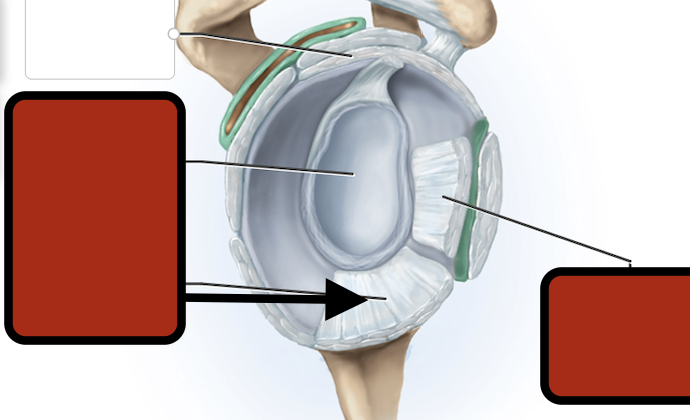
Inf. glenhumeral ligament
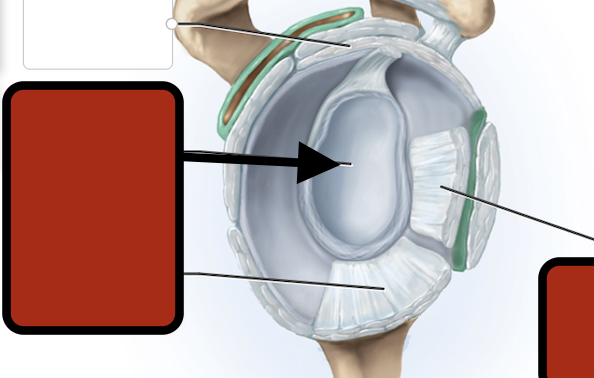
Glenoid cav (articular cartilage)
