alcohols
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what is the functional group in alcohols? (2)
-OH
hydroxyl group
what is the general formula for an alcohol? (1)
CnH(2n+1)OH
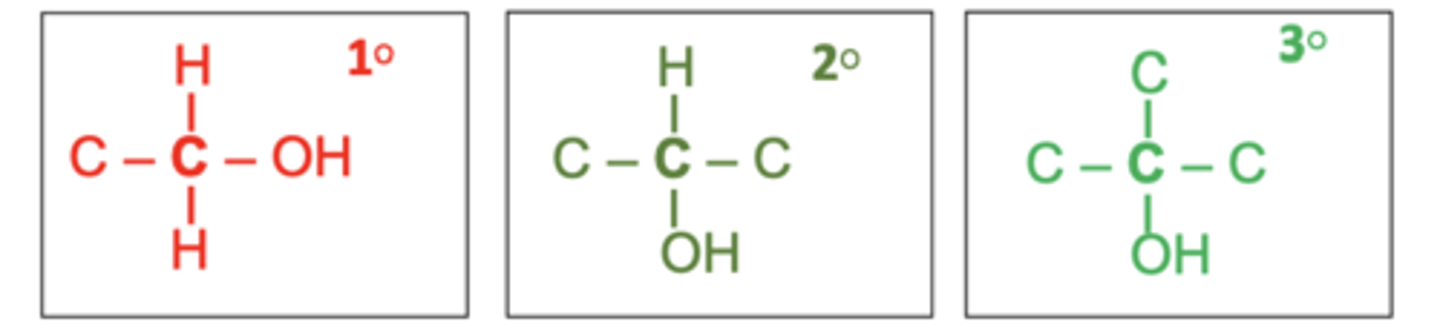
how are alcohols classified? (3)
primary
secondary
tertiary
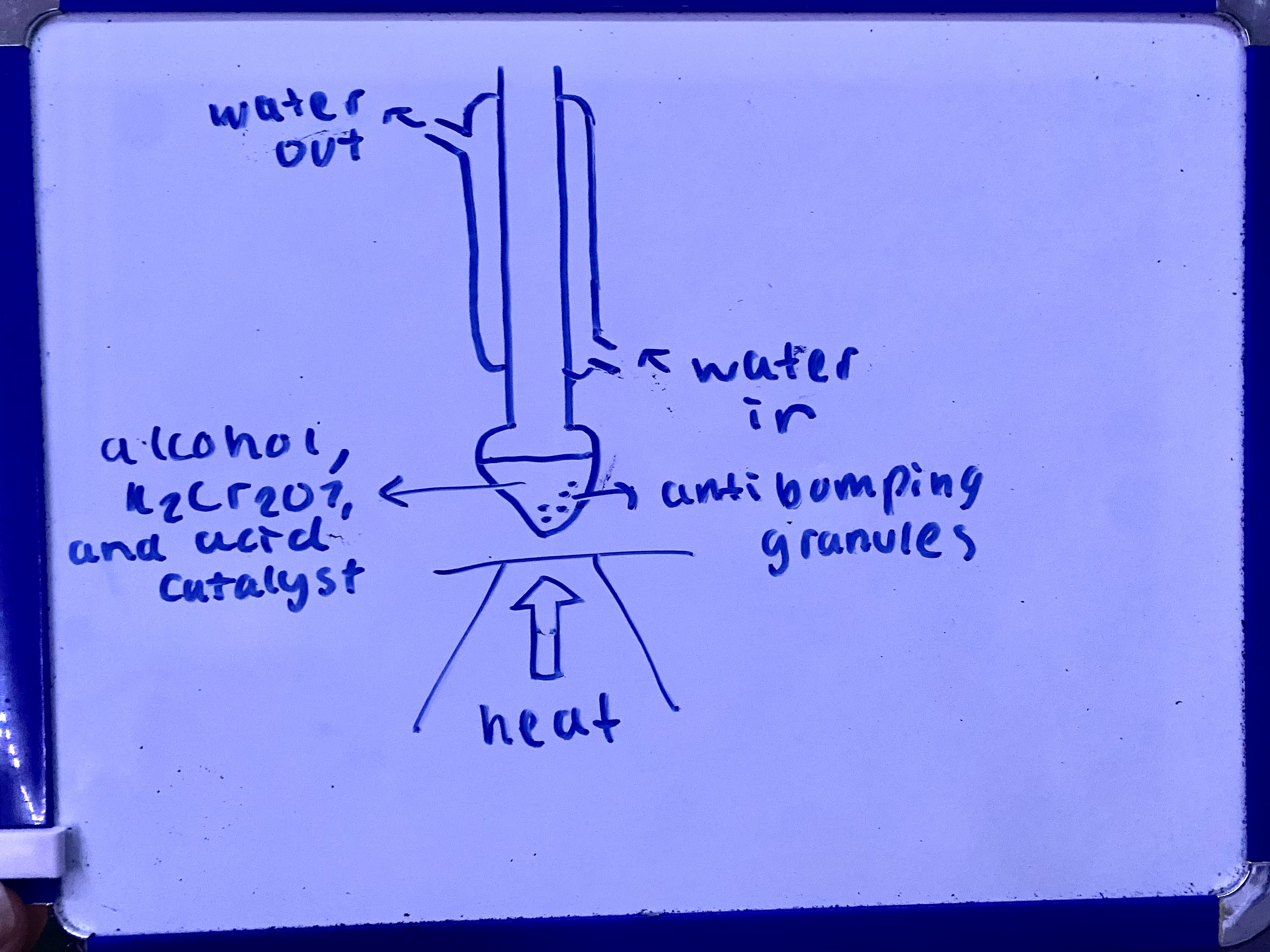
what are the two ways of producing ethanol? (2)
fermentation of glucose
direct hydration of ethene
what is the equation for the fermentation of glucose to produce ethanol? (1)
C6H12O6 → 2CH3CH2OH + 2CO2
what conditions are required for the fermentation of glucose to produce ethanol? (4)
yeast provides enzymes
temperature of 35°C
oxygen-free environment (anaerobic respiration)
15% yield
what is a biofuel, and how is ethanol from fermentation separated? (2)
a biofuel is a fuel derived from biological materials, such as plants or animals
ethanol is separated using fractional distillation
what is the equation for the direct hydration of ethene to produce ethanol? (1)
