random chemistry
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
alcohol (hydroxyl)
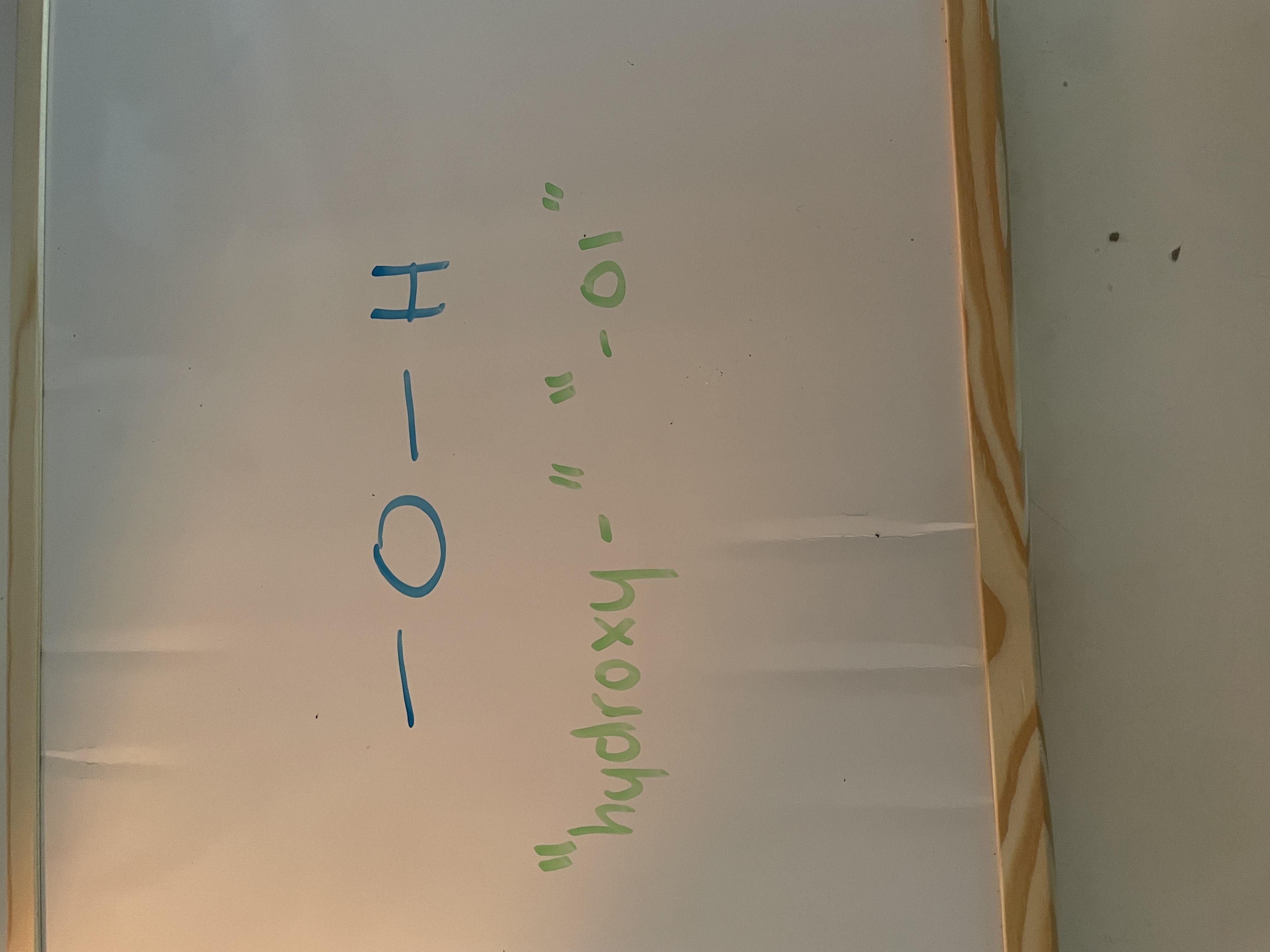
aldehyde (carbonyl)
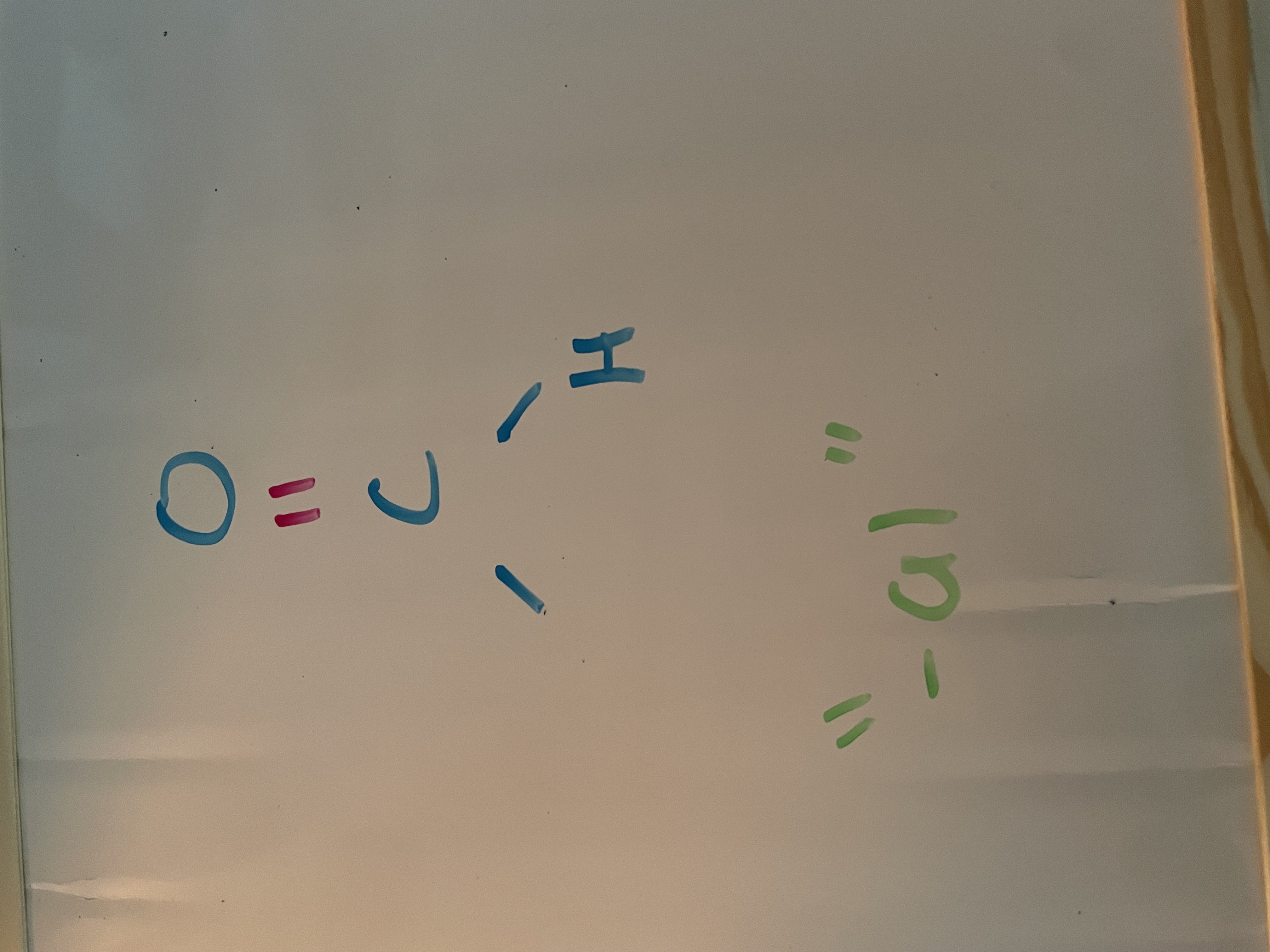
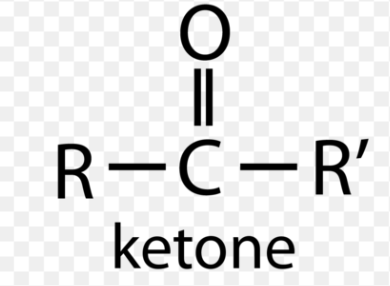
ketone (carbonyl)
carboxylic acid (carbonyl)
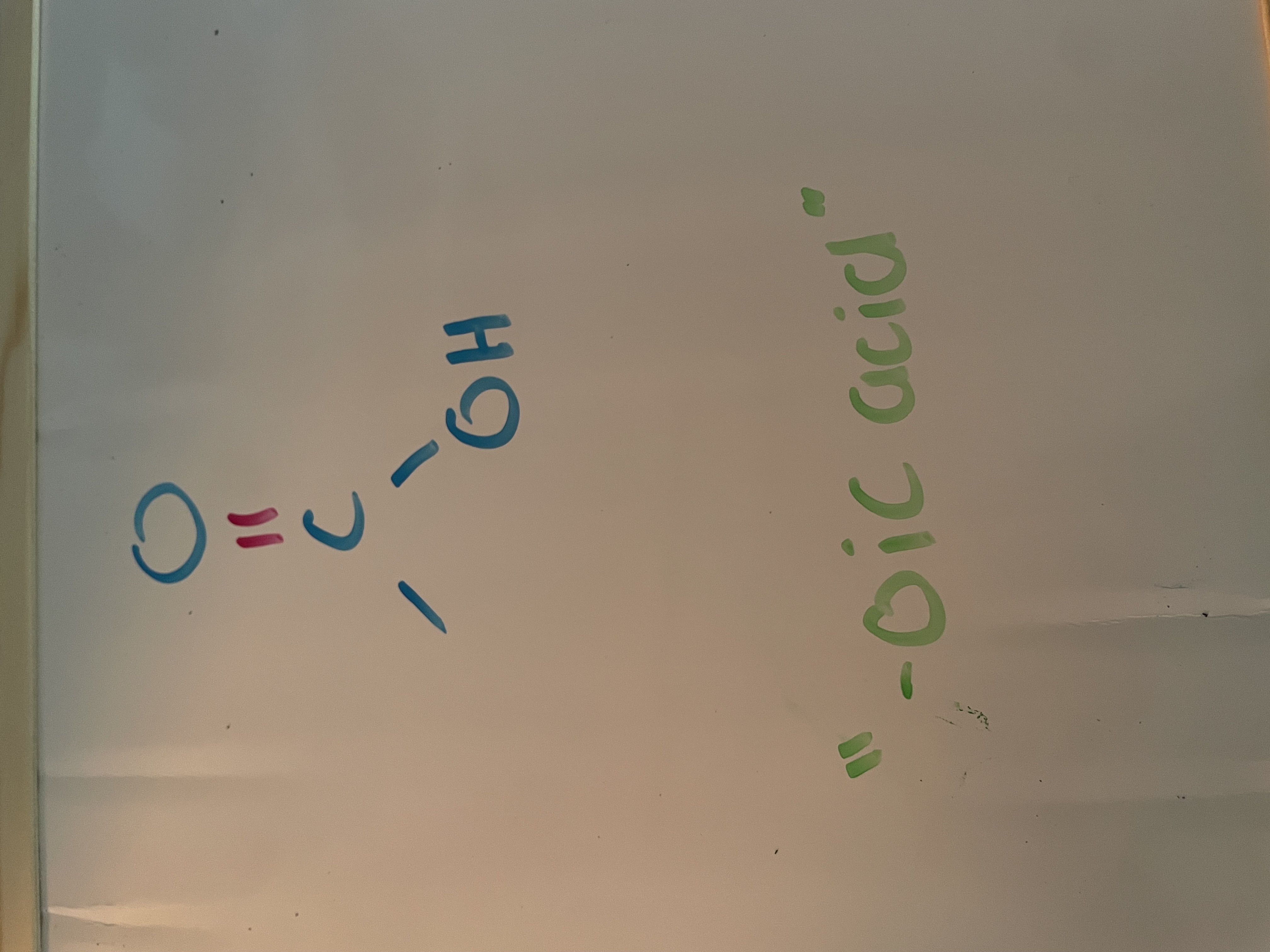
haloalkane (halogens)