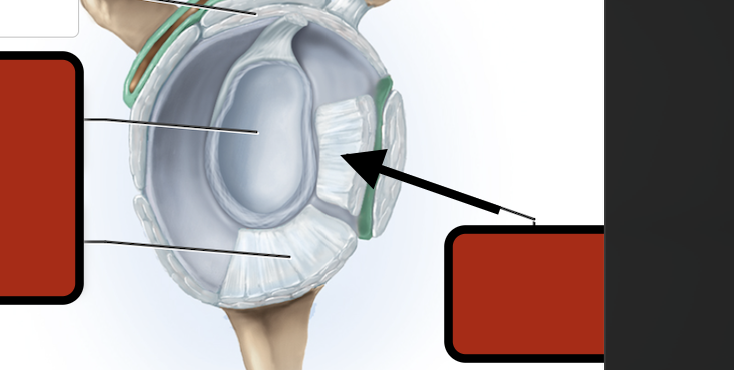
Middle glenohumeral ligament
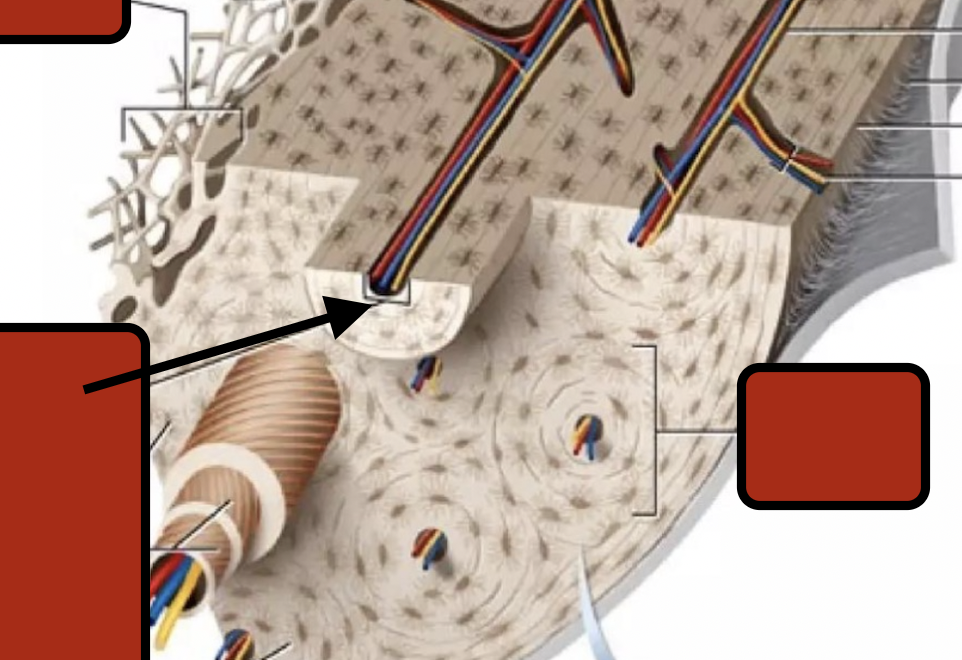
Central Canal
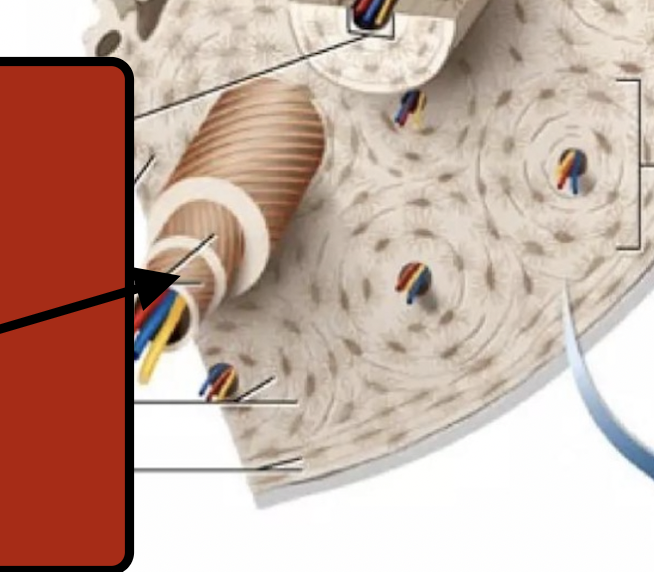
