NERVES
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
what is a nerve made up of
a bundle of neurones
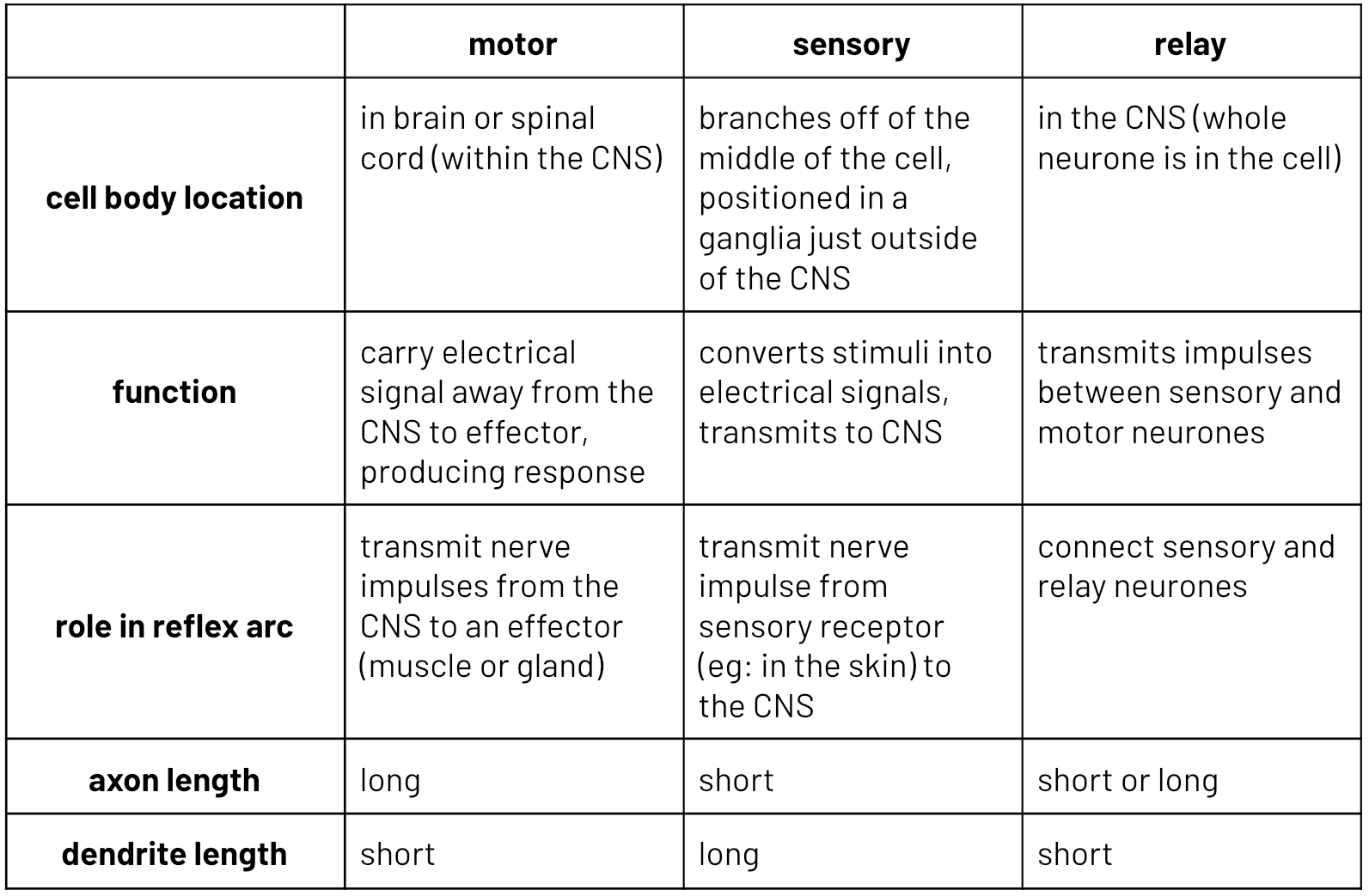
sensory, relay and motor neurones structures
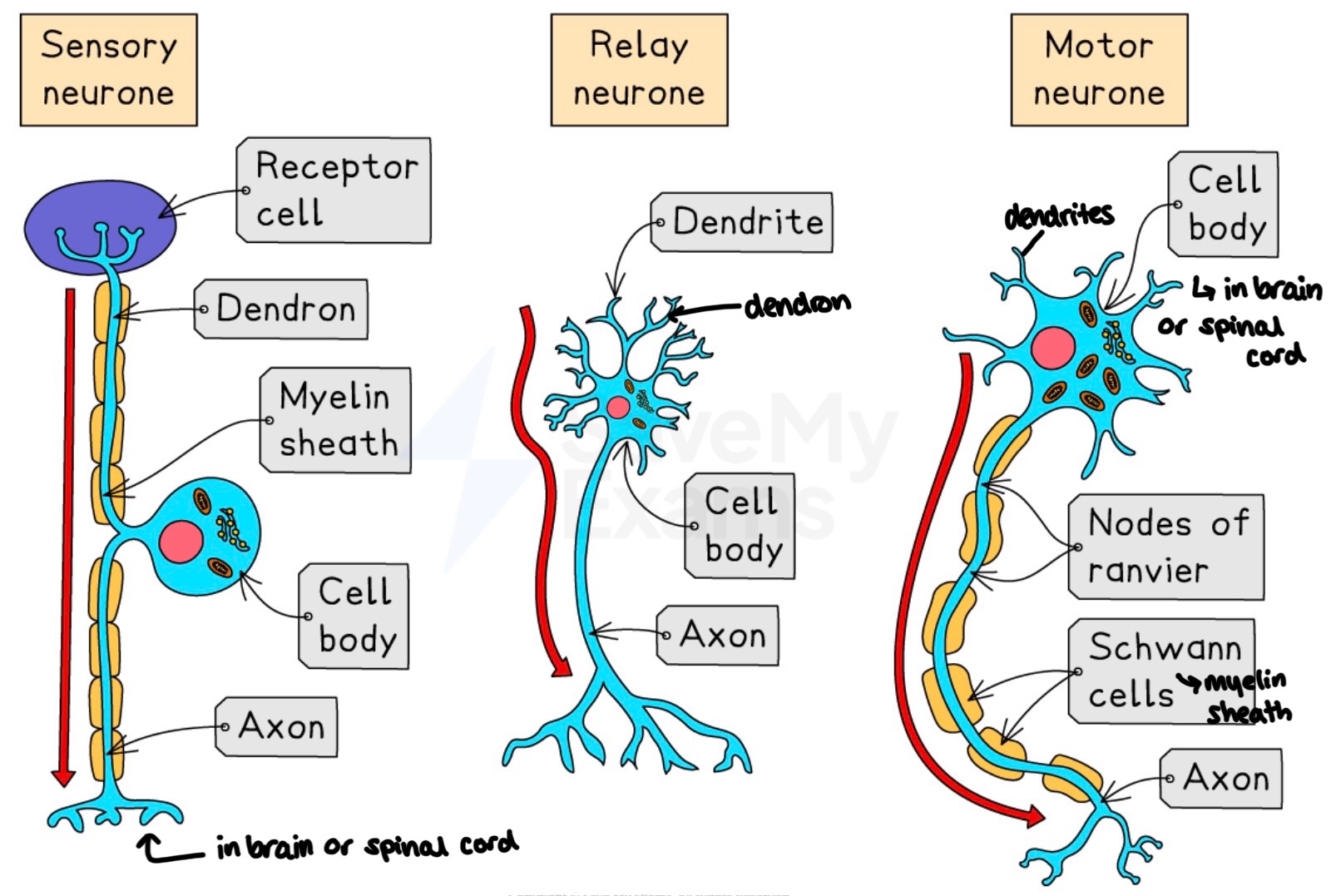
sensory, relay and motor neurones comparison
cell body
contains nucleus
carries genetic code for production of neurotransmitters
dense group of ribosomes and ER
NISSL granules
site of protein synthesis to make neurotransmitter
sensory neuron cell bodies in dorsal root ganglia
motor neuron cell bodies in spinal cord or brain
axon
transmit action potential away from the cell body
can be over 1 m in length
10 µm diameter
allows for rapid transmission of impulse
reduces the number of synapses required which are the area of slower transmission
contains axoplasm and usual cell organelles
dendrite
transmits action potential towards cell body
dendron
allow communication with other neurones
plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer with many protein ion channels
schwann cells
thin cells which have wrapped themselves around the neurone
have a higher than usual phospholipid content in their membranes and fewer ion channels, increasing electrical insulation of the neurone
myelin sheath
the enclosing layer created by schwann cells
nodes of ranvier
regions of uninsulated membrane where ion movement occurs to create action potential
synaptic knobs
Point at which neurotransmitter is released from neurone to transfer the action potential to another neurone
motor end plate
Point at which neurotransmitter is released from neurone to transfer the action potential to a muscle
sensory neurone
cell body positioned in a ganglia just outside of the CNS
transmit nerve impulse from sensory receptor to the CNS.
at the CNS it may sign up with a relay or motor nuerone
motor neurone
transmit nerve impulses from the CNS to an effect (muscle or a gland)
cell body in the CNS
relay neurone
connect sensory and motor neurones
totally within the CNS
myelinated neurones
covered by myelin sheaths
happens when schwann cells wrapped around neurone creating myelin sheath
schwann cell plasma membranes have a higher than usual phospholipid content with few ion channels, therefore iron movement can only occur at the nodes of ravier
this electrically insulate the neurone
what are sensory receptors
Specialised cells
Can detect changes in our surroundings [stimulus]
Initiate a nerve impulse.