C2H4 + H2O → CH3CH2OH
what are the essential conditions for the direct hydration of ethene? (2)
high temperature (300°C)
high pressure (70 atm)
what catalyst is used in the direct hydration of ethene? (2)
concentrated phosphoric acid (H3PO4) or concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
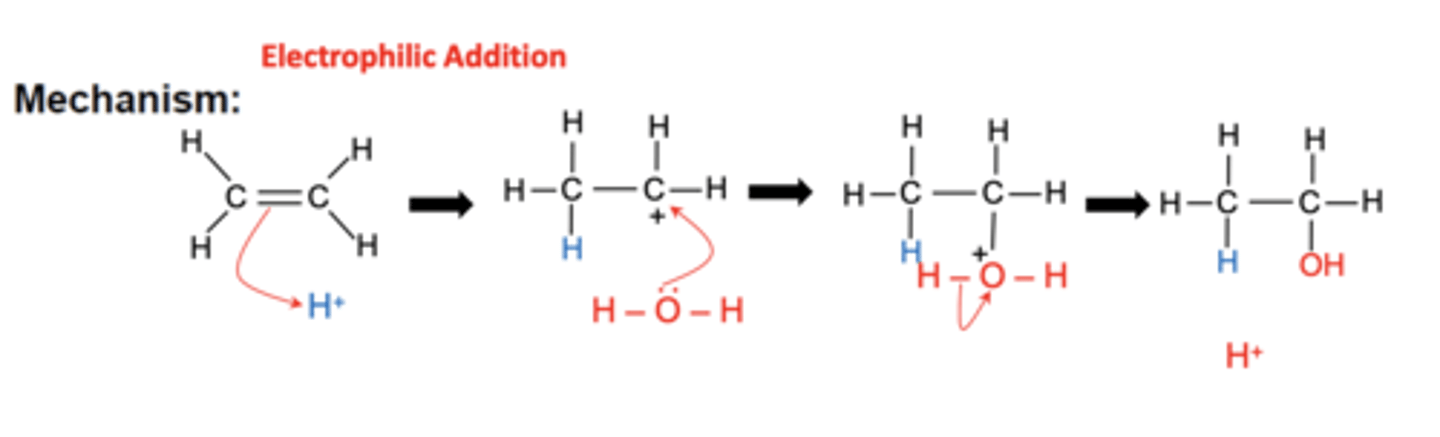
what type of reaction mechanism is involved in the direct hydration of ethene? (1)
electrophilic addition
draw the mechanism for the direct hydration of ethene to produce ethanol (4)
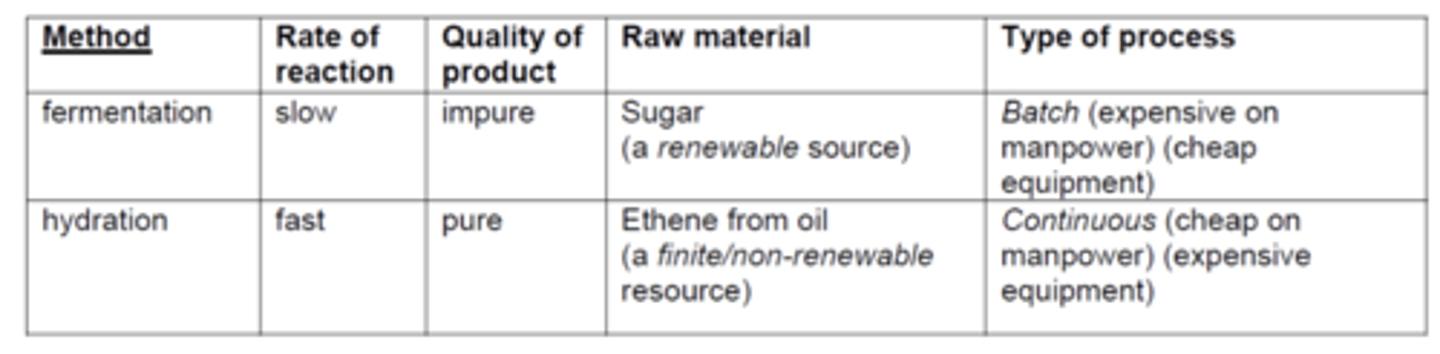
draw a table to compare the two techniques of producing ethanol (10)
why is ethanol made from ethene not considered renewable? (1)
because it originates from crude oil
why is ethanol made by fermentation considered renewable? (2)
sugars used in fermentation come from plants like sugar cane
which can be grown annually, making it a biofuel
what is the environmental concern with current carbon-based fuels? (1)
