BMGT 110 Jeff Miller
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
Businesses' profit to risk assumption relationship
profit is the money earned with salaries and other expenses deducted. Risk is chance entrepreneurs take of losing time/money.
Stakeholders
customers, employees, stockholders, suppliers, dealers, bankers, media, people in community, environmentalists, government leaders. Businesses must respond to needs of them and still make profit.
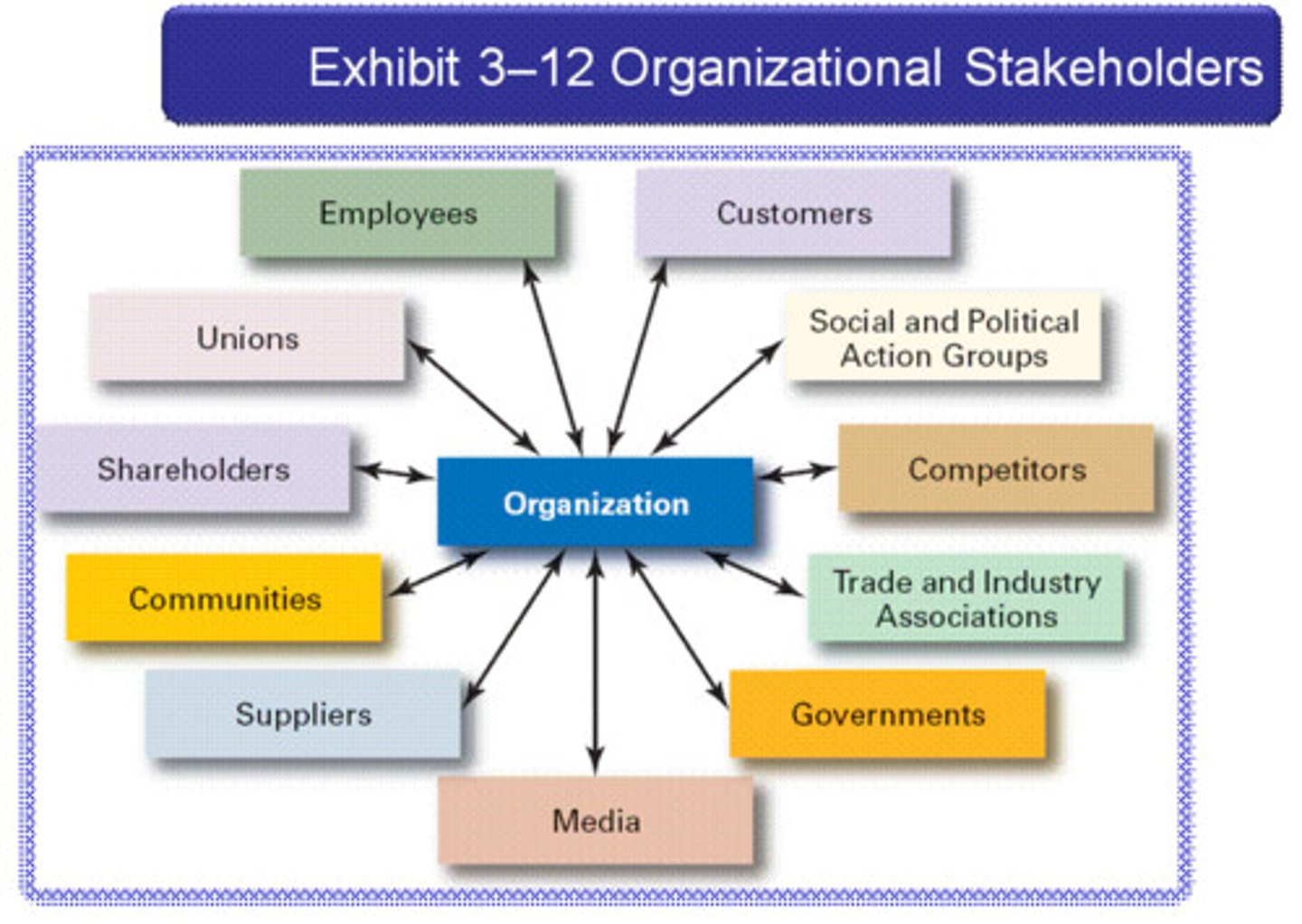
Advantages/Disadvantages of Entrepreneurship
Advantages: freedom to make own decisions, more opportunity and wealth
Disadvantages: more risk and lose benefits from other employers
Five Factors of Production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship, and knowledge.
Efficiency
producing items from least amount of resources
Productivity
amount of output generated with given imput
How businesses beat competiton
high-quality products, exceed customer expectations, more training and authority of employees (empowerment)
2 Major Competitors
China and India
Economics
study of how society produces goods and services and distributes them amoung competing groups
Microeconomics
study that looks at behavior of people and organizations in a market
Macroeconomics
study that looks at nations economy as a whole
Resource Development
study of how to increase resources and create conditions to make better use of resources
Capitalism
factors of production and distribution are privately owned, operated for profit
Monopolistic Competition
large number of sellers produce similar goods that buyers perceive as different
Oligopoly
few sellers dominate market