Collagen fibers
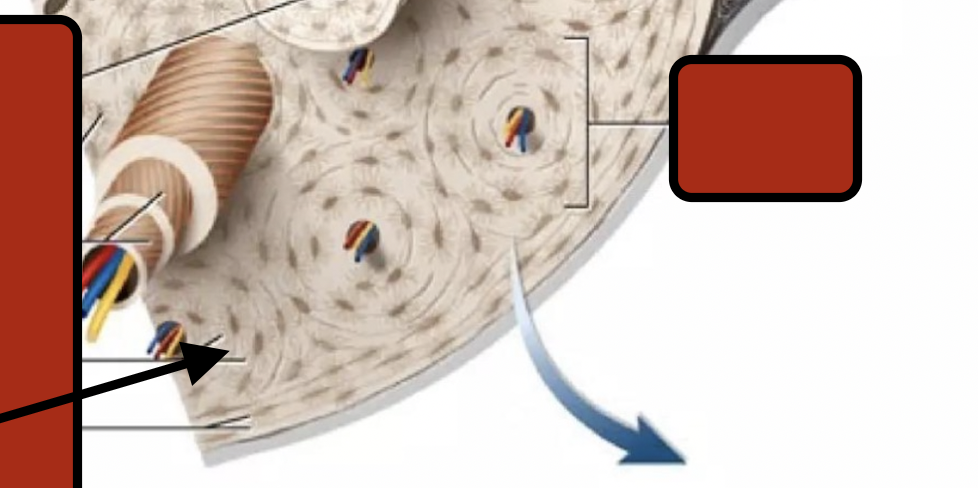
Concentric lamallae
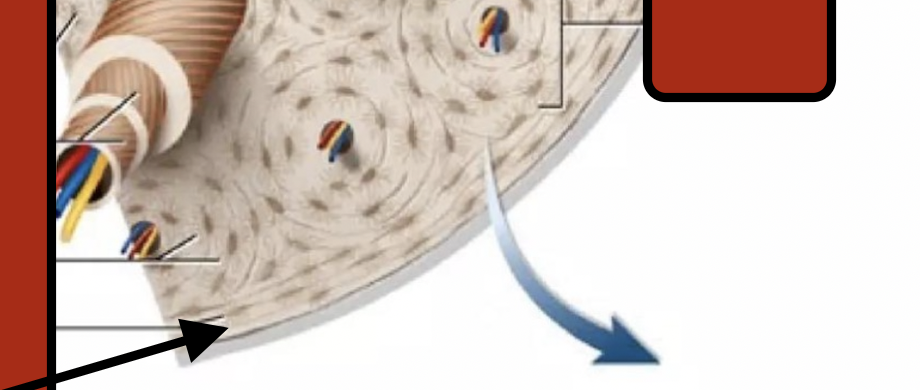
Circumferential lamellae
