hazardous earth
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are possible consequences of global warming?
Biodiversity loss on land and in the oceans
Coastal flooding from sea-level rise
More frequent, stronger hurricanes
Spread of pests and disease
Changing in farming could affect food supplies
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Heat (UV rays) from the Sun reaches the Earth’s atmosphere; some is reflected back into space
Land + oceans absorb the heat
Land + oceans then radiate infrared heat back into the atmosphere
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap some of the heat
Human activity increases greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
What are 3 key characteristics of a tropical cyclone?
Low pressure
Rotation; Coriolis force
Structure; eye of the storm, etc
How do tropical cyclones form?
Warm sea temperatures of 26°C
Lots of moisture in the atmosphere
Rapid cooling
Rising air must condense quickly to generate energy
Winds cannot blow in different directions
Coriolos force for the cyclone to spin
Smaller storms come together to form tropical cyclones
What are the physical hazards of tropical cyclones?
Storm surges
Coastal flooding
Landslides
What causes storm surges?
Water pushed up by the wind in front of the storm has nowhere to go but onto land
Low pressure in the tropical cyclone increases the surge
Slow moving tropical cyclones cause biggest surges
How does coastal flooding occur?
If the land is low lying, storm surges can flood the areas
What triggers landslides?
Rainfall causes flash flooding and triggers landslides on unstable slopes
What is used to predict tropical cyclones?
Satellites spot a tropical cyclone forming and tracks its progress
What factors make a country more or less vulnerable? (+ examples)
Physical — low-lying coastal areas
Social — low quality housing
Economic — better prediction, protection + evacuation technology
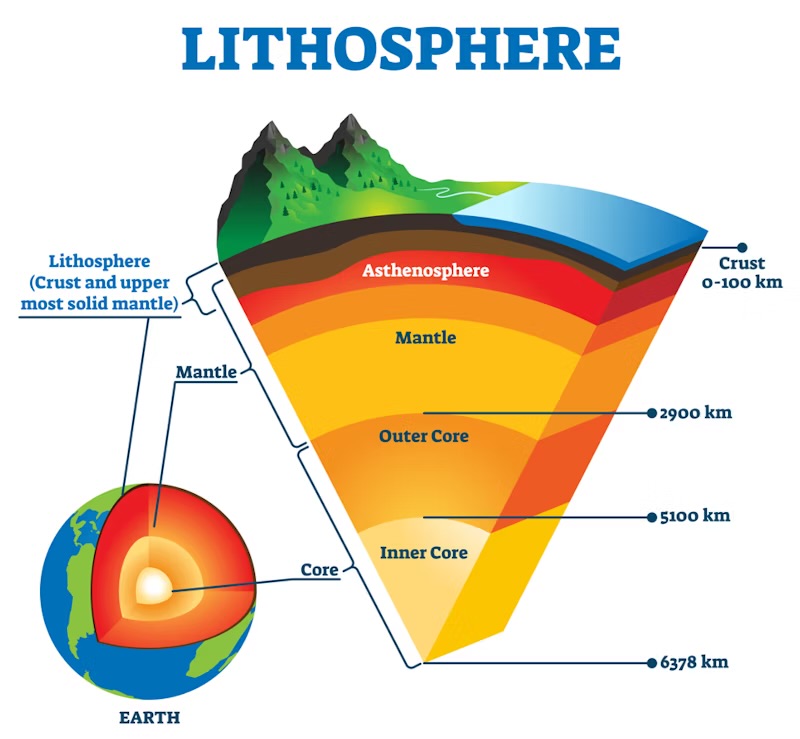
How do convection currents contribute to plate movement?
The core heats the molten rock in the mantle to create a convection current
Heated rock from the mantle rises to the Earth’s surface
At the surface, the convection current moves the tectonic plates in the crust
Molten rock cools and flows back to the core to be reheated
What are hotspots?
Points on the Earth’s crust with very high heat flow, which is linked to increased volcanic activity
Where does the energy produced from earthquakes come from?
Epicentre — the point directly above the focus
Focus — the central point of the earthquakes, greatest release
How to strengthen a building for a earthquake?
Installing a ring beam — stops walls falling outwards
Very strong framework
Strengthen walls
Reinforcing gas + water pipes
What to write to describe the trend of (eg. ice) in a graph?
“Overall, ice increases/declines in the period shown”
If there are fluctuations or not
Range
First ice drop below average
2 reasons tropical cyclones lose energy?
Reach land (1) so they lose access to warm water; source of power (1)
Move into areas with cooler water (1) as they need temperatures of over 26.5°C (1)
One cause of a tsunami?
Earthquakes (1) caused by plate movement (1)
What is one way global atmospheric circulation determines location of high rainfall areas?
At the equator (1) less dense air rises (1) cools and condenses forming clouds (1)
Explain one role of ocean currents?
Redistribution of heat (1) to regulate uneven global temperatures (North Atlantic Drift) (1)
How might climate change affect food? (2)
High temperatures might destroy some crops (1) limiting supply of food (1)
Explain one reason why some places are arid (low rainfall)?
Air cannot rise in high pressure areas (1) so clouds cannot form (1)
What are sunspots and how are they linked to climate change?
Black spots on the surface of the sun, that are hotter areas.
The more sunspots, the higher level of heat given out
Lack of sunspots has caused ice ages
Does a circular or elliptical orbit lead to warmer periods and why?
The more circular the orbit, the warmer temperatures on Earth
The Earth is closer to the sun, so it receives more solar radiation
What is the greenhouse effect?
A natural process by which the natural layer of gases in our atmosphere trap some of the energy from the sun
Keeps our temperature suitable for life