B8.2 Respiration
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
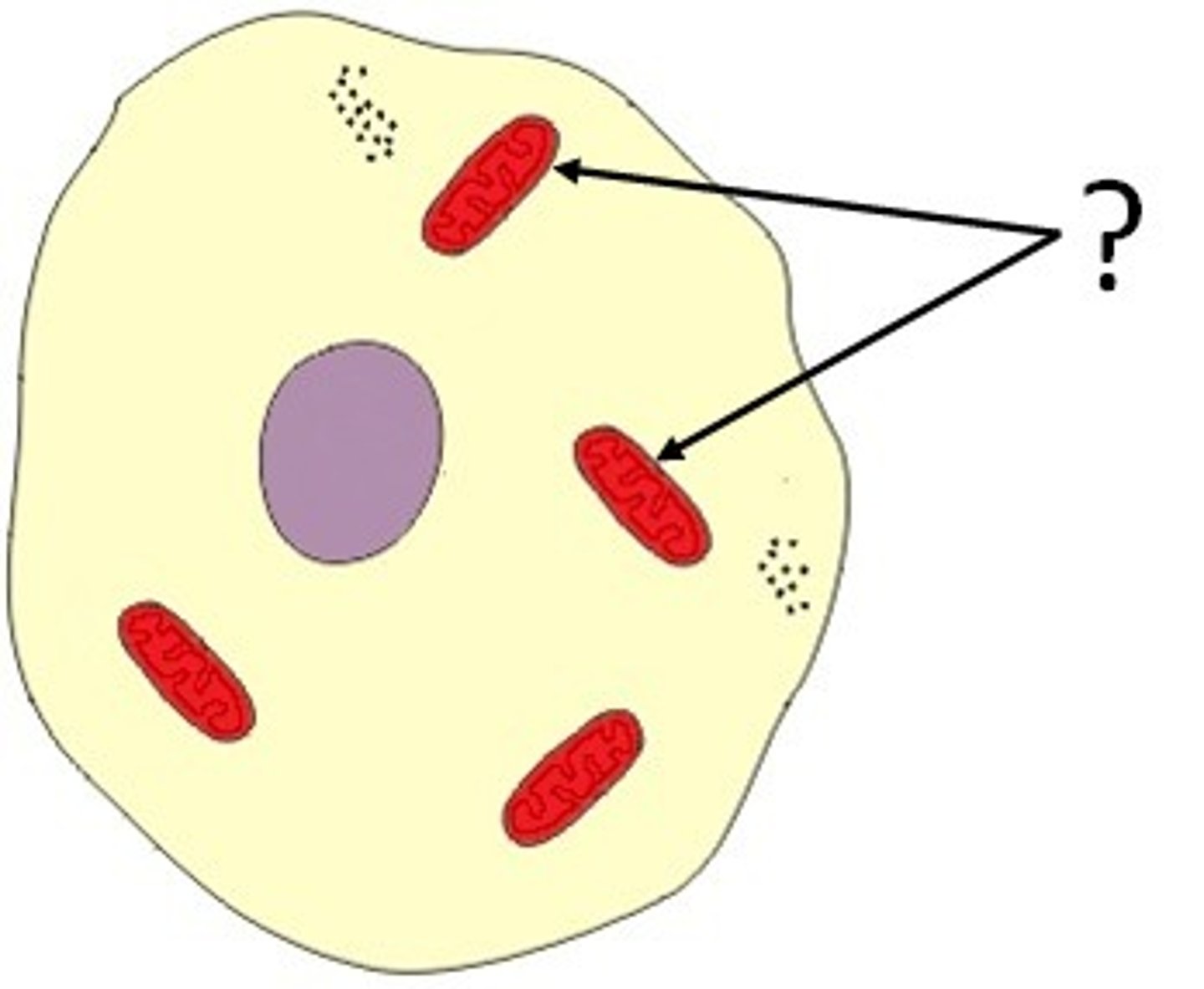
Mitochondria
The site of aerobic respiration in a cell
Aerobic
Respiration using OXYGEN
Anaerobic
Respiration WITHOUT oxygen
Lactic acid
Waste product of anaerobic respiration in humans
Respiration
Release of energy for by cells by breakdown of biological molecules.