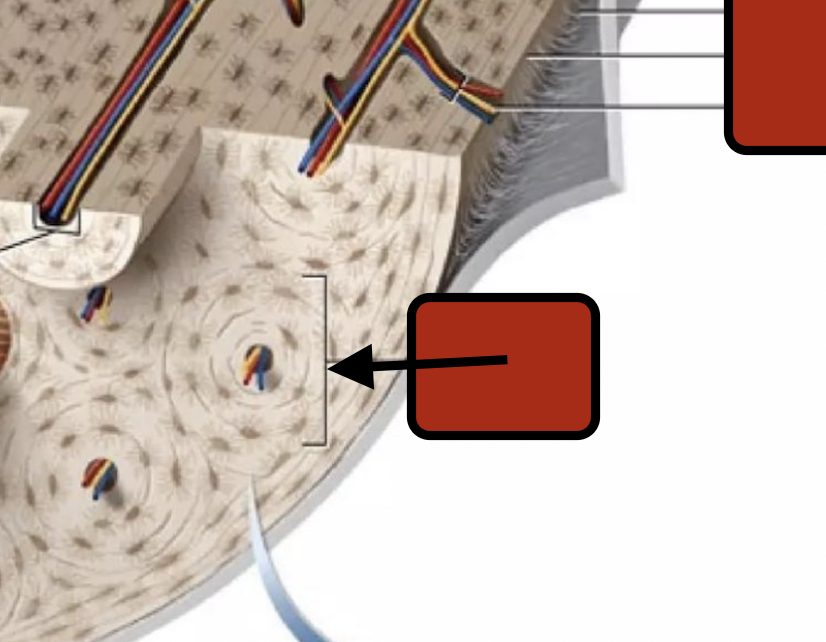
Osteon
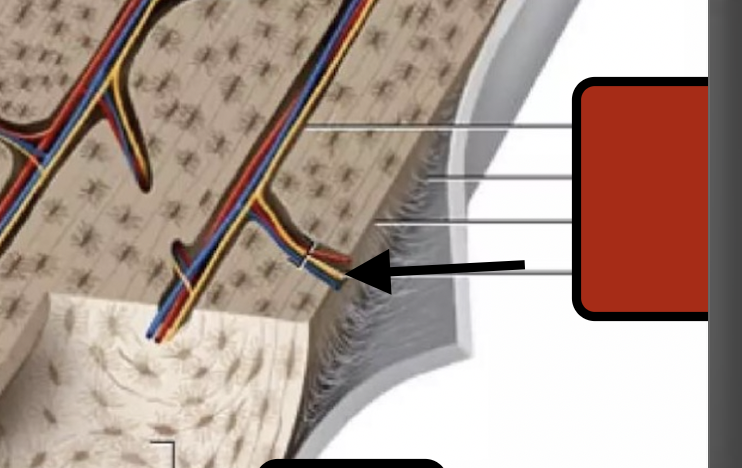
perforating canal
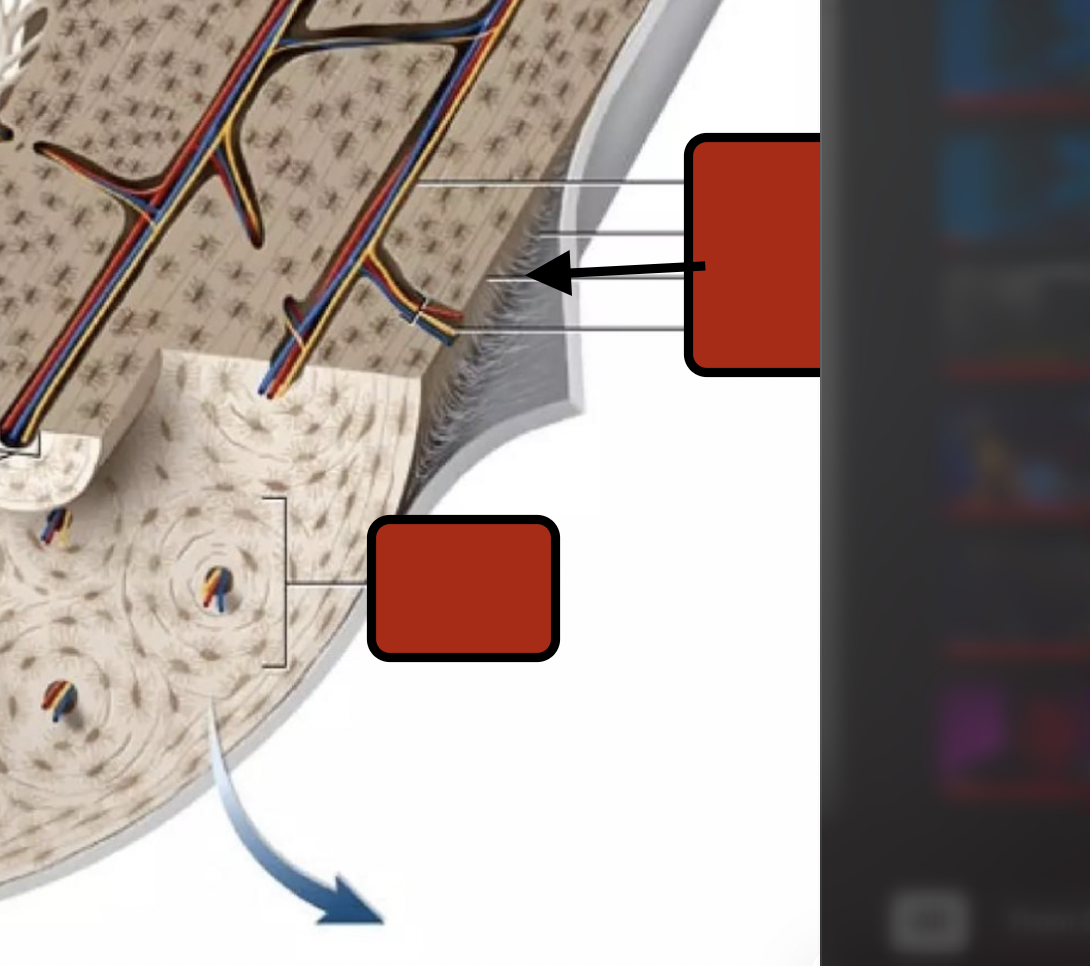
perforating fibers
