L6 - Heart Beat, Contractility and Conductivity
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Blood Flow
Pathway of blood through heart chambers.
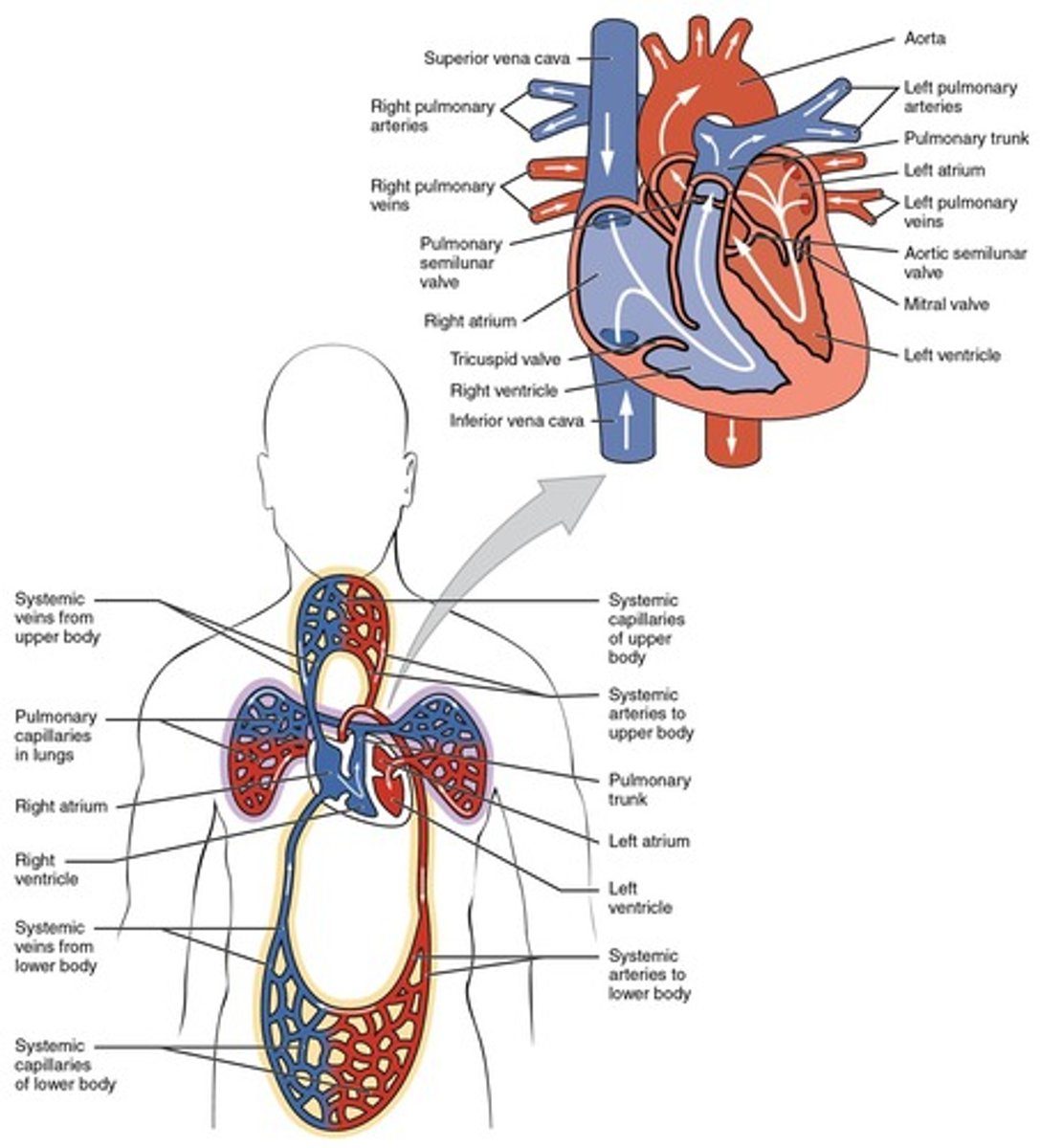
Pulmonary Circulation
Transports low oxygenated blood to lungs.
Systemic Circulation
Delivers highly oxygenated blood to body.
Pericardium
Protective sac surrounding the heart.