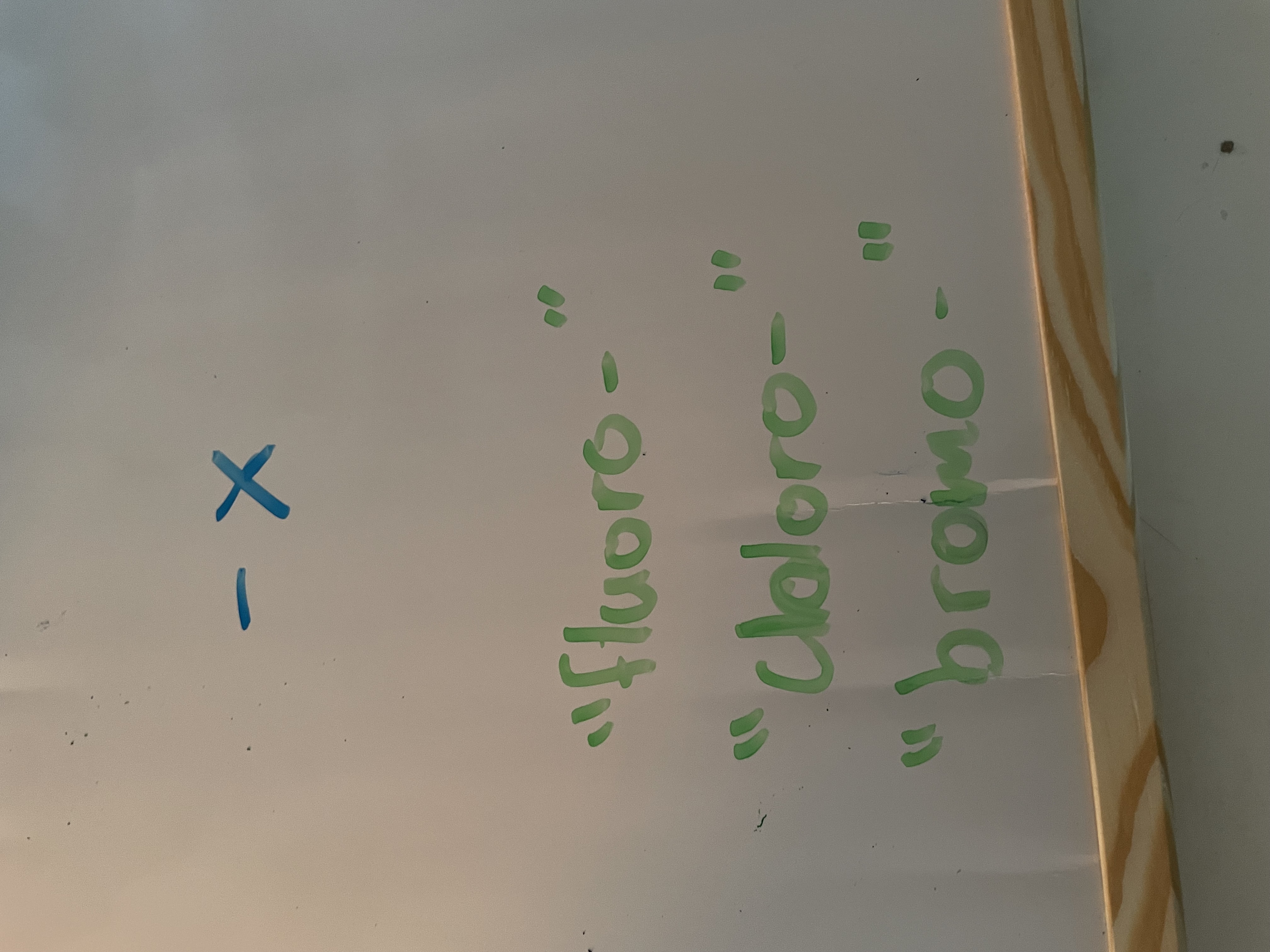
ester (carbonyl)
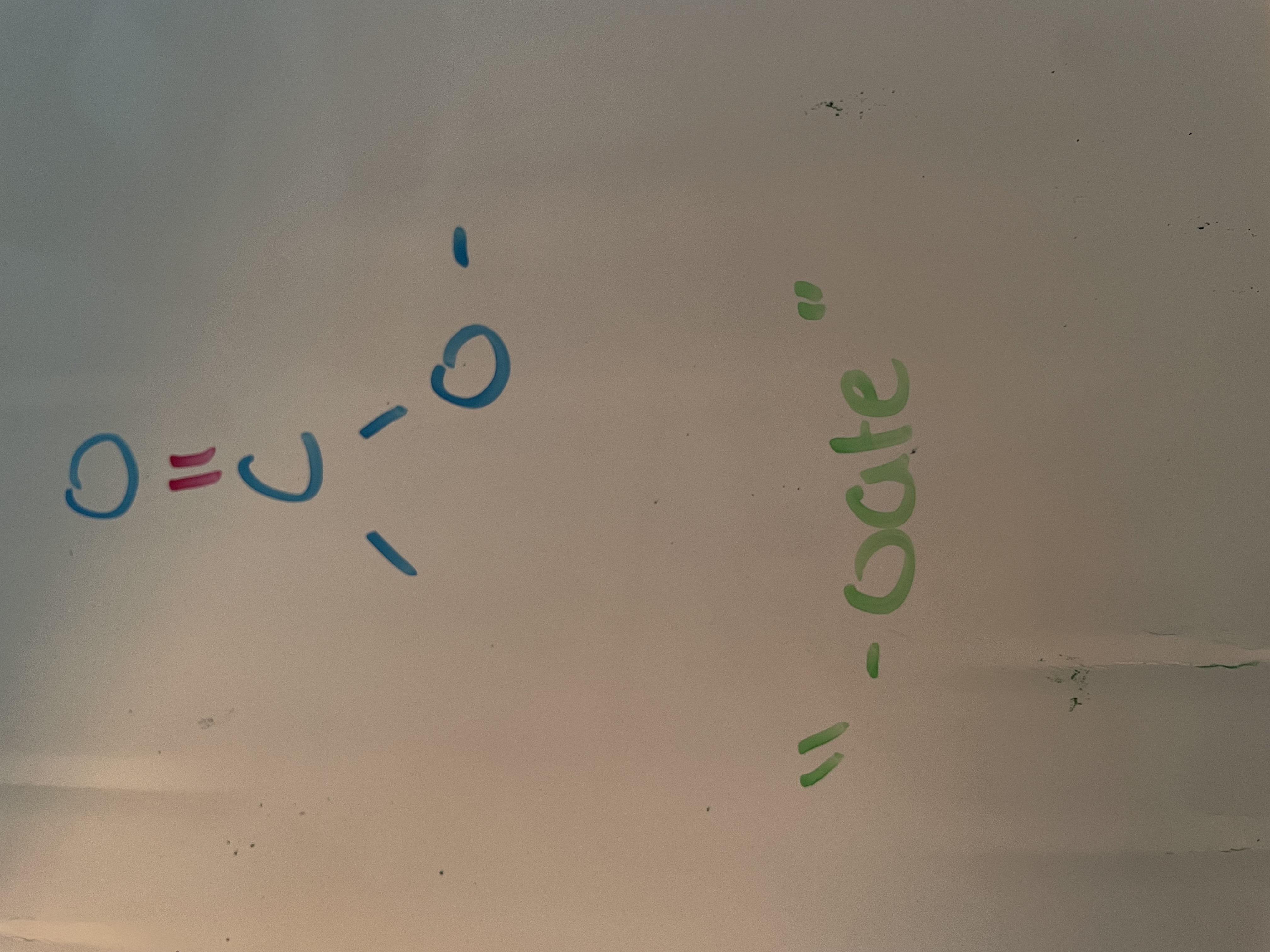
amines (amino)
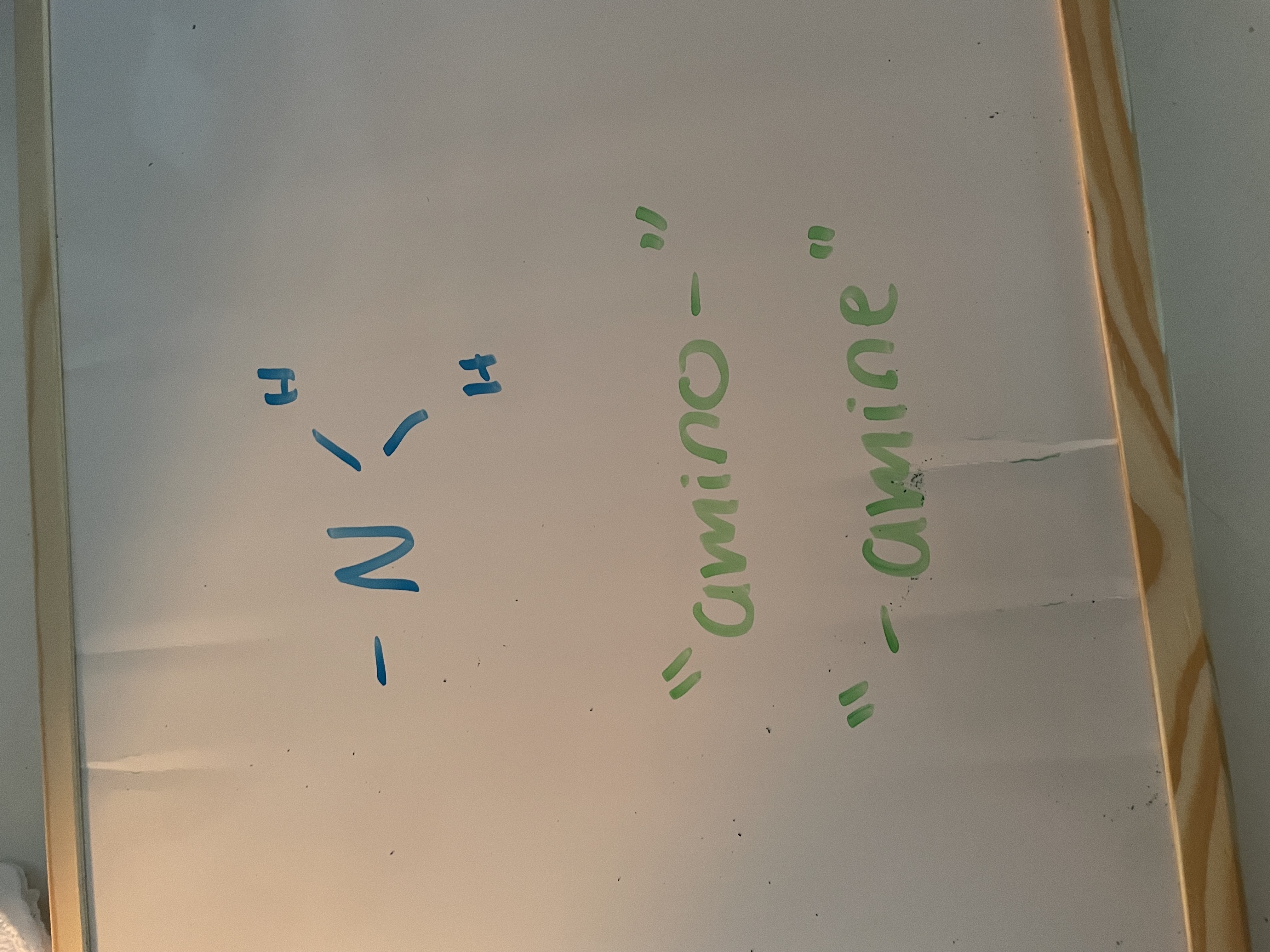
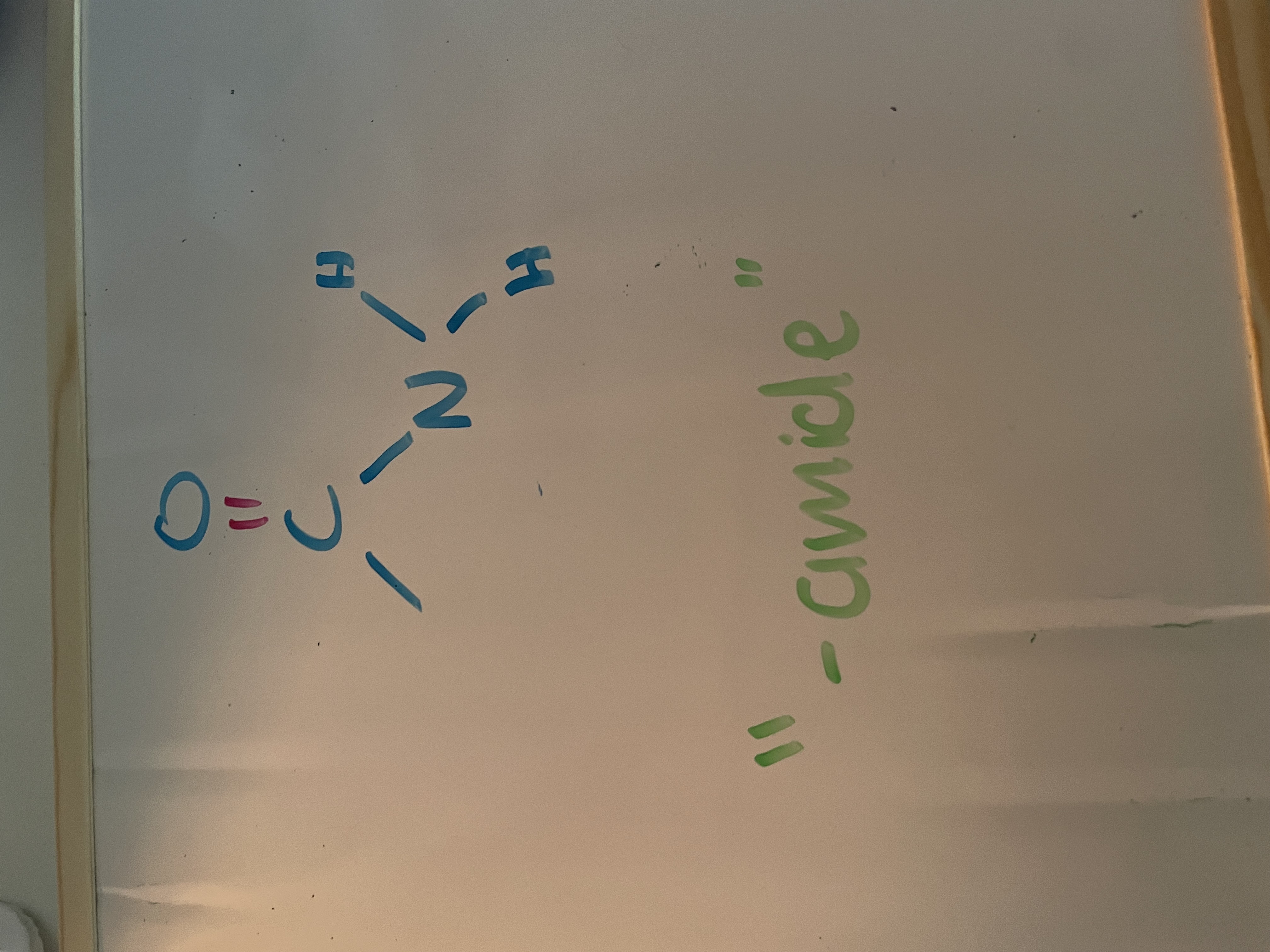
amides
nitriles
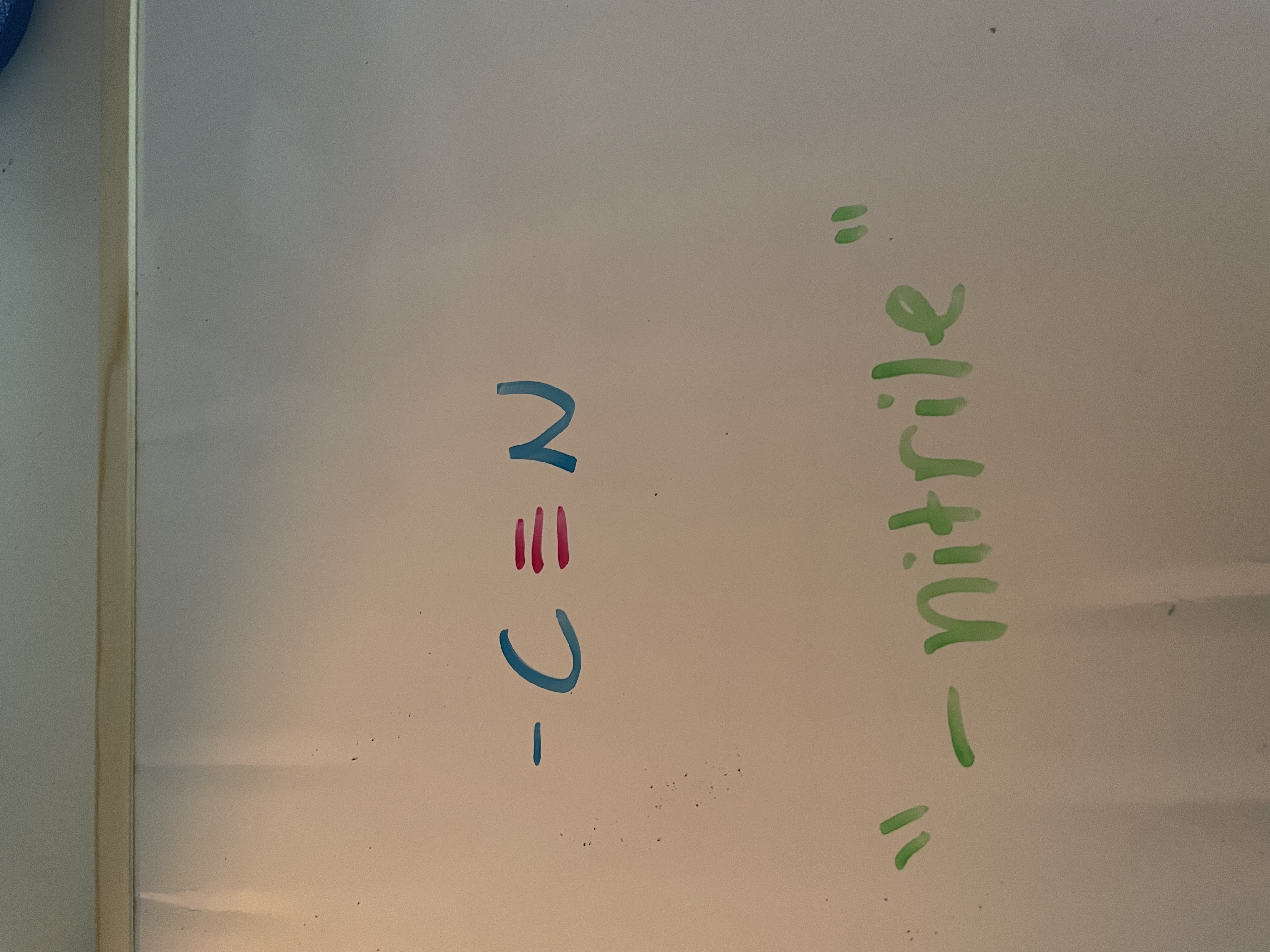
alkane
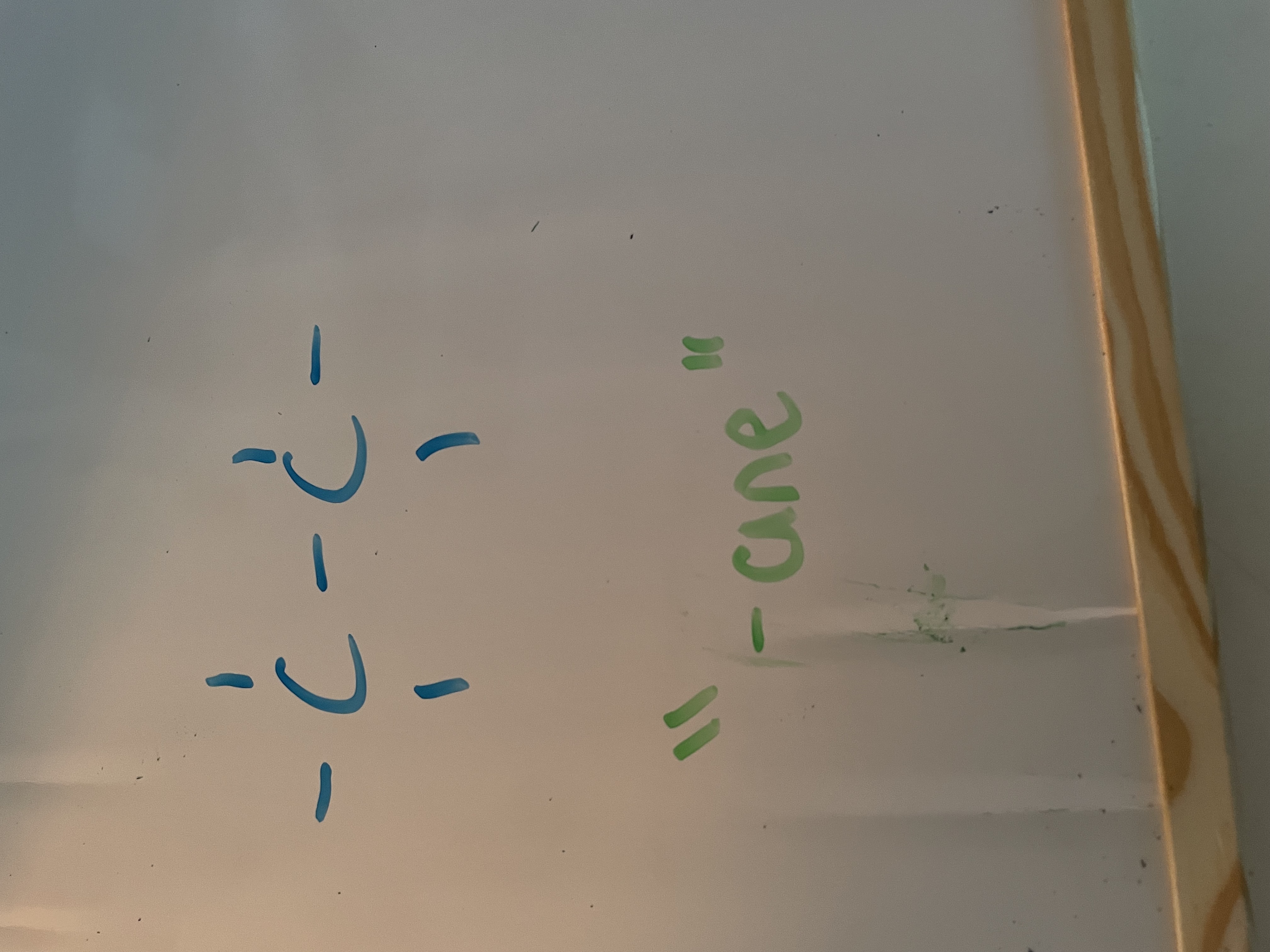
alkene
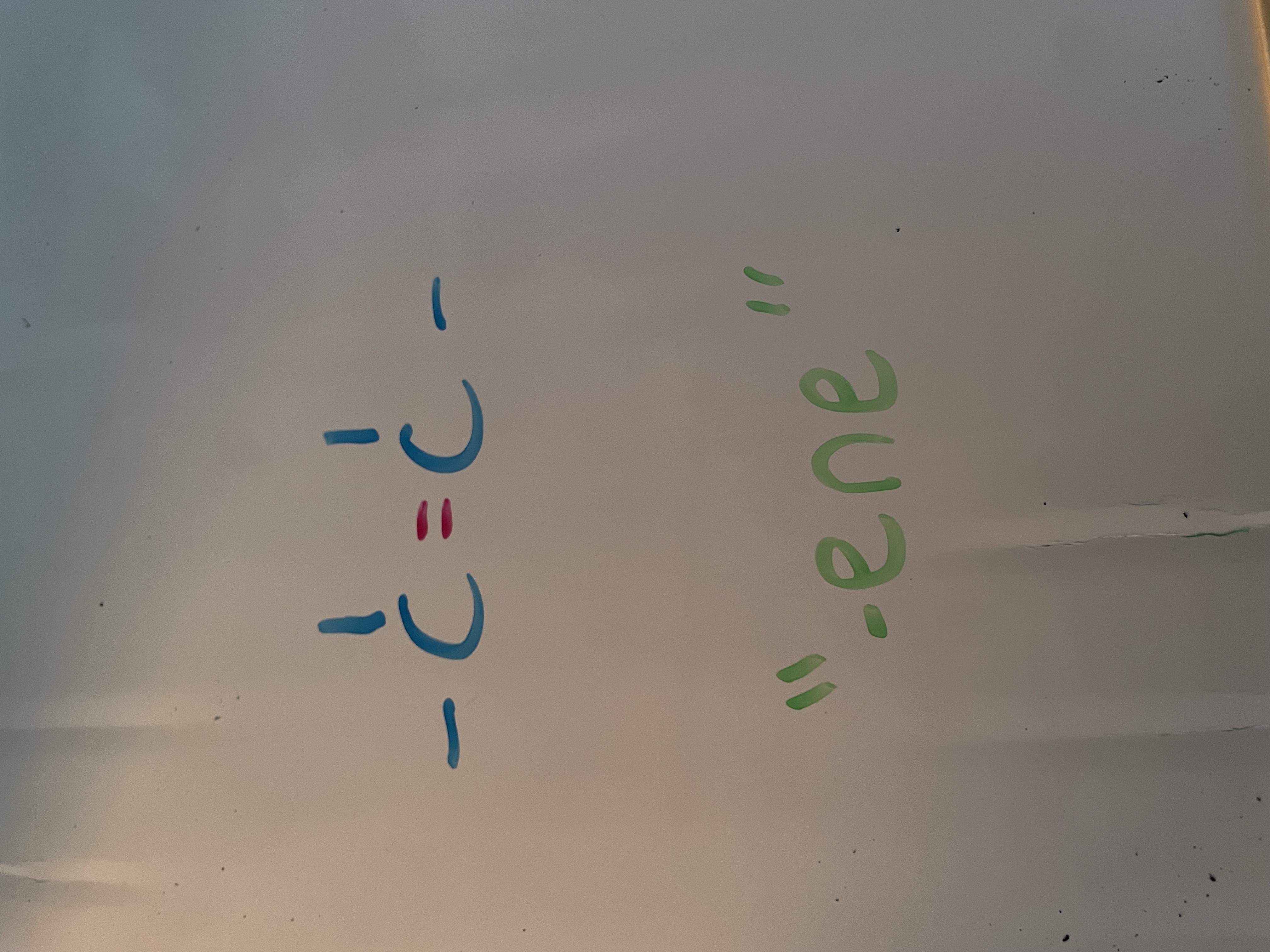