Are transducers.
Are specific to a stimulus
what are transducers
a cell that converts on store of energy to another
stimulus converts to nerve impulse → electrical energy
receptors and the energy changes they detect
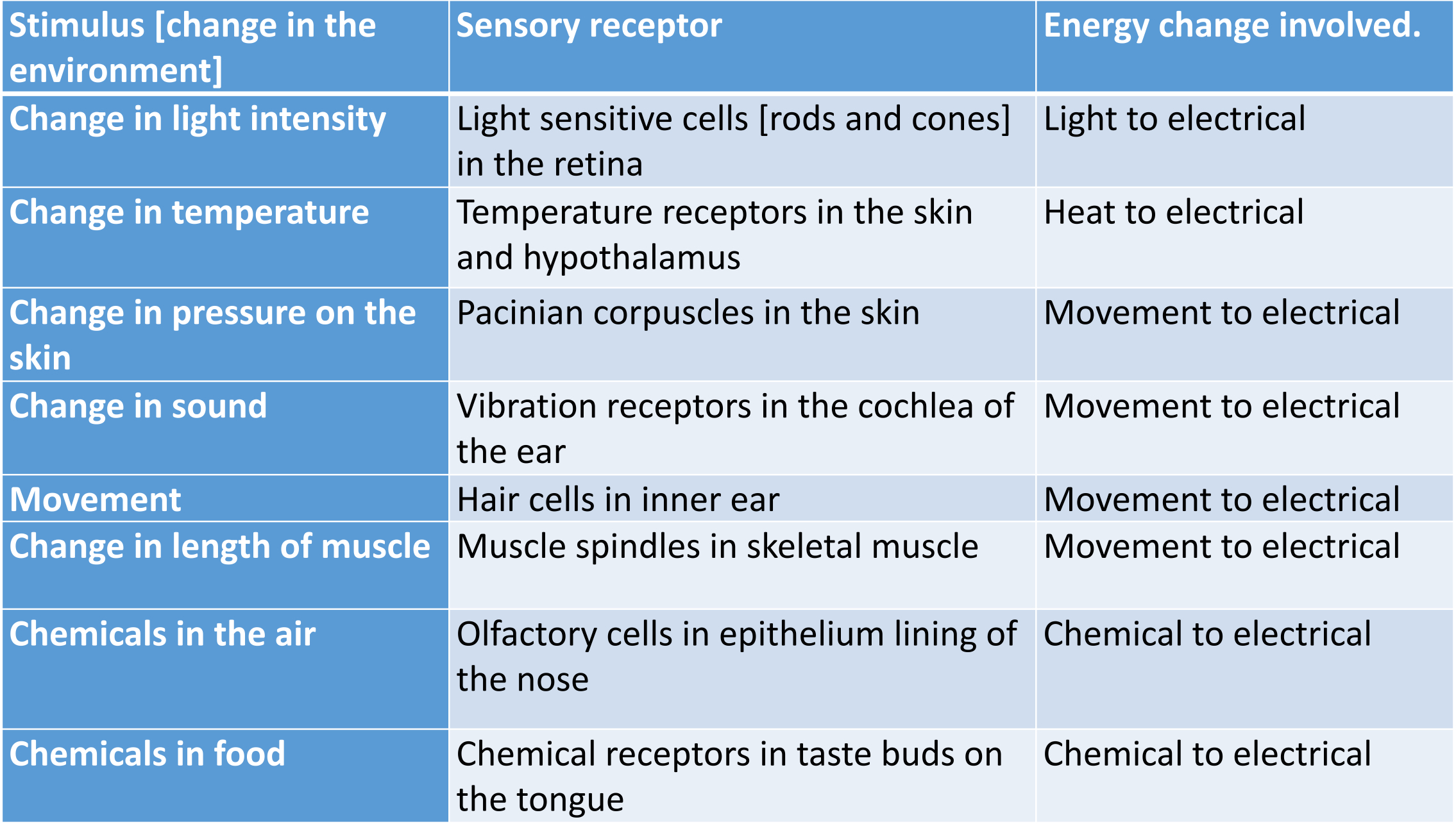
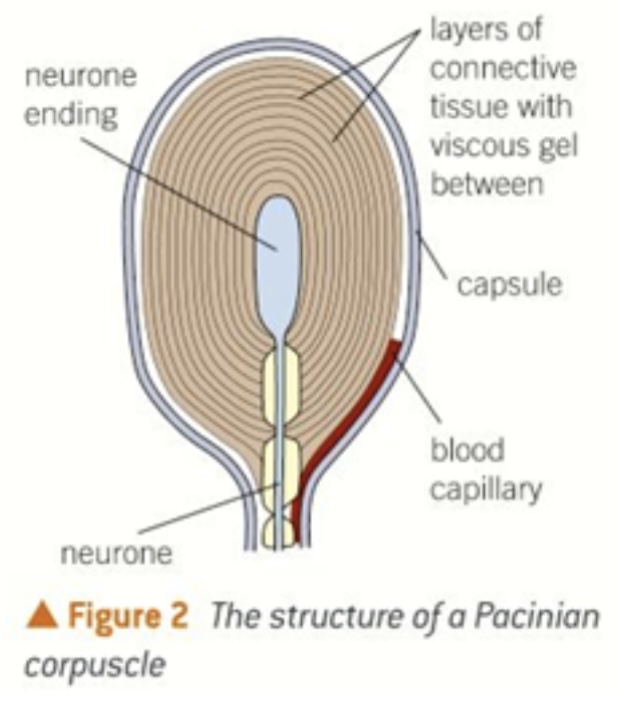
pacinian corpuscle
detects pressure changes on skin
changes deform the layers of connective tissue
pushes against the nerve ending
initiates a nerve impulse.
is sensitive to changes in pressure, so if the pressure becomes constant it will stop initiating nerve impulses
explains why you stop feeling clothes soon after you put them on
polarised
membrane which has a potential difference across it, this is the resting potential.
created by moving Na + and K +
depolarised
loss of polarisation across the membrane
Na + entering cell making inside less negative
resting potential
potential difference across the membrane while the neurone is at rest
approximately -70 MV
action potential
depolarisation of the cell membrane
fleeting reversal of resting potential
approximately +40 MV
hyperpolarisation
potential difference overshoots slightly and becomes more negative than resting potential
approximately -80 mV
repolarisation
time after an action potential has passed when it is impossible to stimulate the cell membrane because NA + voltage voltage channels will not reopen
ensures that action potentials move in one direction and keeps each impulse separate
threshold potential
approximately -50 mV
if depolarisation of the membrane does not reach this value then an action potential is not generated
resting potential (explanation and diagram)
at rest:
neurone membrane kept polarised
some sodium/potassium gated some open.