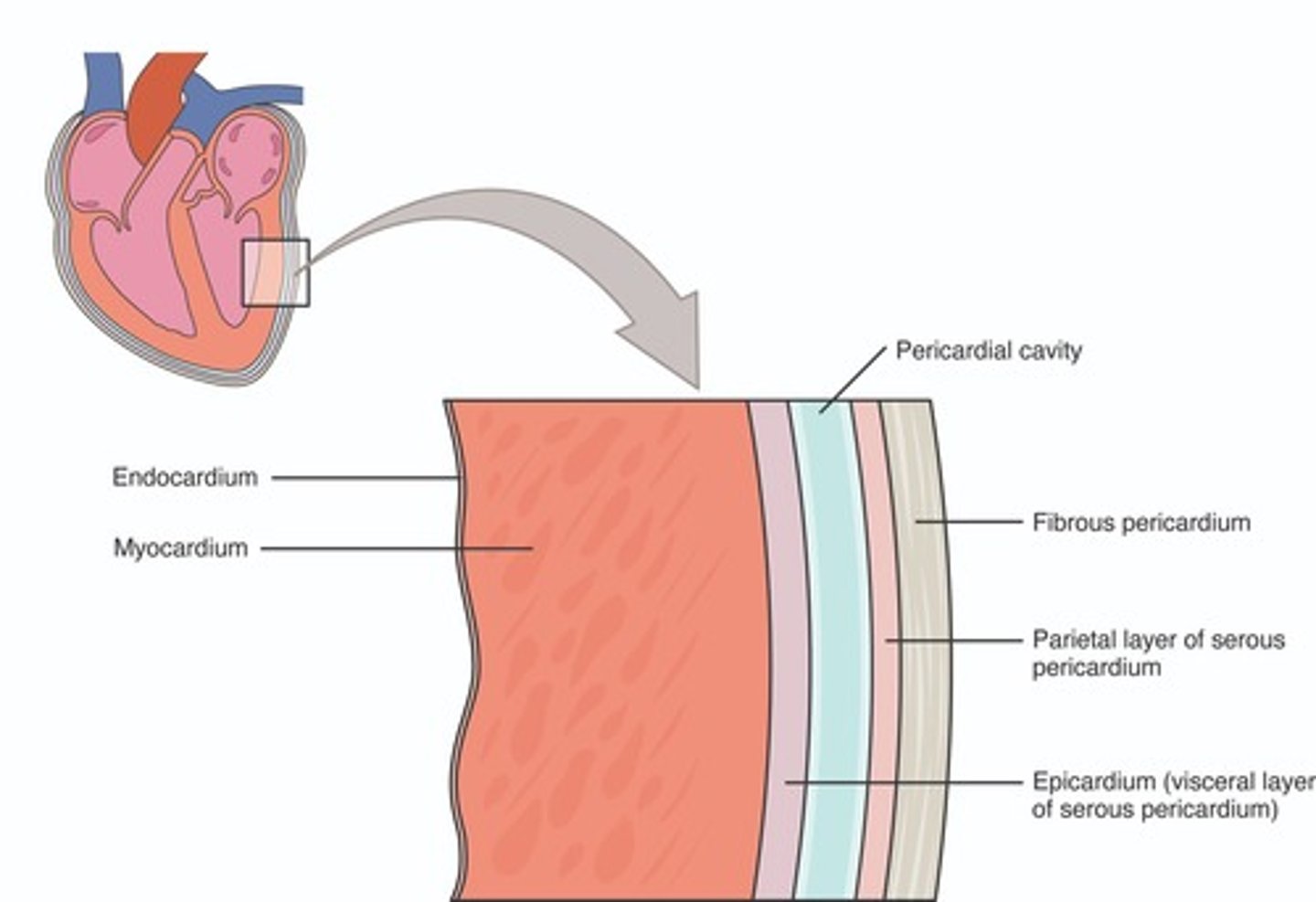
Epicardium
Outer layer of the heart wall.
Myocardium
Muscle layer responsible for heart contractions.
Endocardium
Inner lining of heart chambers.
Atrioventricular Valves
Valves between atria and ventricles.
