NURS 245 Ch. 45: Disorders of the Female Reproductive System
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
anatomy of the female reproductive system
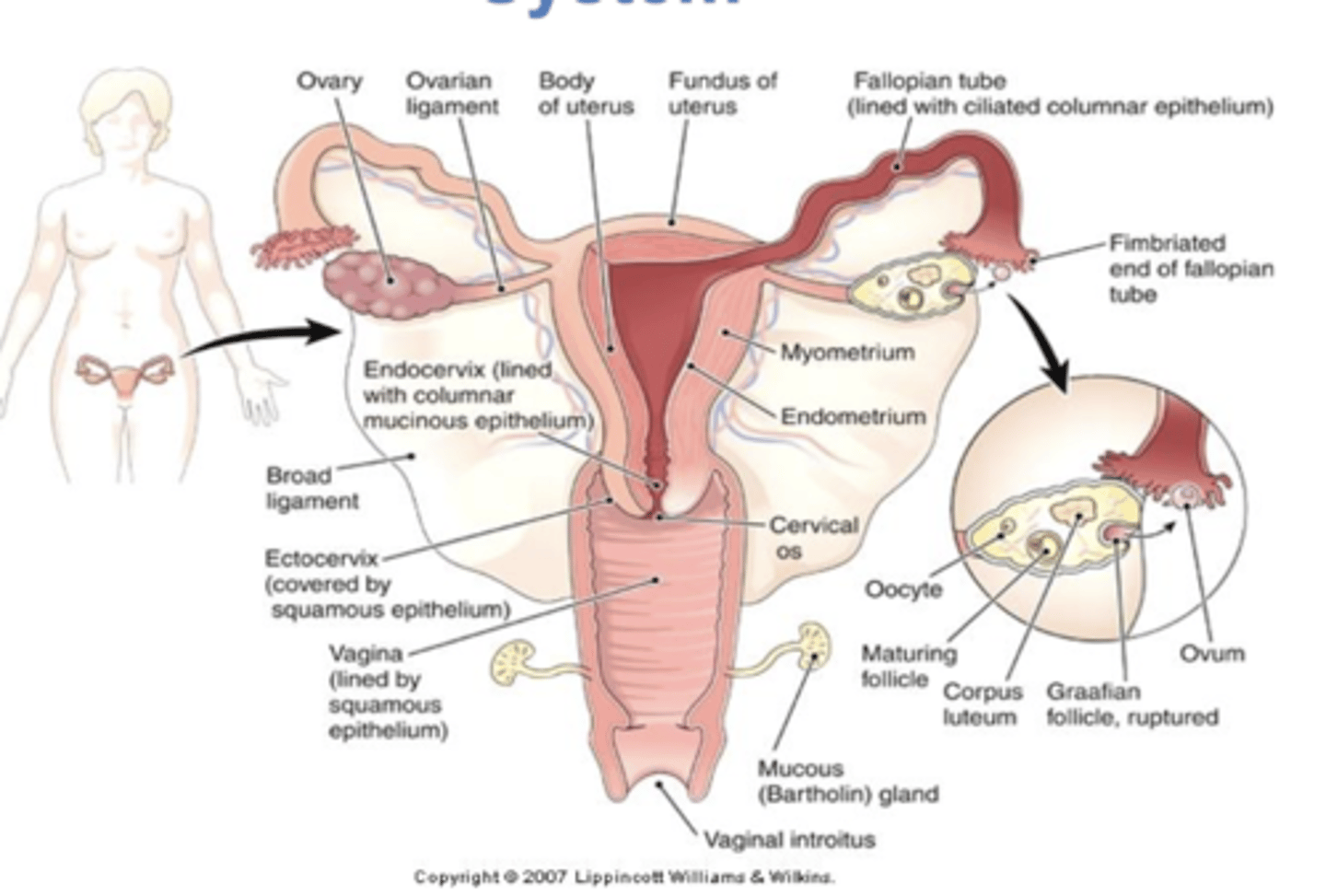
uterus
muscular organ within which fertilized ovum may implant and develop
cervix
opening into the uterus and neck of the uterus
external os - opening from vagina filled with thick mucus that prevents vaginal flora from ascending into the uterus
internal os
fallopian tubes (oviducts)
tubes from ovaries to uterus
ovaries
produce ova and estrogen and progesterone
progesterone
"pro gestation" - maintains pregnancy
important throughout cycle in all women. helps with smooth muscle relaxation, maintains endometrium and breast development. also increases body temperature