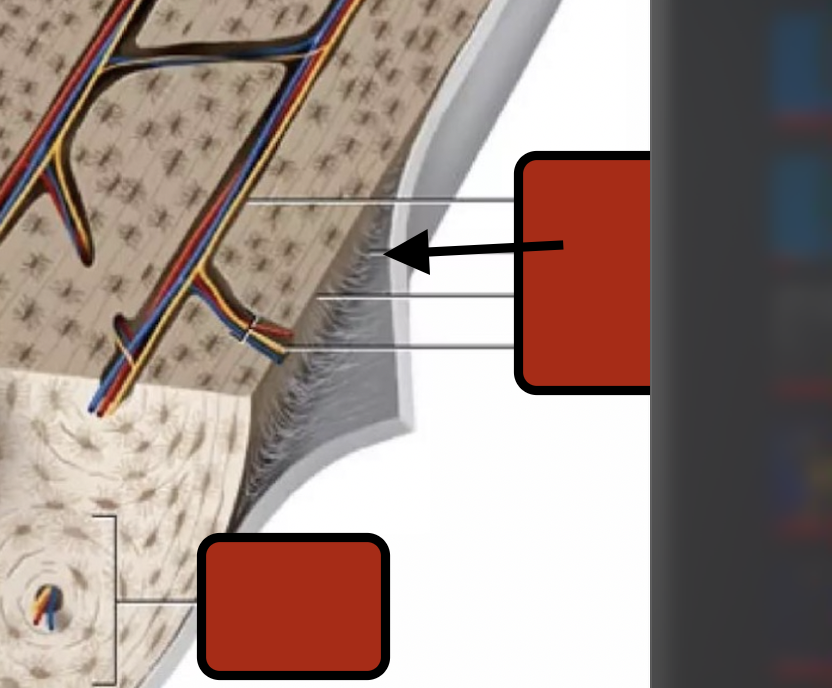
periostium
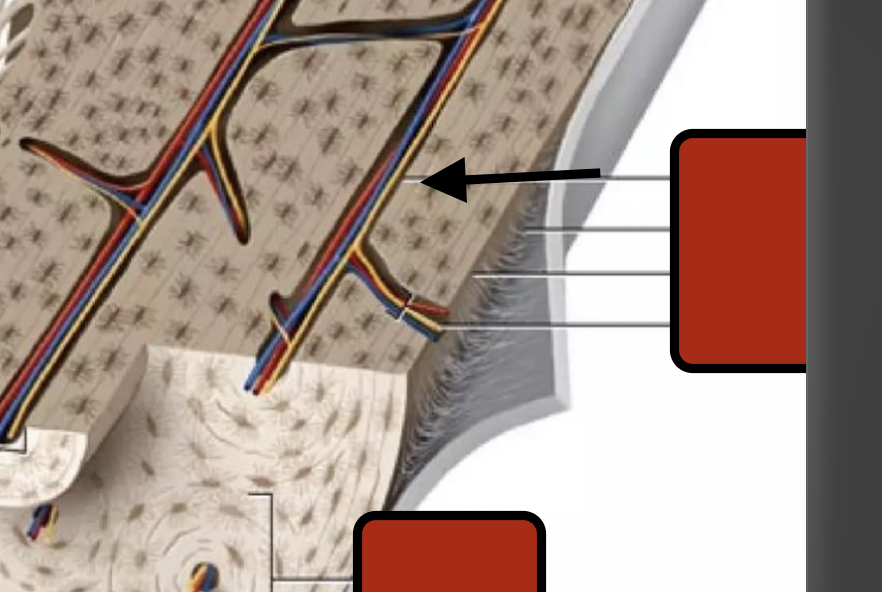
Endosteum
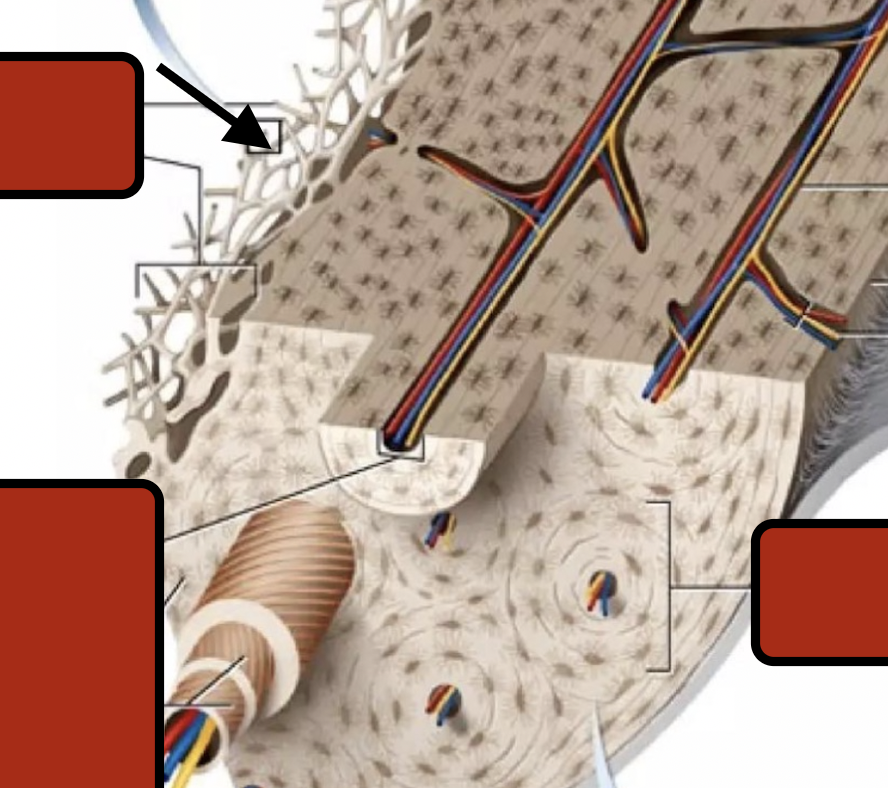