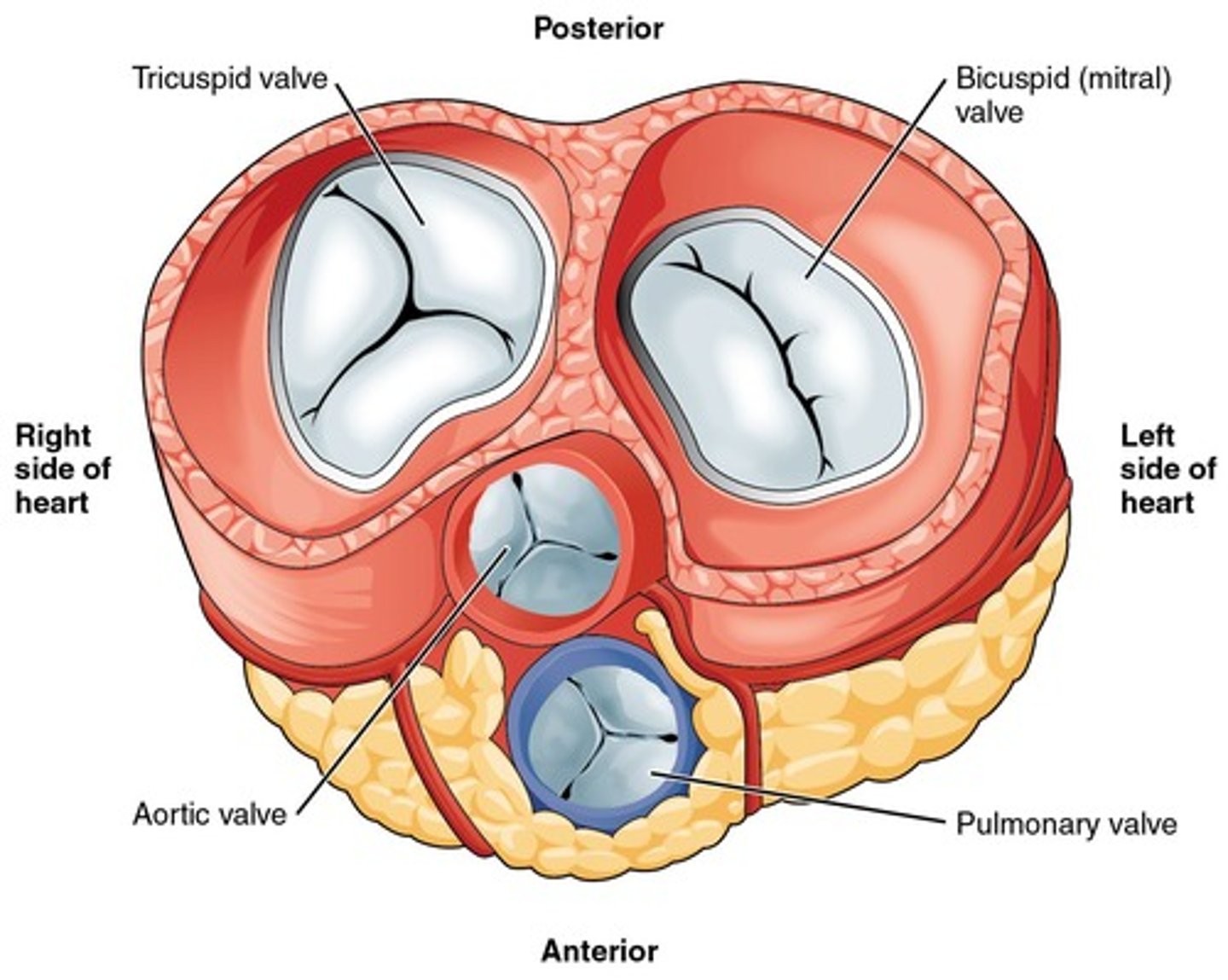
Bicuspid Valve
Also known as the Mitral valve.
Tricuspid Valve
Right atrioventricular valve.
Semilunar Valves
Valves between ventricles and arteries.
Intercalated Disks
Connections between cardiac muscle fibers.