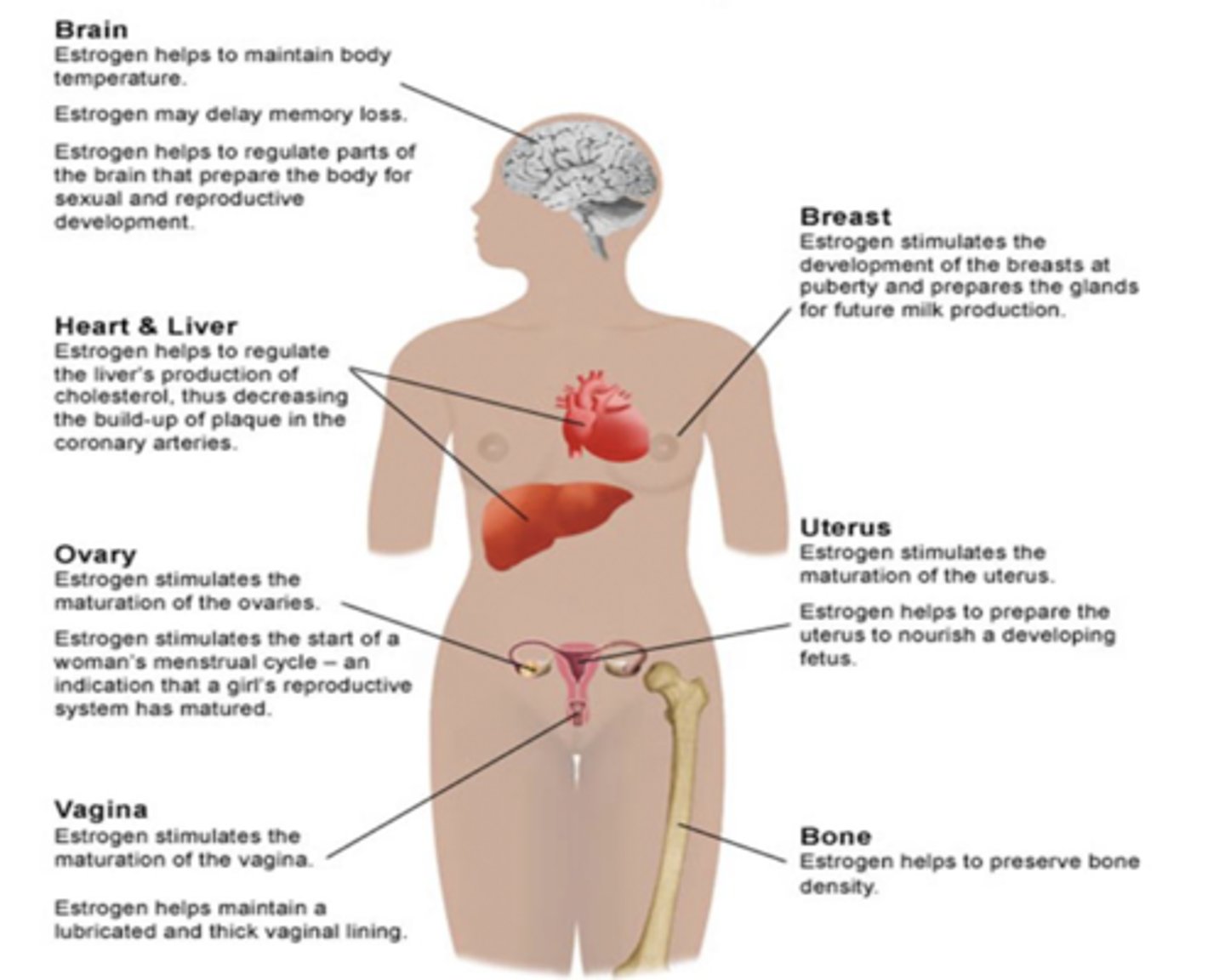
estrogen
helps maintain body temperature, delay memory loss, regulate cholesterol, maturation of ovaries, menstrual cycle start, maturation of the vagina, bone density, nourishing a fetus, development of breasts and glands for milk production
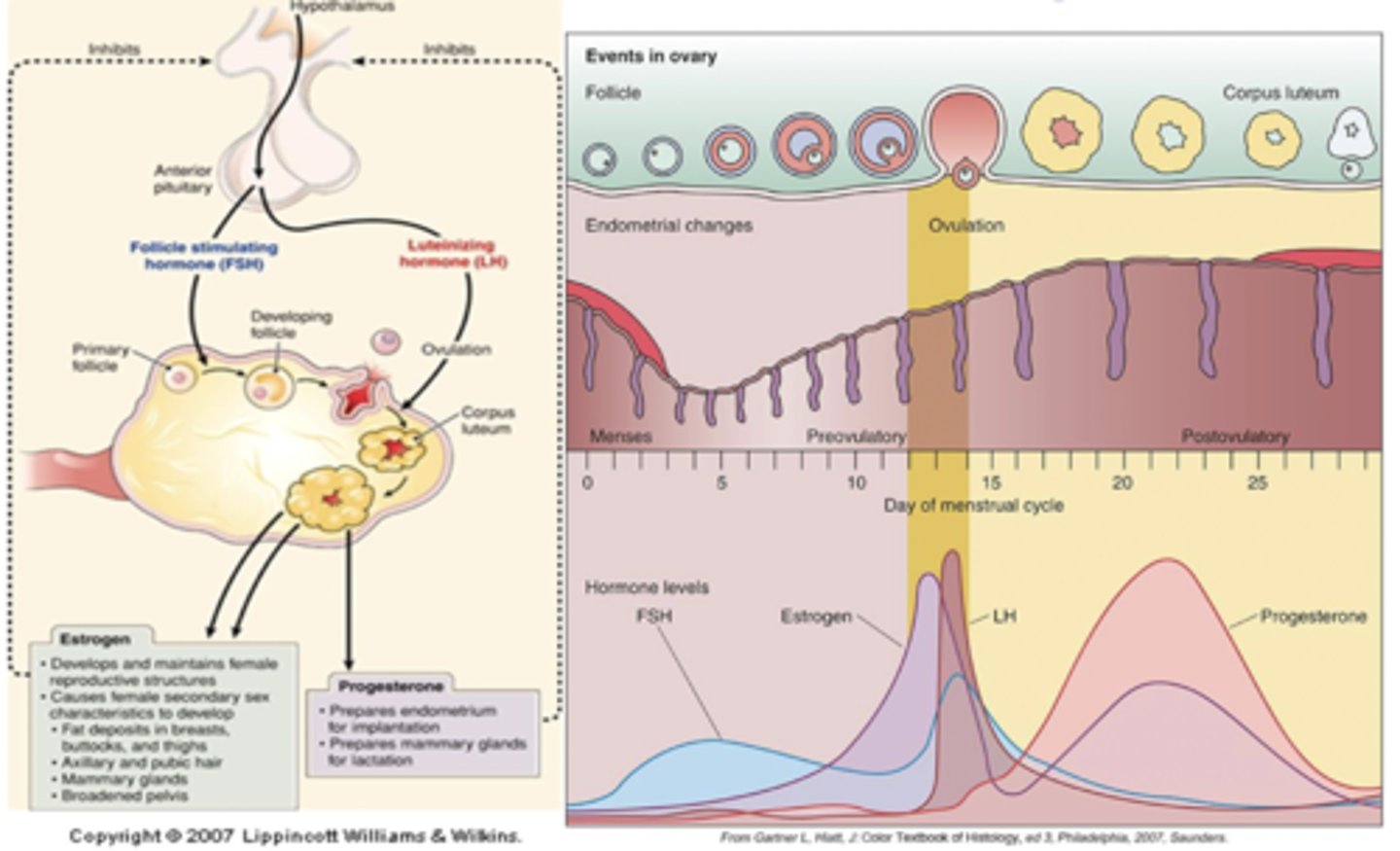
hormones and the menstrual cycle
cycle can be from 21-45 days.. consists of 5 days of menstruation (days 1-5), endometrial proliferation and production of estrogen, maturation of ovarian follicle, and release of LK that causes ovulation.
menstrual cycle
follicle becomes corpus luteum and produces progesterone. endometrium becomes vascularized in prep for implantation 12-14 days before next period
what happens if implantation doesn't occur?