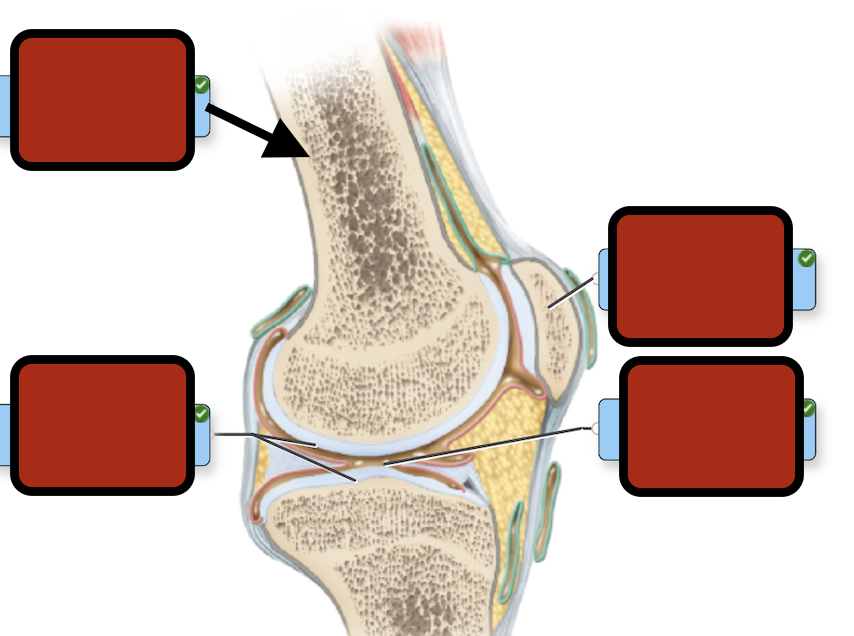
Trabeculae
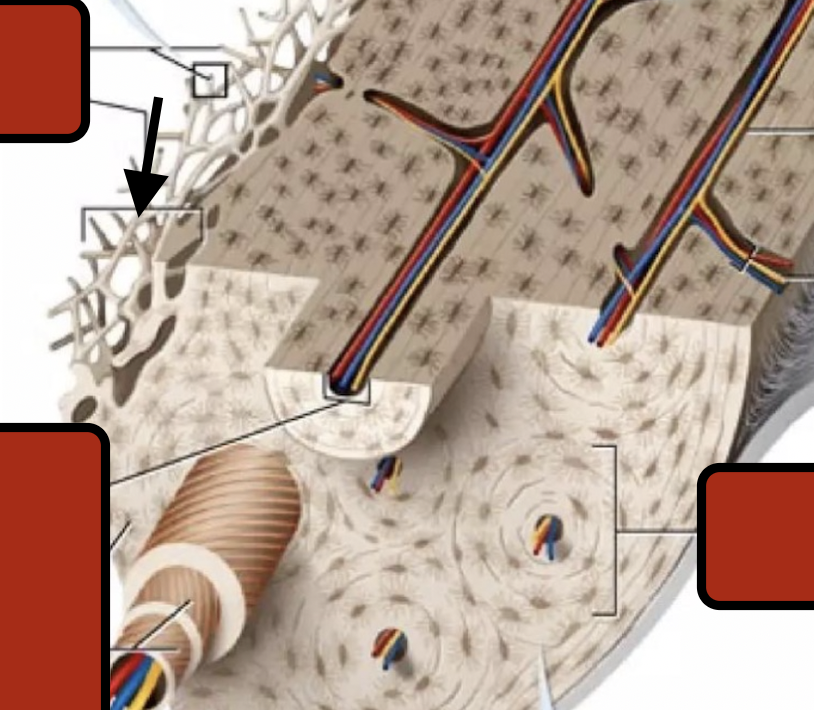
Spongy bone
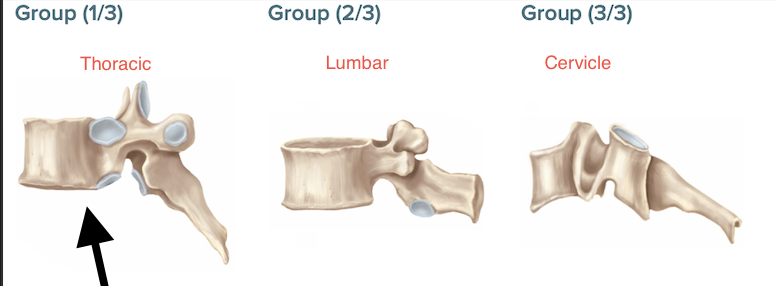
Rib
costal facets