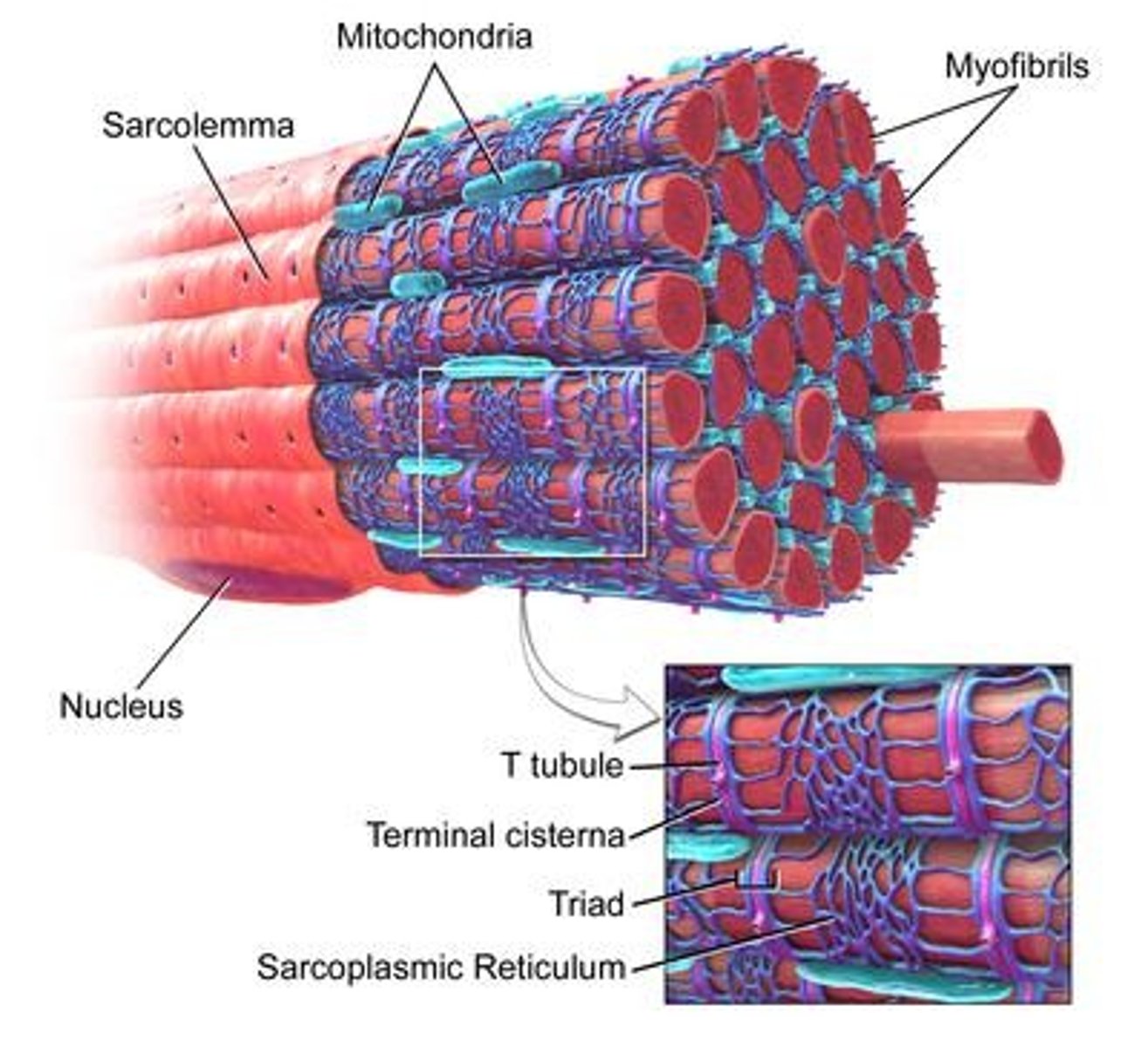
T Tubules
Conduct electrical impulses in muscle cells.
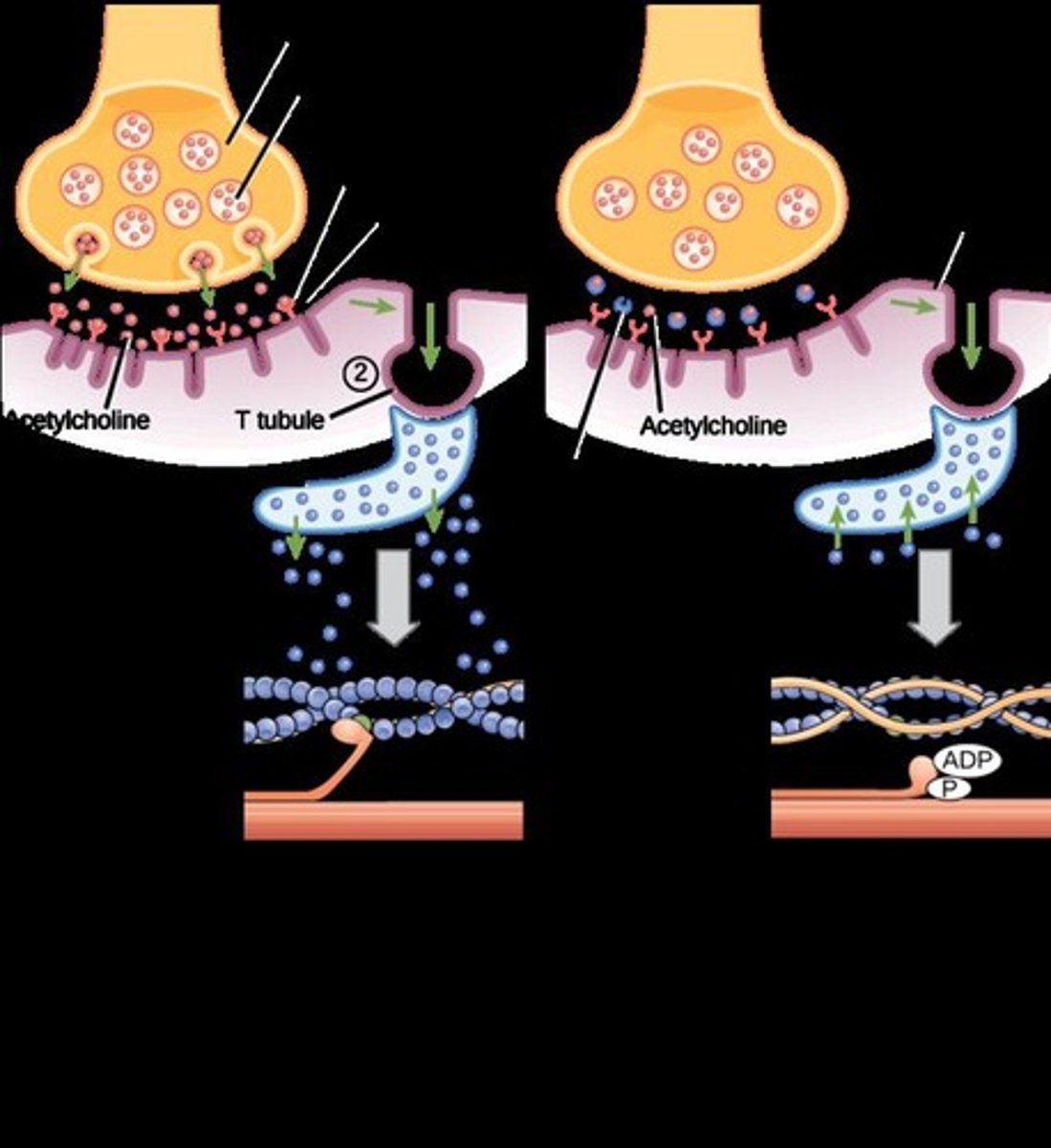
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Calcium storage for muscle contraction.