they release carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming and climate change
why is ethanol made by fermentation sometimes called a carbon-neutral fuel? (2)
the carbon dioxide released during combustion
is balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plant during photosynthesis
is ethanol made by fermentation truly carbon neutral? and why or why not? (2)
no, because additional carbon dioxide is released during transportation, harvesting, and other processes
write the equation for photosynthesis in the growing plant (1)
6H2O + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2
write the equation for the combustion of ethanol (1)
C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
what is the elimination reaction of alcohols also referred to as? (2)
dehydration reaction
turning alcohol into an alkene
what catalyst is required for the elimination reaction of alcohols? (2)
concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) or concentrated phosphoric acid (H3PO4) catalyst
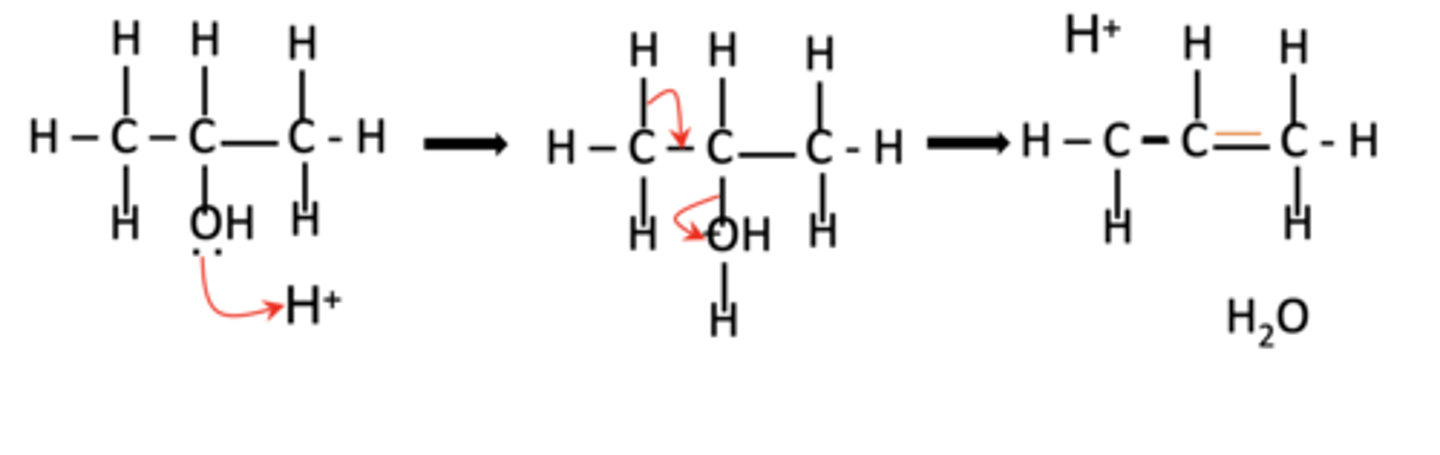
what are the three stages of the mechanism for the elimination reaction of alcohols? (3)
1. a lone pair of electrons on the alcohol oxygen is donated to a proton (H+) from the acid catalyst
2. oxygen gains the proton and becomes positively charged
3. hydrogen is lost from an adjacent carbon, forming a double bond (C=C), and water is eliminated
draw the mechanism of the elimination reaction for propan-2-ol, showing the formation of products (3)
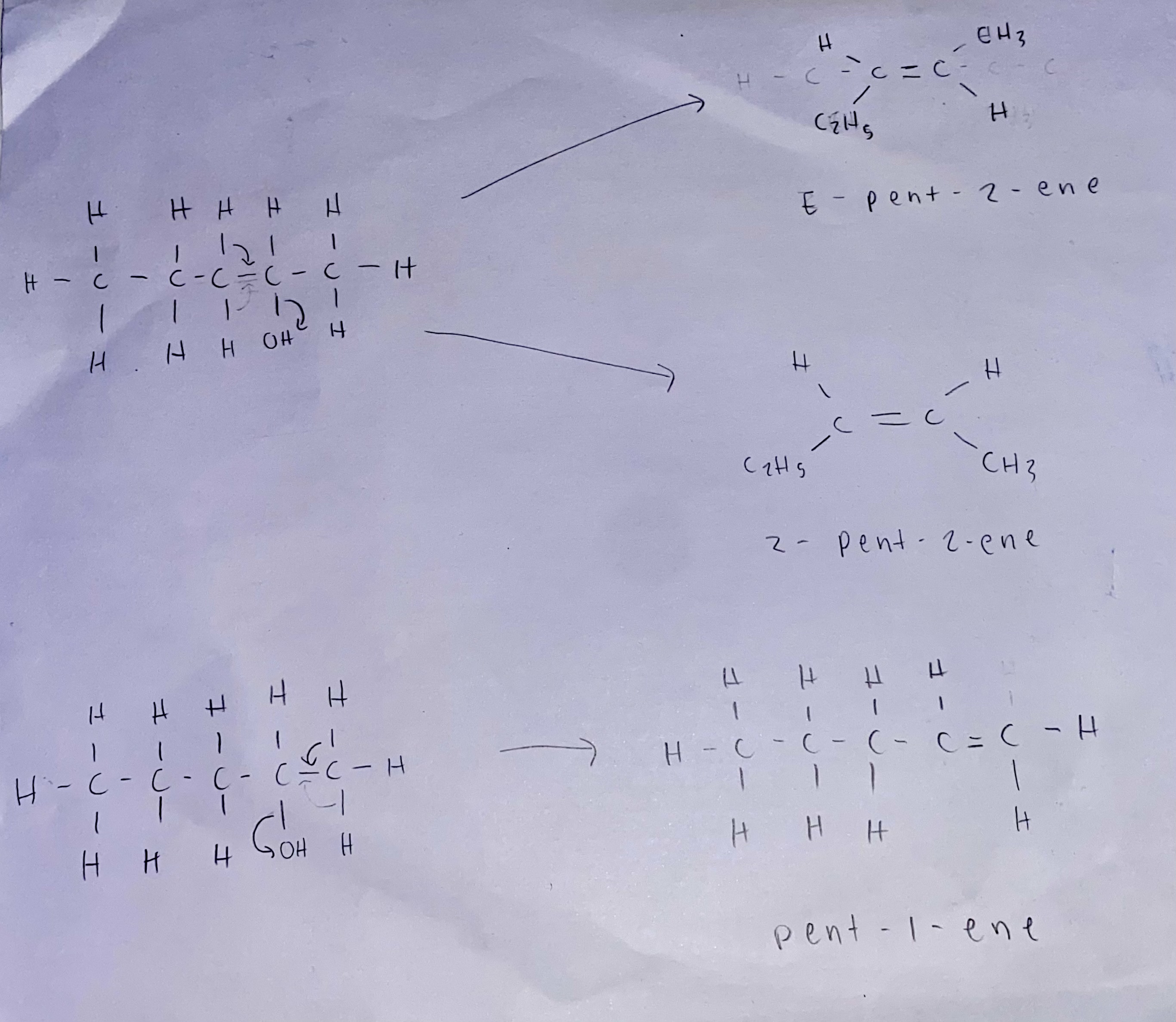
what are the possible alkene products formed in the elimination reaction of pentan-2-ol? (2)
CH3CH2CH2CH=CH2 (pentene)
minor product: E or Z isomers depending on conditions
what reaction can cyclohexanol undergo to form cyclohexene? (2)
cyclohexanol can undergo dehydration using concentrated phosphoric acid
to form cyclohexene and water
what are the possible impurities in the product of cyclohexanol dehydration? (3)