corpus luteum atrophies, uterine muscle contracts (ischemia), endometrium degenerates and is expelled
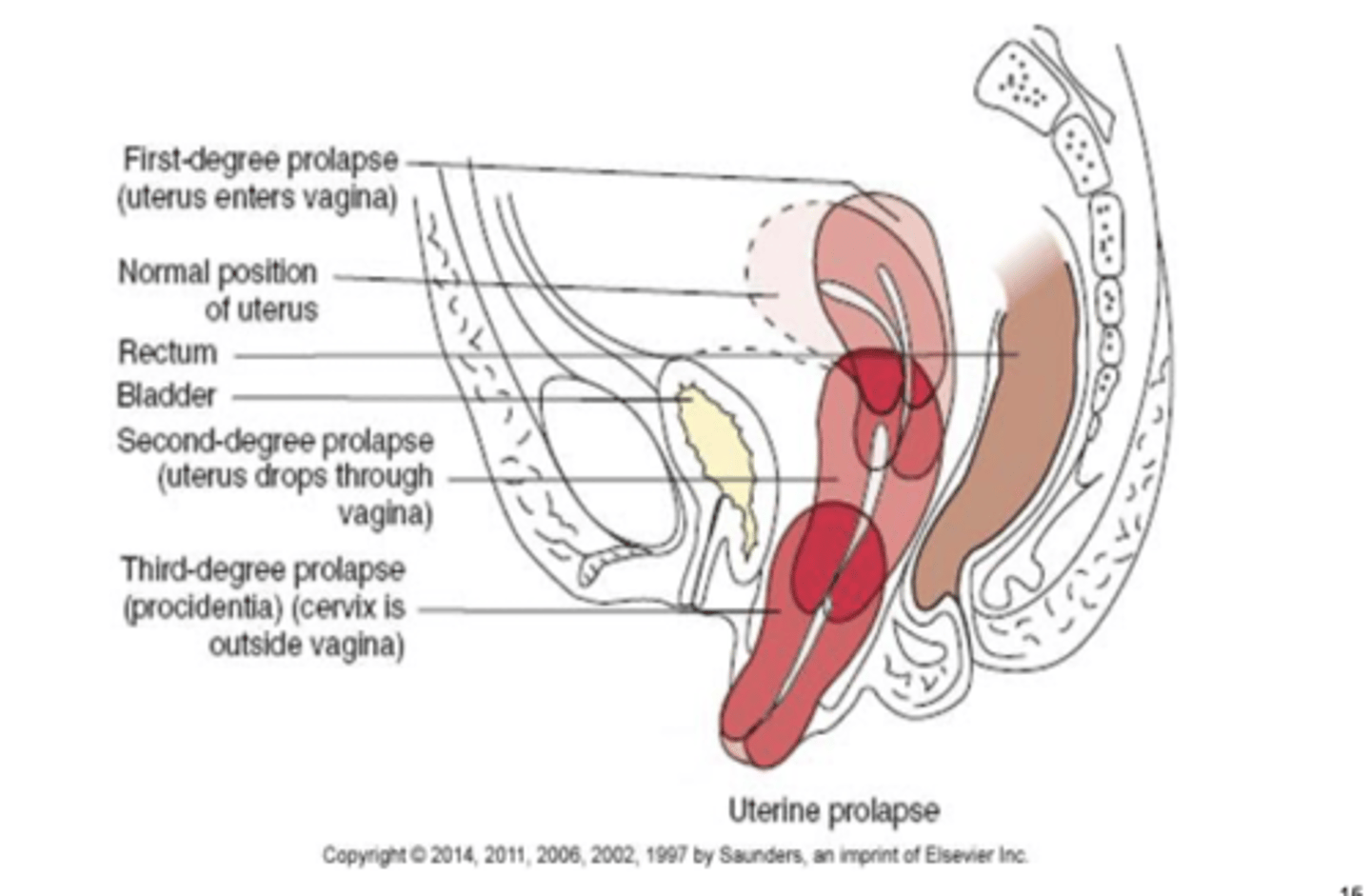
what is the normal position of the uterus?
slightly anteverted and anteflexed, cervix is downward and posterior
retroflexion of the uterus
uterus is tipped posteriorly and can be curved or bent. marked retroversion can cause back pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia. infertility may occur

uterine displacement or prolapse
first-degree prolapse: cervix drops into the vagina
second-degree prolapse: cervix lies at opening of vagina and body of uterus is in vagina
third degree prolapse: uterus and cervix protrude through vaginal orifice
rectocele
protrusion of the rectum into the posterior vagina that can cause constipation and pain
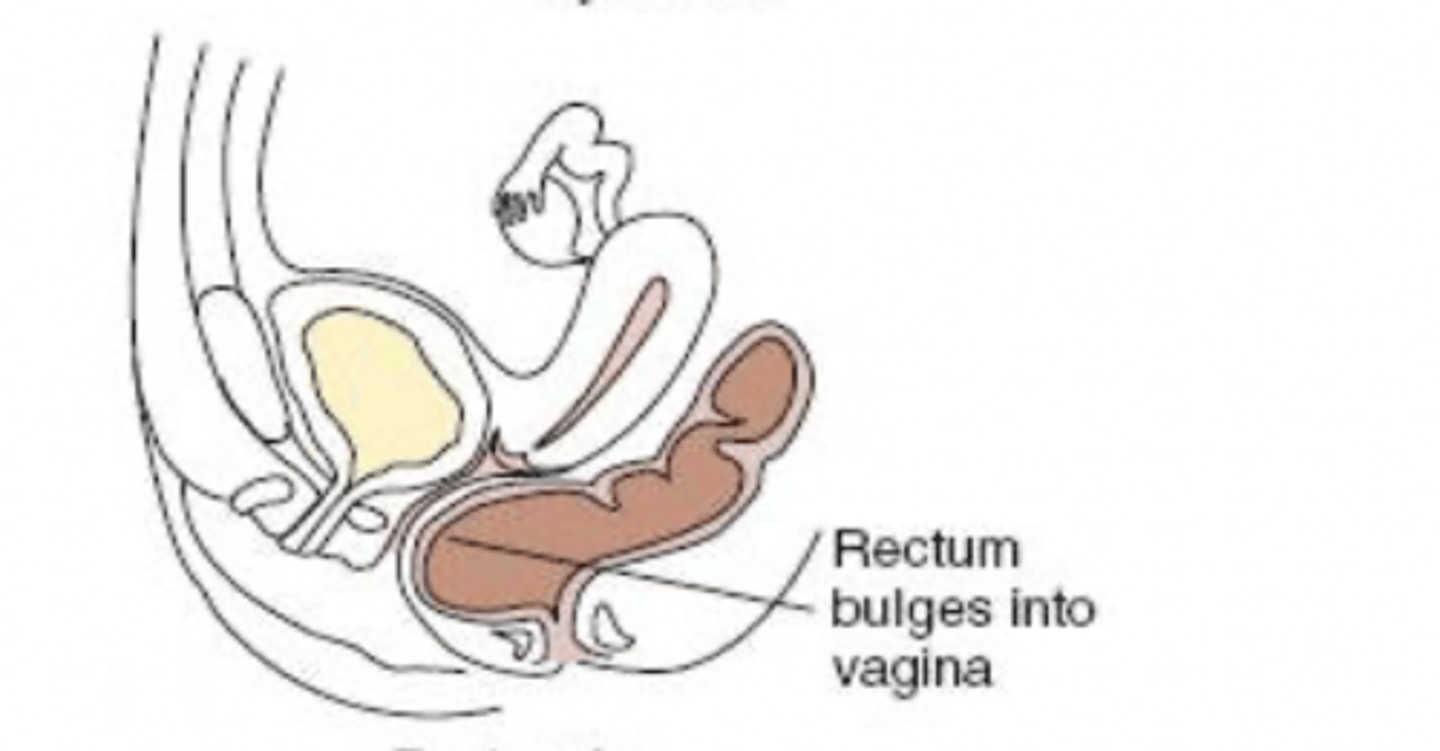
cystocele
protrusion of the bladder into the anterior vagina that can cause UTIs

amenorrhea
absence of menstruation that can be primary or secondary
primary: genetic
secondary: hormone imbalance
dysmenorrhea
painful menstruation caused by excessive release of prostaglandins as a result of endometrial ischemia. usually begins a few days prior to menses and lasts a few after; NSAIDs can help
premenstrual syndrome
begins approx. 1 week before onset of menses
breast tenderness, weight gain, abdominal distension or bloating, irritability, emotional liability, sleep disturbances, depression, headache, fatigue
what can cause abnormal menstrual bleeding?