Sarcomere
Basic unit of muscle contraction.
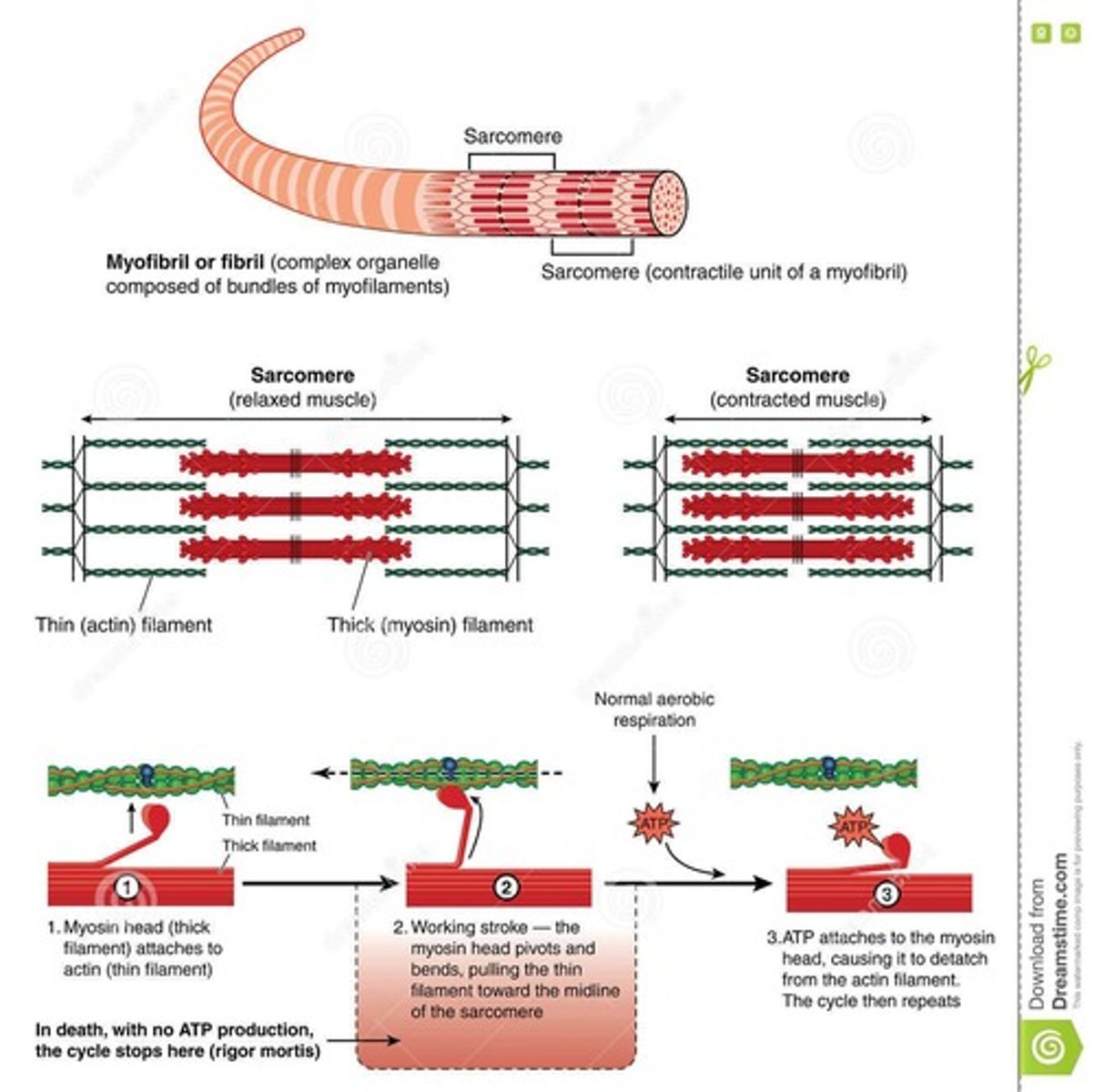
Actin Filaments
Thin filaments involved in muscle contraction.
Myosin Filaments