Monopoly
one seller controls total supply of product/service, sets price

Communism
all economic decisions made by government, control factors of production
Free-Market Economies
market determines what goods/services produced, who gets them, and how economy will grow
Command Economies
government decides what goods/services are produced, who gets them, and how economy will grow
Mixed Economies
some resources made by market, some made by individuals
GDP
total value of good/services produced in a country in a given year
Inflation
rise in prices over time
Disinflation
price increases slowly (inflation rate declining)
Deflation
prices declining
Stagflation
economy is slowing but prices going up
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
monthly statistics that measures inflation and deflation
Producer Price Index (PPI)
index that measures prices at wholesale level
Recession
two or more consecutive quarters of decline in GDP
Depression
severe recession with deflation
Fiscal Policy
govt's efforts to keep economy stable by increasing/decreasing taxes or govt spending

Keynesian Economic Theory
theory that a govt policy of increasing spending and cutting taxes could stimulate economy in recession
Monetary Policy
management of money supply and interest rates by Federal Reserve
Basic Rights Under Capitalism
right to private property, right to own business and keep profits after taxes, freedom of competition, freedom of choice
Sole Proprietorship
business owned and managed by one person

Partnership
business with two or more owners
Corportation
authority to act and have ability apart from owners
Unlimited Liability
business owners are responsible for all debts of business (may have to sell personal possessions to pay business debts)
General Partnership
partnership where owners share operating cost and the liability of business's debts
Limited Partnership
partnership with one of more general partners and one of more limited partners
Limited Liability
stockholders and limited partners are responsible for losses up to amount they invested (private property not at risk)
Master Limited Partnership
acts like corporation, traded on stock exchange, taxed like partnership, avoids corporate tax
Limited Liability Partnership
limits partners' risks of losing personal assets to only their own acts
Merger
result of two firms forming one company

Acquisition
one company purchases another

Vertical Merger
joining two companies involved in different stages of related businesses. (Ex. automobile company joining with a parts supplier OR Soda Company and Artificial Sweetener Company)
Horizontal Merger
joining two firms in same industry (Ex. Pepsi and Coke OR Soda Company and Mineral Water Company)

Conglomerate Merger
joining firms of unrelated industries (Ex. Athletic Shoes and Soda Firm OR Soda Company and Snack Food Company)

Leverage Buyout
attempt by employees, management, or group of investors to purchase an organization primarily through borrowing
Franchise Agreement
someone with a good business sells rights to use business name and sell a product/service to others
Franchisor
company that develops a product concept and sells others the right to make and sell the products
Franchise
right to use business's name and sell its products or services in a given territory