lack of ovulation, hormonal imbalance in pituitary-ovarian axis
menorrhagia
increased amount of duration and flow
metrorrhagia
bleeding between periods
polymenorrhea
short cycles of less than 3 weeks
oligomenorrhea
long cycles of more than 6 weeks
menometrorrhagia
heavy bleeding during and between menstrual periods
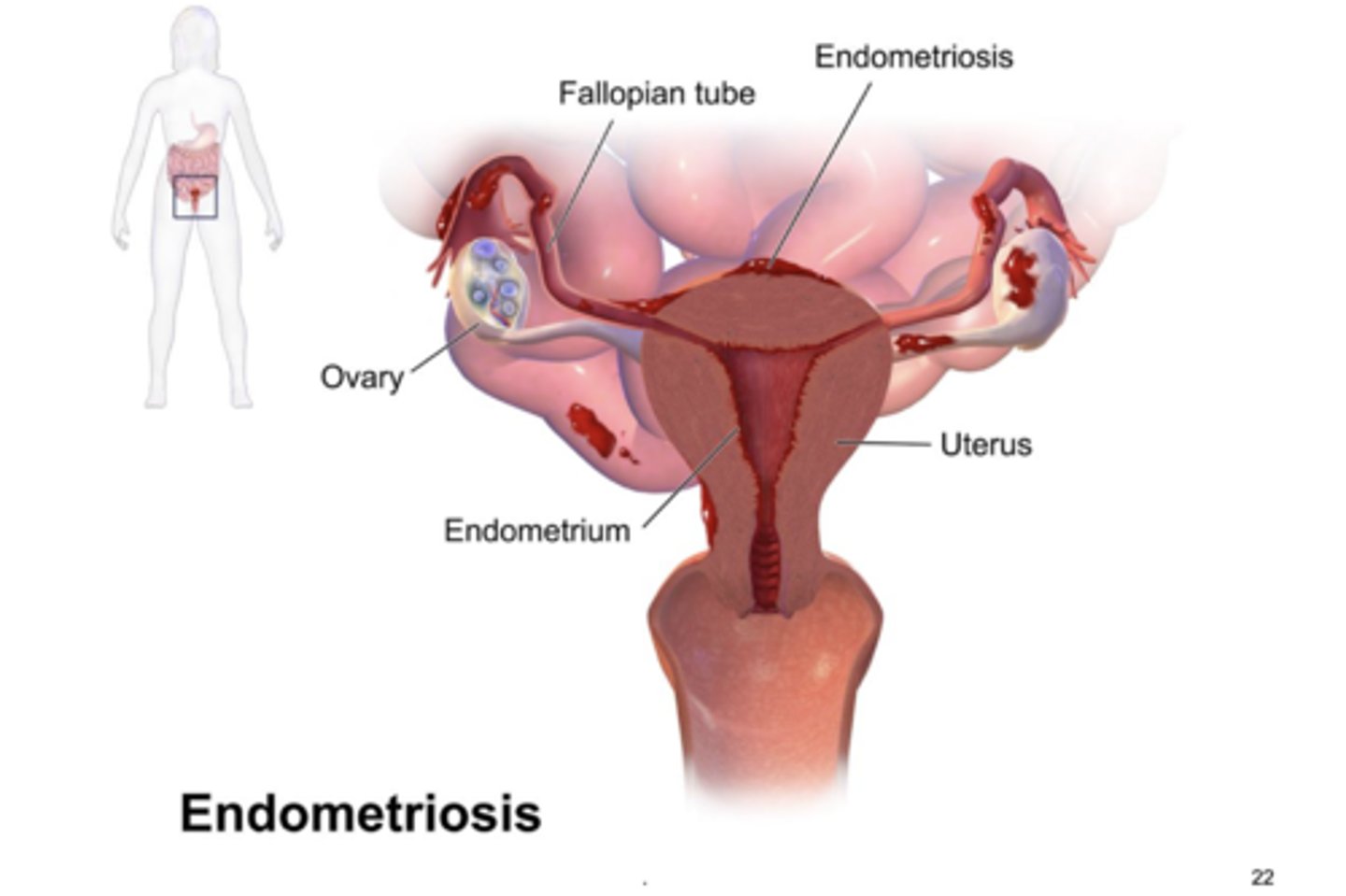
endometriosis
endometrial tissue occurs outside the uterus and ectopic endometrium responds to cyclical hormone changes. bleeding leads to inflammation and pain, fibrous tissue can cause adhesions and obstructions of the involved. treated with hormonal suppression and surgical removal of ectopic tissue
pelvic inflammatory disease
infection of uterus, fallopian tubes and/or ovaries. can be acute or chronic. infection originates as an ascending infection from the lower reproductive tract that can occur due to bacteremia. most infections arise from STDs, nonsterile abortions, or childbirth
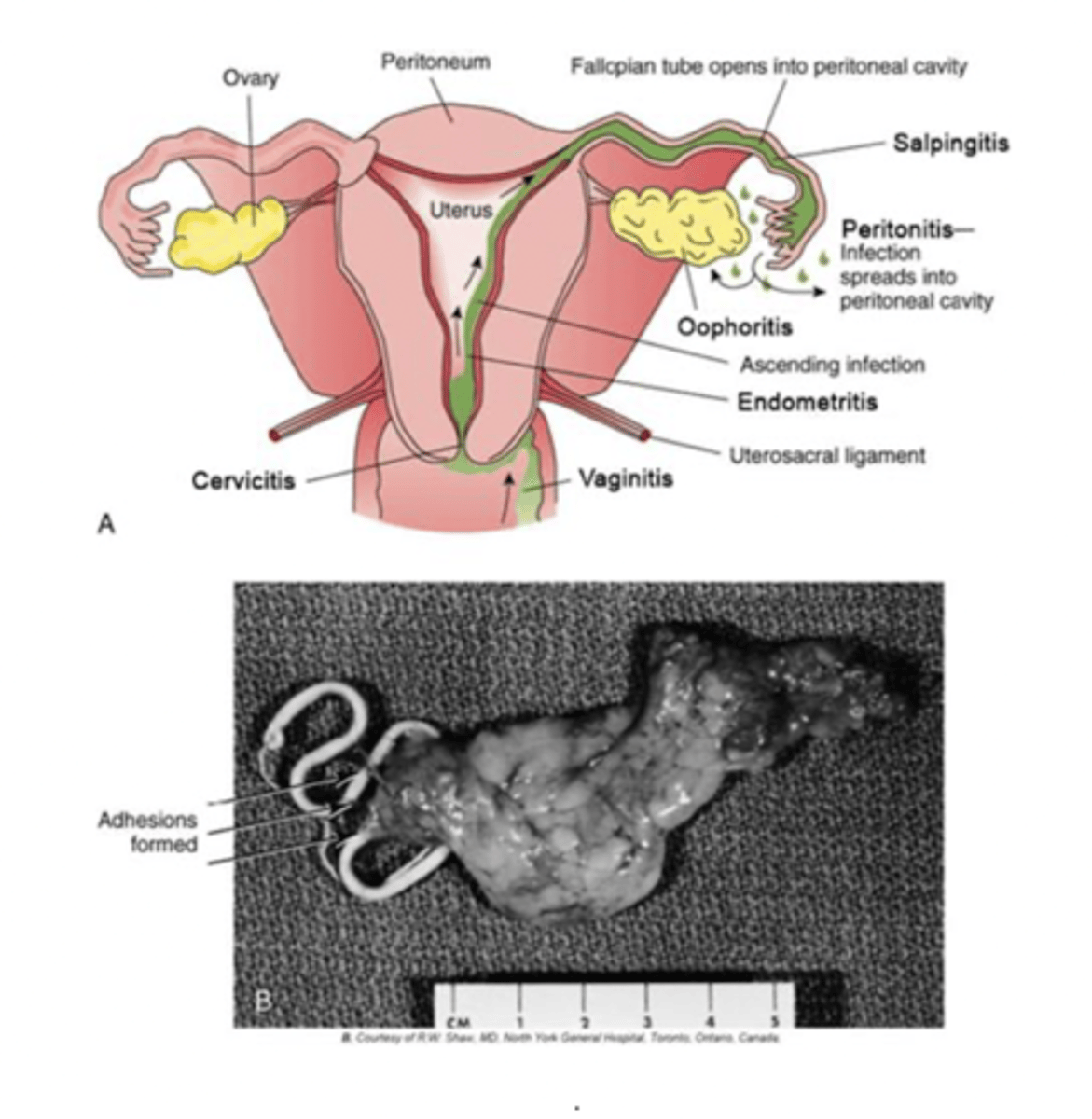
complications of PID
scarring of tubes that increases the risk of infertility and ectopic pregnancy. other acute complications would be pertonitis, pelvic abscesses, and septic shock
signs and treatment of PID
pelvic pain, increased temp, guarding, N/V, leukocytosis, purulent discharge. treatment requires aggressive antibiotic therapy in the hospital