Thick filaments providing mechanical force.
Sinoatrial Node
Primary pacemaker of the heart.
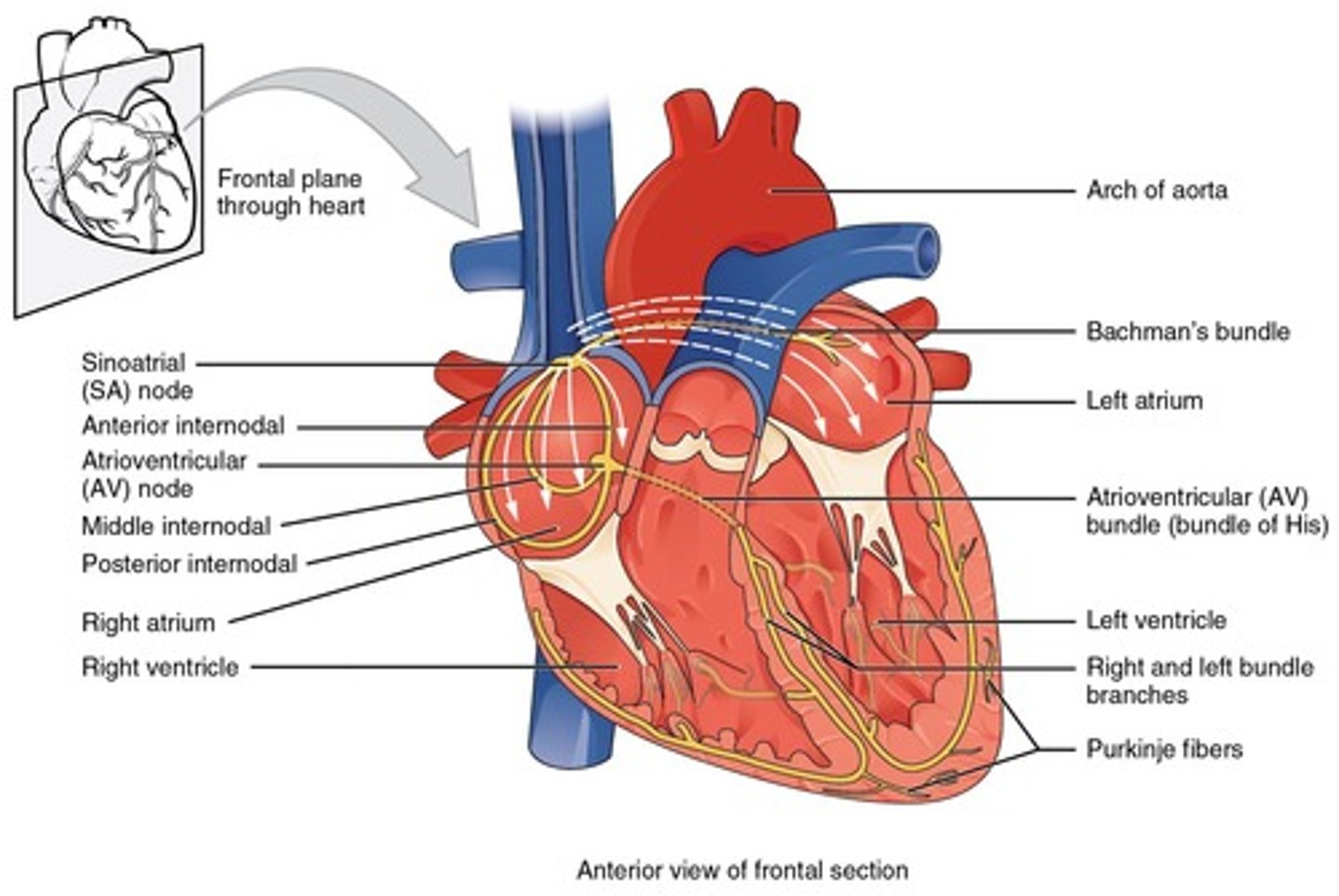
Atrioventricular Node
Secondary pacemaker, delays impulse transmission.