Franchisee
person who buys a franchise
Cooperative
business owned and controlled by people who use it - producers, consumers, or workers with similar needs who pool resources for mutual gain
S Corporation
corporation with limited liability and simpler taxes, company must have fewer than 100 stockholders, cannot derive more than 25% of income from passive sources
Micropreneur
entrepreneurs willing to risk starting a small business, lets them do work they want to do, and offers a balanced lifestyle
Affiliate Marketing
internet-based marketing strategy, business rewards businesses for each customer they send to the website
Intrapreneurs
creative people who work as entrepreneurs within corporations
Enterprise Zones
specific areas governments try to attract business investment by offering lower taxes and other support
Incubators
centers that offer new businesses low-cost offices with basic business services
Venture Capitalists
companies that invest in new businesses in exchange in partial ownership of those businesses
Service Corps of Retired Executives
SBA volunteers from industry, trade associates, education who counsel small businesses at no cost
Four Functions of Managment
planning, organizing, leading, and controlling
Objectives
short-term statements detailing how to achieve the organization's goals
SWOT analysis
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
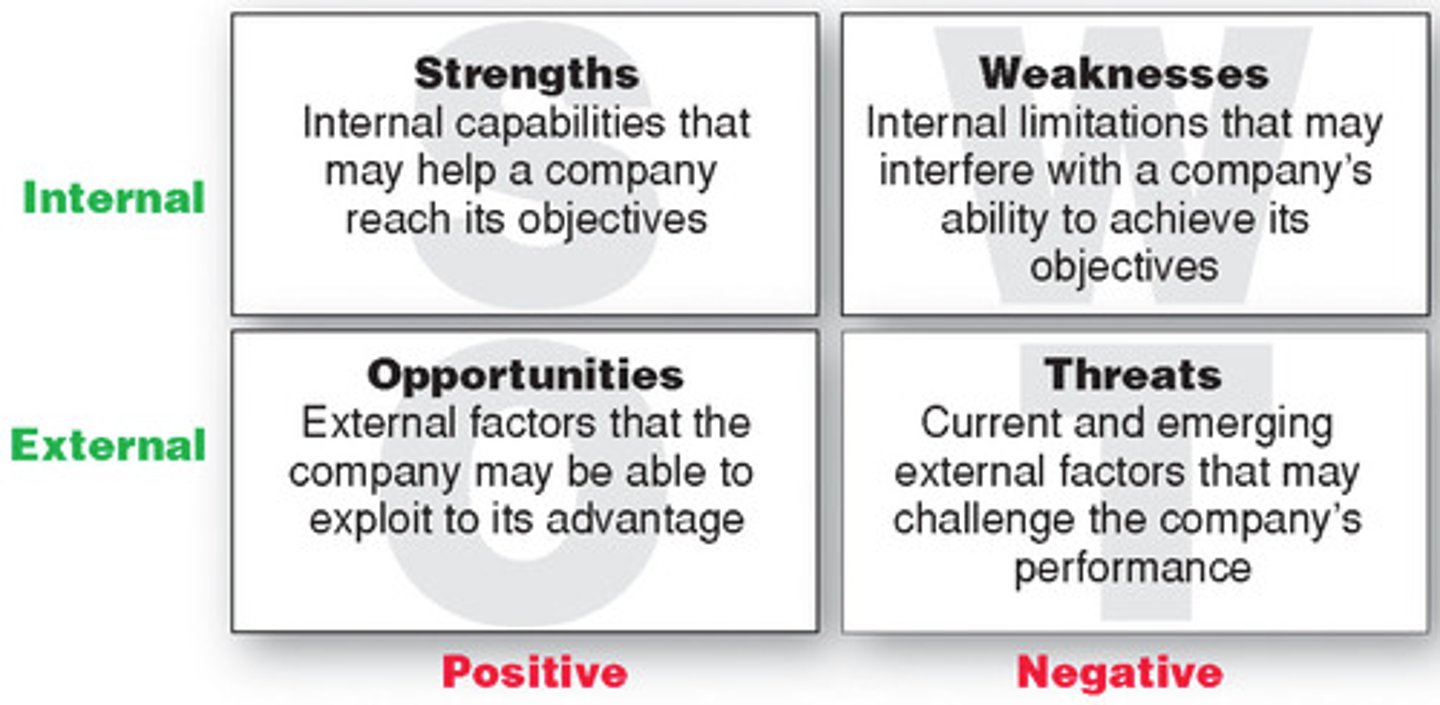
Tactical Planning
detailed, short-term statements about what is to be done, who is to do it, and how it is to be done
Strategical Planning
broad, long-term planning that outlines goals of organization
Operational Planning
setting work standards and schedules necessary to implement company's tactical objective

Contingency Planning
process of preparing alternative courses if primary plans don't achieve objectives