leiomyoma (fibroids)
benign tumor of the myometrium that is common during reproductive years. classified by location and are usually multiple, well-defined masses that cause abnormal bleeding, can interfere with implantation. often are asymptomatic until large growth
risk factors of leiomyoma
genetic factors and higher frequency in black women, red meat and low vegetable intake
symptoms of leiomyoma
50% are asymptomatic - menorrhagia, anemia, urinary frequency, rectal pressure and constipation
polycystic ovarian disease
spectrum of hormonal imbalance coupled with predisposition to insulin resistance. follicles develop but do not ovulate after LH surge. high LH levels continue and stimulates androgen production, which interferes with ovulation. ovaries contain many onovulated follicles called cysts
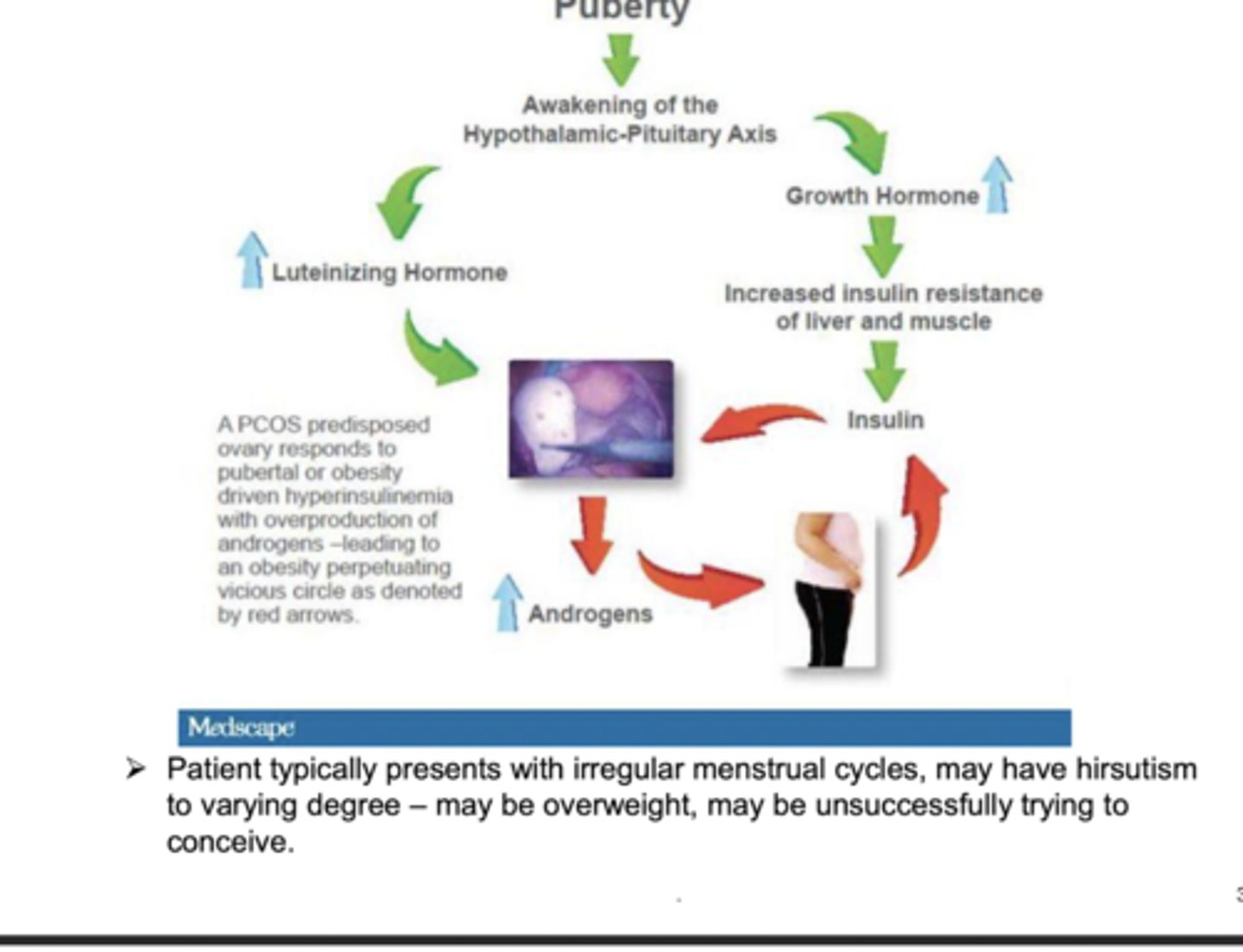
management of POD
regulate menses with oral contraceptives to reduce androgens, metformin, an insulin sensitizer, decreases circulating effect of insulin on ovaries

breast cancer
incidence increases after 20 years old. most tumors are unilateral and early onset is associated with more aggressive growth. most arise from ductal epithelial cells, and metastasis occurs via lymph nodes early in the course of the disease
what is breast cancer treatment influenced by?