acid catalyst (H₃PO₄)
unreacted cyclohexanol
water
how is a separating funnel used to purify cyclohexene after dehydration of cyclohexanol? (1)
used to separate the organic layer (cyclohexene) from the aqueous layer containing impurities
draw and label the apparatus for using a separating funnel (3)
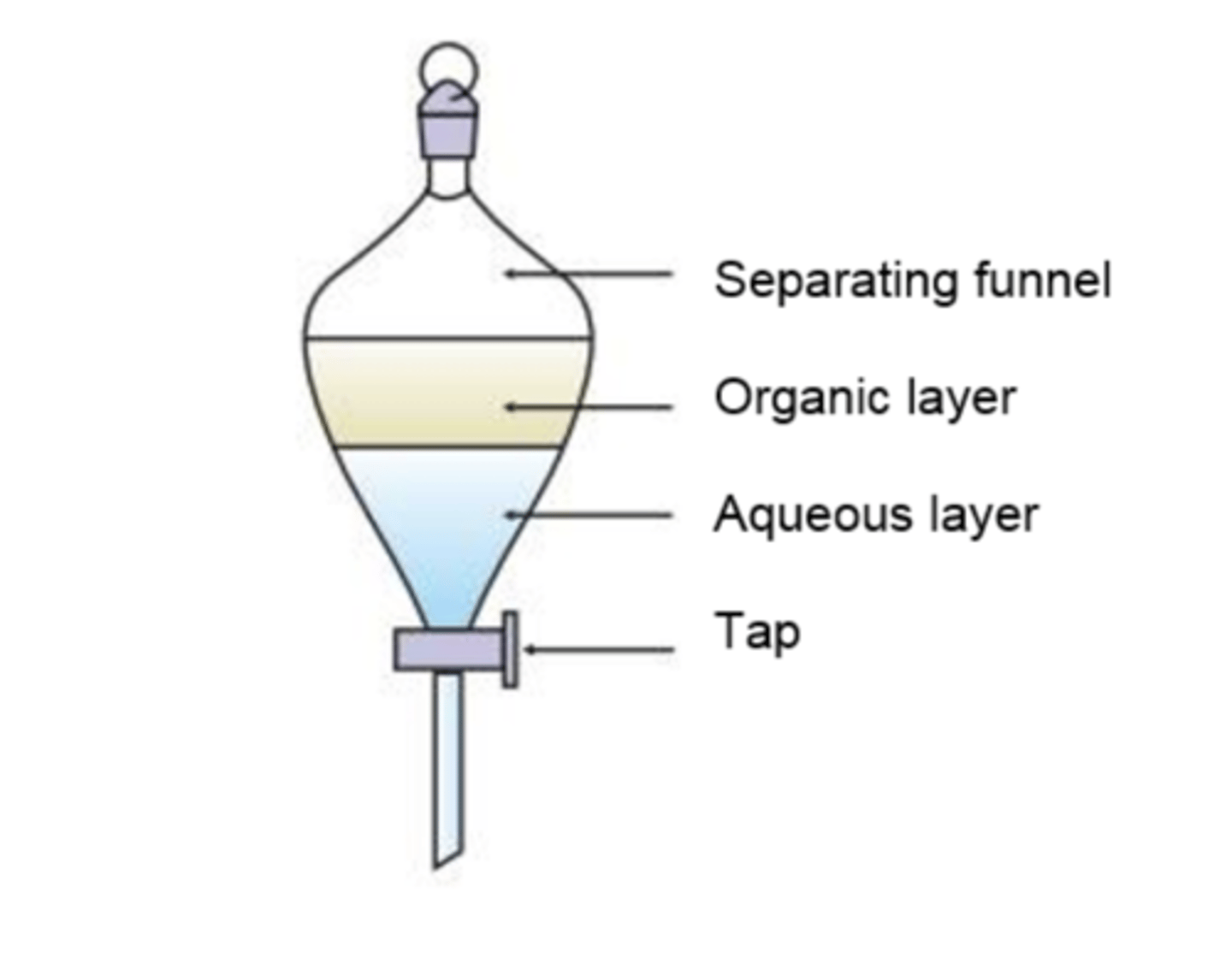
what is the apparatus used to separate two immiscible liquids? (1)
a separating funnel
why is sodium hydrogen carbonate solution added to the impure product? write an equation for the reaction that occurs (2)
to neutralise the acid catalyst
3NaHCO3 + H3PO4 → Na3PO₄ + 3CO2 + 3H2O
why is it important to remove the stopper after shaking the mixture in the practical method? (1)
to prevent the build up of pressure due to CO₂ being produced
how does re-distillation remove unreacted cyclohexanol from the product? (2)
cyclohexanol and cyclohexene have different boiling points
distillation separates the two based on their boiling points