Organization Chart
visual that shows relationship among people and divides organization's work, shows who reports to who
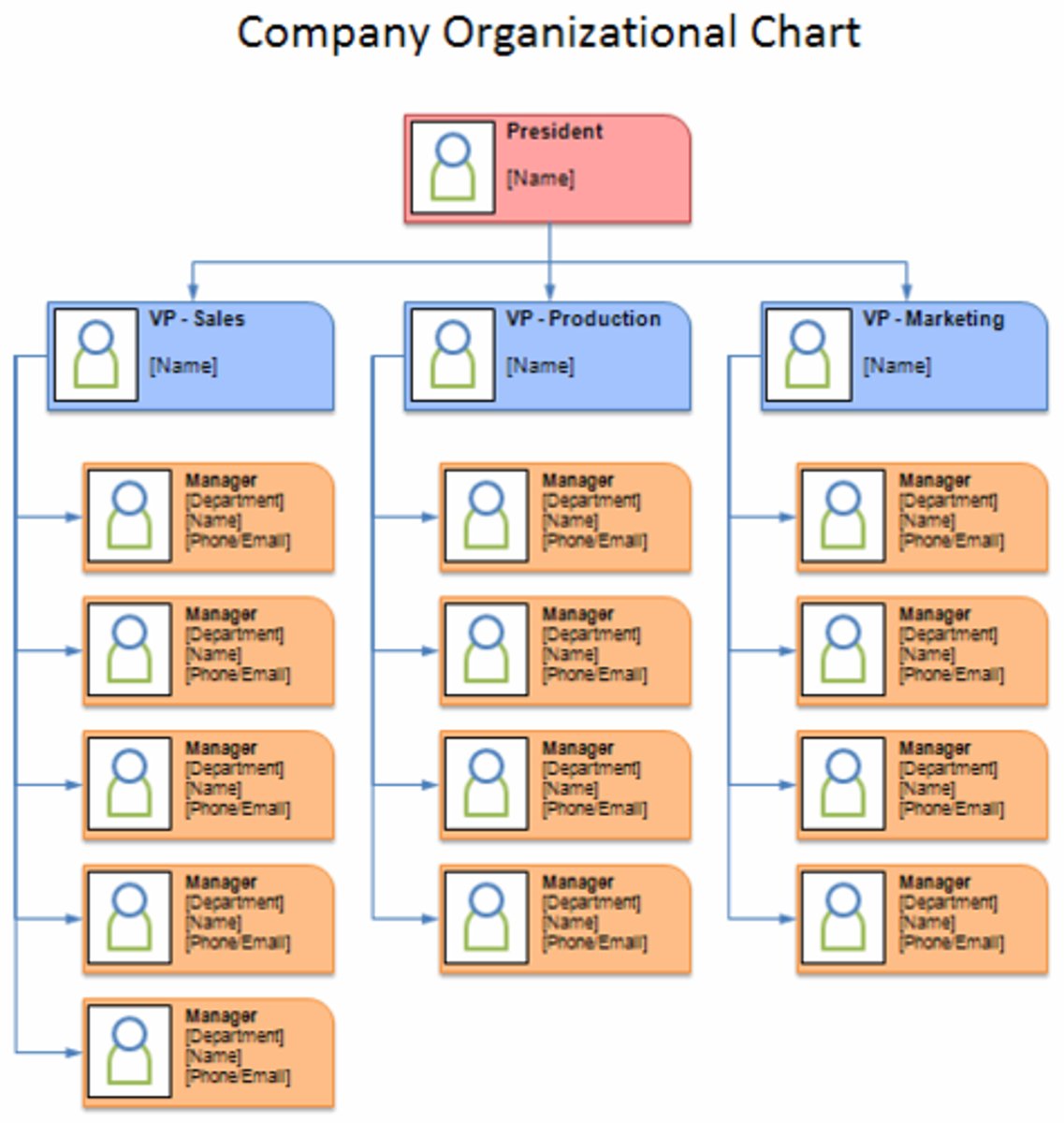
Technical Skills
ability to perform tasks in specific part of department

Conceptual Skills
involve the ability to picture the organization as a whole and relationship of various parts
Transparency
company's facts and figures clear to all stakeholders
Autocratic Leadership
making managerial decisions without consulting others
Participative Leadership
consists of managers and employees working together to make decisions
Free-Rein Leadership
managers setting objectives and employees being relatively free to do whatever it takes to accomplish objectives
Steps of Decision Making
define a situation, describe collected information, develop alternatives, develop agreement, decide which alternative is best, do what is indicated, determine whether decision is a good on
Manager vs. Leader
Managers plan, organize, control functions. Leaders have a vision and inspire others, establish values, emphasize ethics.
Economies Of Scale
companies reduce production costs if they can purchase raw materials in bulk
Bureaucracy
organization with many layers of managers who set rules and regulations and oversee all decisons
Centralized Authority
decision making authority is maintained at top level of managment
Decentralized Authority
decision making authority is delegated to lower level managers more familiar with local conditions than headquarters
Span of Control
optimal number of subordinates a manager supervises
Tall Organization Structure
pyramidal organization chart would be tall because of various levels of management
Flat Organization Structure
few layers of management and a broad span of control
Line Organization
direct two-way lines of responsibility, all people reporting to one supervisor, provides each worker with only one supervisor
Line-And-Staff Organizations
expert advice of staff assistants help in areas such as safety, quality control, computer technology, human resource managament, and investing
Line Personnel
employees part of a chain of command responsible for achieving organizational goals
Staff Personnel
employees who advise and assist line personnel in meeting their goals
Matrix Organization
specialists from different parts of the organization are brought together to work on specific projects for a short-term, still remain part of line and staff structure
Cross Functional Self-Managed Teams
groups of employees from different departments who work together on a long-term basis
Virtual Corportation
temporary networked organization made up of replaceable firms that join and leave as needed
Core Competencies
functions that organizations can do better than any organization in the world
Digital Natives
young people who have grown up using Internet
Restructuring
redesigning an organization so that it can be more effective to serve customer
Inverted Organization
organization that has contract people at the top and chief executive at the bottom of org. chart
Organizational Culture
widely shared values within organization that provide unity and cooperation to achieve common goals
Formal Organization
lines of responsibility, authority, and position; structure shown on org. charts
Informal Organization
system that develops spontaneously as employees meet and form cliques, relationships, and line of authority outside the formal organization
Four Choices in Structuring Orgainzations
centralize or decentralize, breadth of span of control, tall versus flat organization structures and type of departmentalization
Operations Managament
converts resources into goods and services