presence of estrogen or progesterone receptors on tumor cells
predisposing factors of breast cancer
first degree relative, BRCA1 and BRCA2, longer and higher exposure to estrogen, late first pregnancy, lack of exercise, smoking, high fat diet, radiation therapy to chest, cancer of the uterus, ovaries, or pancreas
detection of breast cancer
40% of BCs can be detected only by mammography. mammography has sensitivity of 80-90% and must always be followed up with biopsy. mammograms are better at detecting cancer in older women as breast tissue is often less dense and more glandular
signs and symptoms of breast cancer
Initial sign: single, small, hard, painless nodule
Later: distortion of breast tissue, dimpled skin, discharge from nipple
- Ultrasound or needle biopsy confirms diagnosis
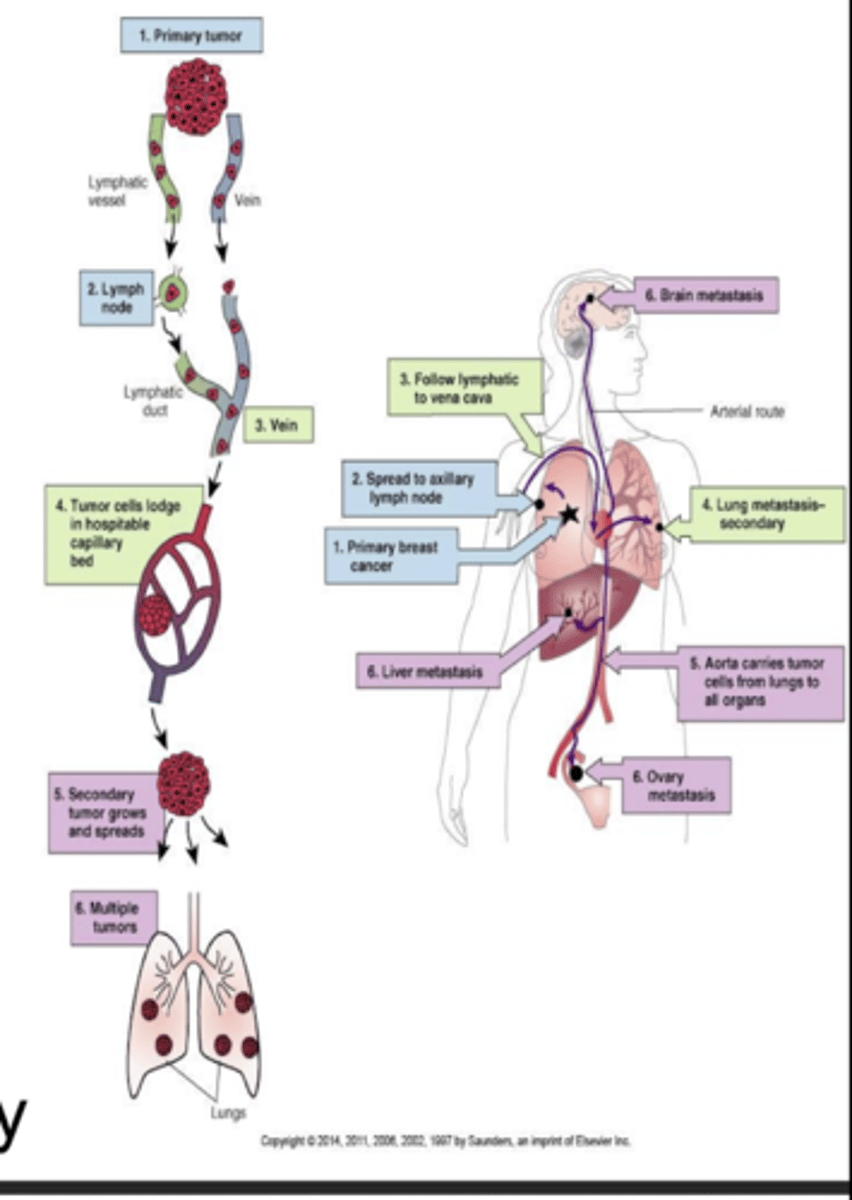
- Metastasis occurs by the time the tumor is 1 to 2 cm in diameter
- Axillary lymph node involvement
- Secondary tumors in: bone, lung, brain, liver
what to look for in clinical and self breast exam
changes in skin texture, retraction or indentation of nipple, atypical fullness or puckering, discharge. most BCs are discovered by accident, but by the time it is palpable 50% have metastisized to lymph nodes. most commonly found in UOQ
Dx metastatic breast cancer
biopsy, sentinel node identification, MRI, PET, digital mammography
how does pregnancy protect from breast cancer?
estriol is increased during pregnancy and binds to breast cell receptors, estradiol decreases due to lack of menstrual cycles
how does breast feeding protect from breast cancer?
reduces life-time of menstrual cycles and estrogen exposure, BC risk decreases by 4% for every year of breast feeding
how does nutrition protect from breast cancer?