how is the purified organic product dried to remove water? (3)
1. pour the organic liquid into a beaker and add a spatula of drying agent (e.g., calcium chloride or magnesium sulphate)
2. swirl and add more drying agent until the liquid changes from cloudy to clear
3. filter to remove the drying agent
what oxidising agent is used to oxidise alcohols? (1)
acidified potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇/H⁺)
what colour change indicates oxidation when using potassium dichromate (VI)? (1)
orange to green
what new bond is formed when alcohols are oxidized? (1)
a carbonyl bond (C=O)
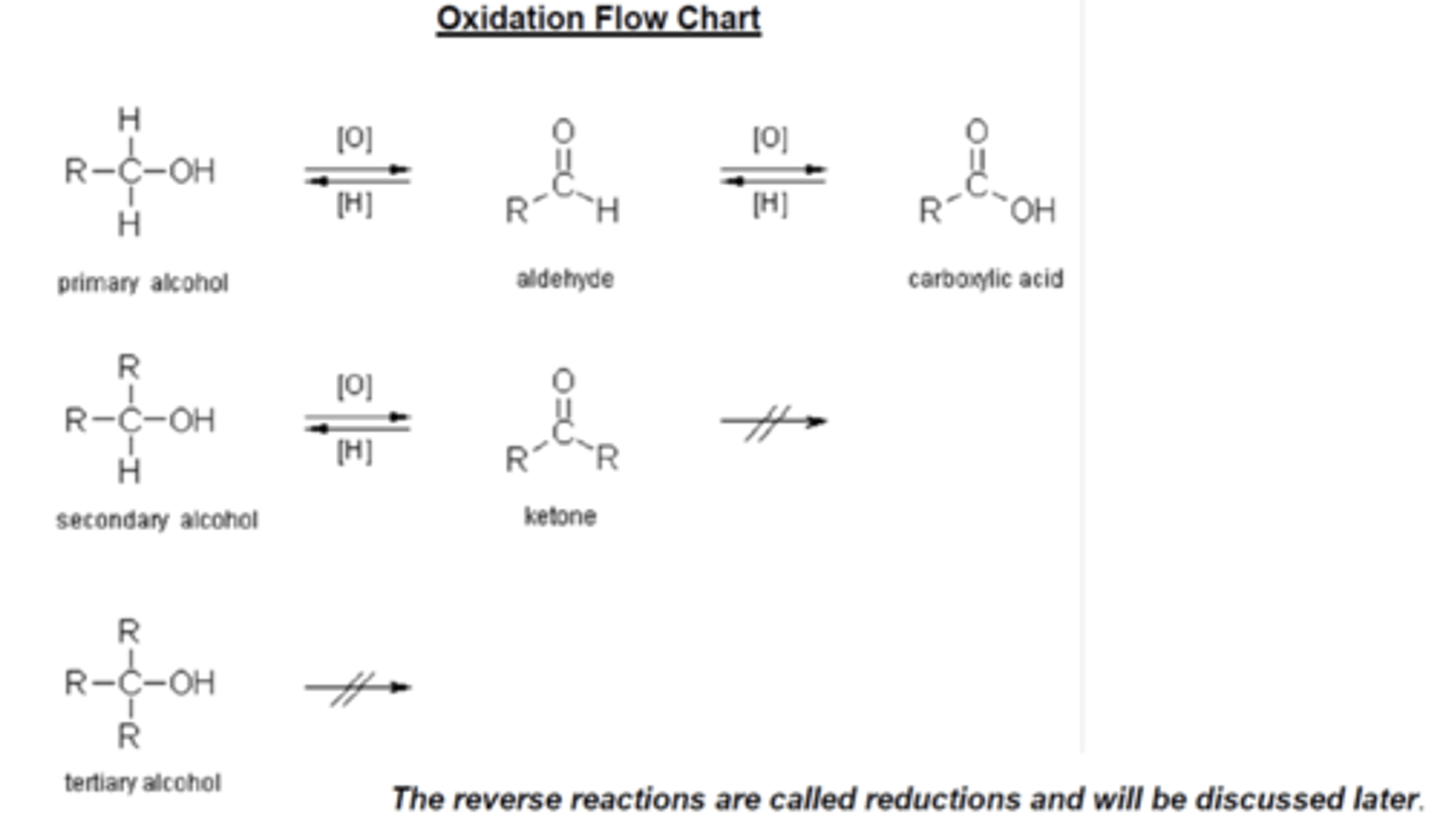
what are the oxidation products of a primary alcohol, including their functional groups? (2)
1. aldehyde (RCHO)
2. then carboxylic acid (RCOOH)
what is the oxidation product of a secondary alcohol, including its functional group? (1)
ketone (RCOR)
can tertiary alcohols be oxidised using acidified potassium dichromate(VI)? (1)
no, tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised
draw the oxidation flowchart showing the products of oxidation for primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols (6)
what are primary alcohols oxidised to, and what apparatus is used? (2)
primary alcohols are oxidised to aldehydes (-CHO)
the apparatus used is distillation
write the equation for the oxidation of ethanol to ethanal (1)
CH₃CH₂OH + [O] → CH₃CHO + H₂O
what are aldehydes oxidised to, and what apparatus is used? (2)
aldehydes are oxidised to carboxylic acids (-COOH)
the apparatus used is reflux
write the equation for the oxidation of ethanal to ethanoic acid (1)
CH₃CHO + [O] → CH₃COOH
what is the overall equation for the formation of ethanoic acid from ethanol (primary alcohol)? (1)
CH₃CH₂OH + 2[O] → CH₃COOH + H₂O
what happens to acidified potassium dichromate (VI) when primary and secondary alcohols are oxidised? (1)
the solution turns from orange to green
how do tertiary alcohols affect acidified potassium dichromate (VI)? (1)
tertiary alcohols have no effect - the solution remains orange
rank ethanal, ethanol, and ethanoic acid from lowest to highest boiling point (3)
ethanal < ethanol < ethanoic acid
why does ethanoic acid have the highest boiling point? (2)
ethanoic acid forms more hydrogen bonds than ethanol and is a larger molecule
leading to stronger van der Waals forces between molecules
why does ethanol have a higher boiling point than ethanal? (2)
ethanol forms hydrogen bonds
which are stronger than the permanent dipole-dipole forces present in ethanal
why does ethanal have the lowest boiling point among ethanol, ethanal, and ethanoic acid? (2)
ethanal only has permanent dipole-dipole forces
which are weaker than hydrogen bonds present in ethanol and ethanoic acid
draw and label the distillation apparatus to form aldehyde / ketone (6)
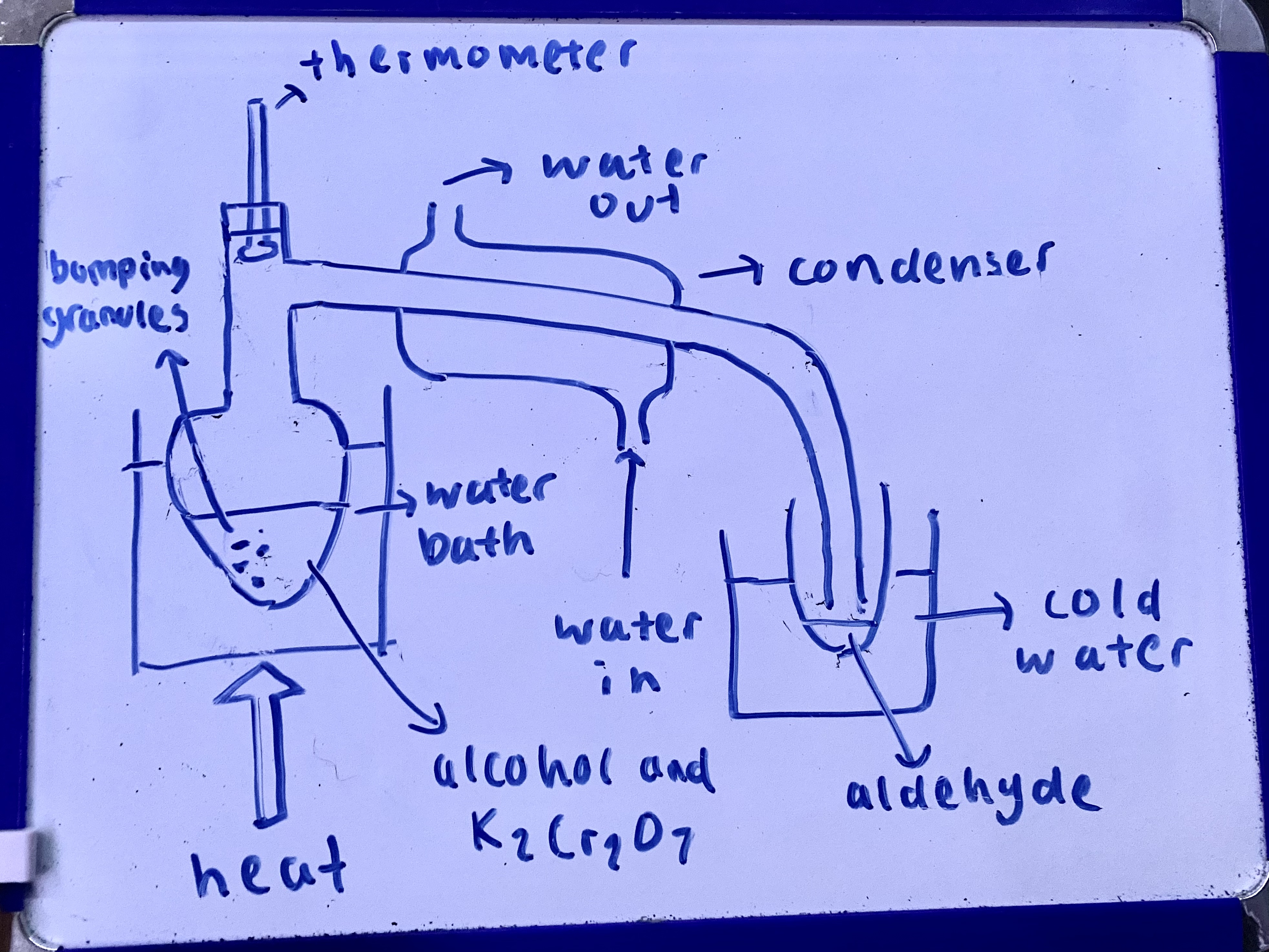
draw and label the reflux apparatus to form carboxylic acid (6)