there are more open K + channels so K + can move back at its concentration gradient
resting potential is due to the Na+/K+ pumps in the membrane
membrane more permeable to K + (Na+ can’t move across) therefore higher concentration of anions inside the cell
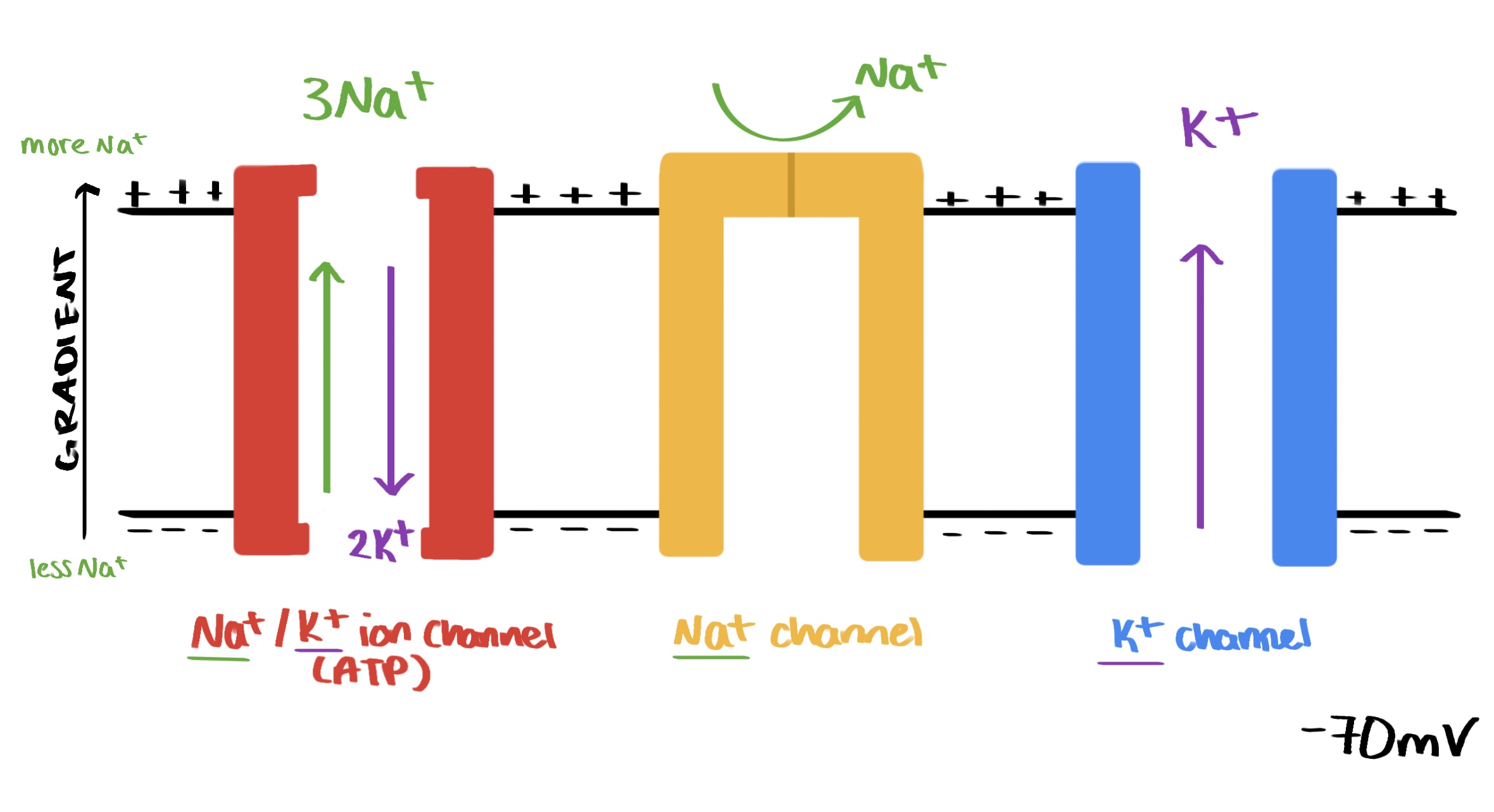
role of sodium potassium ion pump in maintaining resting potential
for every three Na+ pumped out, two K+ are pumped in, maintaining the more negative charge inside the membrane
concentration gradient created so K + diffuses out
role of ion leakage channels in maintaining resting potential
they are more open to K +, so it can move back into the cell, maintaining the electrochemical gradient and the resting potential
why does inhibiting respiration/metabolic poison prevent resting potential
inhibits ATP production (due to no respiration)
ATP required for Na+/K+ pumps to function so resting potential can’t develop
instead there is an equilibrium on either side of the membrane
how is action potential generated in a pacinian corpuscle
when pressure is applied, stretch mediated Na+ channels open and allow Na+ to enter.
if enough enters this will depolarise the membrane.
if the initial depolarisation passes the threshold potential (~50 mV) and action potential will occur
membrane begins to depolarise, causing Na+ voltage gated channels to open
causes more depolarisation, so more Na+ voltage gated channels open (positive feedback)
inside is now positive compared with the outside – action potential has been created
once depolarised to ~+40 mV the Na+ voltage gated channels shut and K + voltage gated channels open (K + diffuses out of neurone causing repolarisation)
when repolarisation has occurred, K + voltage channels stay open too long – causing hyperpolarisation, and K + channels shut
resting potential is re-established by the action of the Na+/K+ pump
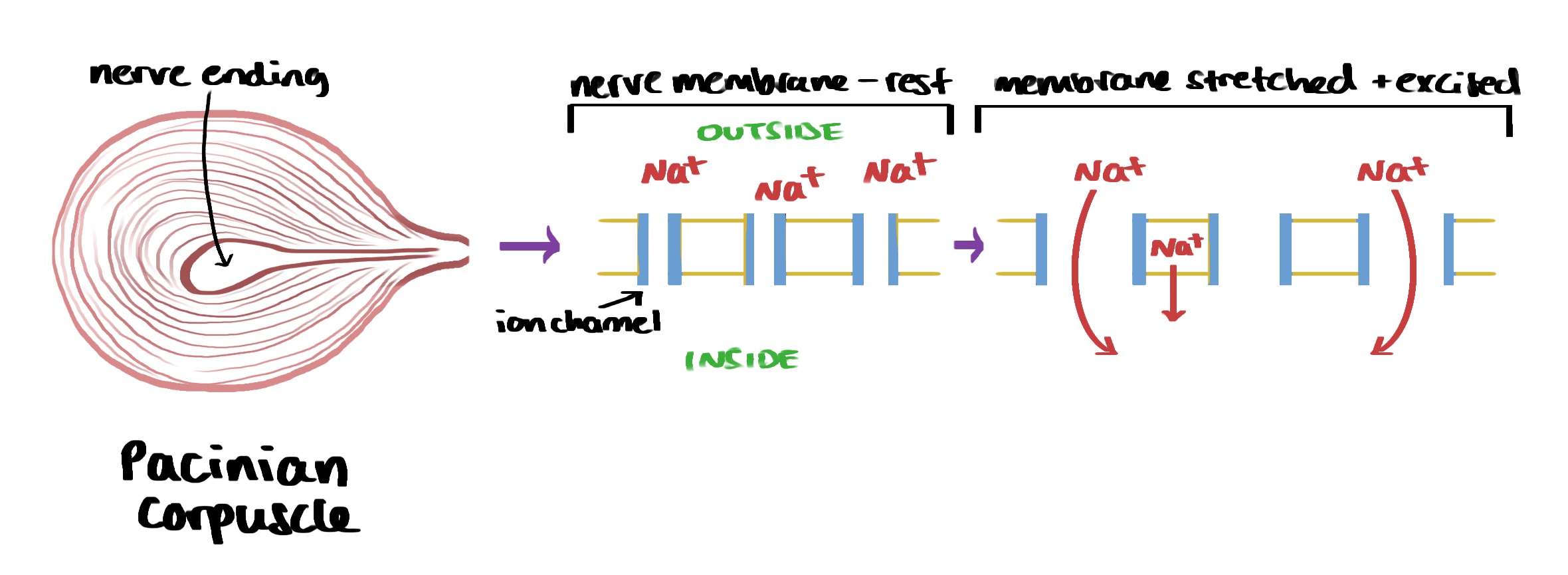
what happens during depolarisation?