Bundle of His
Conducts impulses from AV node to ventricles.
Prepotential
Slow sodium influx before action potential.
Cardiac Cycle
Sequence of events in one heartbeat.
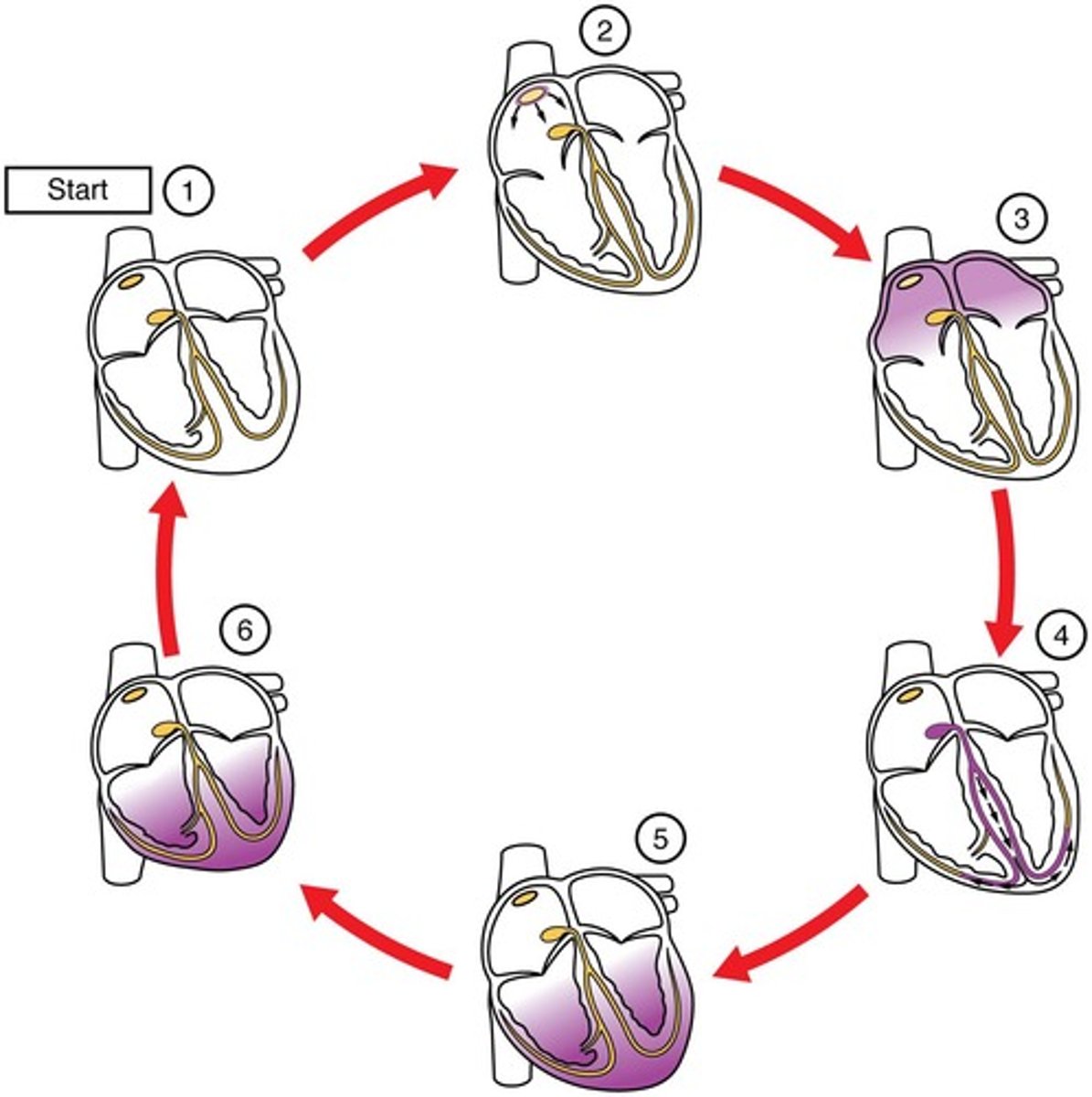
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
Blood volume in ventricles before contraction.