vitamin D3, potassium iodide binds competitively to estrogen receptors
foods high in estriol: brocolli, cauliflower, cabbage
breast cancer treatment
lumpectomy or removal of breast, lymph node removal, tissue biopsy to determine drug treatment, radiation
hormone blocking agents
tamoxifen, raloxifene, toremifene
estrogen receptor blockers
fulvestrant blocks receptors on cancer cells and signals cell to destroy
drugs that inhibit estrogen production
anastrozole, letrozole, exemestane
cervical cancer
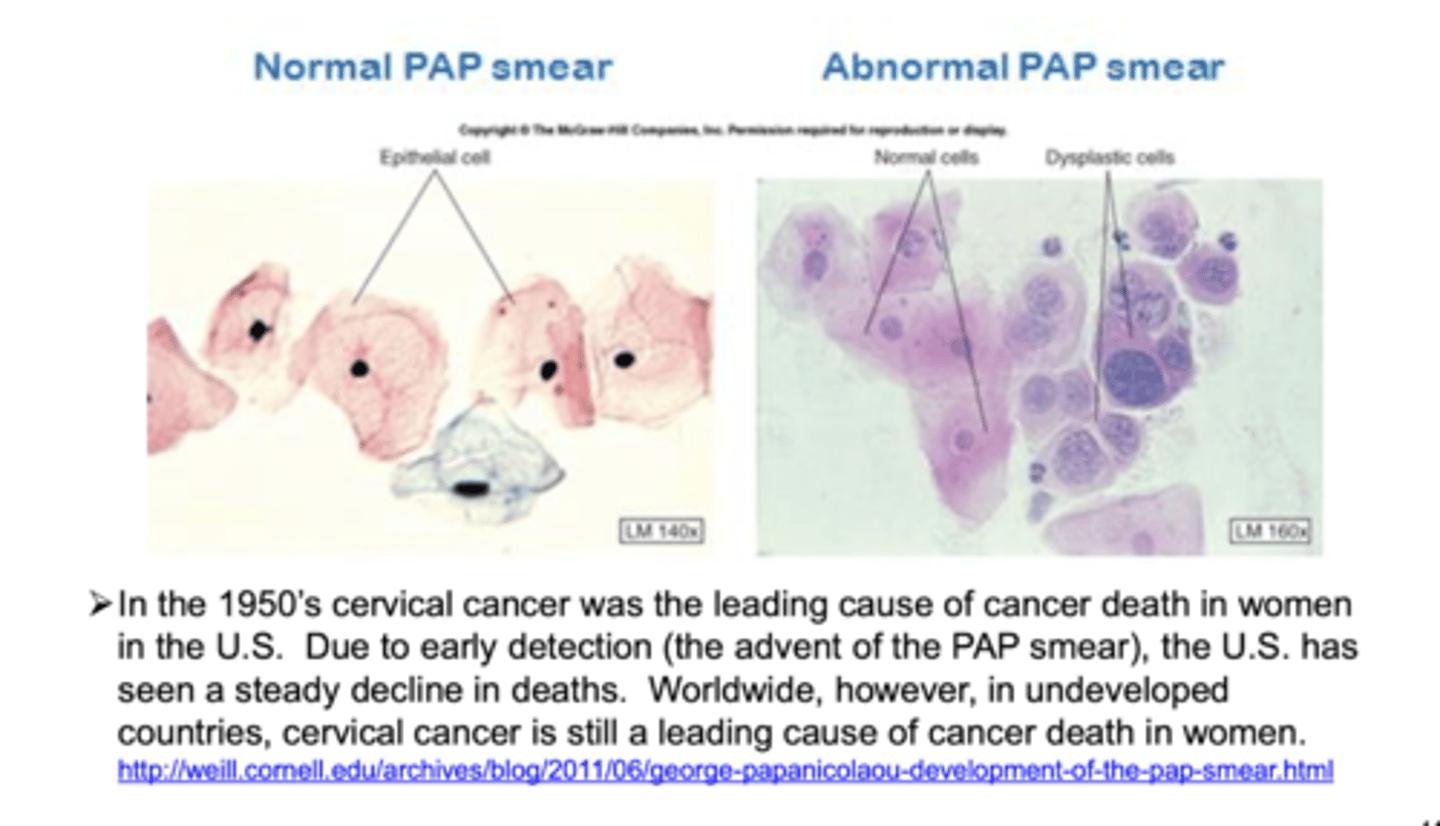
most cases are caused by HPV. vaccines prevent this and routine pap smears of cervical cells are important in identifying early and treatable stages of the disease (age 20)
cervical epithelium
columnar epithelium; exposed to acid in the vagina and transforms to squamous epithelium. transforming cells are more likely to become cancerous
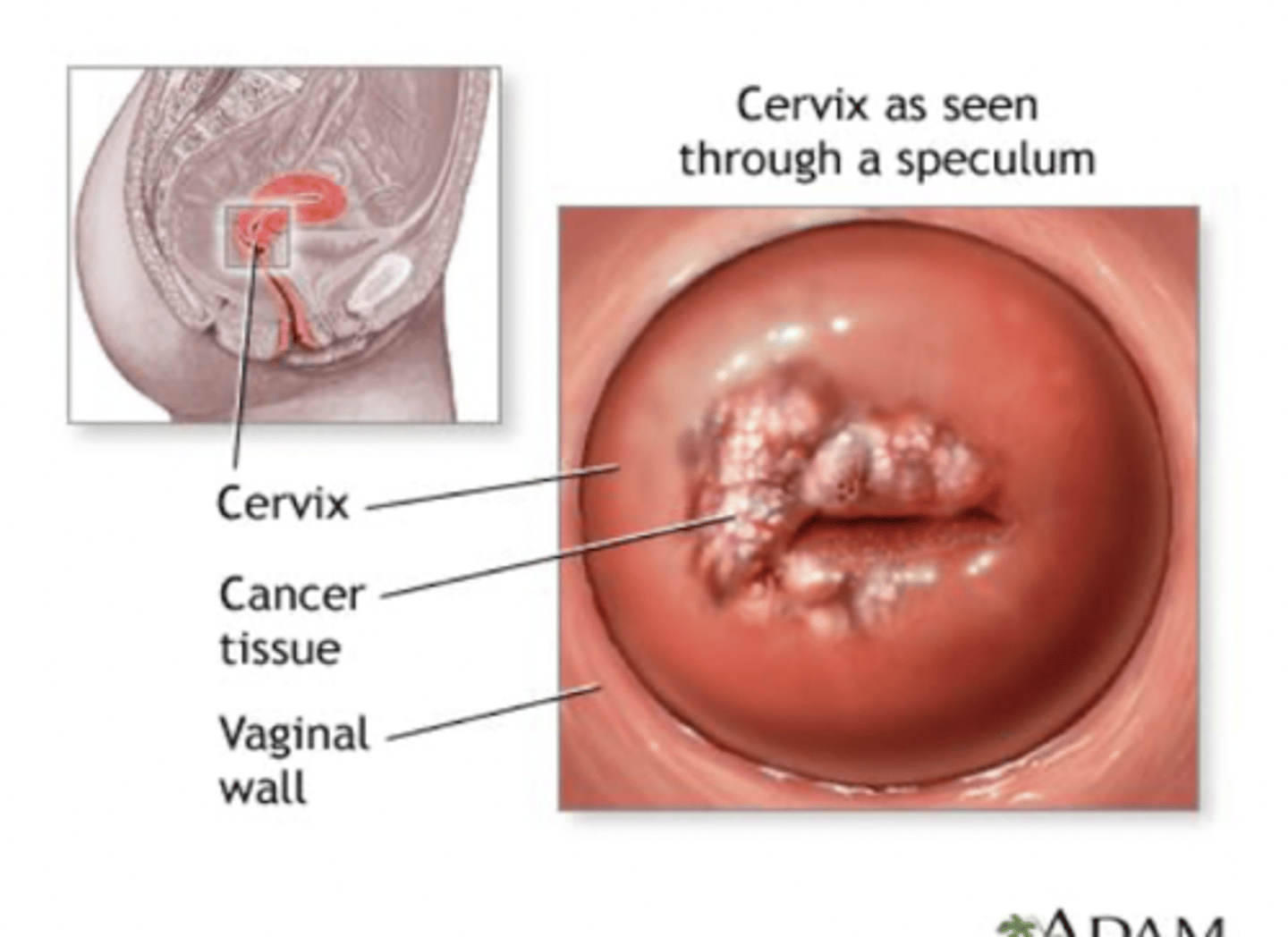
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
abnormal growth of cervical cells
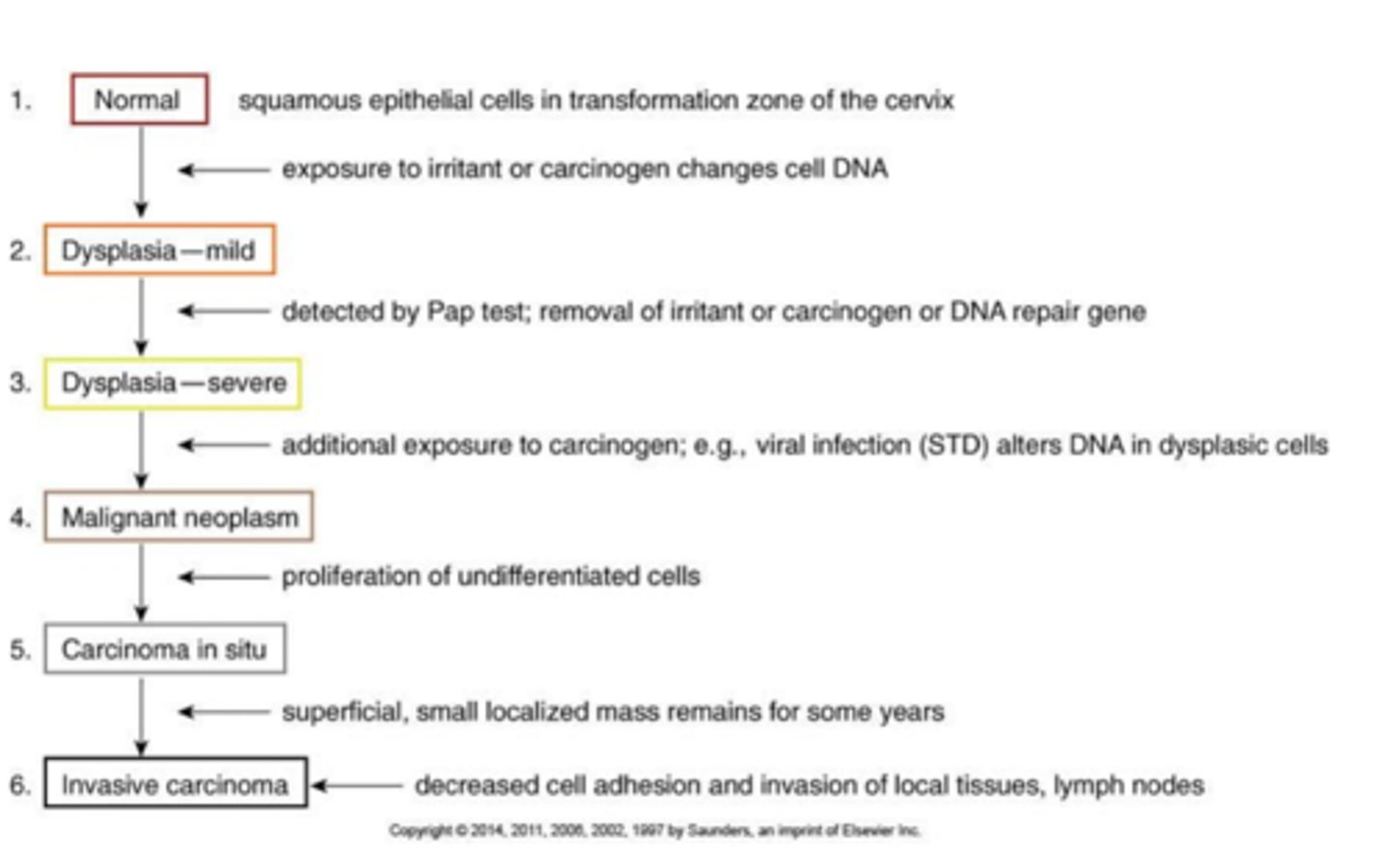
patho of cervical cancer
early dysplasia of cells, abnormal cells showing less differentiation. in situ tumor located on mucosal surface w invasion into submucosa. invasion and spread to adjacent organs, late metastasis
more on development of cancer in the cervix..
squamous epithelial cells in transformation zone are exposed to irritant or carcinogen and changes cell DNA.. detected by Pap smear and are removed. additional exposure or a viral infection alters DNA in dysplasic cells and undifferentiated cells start proliferating. a superficial, small localized mass remains for years and finally invades with decreased cell adhesion and invasion of local tissues and lymph nodes
risk factors of cervical cancer
HPV (type 16 and 18), certain types of sexual behavior can increase risk for HPV (which is mostly in young women and can be present without symptoms or warts.. vaccine)
survival rates of cervical cancer

type 1 uterine cancer
occurs in women in their 40s and accounts for 80% of cases. associated with estrogen excess, obesity, DM, nulliparity, early menarche, late menopause