threshold potential of around -50 mV is reached and voltage gated Na+ ion channels open
Na+ rapidly diffuses in, causing the potential difference to raise to +40 mV
inside of cell is now more positive than the outside
what happens during repolarisation
voltage gated K+ channels open and Na+ channels close
K+ ions quickly diffuse out, repolarising membrane
restores resting potential, inside negative again
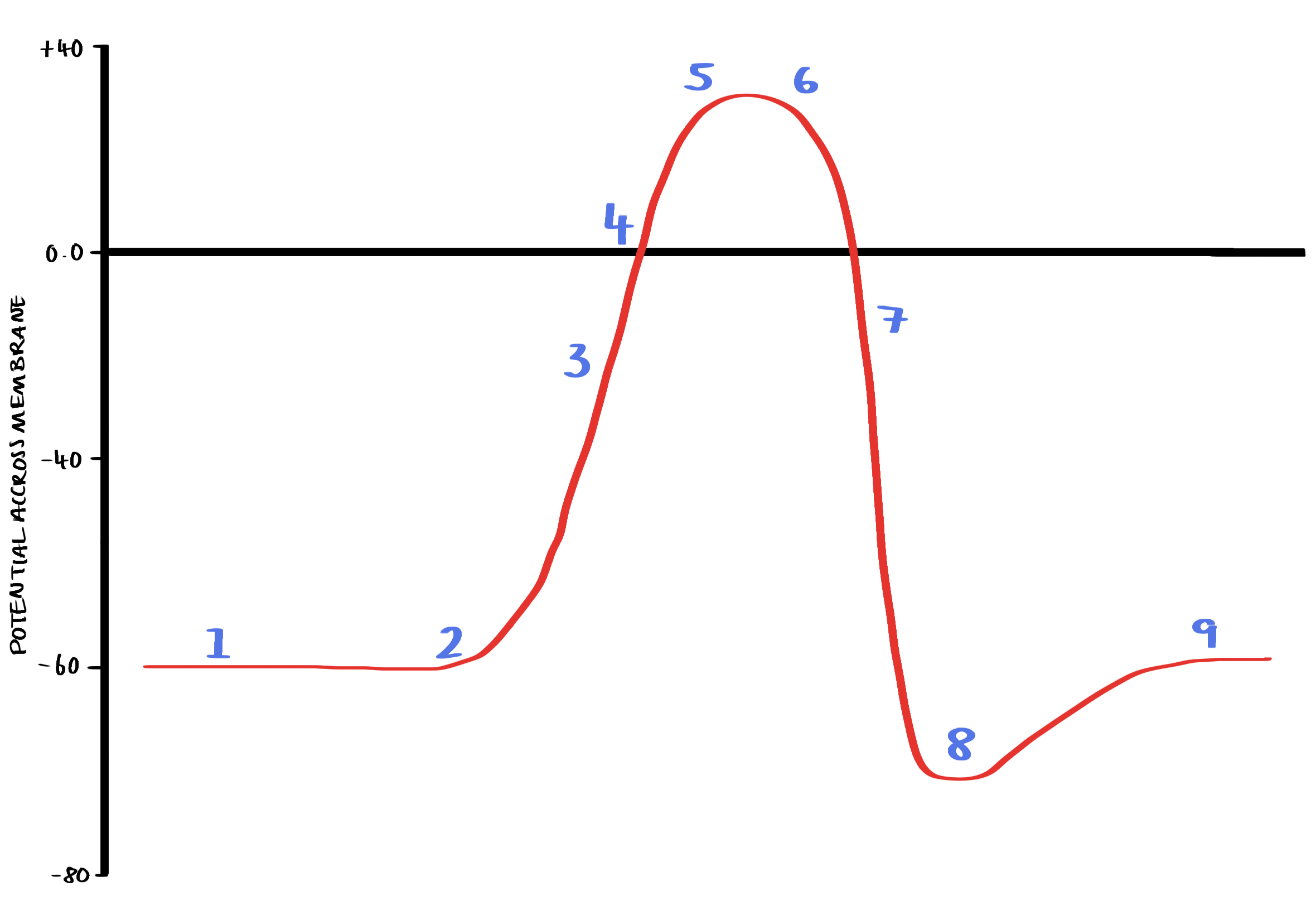
action potential generation (with graph)
The membrane starts in its resting state (polarised) and the inside of the cell is -70 MV compared with the outside.
A stimulus causes Na+ ion channels to open and some Na+ ions diffuse into the cell.
The membrane depolarises – it becomes less negative with respect to the outside and reaches the threshold value of -40 mV
Positive feedback occurs causing nearby voltage gated Na+ channels to open and many Na+ ions diffuse in, as more enter the cell becomes positively charged inside compared with the outside.
The potential difference across the membrane reaches +40 mV, inside of the cell is positive compared with the outside
Na+ ion channels close and K+ channels open
K+ ions diffuse out of the cell bringing the potential difference back to negative inside compared with the outside (repolarisation)
Potential difference overshoot slightly making the cell hyperpolarised.
The original potential difference is restored so that the cell returns to its resting state
propagation of action potential in a non-myelinated neurone
Na+ ions enter the neurone and a local flow of electrical current occurs due to Na+ ions diffusing sideways down the electrochemical gradient (local circuits)
With the arrival of some Na+ ions in the next part of the neurone, the membrane is depolarised.
This change in potential difference causes Na+ voltage gated channels in the next part of the membrane to open.
Na+ ions rapidly diffuse into the neurone, and the action potential has moved along.
Each region of the membrane stimulates the next region to undergo an action potential.
Behind the action potential re-polarisation occurs
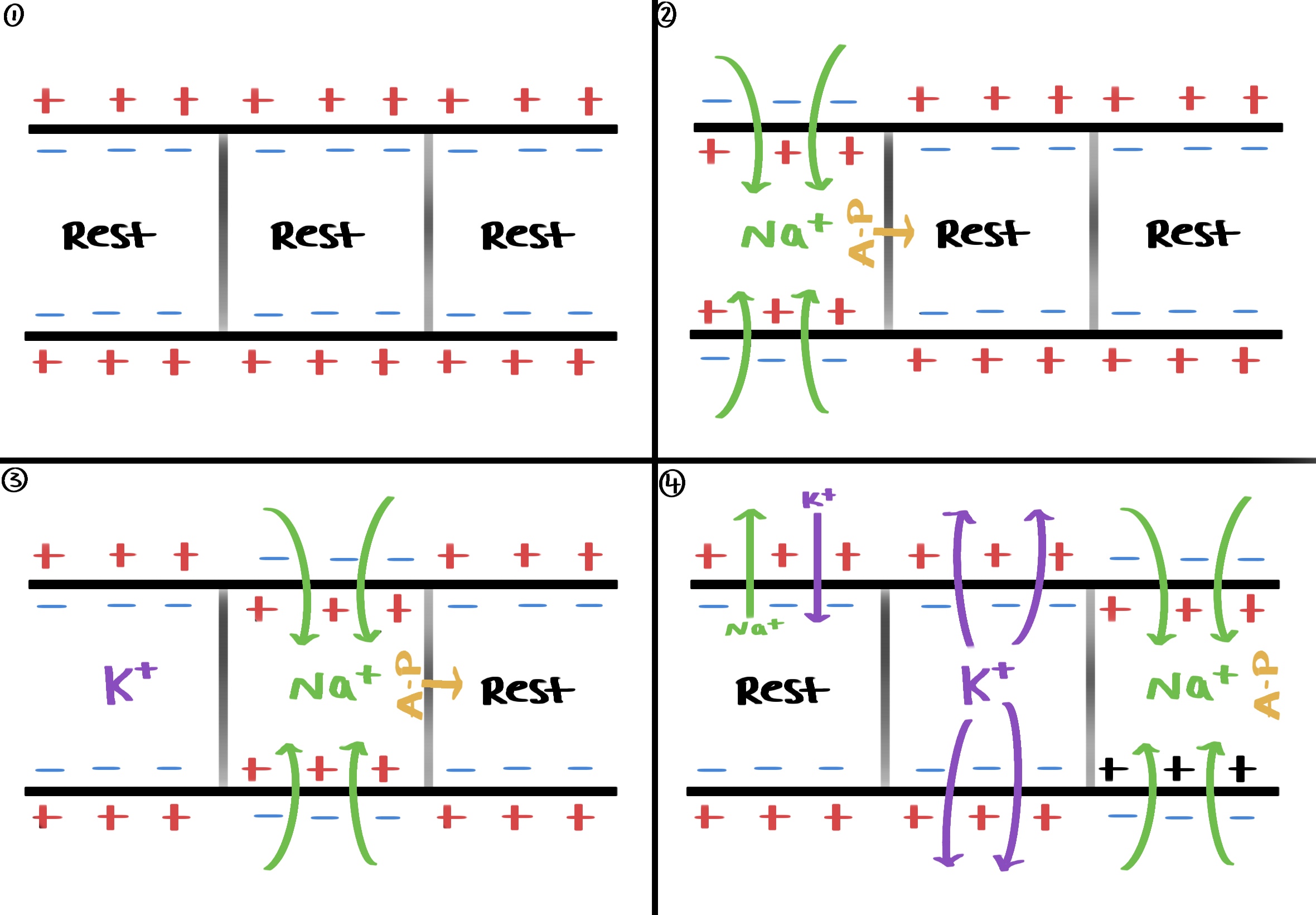
what is the refractory period
a short period of time when the neurone cannot be depolarised again
Na + voltage gated channels cannot reopen even with the raised potential difference.