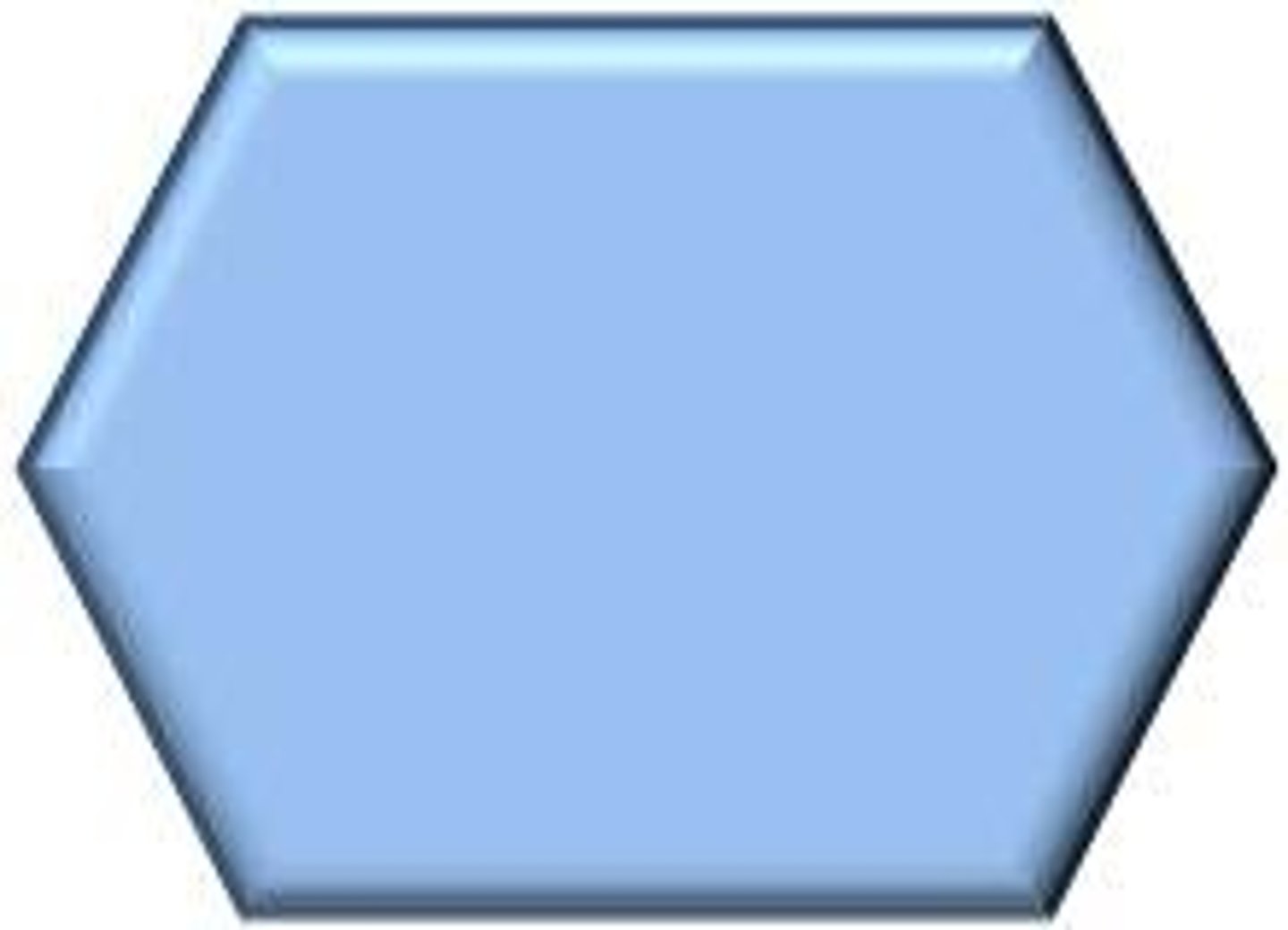
Glucose
A simple, soluble sugar used in respiration

Glycogen
A large, insoluble molecule made of many glucose molecules (used to store glucose in the muscles)
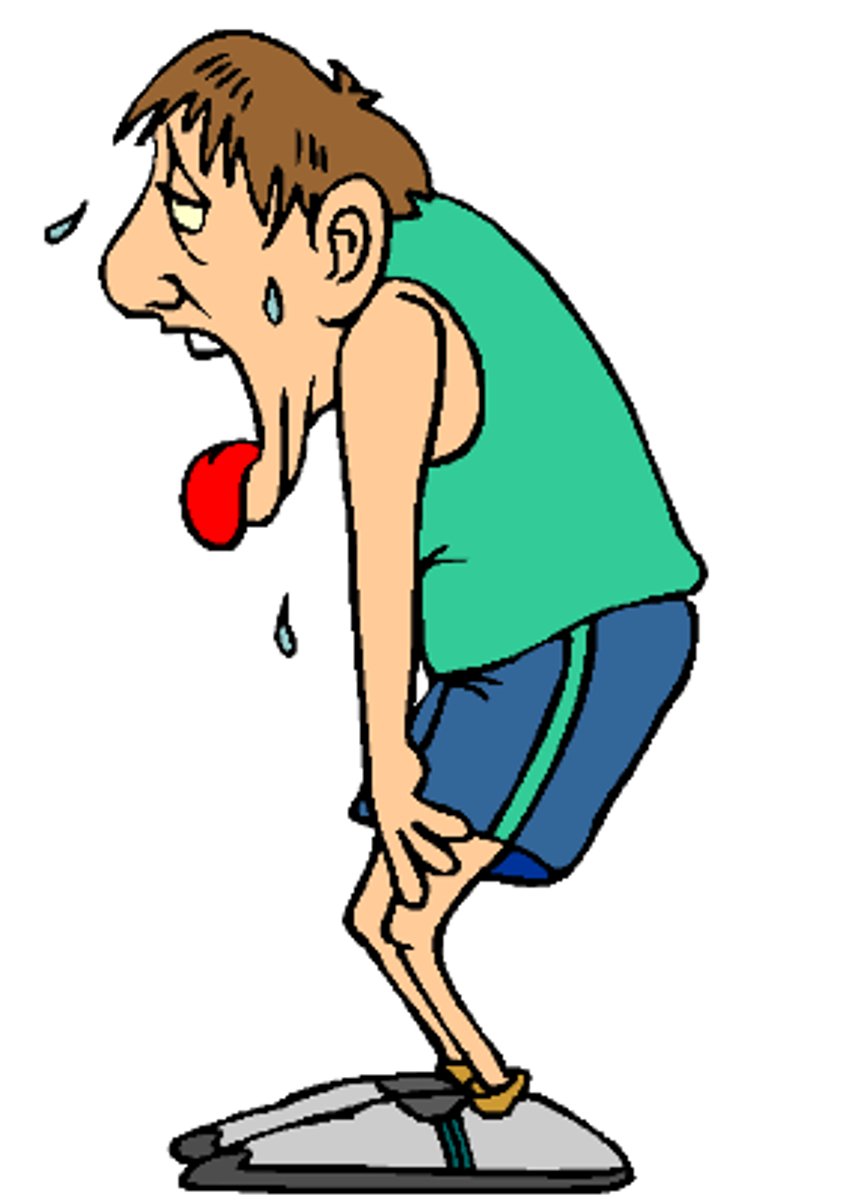
Oxygen debt
The oxygen needed to break down lactic acid after exercise involving ANAEROBIC respiration

Carbon dioxide
Gas produced as a waste product of respiration
Oxygen
Gas needed for AEROBIC respiration
Breathing
The movement of air into and out of the lungs (used to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide)
Uses of energy by cells
Muscle contraction / Building large molecules / Keeping body temperature constant / Active Transport
carbon dioxide and ethanol
products of anaerobic respiration in yeast and plants
ATP
small molecule that carries energy around within a cell (mainly studied at A level)
Accuracy
A description of how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity measured.
Repeatability
How close values are when repeated by the same person with the same equipment
Reproducibility
How close a group of measurements are to each other - these measurements have been taken by different people in different experiments.
Precision
The exactness of a measurement - equipment with small increments have a high level of this.
Validity
The ability of a test to measure what it is intended to measure - when accurate and reliable data have been collected, and a fair test is conducted.
Fair test
When only one variable is changed and all other control variables are kept the same.
Range bars
Measure of variation between repeats.