type 2 uterine cancer
occurs in menopausal women associated with uterine atrophy, poorer prognosis
what is a warning sign in both types of endometrial carcinoma?
abnormal bleeding
uterine cancer
pap smear doesn't detect this cancer.. usually arises from glandular epithelium and is slow growing but invasive. staging is based on degree of localization. treatment is radiation and surgery
estrogen excess
estrogen dominance is when progesterone levels are much lower than estrogen. implicated in hose of female disorders: heavy bleeding, weight gain, migraines, endometriosis, fibroid tumors, increased risk of cancers
managing estrogen excess conditions
managing diabetes and HTN and preventing progression to endometrial cancer are important goals of treatment
ovarian cancer
associated with history of ovarian and breast cancer that causes vague GI symptoms. most cases have metastasized by the time they are discovered and there are no good screening tests available.
ovarian cancer risk factors
ovulatory age (length of time in which ovulation has not been suppressed by pregnancy, lactation or oral contraceptive use). frequency is much lower in countries where women bare numerous children and breastfeed. a high fat western diet and use of talc in genital area have been linked to the disease
specific risk factors of ovarian cancer
obesity, BRCA1, early menarche, nulliparous or late first pregnancy, use of fertility drugs
diagnosis of ovarian cancer
no reliable screening available - large masses are detected by pelvic exam and transvaginal ultrasound.. considered a silent tumor and few are diagnosed in early stages.
treatment of ovarian cancer
progesterone oral contraceptives are somewhat protective.. surgery and chemotherapy are usual treatments
stages of gynecologic cancer
stage 0: rarely used, preinvasive lesions
stage 1: cancer is confined to organ it originated in
stage 2: cancer involves some structures surrounding the organ of origination
stage 3: regional spread of cancer with lymph node involvement
stage 4: distant spread of cancer with metastasis