ensures that the action potential go in one direction only (do not go backwards) so that they don’t combine
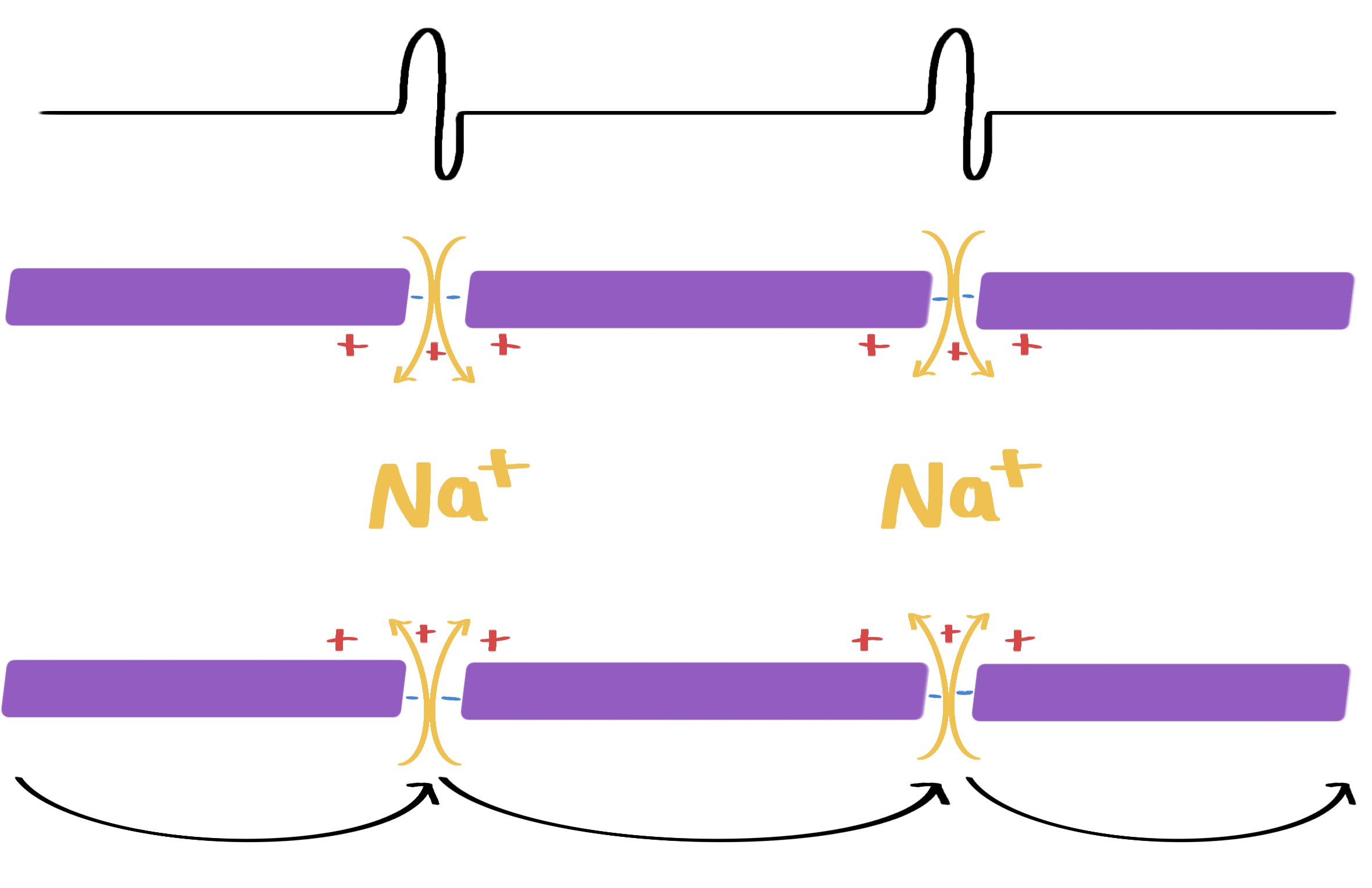
propagation of action potential in a myelinated neurone
schwann cells wrap tightly around the neurone
high phospholipid content with few ion channels.
so Na+ and K+ ions are not present along the outside of the neurone where the myelin sheath is
depolarisation of the membrane can only occur at the nodes of ranvier, and much longer local circuits are created
faster than conduction in non-myelinated neurones, uses less ATP
action potential then jumps between the nodes in a process called saltatory conduction
reduces the amount of repolarisation required
factors that will increase the speed of transmission of an action potential
myelination
temperature increase
more kinetic energy = faster ion diffusion
axon diameter
bigger = faster (less resistance due to less flow of the ions in the cytoplasm)
what is the all or nothing principle
the threshold value will always trigger a response
no matter the size of stimulus, the action potential is the same size
the size of the stimulus can be transmitted by the frequency of the action potentials
diagram of a cholinergic synapse
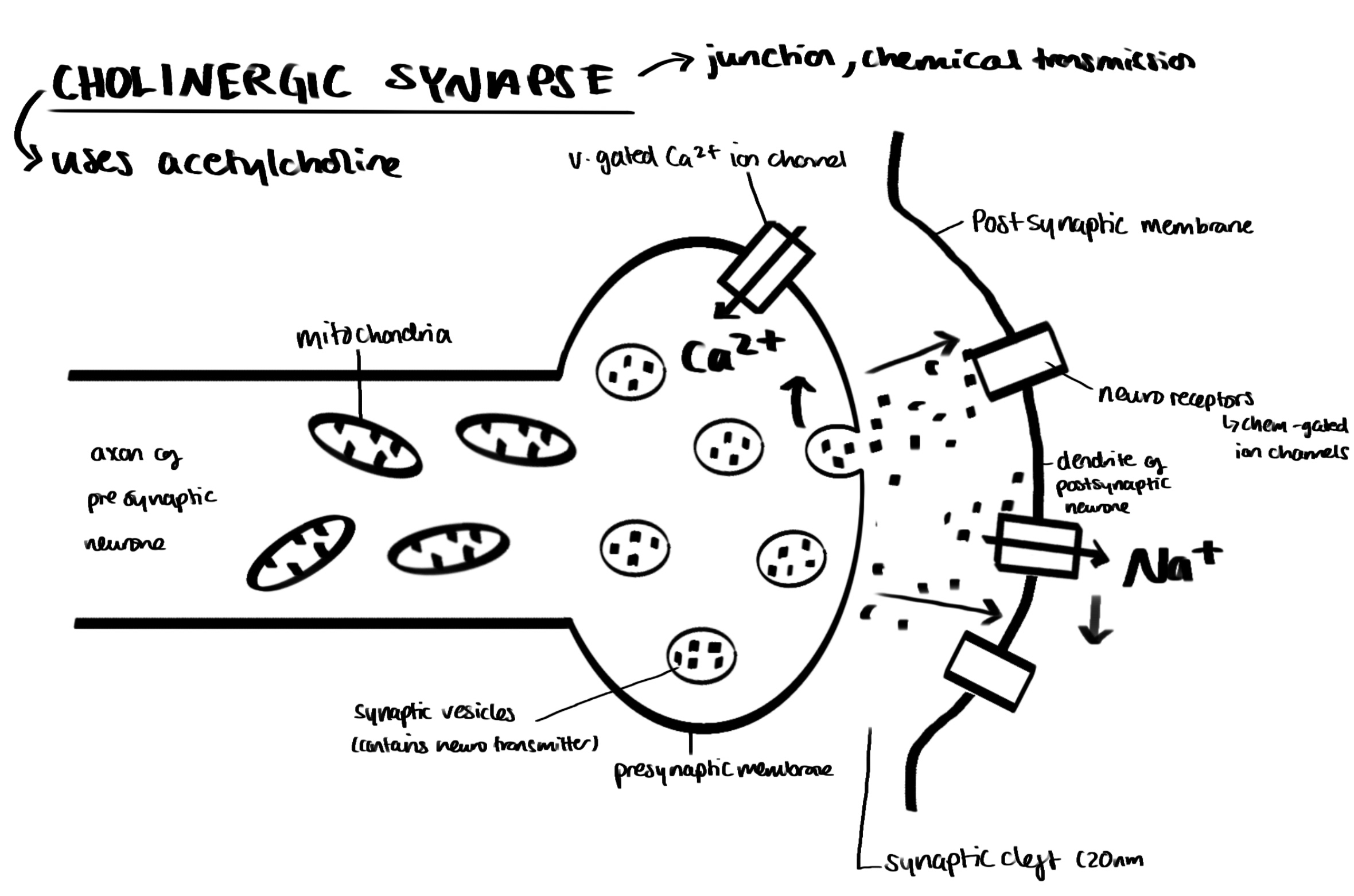
synaptic transmission (with diagram)
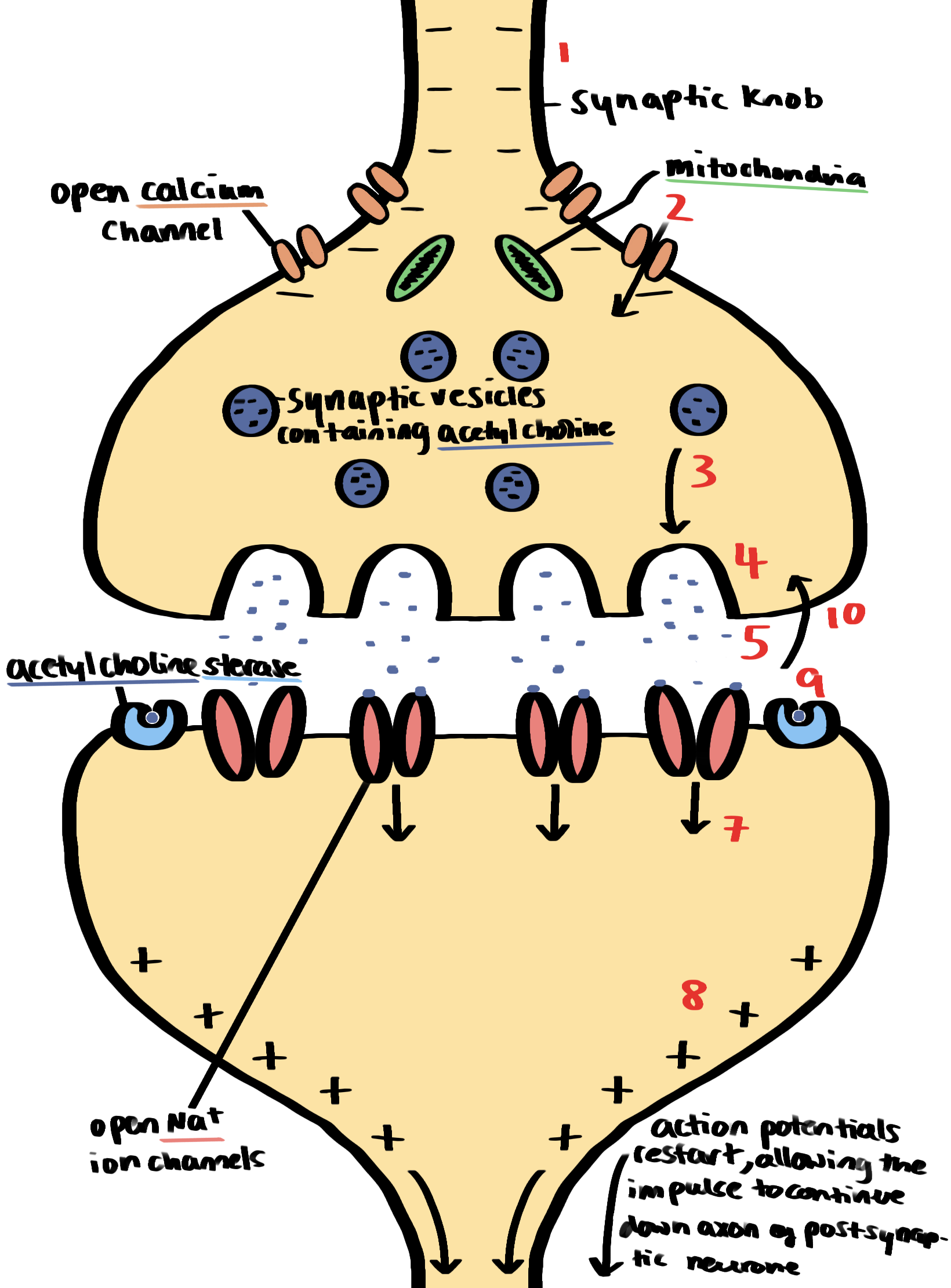
excitatory synapse
eg: acetylcholine
depolarises synaptic membrane
if threshold is reached then action potential is initiated
inhibitory synapse
eg: GABA
causes hyperpolarisation (involves K+ channels) of post synaptic membrane
makes it much less likely that the threshold will be reached
prevents action potential from starting
four roles of synapses