alkyne
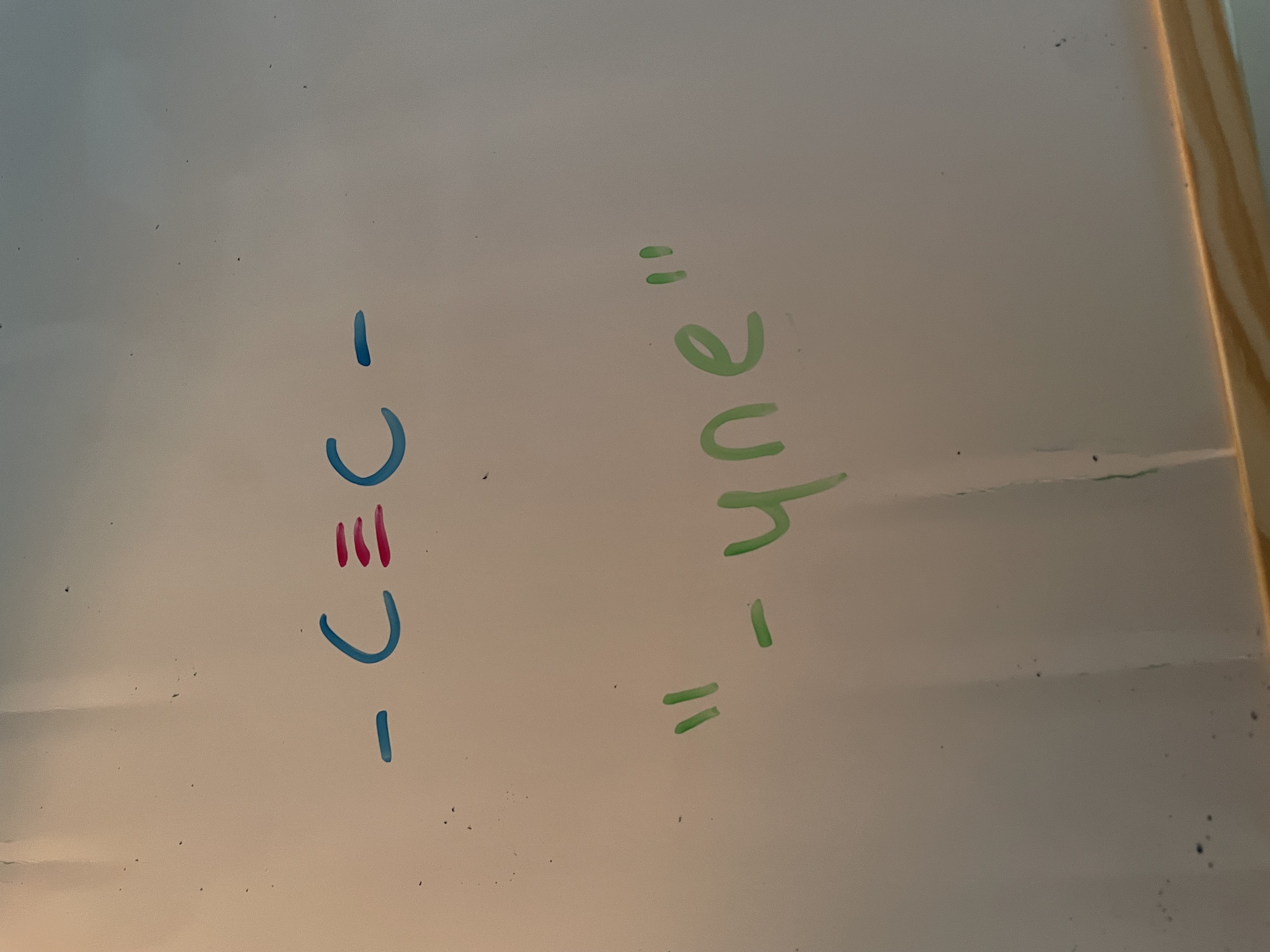
homologous series of hydroxyl
alcohol
homologous series for carbonyl
aldehyde, ketone, ester
homologous series for carboxyl
carboxylic acid
homologous series of halogen
haloalkane
addition
reactants combine to form larger molecule, breaking double bond
condensation
water forms
elimination