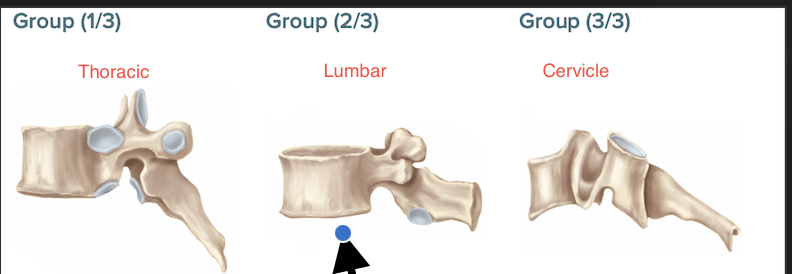
Largest body
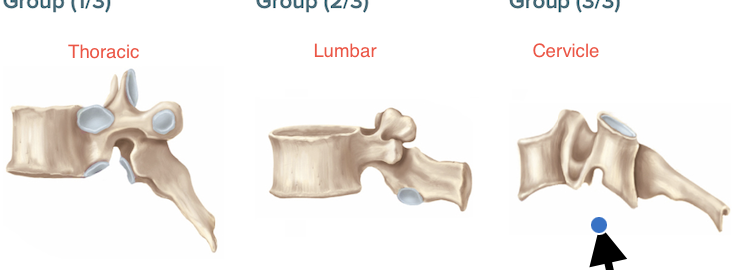
No vertebral body
transverse foramina
Bifid spinous process