to ensure action potentials travel in one direction only (vesicles containing the neurotransmitter are only in the synaptic knob and receptor molecules for neurotransmitter are only in the postsynaptic membrane)
to allow impulses from one neurone to be spread to many neurones
to allow many neurones to feed into one synapse so only one neurone transmits the action potential any further
summation (when the effects of many generator potentials are added together)
spatial summation
when the combined effect of neurotransmitter released from several neurones reaches threshold level in the post synaptic neurone (neurotransmitters → several neurones)
temporal summation
when frequent impulses from one neurone result in enough neurotransmitter being released to reach threshold level in postsynaptic neurone (one neurone → neurotransmitters)
organisation of the nervous system diagram
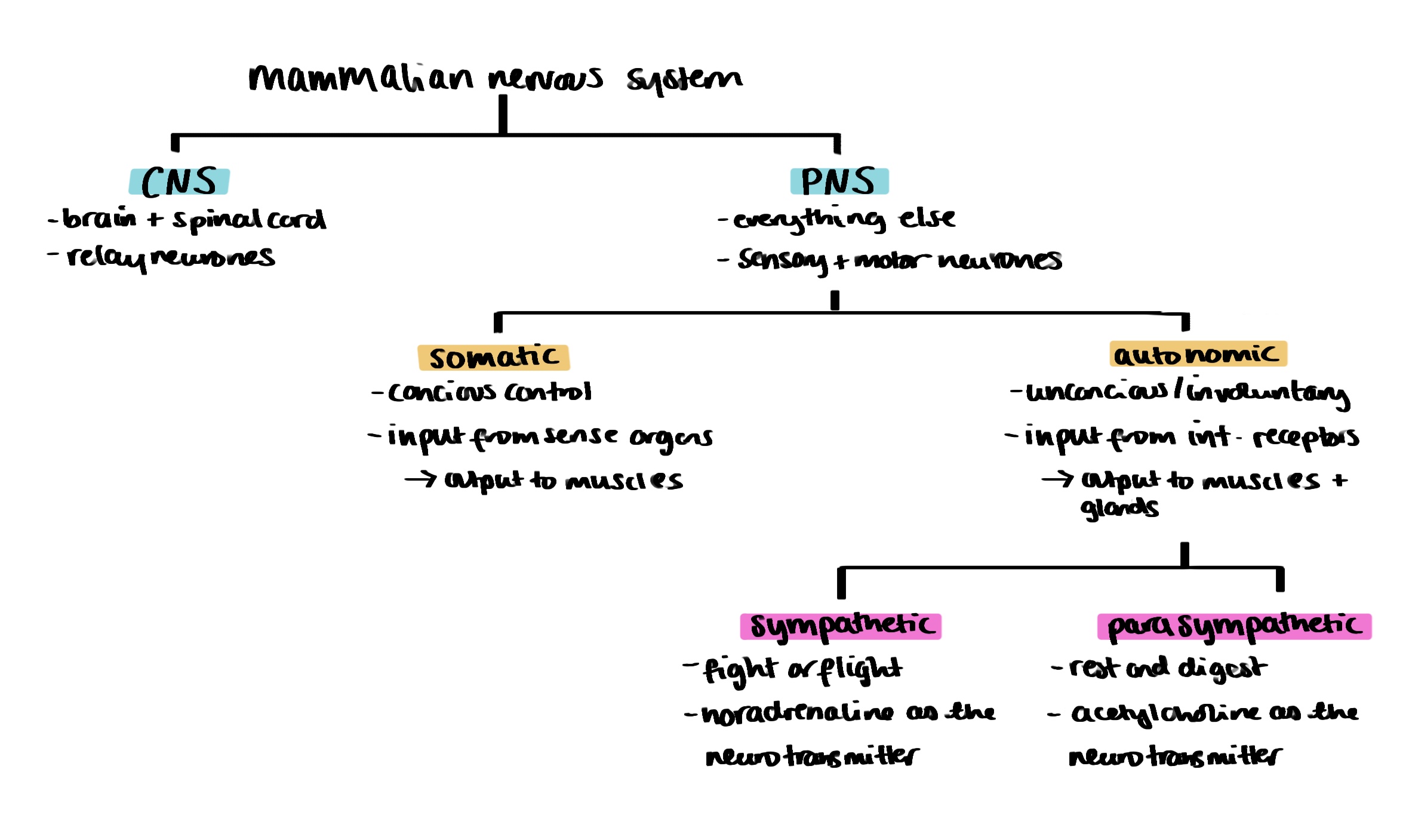
ganglion definition
a cluster of cell bodies (therefore has million of synapses)
structural differences between autonomic and somatic systems
somatic
one neurone
no ganglion
from CNS to skeletal muscle/effector
autonomic
two neurones (preganglionic and motor/postganglionic)
ganglion
from CNS to smooth muscle/effector
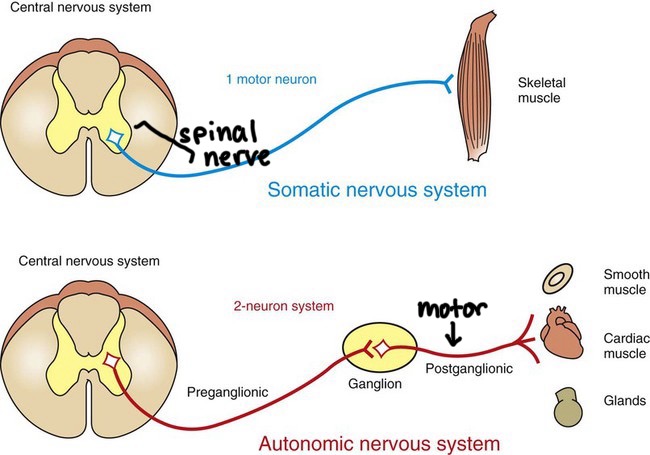
structural differences between parasympathetic and sympathetic systems
parasympathetic
long preganglionic fibre
short postganglionic fibre
ganglion in the effector (more specific)
acetylcholine released at synapse
acetylcholine released at junction with effector
few nerves leading out of CNS
sympathetic
short preganglionic fibre
long postganglionic fibre
ganglion in the adrenal medulla
acetylcholine released at synapse
noradreanline released at junction with effector
many nerves leading out of CNS
what is the difference between white and grey matter
white → myelin sheath
grey → no myelin sheath
