Pulmonology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Lights Criteria
If at least one of the following three criteria is present, the fluid is exudate; if none is present
The ratio of pleural fluid protein to serum protein is greater than 0.5
The ratio of pleural fluid lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) to serum LDH is greater than 0.6
The pleural fluid LDH level is greater than two thirds of the upper limit of normal for serum LDH
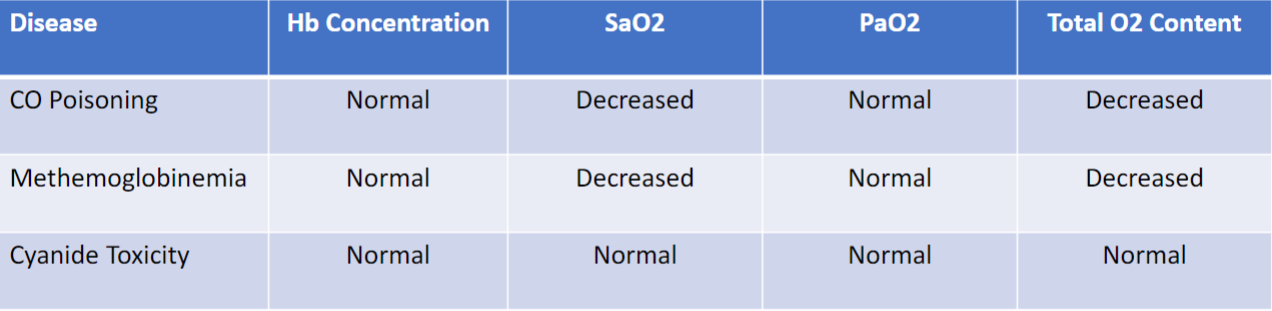
Cyanide Toxicity
Synthetic product combustion (burning of plastics), amygdalin ingestion (apricot seeds)
Headache, dyspnea, drowsiness, cherry red skin, venules in retina may appear red, breath may smell of bitter almonds
Normal PaO2
Venous PaO2 high
Methemoglobin level zero
Elevated lactate (greater than 8)
Treatment: Decontamination, hydroxocobalamin (first line), sodium thiosulfate, or sodium nitrite
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Motor Exhaust, gas heater, fire victims
Headache, vomiting, confusion, visual changes, cherry red skin with possible bulla
Normal PaO2 on ABG
Elevated carboxyhemoglobin
Elevated lactate
Bilateral globus pallidus lesions on MRI
Treatment: High flow oxygen, hyperbaric oxygenation if severe
Methemoglobinemia
Iron in hemoglobin it can become oxidized → Decreased oxygen saturation and oxygen content
Caused by congenital defect or drug induced (anesthetics, dapsone, etc)
Shortness of breath
Cyanosis that is resistant to oxygen
Venous blood may look chocolate brown
Elevated methemoglobin level on ABG/VBG
Treatment is methylene blue
Hb Concentration, SaO2, PaO2, Total O2 in CO, Methemoglobinemia, and Cyanide
Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS)
Symptoms start 6 to 12 hours after altitude change
Diagnosis is subjective – headache, GI symptoms, fatigue, weakness, dizziness
Treatment:
DESCENT
Take an extra day to acclimatize to altitude
Acetazolamide
Supplemental oxygen
High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE)
Usually occurs 2 to 4 days after arrival at altitude
Need two of the four symptoms:
Chest pain
Cough (usually pink frothy sputum)
Dyspnea at rest
Dyspnea at exertion
And two of the four signs:
Central cyanosis
Rales/wheeze
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
CXR shows patchy infiltrates with NORMAL heart size
POCUS may show B lines
ECG with right axis deviation or ischemia
Treatment:
DESCENT
Hyperbaric oxygen chamber
Nifedipine
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (sildenafil)
NEVER DIURETICS
High Altitude Cerebral Edema (HACE)
Severe AMS with new neurologic findings
Ataxia, altered mental status, visual changes, seizure
Appear to be intoxicated, dysarthric, unable to walk in a straight line
Ocular POCUS may show increased optic nerve diameter
Treatment:
IMMEDIATE DESECENT
Supplemental oxygen
Portable hyperbaric oxygen bag
Dexamethasone and acetazolamide
Prevention
Graded ascent:
Maximum daily sleeping elevation gain of 500 meters per day
Acclamation day every 1000 meter gain in elevation
Pharmacologic prophylaxis:
Acetazolamide starting 24 hours prior to ascent
Dexamethasone
Ibuprofen
Nifedipine if a history of HAPE
Adequate hydration
Asbestos Pneumoconioses
Shipbuilding, roofing, plumbing, construction
White calcified supradiaphragmatic and pleural plaques
Linear opacities at the lung bases
Affects the LOWER lobes
Golden brown fusiform rods found in alveolar sputum using PRUSSIAN BLUE stain
Increase risk of bronchogenic carcinoma
Increased risk of Caplan syndrome
Berylliosis Pneumoconioses
Exposure to beryllium in aerospace, electronic, and nuclear industries
Histology shows non-caseating granulomas
Hilar adenopathy
Carries an increased risk of cancer and cor-pulmonae
Affects the UPPER lobes
Coal Worker’s Pneumoconioses
Long term exposure to coal dust
Affects the UPPER lobes
Small round nodular opacities
Increased risk of Caplan syndrome
Leads to progressive massive fibrosis
Silicosis Pneumoconioses
Sandblasting, foundries (glass and pottery)
Carries and increased risk of TB
Increased risk of lung cancer, cor-pulmonale and Caplan syndrome
Affects the UPPER lobes
“Eggshell” calcification of hilar lymph nodes on chest radiograph
Sarcoidosis
African American females and Northern Europeans
Third and fourth decade of life
Usually asymptomatic
Cough, malaise, weight loss, dyspnea, and arthritis
Uveitis
Erythmea nodosum: Painful red and tender nodules on the shins
CXR/CT shows hilar lymphadenopathy and nodules
Biopsy of lymph nodes reveals non-caseating granulomas
PFTs: restrictive / obstructive pattern with decreased diffusion capacity
Increase ACE level, increased IL-2 levels, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, increased alkaline phosphatase
Treatment: systemic corticosteroids
Pulmonary Edema
Cardiogenic: High pulmonary capillary pressure (pulmonary artery wedge pressure)
Non-Cardiogenic: Radiographic evidence of alveolar fluid accumulation without hemodynamic evidence to suggest a cardiogenic etiology
Cardiogenic: Dyspnea, Dyspnea on exertion, Orthopnea, PND, Past Medical History of Myocardial Infarction and CHG
Non-Cardiogenic: Infection, Blood transfusion, Overdose, Hiking, Drowning, Sepsis, Pneumonia
S3 gallop
JVD
Peripheral edema
Enlarged liver
Crackles / Rales
Ascites
Warm Extremities – Non-Cardiogenic
Cool Extremities – Cardiogenic
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Subsequent inflammatory response to underlying injury leads to damage to epithelial barriers (exacerbated by mechanical stretch) and accumulation of protein-rich edema fluid in alveoli
Alveolar damage results in ventilation-perfusion mismatch (V/Q mismatch) → Increased shunting (alveoli unable to exchange oxygen) and dead space (microvascular injury leading to lack of perfusion)
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Diagnosis
A – Abnormal Chest radiograph (bilateral lung opacities)
R – respiratory failure within one week of insult
D – decreased PA02/Fio2 (ratio less than 300)
S – symptoms not due to Heart Failure
Transudative Pleural Effusion

Exudative Pleural Effusion