substituents are removed, adding double or triple bond
substitution
one functional group is replaced by another
oxidation and reduction
oxidation is loss electrons reduction is gain electrons
proteins and what they contain
polymers of amino acids containing amino + carboxyl group
what enzymes do
increase reaction rate
3 types of simple carbohydrates
monosaccharides (glucose, fructose), polysaccharide (small) and disaccharide
how are disaccharides formed
condensation
how is lactose formed
B glucose + B galactose
3 types of complex carbs
glycogen, cellulose, amylose
endothermic reaction
chemical reaction that absorbs heat
exothermic reaction
chemical reaction that releases heat
what happens when pressure is increased
shift to side with less moles
what happens when volume decreased
pressure is increased
what effect do catalyst have
none
In galvanic and electrolytic cell reduction is at…
cathode
In galvanic and electrolytic cell oxidation is at…
anode
3 points about galvanic cell
converts chemical to electrical energy using salt bridge
anode is negative and cathode is positive
spontaneous reaction (positive number)
3 points about electrolytic cells
converts electrical energy to chemical
anode is positive and cathode is negative
non- spontaneous reaction
4 parts of a titration set up
buret, titrant (known solution), analyte (unknown solution), stocpcock
if Kc is < 1
left equilibrium
if Kc > 1
right equilibrium
an acids conjugate base…
donated proton
a bases conjugate acid…
accepted a proton
If Ka (acid dissociation) is large…
lots of product and strong acid (same for Kb)
formula to find concentration
C = n/V
formula to find number of moles
n = n/MM
the rules for complex half equations

rules for oxidation numbers