mainly synapses and cell bodies
relay neurones make up most of the grey matter (mostly un myelinated)
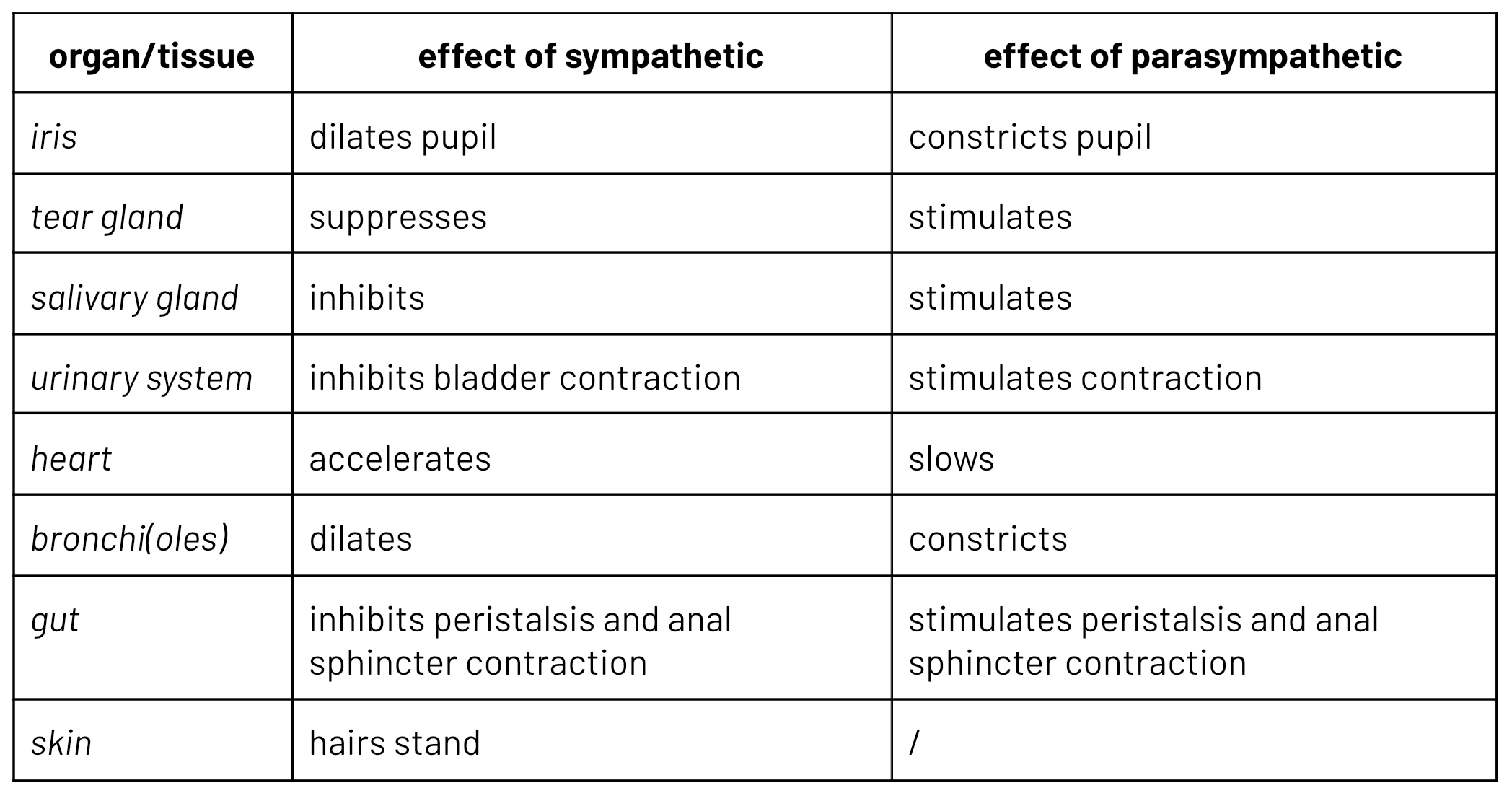
effect of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems on tissues
antagonistic actions
gross structure of the human brain (diagram)
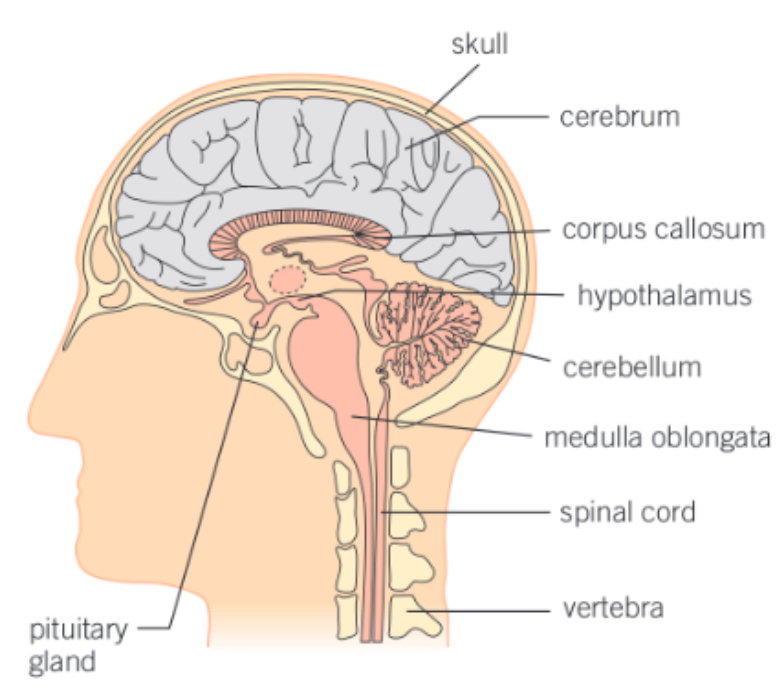
skull
bones called cranium
protect delicate nervous system
meninges
membranes, surround CNS
secrete cerebral spinal fluid
offer protection
cerebral spinal fluid
secreted by meninges
provides protection
absorbs mechanical shock
provides nutrients and oxygen to brain cells
ventricles
spaces within the brain filled with cerebral spinal fluid
corpus callosum
tissue
connects left and right cerebral hemispheres
allows the two sides to communicate
each controls opposite sides of the bosy
ascending and descending nerve tracts cross over in the medulla oblongata
grey matter and white matter in the brain
grey
outer 2mm
site of cell bodies and synapses
highly folded, communication happens here, lots of connections due to large surface area
white
connects different parts of the cortex together
cerebrum
controls higher brain function (conscious thought, conscious actions, emotion, reasoning, memory)
sensory organs → processes → initiates impulses
sensory areas
receives impulse/sensory information directly from receptors
association areas
compares sensory information receives with previous experiences and other association areas in order to interpret what the input means and judge an appropriate response
motor areas
initiate nerve impulses to voluntary muscles/effectors
cerebellum
controls unconscious functions (eg: posture, balance, non-voluntary movement)
contains over half the neurones in the brain
many of it’s processes require learning before becoming automatic