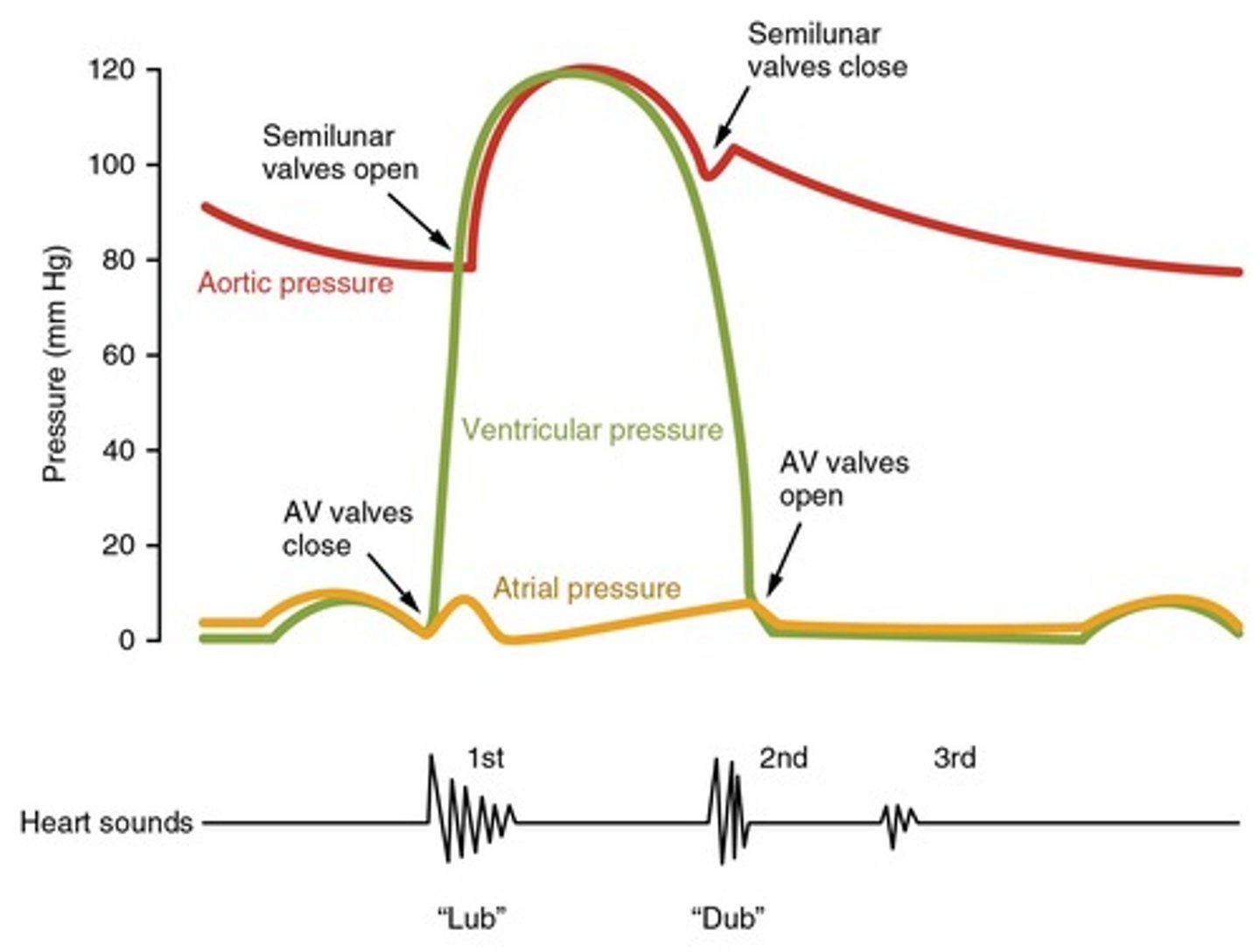
End Systolic Volume (ESV)
Blood volume in ventricles after contraction.
Heart Failure
Inability of heart to meet body's demands.