damage results in jerky/uncoordinated movement
medulla oblongata
used in automatic control (eg: heart, breathing rate)
autonomic control over non skeletal muscles
controls swallowing, vomiting, coughing
hypothalamus
regulatory centre for temperature and water balance
has two centres → sympathetic and parasympathetic
controls homeostatic mechanisms by negative feeback
temperature regulation, osmoregulation, produces hormones, feeding, sleeping, aggression
pituitary gland
stores and releases hormones that regulate many body functions
has two lobes
posterior pituitary → stores and releases hormones from hypothalamus
anterior pituitary → produces it’s own hormones, moved into the blood via releasing factors
basic reflex arc
receptor
sensory neurone
relay neurone
motor neurone
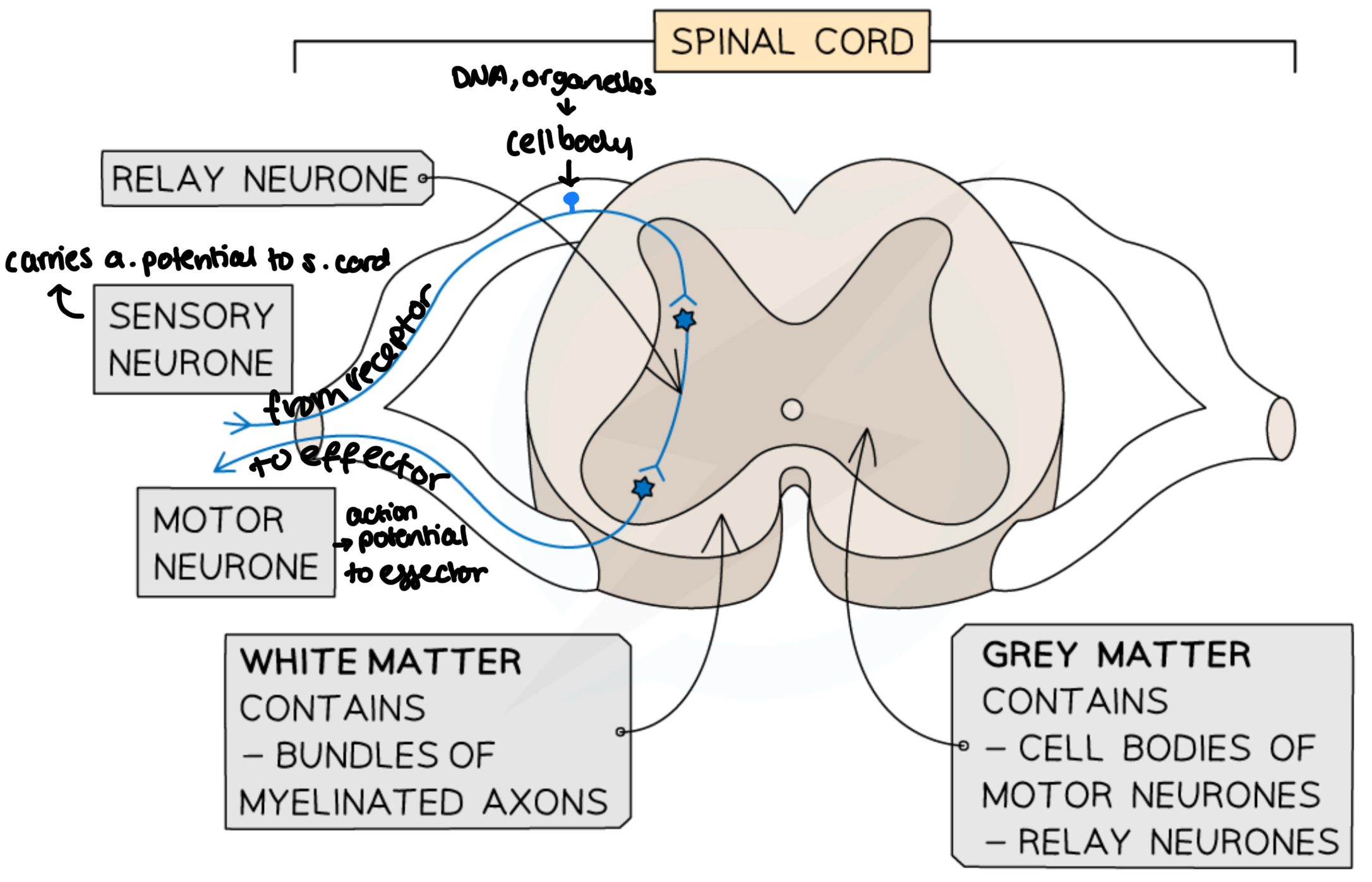
what is a reflex action?
response to changes in the environment, no brain processing to coordinate movement
short pathway/rapid
how do reflex actions increase survival?
immediate → removes from danger
innate → not learned, gives protection from birth
involuntary & invariable → same response every time, brain freed up for more complex decisions
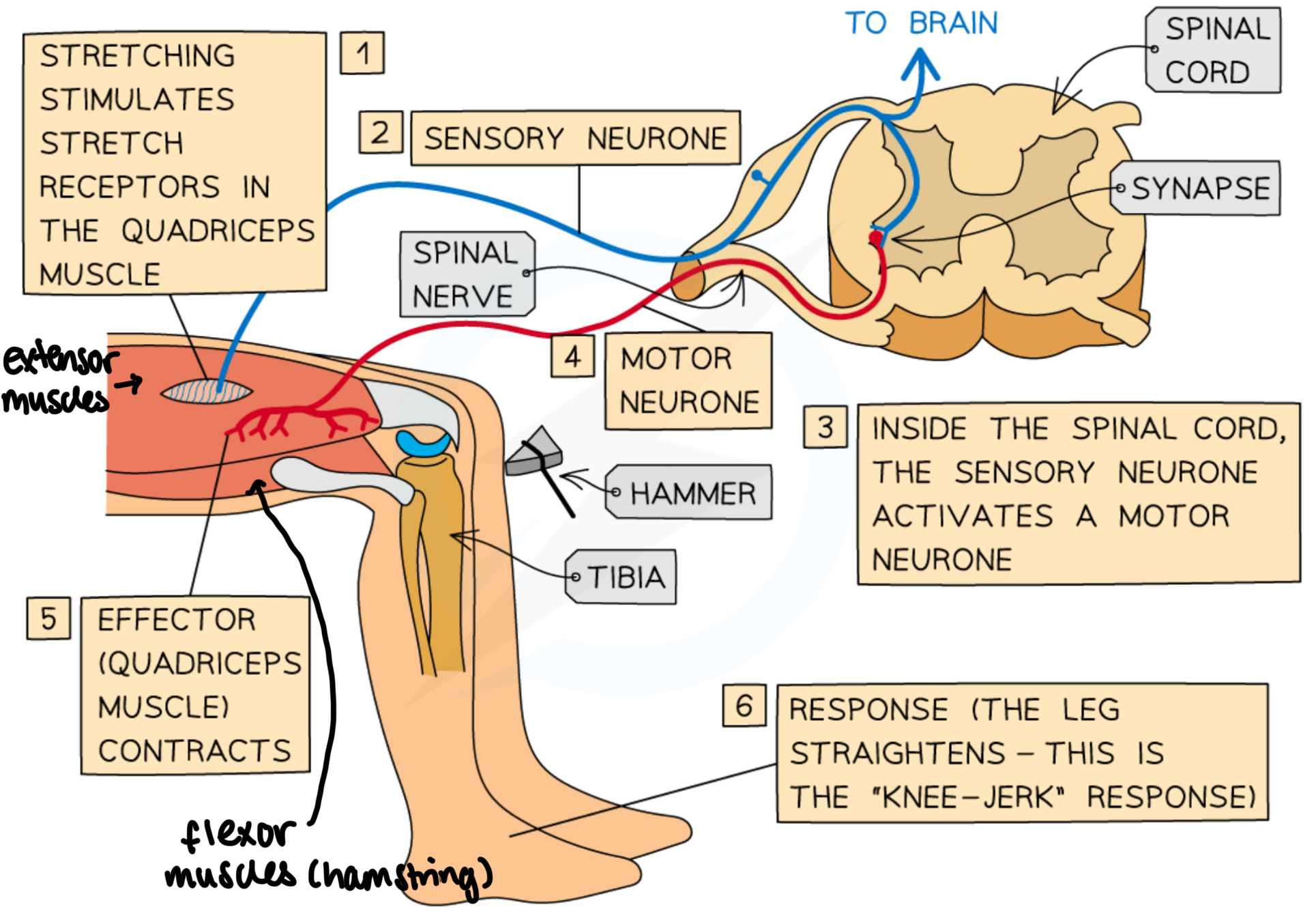
knee jerk reflex
used to help maintain posture/balance/help if you trip
consists of only two neurones (sensory & motor)
spinal reflex → neural circuit only goes up to spinal cord
stimulus starts reflex arc, causes extensor muscles on top of the thigh to contract
at the same time, a relay neurone inhibits the motor neurone of the flexor muscle, causing to to relax
contraction coordinated with relaxation of antagonistic flexor hamstring muscles, causing leg to kick
absence of reflex → can indicate nervous problems
overreaction → multiple oscillation can indicate cerebellar disease